Development of a project management system in medium business organizations
Until now, among managers of organizations there is often the opinion that a project management system (hereinafter referred to as an EMS or System) is software that automates project management processes, which, as a rule, are calendar-resource planning processes.
In fact, in the updated interpretation of the PMI PMBoK (4-th edition) knowledge book [1], the EMS is a set of processes, tools, methods, methodologies, resources and procedures for managing a project.
At the same time, it is worth paying attention to the fact that the project methodology is a three-level structure “PRODUCT - BUSINESS - STRATEGY”:
Level 1 (PRODUCT) - project management;
Level 2 (BUSINESS) - program management;
Level 3 (STRATEGY) - project portfolio management.
Moreover, the PRODUCT level (Project Management) is the base level, the starting point, for the construction of the remaining levels - BUSINESS and STRATEGY (see Figure 1).
')
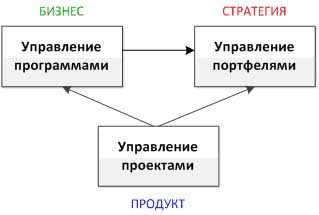
Figure 1 - The three-level structure of the project methodology
Why organizations of EMS and project activities?
The project management system allows you to effectively carry out projects that lead to qualitative changes within organizations, which in turn allows organizations to gain new competitive advantages.
Examples of such projects include building infrastructure, entering an IPO, launching a new product or service, etc.
The value of a project management system is especially high at the stage of growth of an organization, when it already has experience in the local market and is trying to transfer an already tested business model to the republican or international market. At this time, organizations are implementing large-scale development programs consisting of a dozen projects.
Key elements of the Project Management System
There are many interpretations of the composition of the elements of the SUP. From this set to the key elements of a sustainable system, the following can be attributed (see Figure 2):
- Methodological;
- Organizational;
- Software and technical;
- Motivational.
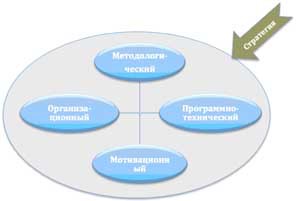
Figure 2 - Key elements of a sustainable project management system
Methodological element of an EMS
It is a complex of methods, tools, tools, theories and approaches used in the framework of ongoing projects. Those. This is a project management methodology that defines how to do the work.
Organizational element SOUP
Determines the order of activities and interaction of project participants. Consists of 3 components:
- Project and organizational structures and management and control bodies (for example, the project office, the Coordination Committee, the Steering Board, etc.);
- Members of project teams and project management bodies;
- Documentation support for EMS (regulations for interaction of project participants, procedures for managing various stages of a project, detailed instructions for executing procedures, templates for management documents, regulations on management bodies and job descriptions).
Software and hardware element SUP
At its core, it is a software and hardware complex for calendar and resource planning that can be integrated with financial planning and accounting systems, document management, personnel management, and reporting system.
Motivational element
It is a complex of motives that induce to perform functions that ensure effective project management.
As shown in Figure 2, the development of these elements is influenced by the strategy of the organization.
Why these elements and not others?
Consider a little theory, namely the work of M.Kh. Meskon "Fundamentals of Management" [2], where the author defines the management process as a set of functions of planning, organization, motivation and control, united by connecting communication and decision-making processes (see Figure 3).
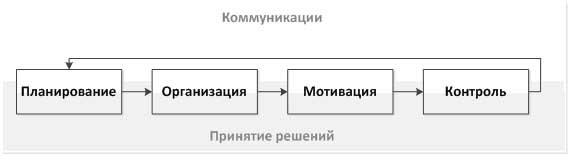
Figure 3 - Key functions of the management process
In this regard, there is an assumption that the minimum set of elements of a stable EMS, should ensure the implementation of at least these functions.
Table 1 provides information on the relationship of key management functions with the elements of an EMS.
Table 1
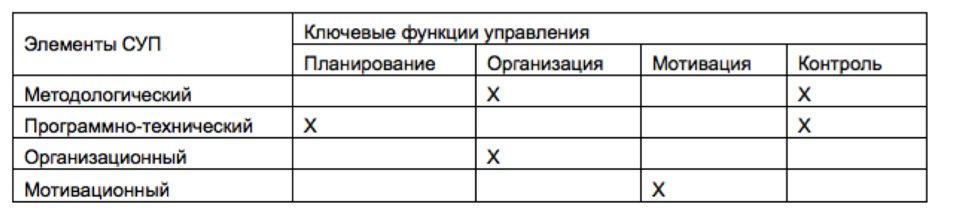
As can be seen from the table, the group of elements of the EMS provides for the implementation of all key management functions.
Certain connections are established between the SUP elements. The basic element in the project management system is Methodological, which is a complex of processes, methods, procedures of project management, allowing to perform the control function by comparing current processes, methods and procedures with those that should be performed in accordance with the chosen methodology.
The organization of work in accordance with the established methodology is provided by the organizational element of the project management system that performs the functions of a project management office, project teams, a management committee, using documentation support containing a description of the regulations, procedures and templates of project documents.
The software and technical element provides calendar and resource planning of work in accordance with the processes of the Methodological element, their relationship with the financial planning and accounting system, personnel management, document management and reporting system.
The motivational element ensures the implementation of the processes and functions of the methodological, program-technical and organizational elements by forming motivational locks that encourage the participants in the project activity to correctly perform the necessary procedures and functions. The complex of motives is a kind of “cementing solution” for the entire System, keeping all its elements as one and ensuring its stability. An example of relationships between the elements of the EMS is presented in Figure 4.
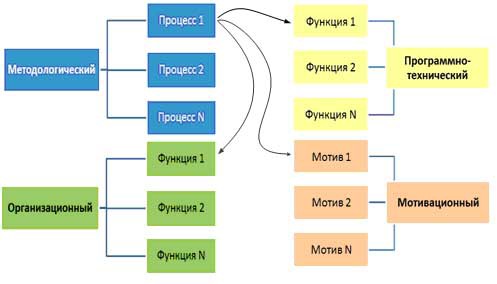
Figure 4 - An example of relationships between elements of a project management system
Evolution of the development of EMS in organizations
Management activities within an organization can be divided into three types:
- Operational management (response to abnormal situations)
- Project management (targeted change systems)
- Operational management (constantly repeating processes)
The share of each type of management activity in the total volume depends on the stage of the life cycle at which the organization is located. In turn, the share of project management depends on the degree of development of EMS in the organization.
The dependence of the share of project management on the life cycle of an organization is shown in Figure 5 [3].
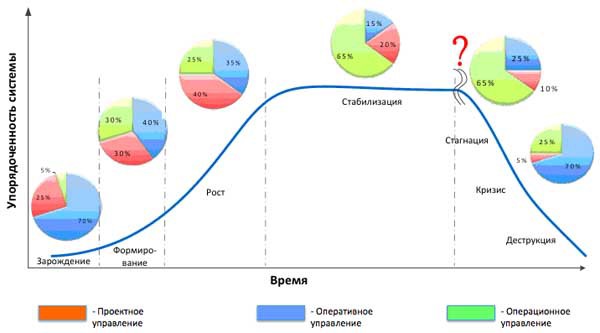
Figure 5 - Dependence of the share of project management on the life cycle of the organization
At the stage of inception in the organization, specific goals and terms of business development are set. A program or project is being implemented, which should show the viability of the organization as it was conceived. There is no project management system. Project management is practically not used (the share is about 25%). The main tool is operational management. The planning horizon in the organization ranges from one month to one year. Typically, the deviations in terms and costs range from 100 to 300% of the planned. At this stage, a weak perception of the owners and managers about the state of the internal and external environment of the organization is characteristic. The duration of this stage for the organization of medium-sized businesses is about 2–3 years.
At the stage of Business Formation, project management, as a rule, focuses on buying the missing assets and on creating an efficient business model. The share of project management is higher and is about 30%. The duration of the stage for the organization of medium-sized businesses is 3-4 years.
Growth stage is associated with the struggle for a share of the national market. Project management is used in large-scale expansion programs in regional or international markets. At this stage, the project management system is most in demand. The share of project management is higher and is about 40%. The duration of this stage for the organization of medium-sized businesses is about 4-5 years.
Closer to the Stabilization stage, project management becomes more operational (projects become cyclical, most projects are typical). At the Stabilization stage in an organization, the need arises for the implementation of innovative projects that would help it maintain a competitive advantage by introducing new products and services to the market. The period of this stage can vary greatly and depends on the quality of management of the organization. The share of project management is reduced and is about 20%.
The degree of development of a project management system in an organization depends on its level of technological maturity in the field of project management and the life cycle stage in which it is located.
If, for example, we take Gerold Kerzner’s 5-level maturity model (see Figure 6) [4], then the dependence of the maturity level of project management on the organization’s life cycle will look like this (see Figure 7).

