History of Chinese Astronautics
Actually, I got a smartphone in my hands, which fully supports navigation using the Chinese navigation system 北斗 (Ursa Major). These smartphones should enter the market in mid-late 2014, but this is not the case.
I thought about what this system works on, who and what brought these satellites into orbit and decided to write a brief overview of the history of the development of Chinese space exploration. Who cares - welcome under cat. Many heavy photos.

Why is Chinese astronautics called a taykonavtika? Do not suffer, residents of Thailand and Taiwan have nothing to do with it. Just in Chinese space sounds like 太空 (Taekong), which means “too empty”.
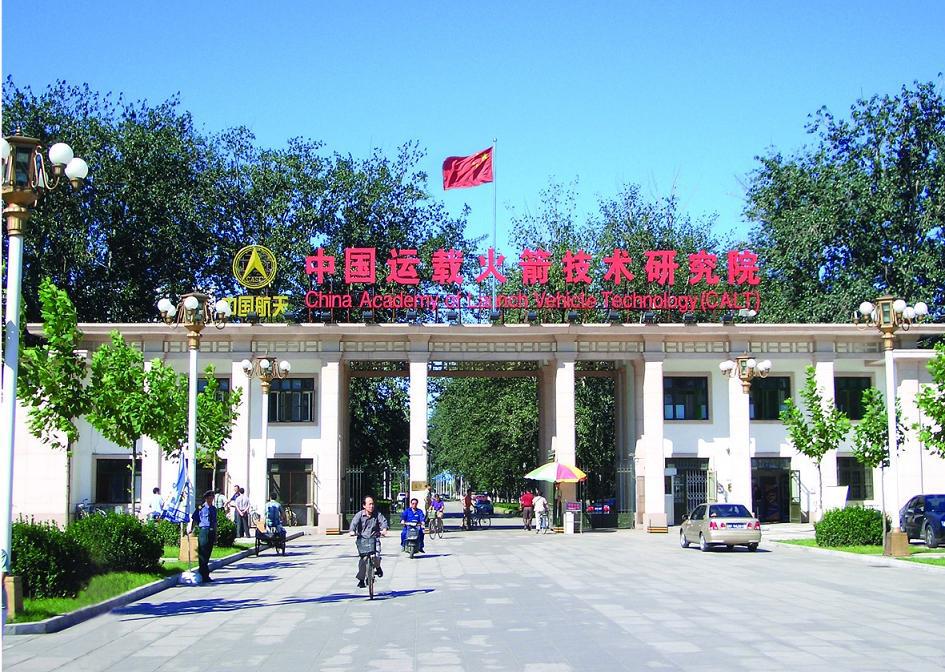
The date of birth of the Chinese cosmonautics can be considered November 16, 1957. It was on this day was founded 中国 运载火箭 技术 研究院 (Chinese Research Institute for carrier rockets) .
Then, of course, he looked a little different.

