IT guy on vacation: what about the telescope?

You read the post about what to watch in the sky , see for yourself, showed your friends and became interested in the topic. The logical next wish is to buy a telescope and look at the same beauties with a well-armed eye. But this task is not as simple as it may seem, the choice depends on various parameters. Therefore, a post with a description of various optical schemes of telescopes, mount, I think, will be useful.
Necessary demotivation and objects for observation
In order not to feel sorry for the money spent, it is necessary to make a somewhat demotivating introduction.
Human factor
First, we must understand that the volume and quality of beauty depends on your efforts. Astronomy does not refer to entertainment like "hit the button and enjoy." It is necessary to think in advance about the answers to the following questions:
- Budget. The cost of additional accessories can be equal to and easily exceed the cost of the telescope, keep this in mind when forming the budget constraints on the model cost.
- Place of observation. Where do you plan to watch? In the city from the balcony, in the country, to go out of town, to the village, in the wilderness or in general abroad?
- Storage and transportation. Where and in what form are you going to store the telescope? How to transport to the place of observation from the previous item? How often? How to pack and on what type of transport to transport?
- Desired objects of observation. Are there any types of objects that you really want to watch?
- The format of the observations. Are you going to observe visually or do astrophotography? Will you watch alone, with family / friends / like-minded people?
It would also be highly desirable to get a personal experience of observations through a telescope. There are many options for how to do this:
- Ask around friends, suddenly who has?
- View the presence of astroclubs in your city (in social networks or on Astroforum ).
- Go to the evening of sidewalk astronomy, they are carried out by planetariums and shops selling telescopes.
')
Technique surpassed man
Secondly, you should not incite yourself with photographs of nebulae from the Hubble telescope, you will not see this for sure. Unfortunately, the human eye cannot accumulate photons as a film or camera matrix, and twilight vision does not distinguish colors well. Therefore, what you see yourself, as a rule (there are exceptions!), Will look worse than on a photo from the Internet. Therefore, I have compiled a small list with illustrations of what objects in a telescope will look like. The list is sorted by simplicity for observations and subjective beauty of objects.
Moon
The moon is one of the few objects that are visually more impressive than in the photo. In the eyepiece, the Moon is very bright, clear, visually very large, and very beautiful. It is best to observe the moon in the first and last quarter (i.e., when about half of the disk is visible). In this case, on the border of light and shadow (the terminator line), the relief is very clearly visible - craters of various heights, roughness of the seas and other beauties. The moon is the easiest and observable object that is visible every month, changes every day, and never bothers. I took a photo of the Tver Astroclub and edited it a bit to create the most similar look:

When using a larger zoom you can look at some beautiful elements of the landscape, for example, Rainbow Bay:

Planets
The second most accessible type of objects. Planets replace each other on schedule, so this cycle is hardly annoying, but, alas, they are much worse seen in amateur telescopes than on astrophoto, not to mention photos from observatories, Hubble or interplanetary vehicles.
Jupiter Large, bright and beautiful planet. Two bands on the disk and four Galilean satellites are visible in the telescope, which became the first objects discovered on the first Galilean telescope. Io, Europe, Ganymede, Callisto swirl around the disk of the planet with bright dots, sometimes lining up in beautiful figures - triangles, broken lines. In the eyepiece of the telescope it will look something like this:
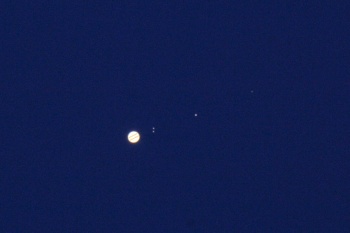
If you look closely, you can see two bands on the disk. In this photo I had to add them, the eye has a better dynamic range than that of a simple amateur astrofoto.
Saturn The next most beautiful object, its uniqueness is rings. In the eyepiece, it seems painted, but the sight is very beautiful. In a small amateur telescope, the Cassini gap is not always visible; in two years I saw it once and not with absolute certainty.