Figure 6 - Herold Kerzner's model of maturity
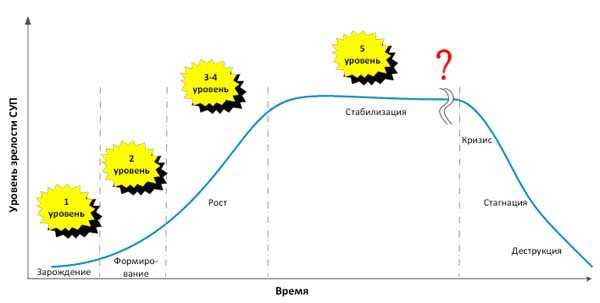
Figure 7 - The dependence of the level of maturity of project management from the life cycle of the organization
The level of development of the project management system depends on the degree of development of its elements, and also depends on the level of maturity of the organization in the field of project management. Information on this dependence as an example is presented in Figures 8 - 12. In these figures, the “Strategic” element is external to the EMS and is shown for information and comparability.
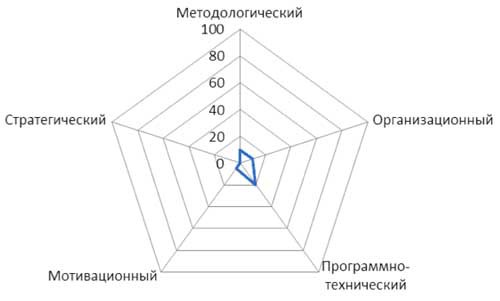
Figure 8 - The degree of elaboration of the elements of the SUP (1 level of maturity)