')
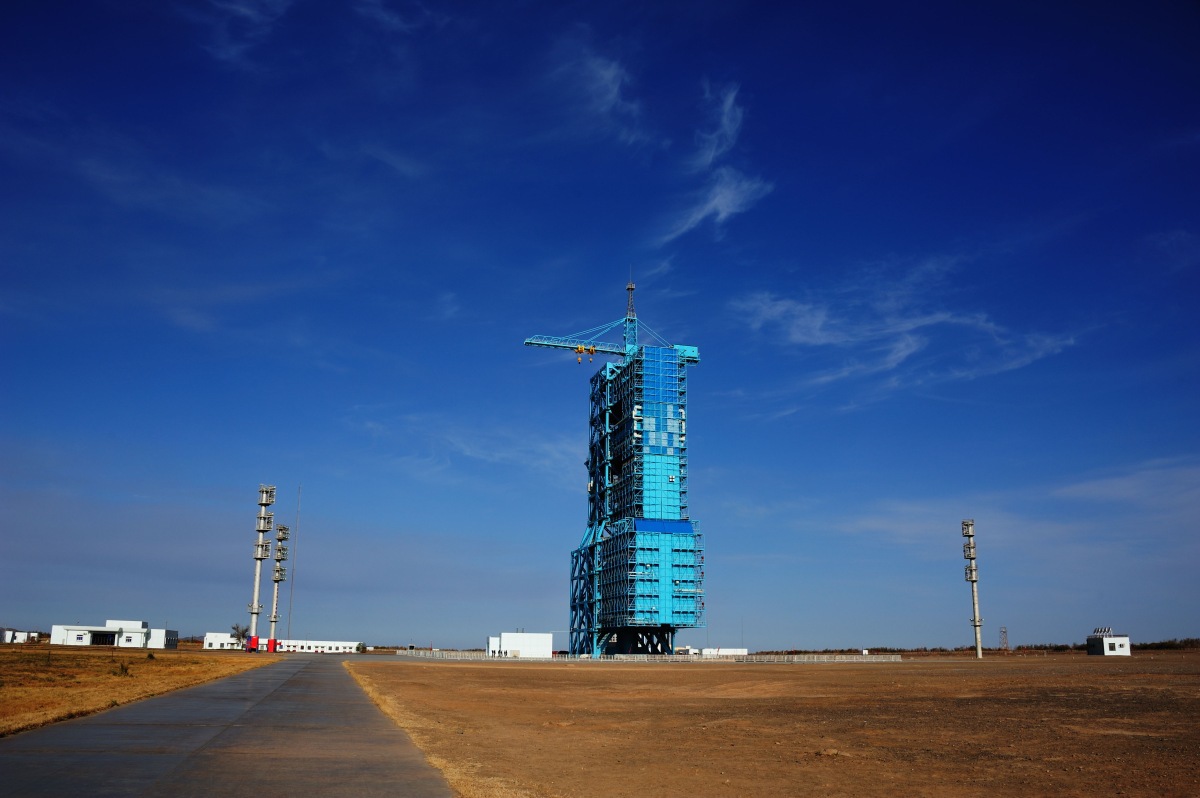
The first spaceport was built a year later - in October 1958. They called it 酒泉 卫星 发射 中心 (Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center), it is located in the autonomous region of Inner Mongolia near the city of the same name 酒泉 (Jiuquan), which, by the way, is in the neighboring province (Gansu). The area is 2800 square kilometers.

It was from this cosmodrome on November 5, 1960 that the first rocket was launched. True, the goals of this rocket were far from peaceful. 一号 (East Wind-1) was the first short-range ballistic missile made in China (up to 1000 km). Now her layout is stored in the Museum of the PLA.

Therefore, some people still consider the birthday of the Taikonautics precisely on April 24, 1970. On this day, the first peaceful satellite made in China was launched from the Jiuquan cosmodrome - 东方 红 一 (Red East-1)

As a launch vehicle, 长征 一号 (Great Trip 1) was used - the first launch vehicle made in China. In total, two versions of the CZ-1 and CZ1-D were released. The second series differed from the first by a slightly reduced length and an increased useful mass, which it was able to put into orbit. Used a three-stage layout.
According to some reports, the first launch with the same satellite was held a year earlier - November 16, 1969, but failed. Official sources do not have such information.

A new modification of this family of launch vehicles CZ-2 was first launched on November 5, 1974. Due to a wire break in the control system, the rocket lost orientation in space and fell to the ground.

Work was carried out on the rocket, and its new modification CZ-2C F-01 on November 26, 1975, successfully launched into orbit the first satellite in China, which then successfully landed on Earth.

