Dedicated servers underwater, literally !? Prospects for breeding fish in servers?
We all know that water and electronics are a dangerous combination, but is it always? Can modern technology change this view?
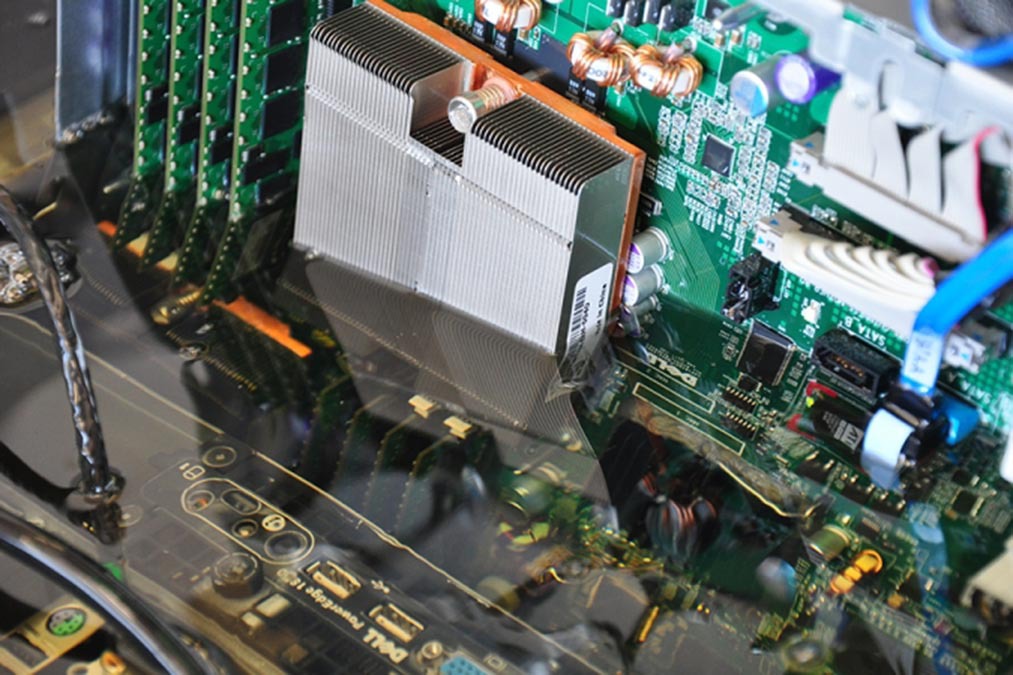
In this article we will consider the possibility, advantages and disadvantages of placing servers in a liquid and discuss possible exploitation problems. Let us show how it all can look in practice and really work. We will also discuss the question of why fish can or cannot swim in servers :)
')
For a long time, energy loss and cooling costs during server operation did not give rest to many, including us, as the number of servers used by our subscribers is constantly growing rapidly, we are increasingly thinking about creating our own data center in the foreseeable future. And when more than half of the energy consumed by the entire data center is spent on air cooling, thanks to which it is possible to divert the released heat from the equipment with an efficiency ratio of 1.7, one wonders how to improve cooling efficiency and minimize energy losses?

It is known from the physics course that air is an extremely inefficient conductor of heat, since its thermal conductivity is 25 times lower than the thermal conductivity of water. It is more suitable for thermal insulation, rather than for heat sink. It also has a very small heat capacity, which means that it must constantly be intensively mixed and supplied with large volumes for cooling. Another thing is water and liquids. They are used in data center cooling systems in the form of a heat exchanger in order to increase the overall efficiency ratio, but they are not in direct contact with liquid servers, only through the air gap and / or radiator (for cooling the chipset, for example), which allows increasing the mechanical efficiency ratio of the cooling system ( mPUE) to 1.2 or even to 1.15 when using the external environment for cooling purposes.