Figure 9 - The degree of study of the elements of the SUP (level of maturity 2)
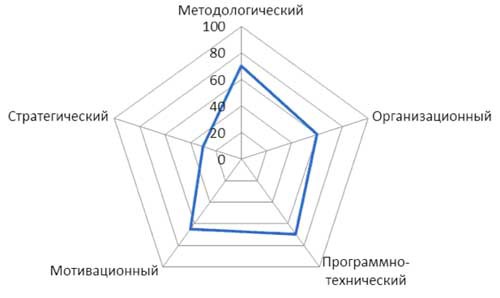
Figure 10 - The degree of elaboration of the elements of the SUP (3 level of maturity)
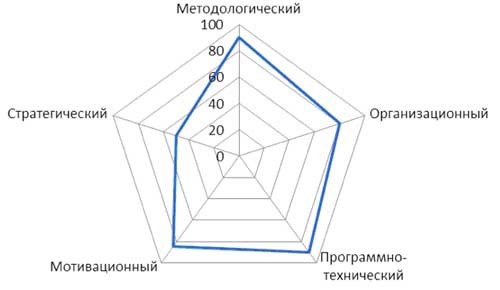
Figure 11 - The degree of elaboration of the elements of the SUP (level of maturity 4)
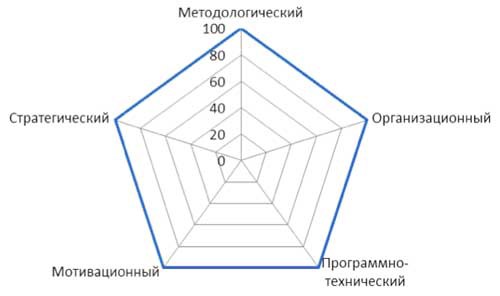
Figure 12 - The degree of elaboration of the elements of the EMS (level of maturity 5)
The process of developing a project management system usually occurs in the following order:
- Training of staff in project management;
- The development of management practices;
- Understanding the results;
- Generalization of the results, conceptualization, building patterns of action;
- Formation of experience.
- This process is iterative.
At the same time, the method shown in Figure 13 is more effective. Using this approach in developing a project management system will help accelerate maturation in the field of project management for a medium-sized business organization, according to expert estimates, by about 10% to 20%.
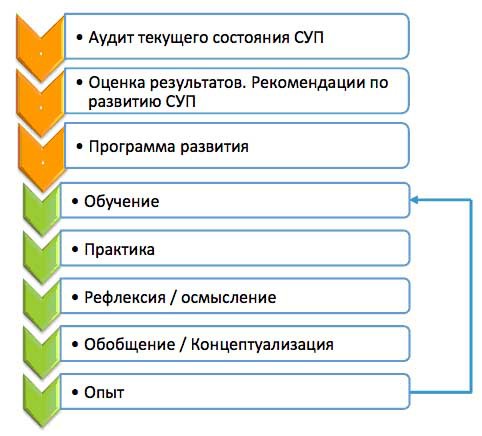
Figure 13 - The process of developing a project management system
Recommendations
In conclusion, I would recommend to use the professional assessment of the technological maturity of the organization in the field of project management, which allows you to correctly draw up a program for the earliest development of the project management system taking into account the current strengths and weaknesses of the organization and gain new competitive advantages in the most optimal and fast way.
References:
1. PMI, Guide to the Body of Knowledge on Project Management. Fourth edition, 2008
2. Meskon M. Fundamentals of Management: Moscow, Publishing House "Delo", 1997.
3. Chernov D.V. The role of project management at different stages of the life cycle of the organization. Project and Program Management №01 (29) 2012.
4. Malinin M.V. Modern maturity models of organizational project management. Project and Program Management №3 2011.
In fact, in the updated interpretation of the PMI PMBoK (4-th edition) knowledge book [1], the EMS is a set of processes, tools, methods, methodologies, resources and procedures for managing a project.
At the same time, it is worth paying attention to the fact that the project methodology is a three-level structure “PRODUCT - BUSINESS - STRATEGY”:
Level 1 (PRODUCT) - project management;
Level 2 (BUSINESS) - program management;
Level 3 (STRATEGY) - project portfolio management.
Moreover, the PRODUCT level (Project Management) is the base level, the starting point, for the construction of the remaining levels - BUSINESS and STRATEGY (see Figure 1).
')