Venus . A very bright star in the morning or evening sky in a telescope is visible evenly white, but it has a unique feature — it has phases:

Mars Mars is already in a zone of disappointment. In a small amateur telescope, you can only make sure that it is red:

Mercury and Uranus are far away in the zone of frustration. If it’s very interesting, you can find them, but there’s really nothing to look at.
Multiple stars
The color of the stars is already visible in the telescope. And if a double star is multicolored, then it is very beautiful. The brightest representatives are Albireo in the Swan and Carl's Heart in the Dog Hounds.

Albireo, for better perception of color, you can slightly defocus the telescope.
Open clusters
Open clusters are a second type of object that is more impressive than their photos. When he first saw Hi / Ash Persei in a telescope, one of my friends recalled the final of Space Odyssey - “God! It's full of stars! ”
Pleiades . The eye does not see the blue nebulae, which are visible on good astrophoto, but the blue tint of stars will be visible. The Pleiades are so large that they fit entirely into the eyepieces with a slight increase.

Hee / Ash Perseus
Very beautiful two open clusters nearby:

No, it’s still better to watch live
Globular clusters
It's all sadder. In the amateur telescope, globular clusters are seen as dull spots, but if you are lucky with the conditions of observation, you can still see that they are formed by thousands and millions of stars.

A large cluster of Hercules.
Nebulae
Everything is very sad here. Because of the properties of the eye, nebulae are, firstly, black and white, secondly, very weakly visible, and thirdly, you have to travel far beyond the city to dark places in order to see them more or less noticeable.
Orion Nebula

M57. Ring Nebula in Lira

And do not say that you see nothing here.
The sun
By purchasing a special filter, you can look at the sun. In the usual filter visible sunspots, granulation (looks like a mesh surface).

The passage of Venus across the disk of the Sun, 2012, at the top are visible sunspots.
ATTENTION: In the absence of a special filter, do not point the telescope at the Sun. A melting or even an explosion of fixed eyepieces and an irreversible blindness of the eye when trying to look through the eyepiece is possible. The use of smoked glasses, cooking foil or other surrogates instead of a special solar filter is unacceptable!
Other
With some luck and dexterity, one can observe planes flying past, the ISS (four rows of solar batteries are quite distinguishable), Chinese lanterns, and so on.
Also pay attention to the "Eyepieces" plugin that comes in the delivery of Stellarium. If you enter the parameters of the telescope and eyepiece, Stellarium will show the size of the object in the eyepiece.
Materiel
In order to speak objectively about telescopes, it is necessary to figure out which telescopes are and what advantages and disadvantages they have.
Terms and Definitions
The aperture is the diameter of the main mirror of the telescope. In simple words, the larger the aperture, the better you can see. The maximum real magnification of a telescope is two apertures. In real life, the telescope is rarely used at magnifications of more than 150-200, you should not chase the magnification. Also, the atmosphere is rarely good enough for telescopes with an aperture of more than 300 mm to fully express themselves.
The focal length is the distance at which the telescope builds an image of an infinitely distant object. Knowledge of the focal length is necessary to calculate the magnification of the eyepiece: zoom is the focal length of the telescope divided by the focal length of the eyepiece. For example, for a telescope with a focal length of 900 mm, an eyepiece of 10 mm will give an increase of 900/10 = 90x. Note that telescopes with small focal lengths require very short-focus eyepieces to achieve high magnifications. For example, a telescope with an aperture of 114 mm and a focal length of 500 mm will require a 2.5 mm eyepiece for its maximum magnification. Such eyepieces are expensive and inconvenient for observation.
The relative aperture is the ratio of the aperture to the focal length. Important for astrophotography parameter, it can be approximately compared with the aperture of the camera. For visual observations, it is important that telescopes with a relative aperture of less than 1/6 have distortions at the edge of the field of view of the eyepiece.
Thermal stabilization . A telescope whose temperature is different from the ambient temperature creates additional distortion of the image. The shorter the heat setting time, the better. Unfortunately, in some types it is quite large, and also, the time of thermal stabilization increases with the size of the telescope.
Alignment is the process of combining the optical axes of the telescope elements. Depending on the design, it can be made at the factory for the entire life cycle, or it will have to do it with some regularity on its own.
Optical schemes of telescopes
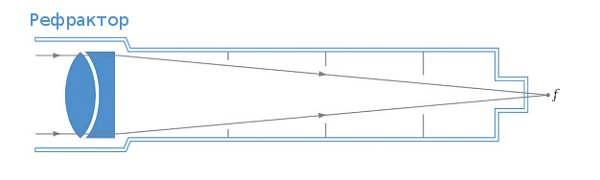