Carrier rockets CZ-2 in various versions are still being made. These are lightweight units capable of launching a cargo weighing 3,850 kg into low-Earth orbit and 1250 kg into geo-transfer orbit.
The following successful launches were carried out in 1976, 1978, 1982 and 1983. All these were satellites, which then returned to Earth.
January 29, 1984 there was another failure. At the first real launch of the rocket, the CZ-3, which carried the satellite 东方 红 二号 (Red East-2) due to unidentified interference, the third stage of the rocket did not enter the planned orbit.
After that, an average of two to three launches a year took place. Two new spaceports were built, the family of launch vehicles was systematically improved.
A significant event took place on April 7, 1990 - the satellite 亚星 一号 (“Star of Asia -1”) was launched - the first commercial satellite in China built for foreign partners. That is, from this point on, the taikonautics began to bring money to the country's budget. After this incident, more and more countries began to use the services of the PRC - from Thailand to Brazil.

On November 20, 1999, a new epoch-making event took place - the first unmanned aerial vehicle 神舟 一 1 (Sky Boat-1) was developed and launched. The launch vehicle was the same “Great March”, but new modifications

On May 25, 2003, another landmark was passed - the first satellite of the 北斗 一号 navigation system (Big Bear-1) was launched.
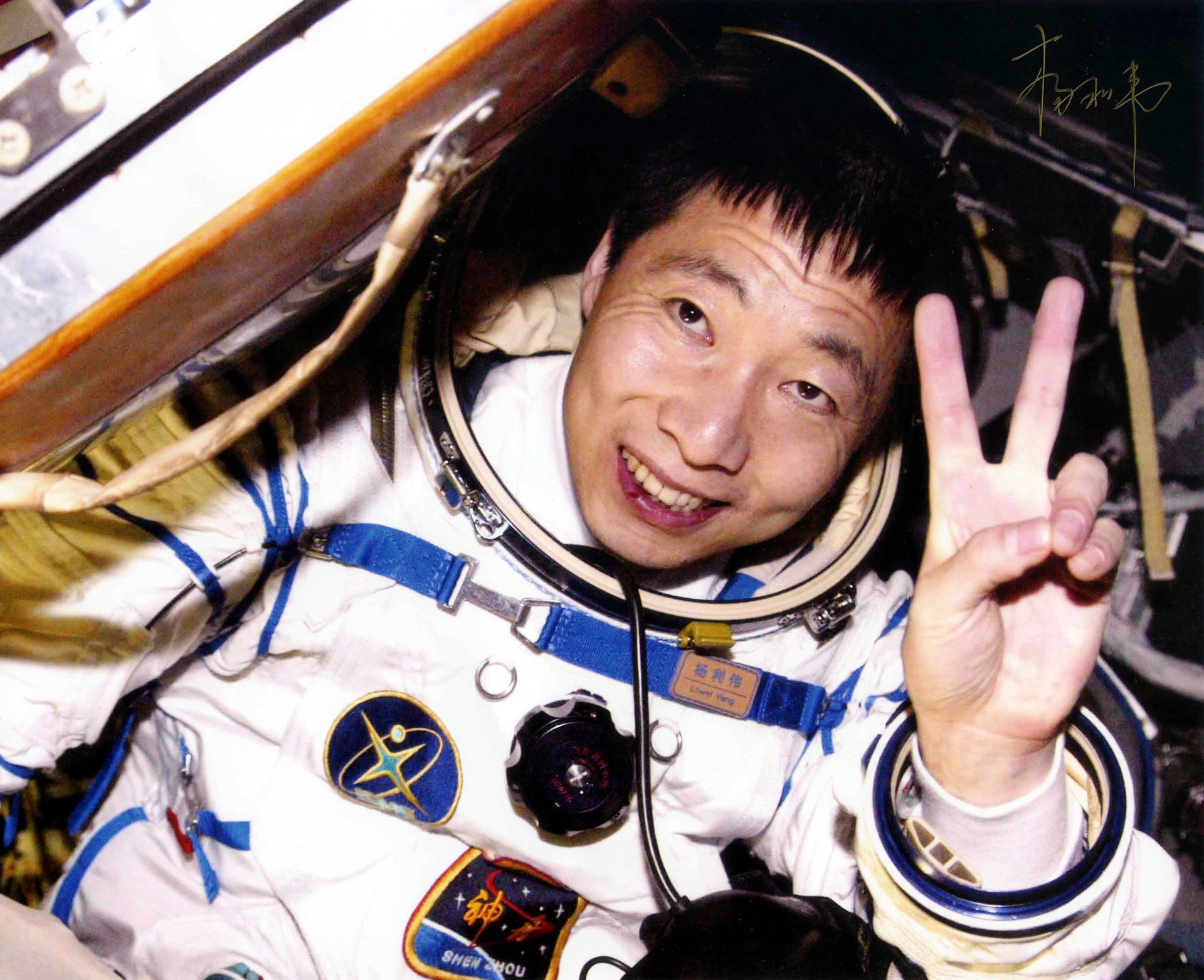
On October 15, 2003, the first Chinese cosmonaut, 杨利伟 (Yang Li Wei), was noted in space.