Figure 1 - The three-level structure of the project methodology
Why organizations of EMS and project activities?
The project management system allows you to effectively carry out projects that lead to qualitative changes within organizations, which in turn allows organizations to gain new competitive advantages.
Examples of such projects include building infrastructure, entering an IPO, launching a new product or service, etc.
The value of a project management system is especially high at the stage of growth of an organization, when it already has experience in the local market and is trying to transfer an already tested business model to the republican or international market. At this time, organizations are implementing large-scale development programs consisting of a dozen projects.
Key elements of the Project Management System
There are many interpretations of the composition of the elements of the SUP. From this set to the key elements of a sustainable system, the following can be attributed (see Figure 2):
- Methodological;
- Organizational;
- Software and technical;
- Motivational.

Figure 2 - Key elements of a sustainable project management system
Methodological element of an EMS
It is a complex of methods, tools, tools, theories and approaches used in the framework of ongoing projects. Those. This is a project management methodology that defines how to do the work.
Organizational element SOUP
Determines the order of activities and interaction of project participants. Consists of 3 components:
- Project and organizational structures and management and control bodies (for example, the project office, the Coordination Committee, the Steering Board, etc.);
- Members of project teams and project management bodies;
- Documentation support for EMS (regulations for interaction of project participants, procedures for managing various stages of a project, detailed instructions for executing procedures, templates for management documents, regulations on management bodies and job descriptions).
Software and hardware element SUP
At its core, it is a software and hardware complex for calendar and resource planning that can be integrated with financial planning and accounting systems, document management, personnel management, and reporting system.
Motivational element
It is a complex of motives that induce to perform functions that ensure effective project management.
As shown in Figure 2, the development of these elements is influenced by the strategy of the organization.
Why these elements and not others?
Consider a little theory, namely the work of M.Kh. Meskon "Fundamentals of Management" [2], where the author defines the management process as a set of functions of planning, organization, motivation and control, united by connecting communication and decision-making processes (see Figure 3).

Figure 3 - Key functions of the management process
In this regard, there is an assumption that the minimum set of elements of a stable EMS, should ensure the implementation of at least these functions.
Table 1 provides information on the relationship of key management functions with the elements of an EMS.
Table 1

As can be seen from the table, the group of elements of the EMS provides for the implementation of all key management functions.
Certain connections are established between the SUP elements. The basic element in the project management system is Methodological, which is a complex of processes, methods, procedures of project management, allowing to perform the control function by comparing current processes, methods and procedures with those that should be performed in accordance with the chosen methodology.
The organization of work in accordance with the established methodology is provided by the organizational element of the project management system that performs the functions of a project management office, project teams, a management committee, using documentation support containing a description of the regulations, procedures and templates of project documents.
The software and technical element provides calendar and resource planning of work in accordance with the processes of the Methodological element, their relationship with the financial planning and accounting system, personnel management, document management and reporting system.
The motivational element ensures the implementation of the processes and functions of the methodological, program-technical and organizational elements by forming motivational locks that encourage the participants in the project activity to correctly perform the necessary procedures and functions. The complex of motives is a kind of “cementing solution” for the entire System, keeping all its elements as one and ensuring its stability. An example of relationships between the elements of the EMS is presented in Figure 4.