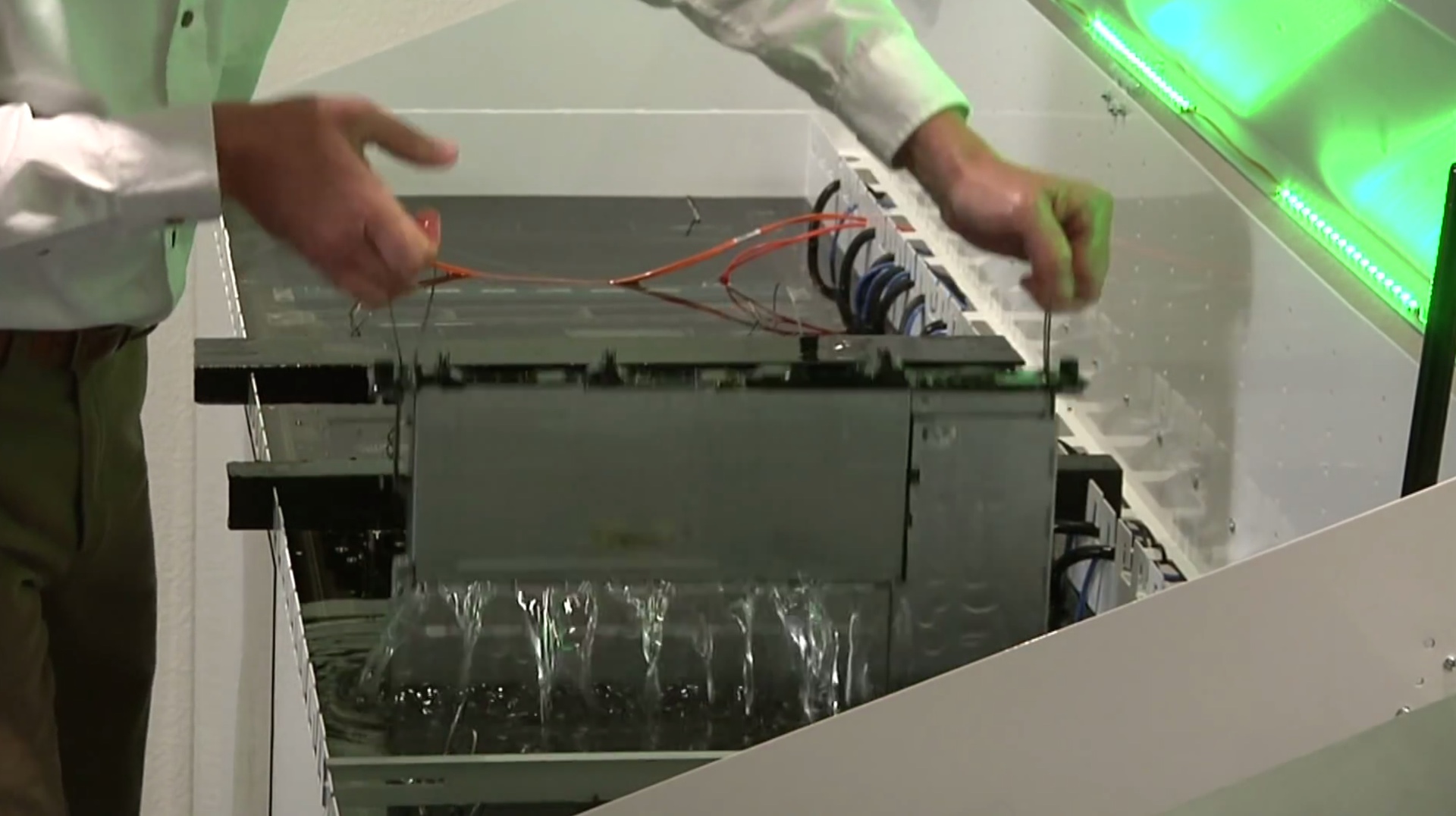
But how to cool the server most efficiently? There is only one way out - to place it completely in a liquid (of course, a dielectric), preferably with the greatest possible thermal conductivity and heat capacity, which will not adversely affect the server components. And mineral oil can be such a dielectric. The idea, unfortunately and fortunately, was not new - for several years several companies have been developing and implementing it in various variations and with different efficiencies. Modern technologies allow you to build an "underwater" Data Center! But what are the advantages and disadvantages of this solution?
Cooling in a liquid now saves up to 95 percent of the electricity that is commonly used for cooling in Data Centers and, as a result, up to 50% of all energy consumed by Data Center.

The cooling system in the liquid saves up to 60% of funds during the construction of the Data Center, as there is no need to purchase expensive chillers, HVAC (heating ventilation air cooling) systems, construction of cold / hot corridors, use of raised floor, etc.