Refractor , a lens telescope. Historically, the first type is widespread so far. Modern refractors exist in two forms - achromats and apochromats. Achromats correct all image distortions (aberrations), except chromatic. They are cheap, but the objects observed in them have colored edges, which degrades the image. Apochromats eliminate chromatic aberration, but they are much more expensive.
Advantages:
- Minimum service. Factory adjustment is maintained for years, the pipe is closed from dust and moisture.
- Very fast thermostabilization.
- The aperture works completely (there are no elements blocking a part of the aperture in the tube), greater image contrast
Disadvantages:
- Chromatic aberration for achromats, price for apochromats.
- There are no large apertures (large lenses are very difficult and expensive to make). 150 mm is already very expensive, there is practically no larger aperture.
- Long pipe (may be a disadvantage)
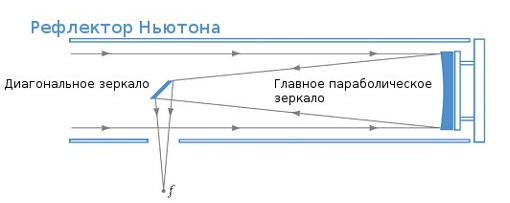

Reflector , he is a mirror telescope. It was created by Newton as a solution to the problems of the lens telescopes of that time. Despite the presence of other mirror schemes, it is the Newton scheme that is extremely popular now.
Advantages:
- Lack of aberration, excellent image quality.
- The cheapest millimeter aperture - with the growth of the aperture of the reflectors more and more relative to other schemes.
- A short thermal stabilization time, which, however, increases with the size of the telescope.
Disadvantages:
- A secondary mirror with holders "eats" part of the aperture. Stretch marks of the holder give the characteristic "rays" of stars on astrophoto.
- Open tube Over time, the mirror becomes dirty with dust.
- Necessity adjustment. After transportation, the adjustment of the reflector may get lost, and it will need to be restored. Fortunately, with experience this is a matter of a few minutes.
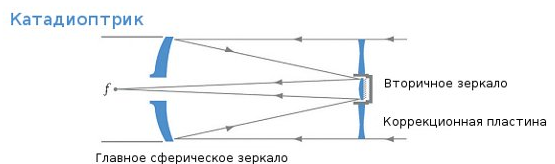

Katadioptrik , he is a mirror-lens telescope. Appeared in the 20th century. By the way, together with the names of Galileo and Newton, the telescope schemes perpetuated the domestic astronomer Maksutov , the inventor of one of the popular mirror-lens telescope schemes - the Maksutov-Cassegrain scheme.
Advantages:
- Compactness. The shortest telescopes.
- A closed pipe protects the mirror from dust.
- Lack of aberration.
disadvantages
- A shorter image due to the central screening area, the aperture does not work completely.
- The most expensive millimeter aperture.
- Long thermal stabilization time.
Mounts
The mount is an adapter between a telescope and a tripod. It depends on her how comfortable you will be to observe, how much weight you will carry with you, and how much the telescope will shake during observations.
By principle, the devices are divided into alt-azimuthal and equatorial.

Alt-azimuth mount has two axes - azimuth and altitude, hence the name. It ignores the fact that the axis of rotation of the Earth is at an angle to the horizon.
Advantages:
- Simple, lightweight, lifting.
- No additional preparation for observations is needed.
Disadvantages:
- The object must be accompanied by two axes.
- The object slowly turns into a field of view, which complicates astrophotography.
- Generally unsuitable for observing the zenith area.
A little to the side is Dobson's alt-azimuth mount, more about it below.