The number of launches increased from year to year. If in 2006 there were 6 launches, then in 2007 there were already 10 launches, in 2008 - 11, in 2010 - 15, 2011 and 2012 - until 19.
On October 24, 2007, the first Chinese moon satellite 嫦娥 一号 (Moon Fairy 1) was launched.
On September 27, 2008, the first taykonavt went into outer space. His name was 翟志刚 (Zhai Zhigang). The flight took place on 神舟 七号 (Heavenly boat-7)

On October 1, 2010, the second moon satellite was launched.
On June 18, 2012, the first female Taikonaut visited space - 刘洋 (Liu Yang)

And since 2012, the Chinese Space Agency has realized that space must be promoted. Only recently, it became possible to find photos / videos / texts about taikonauts and space projects on the web.
Everything is controlled from 航 飞行天 飞行 控制 中心 (Beijing Mission Control Center).

People enjoy success. Only recently, photo-video was allowed in the TsUP room.

Chairman of the People's Republic of China Hu Jintao congratulates the crew of the ship-九号 (Sky Boat-9).

Media presence is allowed at the landing sites of modules and ships.
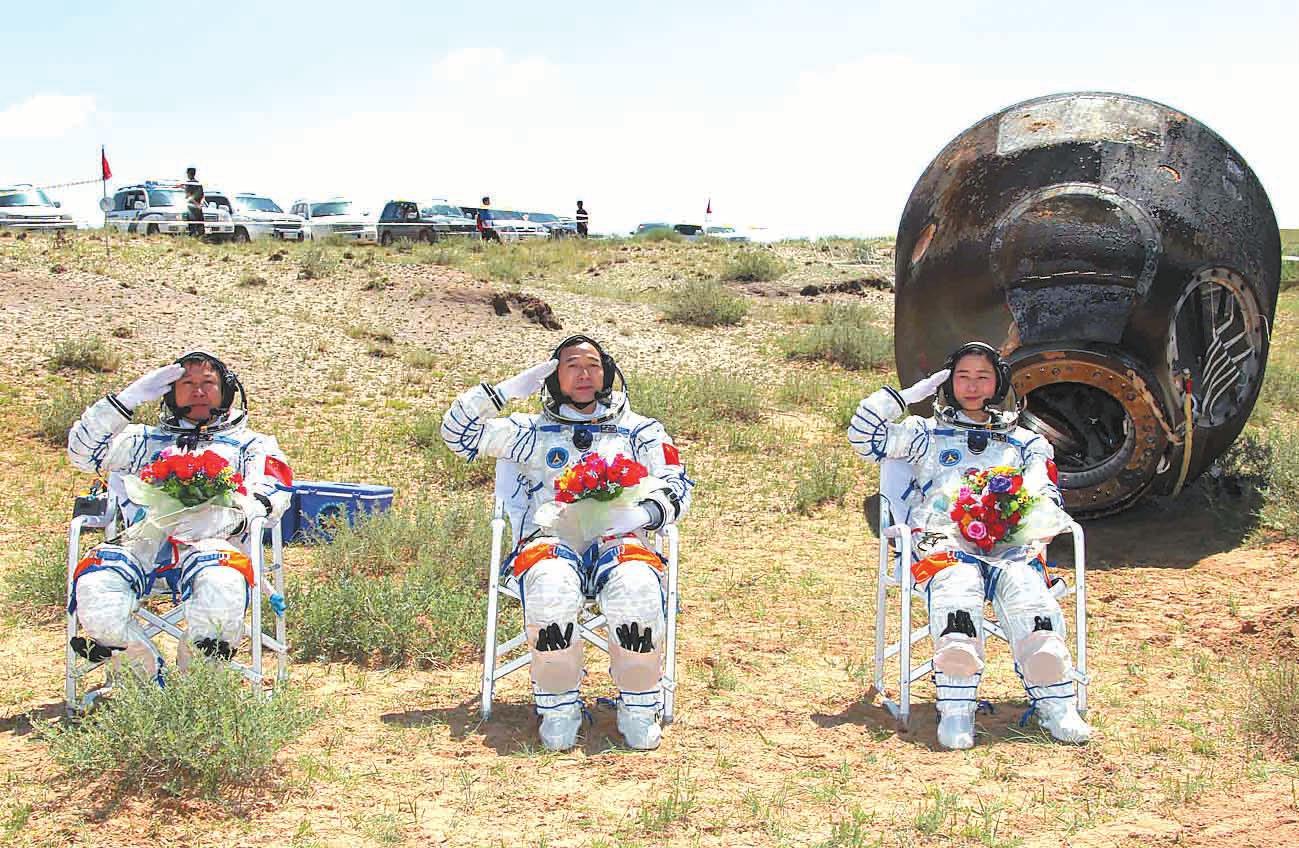