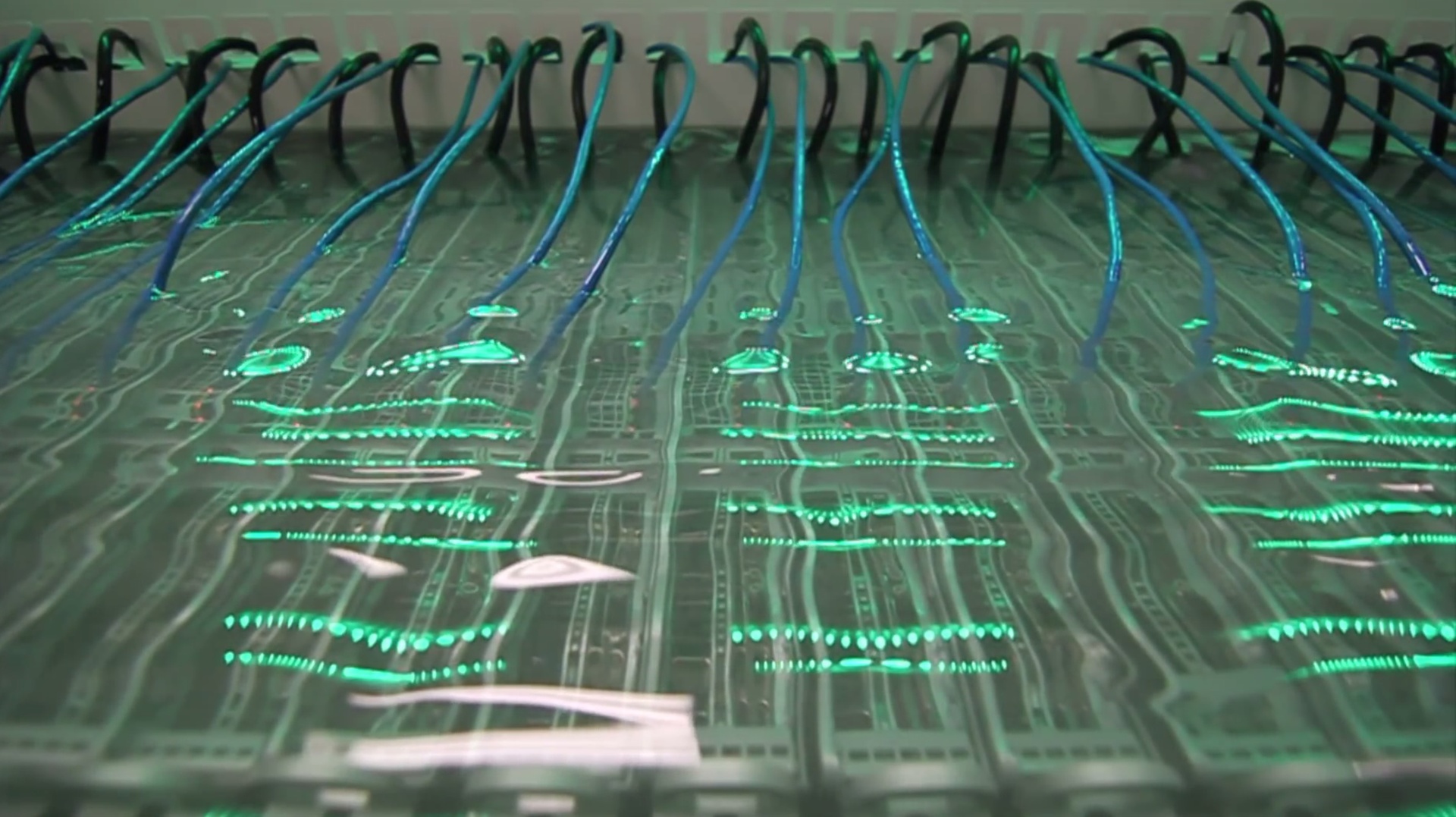
SSDs can be immersed in coolant, of course while maintaining performance :), without any modifications, as in the rest of the rest of the standard server components, with the exception of hard drives. Hard drives will require the use of additional devices, because they will not be able to rotate effectively in liquid.