Figure 4 - An example of relationships between elements of a project management system
Evolution of the development of EMS in organizations
Management activities within an organization can be divided into three types:
- Operational management (response to abnormal situations)
- Project management (targeted change systems)
- Operational management (constantly repeating processes)
The share of each type of management activity in the total volume depends on the stage of the life cycle at which the organization is located. In turn, the share of project management depends on the degree of development of EMS in the organization.
The dependence of the share of project management on the life cycle of an organization is shown in Figure 5 [3].

Figure 5 - Dependence of the share of project management on the life cycle of the organization
At the stage of inception in the organization, specific goals and terms of business development are set. A program or project is being implemented, which should show the viability of the organization as it was conceived. There is no project management system. Project management is practically not used (the share is about 25%). The main tool is operational management. The planning horizon in the organization ranges from one month to one year. Typically, the deviations in terms and costs range from 100 to 300% of the planned. At this stage, a weak perception of the owners and managers about the state of the internal and external environment of the organization is characteristic. The duration of this stage for the organization of medium-sized businesses is about 2–3 years.
At the stage of Business Formation, project management, as a rule, focuses on buying the missing assets and on creating an efficient business model. The share of project management is higher and is about 30%. The duration of the stage for the organization of medium-sized businesses is 3-4 years.
Growth stage is associated with the struggle for a share of the national market. Project management is used in large-scale expansion programs in regional or international markets. At this stage, the project management system is most in demand. The share of project management is higher and is about 40%. The duration of this stage for the organization of medium-sized businesses is about 4-5 years.
Closer to the Stabilization stage, project management becomes more operational (projects become cyclical, most projects are typical). At the Stabilization stage in an organization, the need arises for the implementation of innovative projects that would help it maintain a competitive advantage by introducing new products and services to the market. The period of this stage can vary greatly and depends on the quality of management of the organization. The share of project management is reduced and is about 20%.
The degree of development of a project management system in an organization depends on its level of technological maturity in the field of project management and the life cycle stage in which it is located.
If, for example, we take Gerold Kerzner’s 5-level maturity model (see Figure 6) [4], then the dependence of the maturity level of project management on the organization’s life cycle will look like this (see Figure 7).

Figure 6 - Herold Kerzner's model of maturity

Figure 7 - The dependence of the level of maturity of project management from the life cycle of the organization
The level of development of the project management system depends on the degree of development of its elements, and also depends on the level of maturity of the organization in the field of project management. Information on this dependence as an example is presented in Figures 8 - 12. In these figures, the “Strategic” element is external to the EMS and is shown for information and comparability.

Figure 8 - The degree of elaboration of the elements of the SUP (1 level of maturity)

Figure 9 - The degree of study of the elements of the SUP (level of maturity 2)

Figure 10 - The degree of elaboration of the elements of the SUP (3 level of maturity)

Figure 11 - The degree of elaboration of the elements of the SUP (level of maturity 4)

Figure 12 - The degree of elaboration of the elements of the EMS (level of maturity 5)
The process of developing a project management system usually occurs in the following order:
- Training of staff in project management;
- The development of management practices;
- Understanding the results;
- Generalization of the results, conceptualization, building patterns of action;
- Formation of experience.
- This process is iterative.
At the same time, the method shown in Figure 13 is more effective. Using this approach in developing a project management system will help accelerate maturation in the field of project management for a medium-sized business organization, according to expert estimates, by about 10% to 20%.

Figure 13 - The process of developing a project management system
Recommendations
In conclusion, I would recommend to use the professional assessment of the technological maturity of the organization in the field of project management, which allows you to correctly draw up a program for the earliest development of the project management system taking into account the current strengths and weaknesses of the organization and gain new competitive advantages in the most optimal and fast way.
References:
1. PMI, Guide to the Body of Knowledge on Project Management. Fourth edition, 2008
2. Meskon M. Fundamentals of Management: Moscow, Publishing House "Delo", 1997.
3. Chernov D.V. The role of project management at different stages of the life cycle of the organization. Project and Program Management №01 (29) 2012.
4. Malinin M.V. Modern maturity models of organizational project management. Project and Program Management №3 2011.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/223101/
All Articles