Media presence allowed on spaceports

Conducted video negotiations with the crews of the space station live.
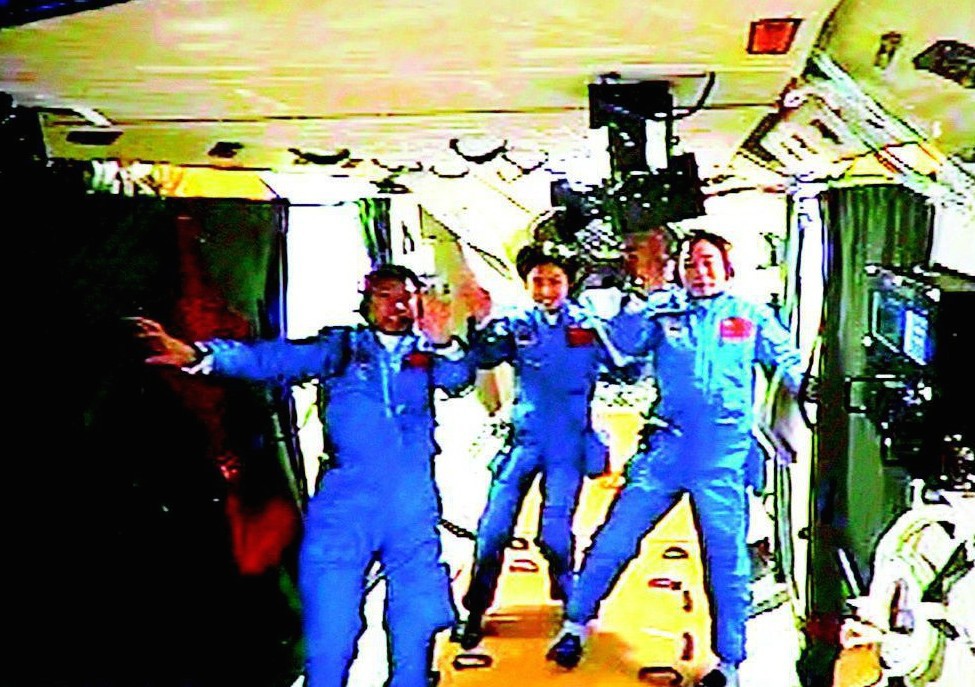