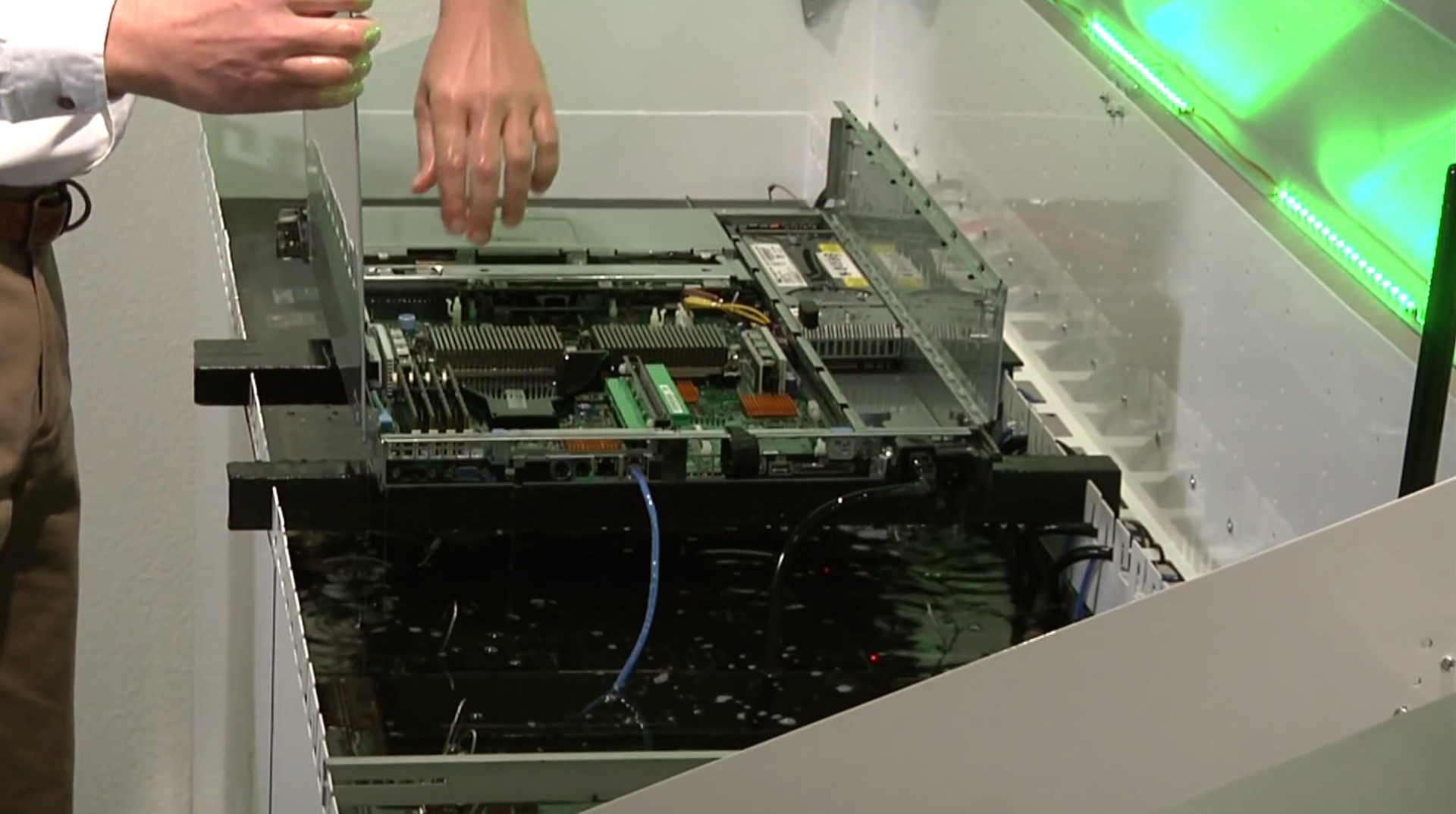
Since the coolant is a dielectric (does not conduct electricity) - there is no need to dry the servers and drain the entire system to work in a cabinet or with a specific server. Nevertheless, this liquid should be non-toxic, odorless (with minimal evaporation) and not aggressive towards the server components, for example, do not dissolve the rubber insulation of wires, etc. Finding the right and effective mineral oil is not an easy task. Not every mineral oil is suitable for the task of cooling in a liquid. And depending on the selected oil, we will get different permissible power of the equipment in the 42-unit cabinet, the heat from which the system is able to divert.