Equatorial , it is German, the mount has a third, additional axis, due to which it can be installed parallel to the axis of rotation of the Earth.
Advantages:
- It is easy to accompany the object manually, even on the budget mounts there is a place for mounting a simple motor, which greatly facilitates the tracking of the object.
- No problem with the availability of zenith.
- The field of view remains motionless, it is good for astrophoto.
Disadvantages:
- The mount is more complex and heavy, it includes a very heavy counterweight.
- The mount requires additional operations before and after observations.
Also the mount can be motorized and computerized.
- In the simplest version, the equatorial mount is equipped with an analog or digital motor to accompany the object. Guidance is carried out manually.
- A more complex option is the drives on both axles of the mount, allowing you to direct the telescope at an object from the console (if there is a port from a laptop with the appropriate software) and track it automatically.
- The most difficult option is a computerized mount with its own database of objects, which can be independently guided and accompanied by an object. The most advanced mounts can be equipped with a GPS / GLONASS and a compass for fully automatic preparation for observation.
Automation makes life a lot easier, but you need to keep in mind that this is extra money, which in the case of a limited budget can be spent on a more powerful telescope.
Precautionary measures
What mistakes can be made when choosing a telescope?
Buying a telescope in the hypermarket . Now there are many specialty stores with branches in major cities and delivery in Russia. It is not worth the risk of buying a telescope of unknown manufacturer with an unknown quality.
Too greedy . Refractors with an aperture of no more than 60 mm, reflectors of no more than 76 mm and catadioptrics of no more than 80 mm are not serious tools, as a rule, they are on very flimsy mountings, and if you really need money, you should dig into a normal tool or switch to binoculars.
Newtons with proofreader . There are models of Newton's reflectors with a corrector in the focuser node. They are shorter than regular Newtons, but add distortion.
Short-focus refractors, achromats . As in the previous case, for the reduction of the size paid image quality. Such telescopes are more chromatic.
Selection logic
If you clearly understand your desires and limitations, the choice will not be very difficult. There are several typical scenarios that can be mentioned.
Balcony visual observations in the city
For observation on the balcony is important telescope compactness. Therefore, with a limited budget, refractors on an azimuth mount are more preferable - with a refractor most of the pipe will stick out, and the azimuth mount is easier to handle. If there is a lot of money, then you can think about katadioptrik on a motorized mount. In any case, you should not chase the aperture strongly, 100-150 mm for the city is enough. However, these tips are advisory, I quite successfully exploit the reflector on the equatorial mount on the balcony, because when choosing a telescope I wanted a larger aperture without chromatism in a limited budget, and the purchase of a drive for mounting was planned.
Observations in the country / outside the city
If there are no problems with the space for the telescope and its transportation, then, if there is a budget, you can think about a large aperture. A large aperture at a reasonable price is Newton's reflector. Also, a large aperture requires an expensive, heavy and complex classic mount. Therefore, the Dobson mount was developed, in which there is no tripod, and the telescope is mounted on the “stool” -lapboard:
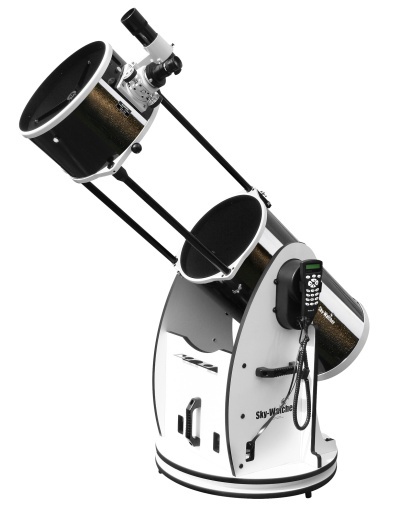

Pay attention to the fact that the pipe is foldable - it increases mobility. There are non-folding models, cheaper.
This design allows telescopes to produce a very large aperture of 400 mm and above. Such a telescope height from the person.
Conclusion
On Habré, they also wrote about the lease of the telescopic time , this may interest someone as an alternative. There is a site with broadcasts of interesting astronomical events , data from telescopes with comments in English are shown there.
Astrophoto is a separate large topic, with its requirements, I was not interested in it, therefore I did not write anything besides the most basic information.
I recommend the largest Russian Astroforum , there is a section "Advise a telescope."
As a source for pictures, we used arm_ann photos, an excellent RealSky resource , and the Two Archers resource.
KDPV - Astrofest 2014 .
PS Eyepieces and stuff left behind so that the article does not turn out too long. If there is a desire, there will be a continuation with a story about eyepieces that I have bought, etc.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/224023/
All Articles