The last launch was currently held March 31, 2014. According to official data, there were 189 launches, of which 8 ended in failure, a partial failure - 1. To date, there are three launch sites in the PRC - 太原 (Taiyuan), 酒泉 (Jiuquan) and 西昌 (Xichang).
The launch vehicle family includes several models - from ultralight CZ-2 to super-heavy CZ-9, which will take up to 130 tons to a low orbit and up to 50 tons to a geostationary orbit

There is its own space station in orbit, which has already been visited by several dozen Taekonauts. The second model is being prepared for launch, after which the first will be decommissioned.

Phones with support for the Chinese navigation system 二号 (Ursa Major-2) will enter the market by 2015, and by 2020, satellites of this system will serve the entire territory of the Earth.
In general, we continue to follow with interest ...
I did not mention the moon rover - there is enough information about it in the Russian-speaking segment of the Internet.
Thank you all for your attention. I hope it was interesting.
Interesting links:
A gorgeous presentation about the state of taikonautics for 2012
History of launches of Chinese spacecraft
China Space Agency
Chinese Research Institute for Launch Vehicles
I thought about what this system works on, who and what brought these satellites into orbit and decided to write a brief overview of the history of the development of Chinese space exploration. Who cares - welcome under cat. Many heavy photos.

Why is Chinese astronautics called a taykonavtika? Do not suffer, residents of Thailand and Taiwan have nothing to do with it. Just in Chinese space sounds like 太空 (Taekong), which means “too empty”.
The date of birth of the Chinese cosmonautics can be considered November 16, 1957. It was on this day was founded 中国 运载火箭 技术 研究院 (Chinese Research Institute for carrier rockets) .
Then, of course, he looked a little different.

Chinese Research Institute for Launch Vehicles
')
The first spaceport was built a year later - in October 1958. They called it 酒泉 卫星 发射 中心 (Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center), it is located in the autonomous region of Inner Mongolia near the city of the same name 酒泉 (Jiuquan), which, by the way, is in the neighboring province (Gansu). The area is 2800 square kilometers.

Launch Table of Jiuquan Cosmodrome
It was from this cosmodrome on November 5, 1960 that the first rocket was launched. True, the goals of this rocket were far from peaceful. 一号 (East Wind-1) was the first short-range ballistic missile made in China (up to 1000 km). Now her layout is stored in the Museum of the PLA.

Rocket "East Wind-1" before launch
Therefore, some people still consider the birthday of the Taikonautics precisely on April 24, 1970. On this day, the first peaceful satellite made in China was launched from the Jiuquan cosmodrome - 东方 红 一 (Red East-1)

Postcard of the Post of China with the Red East-1 satellite depicted on it
As a launch vehicle, 长征 一号 (Great Trip 1) was used - the first launch vehicle made in China. In total, two versions of the CZ-1 and CZ1-D were released. The second series differed from the first by a slightly reduced length and an increased useful mass, which it was able to put into orbit. Used a three-stage layout.
According to some reports, the first launch with the same satellite was held a year earlier - November 16, 1969, but failed. Official sources do not have such information.

Launch vehicle 长征 一号 (Long march-1) with satellite 东方 红 一号 (Red East-1) at the Jiuquan cosmodrome.
A new modification of this family of launch vehicles CZ-2 was first launched on November 5, 1974. Due to a wire break in the control system, the rocket lost orientation in space and fell to the ground.

The rocket "Great campaign-2" after takeoff and a few seconds before the fall
Work was carried out on the rocket, and its new modification CZ-2C F-01 on November 26, 1975, successfully launched into orbit the first satellite in China, which then successfully landed on Earth.

Satellite landing
Carrier rockets CZ-2 in various versions are still being made. These are lightweight units capable of launching a cargo weighing 3,850 kg into low-Earth orbit and 1250 kg into geo-transfer orbit.
The following successful launches were carried out in 1976, 1978, 1982 and 1983. All these were satellites, which then returned to Earth.
January 29, 1984 there was another failure. At the first real launch of the rocket, the CZ-3, which carried the satellite 东方 红 二号 (Red East-2) due to unidentified interference, the third stage of the rocket did not enter the planned orbit.
After that, an average of two to three launches a year took place. Two new spaceports were built, the family of launch vehicles was systematically improved.
A significant event took place on April 7, 1990 - the satellite 亚星 一号 (“Star of Asia -1”) was launched - the first commercial satellite in China built for foreign partners. That is, from this point on, the taikonautics began to bring money to the country's budget. After this incident, more and more countries began to use the services of the PRC - from Thailand to Brazil.

Even newspapers wrote about it -)
On November 20, 1999, a new epoch-making event took place - the first unmanned aerial vehicle 神舟 一 1 (Sky Boat-1) was developed and launched. The launch vehicle was the same “Great March”, but new modifications

Unmanned aerial vehicle 神舟 一号 (Sky Boat-1)
On May 25, 2003, another landmark was passed - the first satellite of the 北斗 一号 navigation system (Big Bear-1) was launched.

On October 15, 2003, the first Chinese cosmonaut, 杨利伟 (Yang Li Wei), was noted in space.

The number of launches increased from year to year. If in 2006 there were 6 launches, then in 2007 there were already 10 launches, in 2008 - 11, in 2010 - 15, 2011 and 2012 - until 19.
On October 24, 2007, the first Chinese moon satellite 嫦娥 一号 (Moon Fairy 1) was launched.
On September 27, 2008, the first taykonavt went into outer space. His name was 翟志刚 (Zhai Zhigang). The flight took place on 神舟 七号 (Heavenly boat-7)

On October 1, 2010, the second moon satellite was launched.
On June 18, 2012, the first female Taikonaut visited space - 刘洋 (Liu Yang)

And since 2012, the Chinese Space Agency has realized that space must be promoted. Only recently, it became possible to find photos / videos / texts about taikonauts and space projects on the web.
Everything is controlled from 航 飞行天 飞行 控制 中心 (Beijing Mission Control Center).

People enjoy success. Only recently, photo-video was allowed in the TsUP room.

Workers of the Beijing MCC rejoice at the successful launch of the orbital station 天宫 一号 (Heavenly Palace-1)
Chairman of the People's Republic of China Hu Jintao congratulates the crew of the ship-九号 (Sky Boat-9).

June 26, 2012
Media presence is allowed at the landing sites of modules and ships.

June 29, 2012
Media presence allowed on spaceports

June 11, 2013
Conducted video negotiations with the crews of the space station live.

The last launch was currently held March 31, 2014. According to official data, there were 189 launches, of which 8 ended in failure, a partial failure - 1. To date, there are three launch sites in the PRC - 太原 (Taiyuan), 酒泉 (Jiuquan) and 西昌 (Xichang).
The launch vehicle family includes several models - from ultralight CZ-2 to super-heavy CZ-9, which will take up to 130 tons to a low orbit and up to 50 tons to a geostationary orbit

There is its own space station in orbit, which has already been visited by several dozen Taekonauts. The second model is being prepared for launch, after which the first will be decommissioned.

Chinese Orbital Space Station 天号 一号 (Heavenly Palace-1)
Phones with support for the Chinese navigation system 二号 (Ursa Major-2) will enter the market by 2015, and by 2020, satellites of this system will serve the entire territory of the Earth.
In general, we continue to follow with interest ...
I did not mention the moon rover - there is enough information about it in the Russian-speaking segment of the Internet.
Thank you all for your attention. I hope it was interesting.
Interesting links:
A gorgeous presentation about the state of taikonautics for 2012
History of launches of Chinese spacecraft
China Space Agency
Chinese Research Institute for Launch Vehicles
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/223427/
All Articles