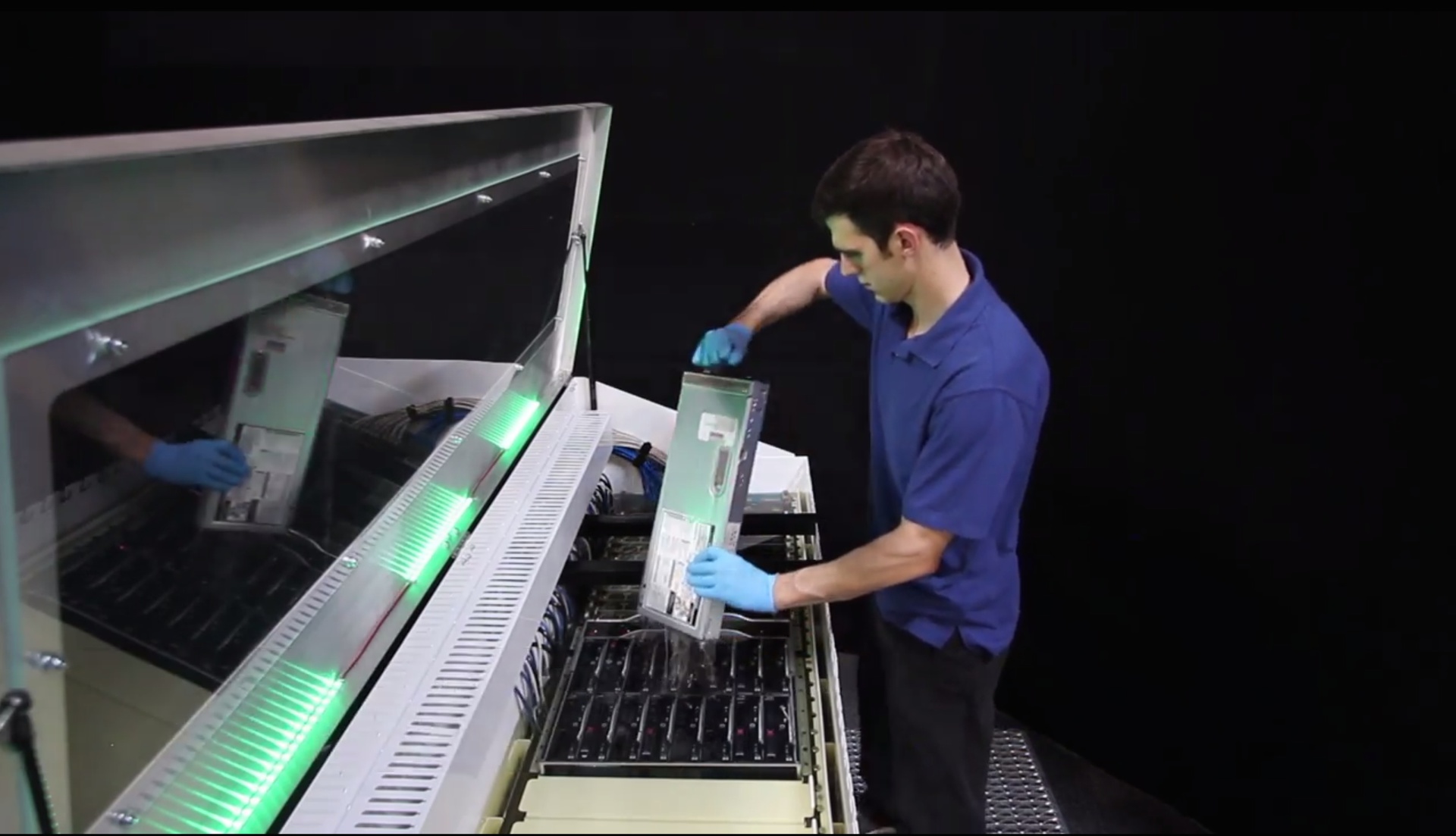

If we talk about the effectiveness of cooling in the liquid as a whole, the system allows to achieve PUE 1.03. But how is this possible, you ask, if the use of mineral oil for cooling saves only 95% of energy? Due to what we can get additional efficiency of 2%?

The answer is simple, cooling in the liquid saves the energy consumed by the servers, due to the fact that they no longer need to install coolers for cooling, as well as due to the fact that the leakage of currents from the chips decreases, as they are reliably isolated and work at a constant temperature (a change in temperature contributes to the leakage of currents). And as a result, we save on the cooling system, as it can now occupy less volume, because it needs to remove less heat. This gives a gain of those cherished 2 percent on cooling, but we get not only that. The servers themselves begin to consume energy by 10-20 percent less than servers with different cooling. PUE total Data Center is growing.
Mineral oil is able to effectively protect against corrosion and dust, due to the fact that unlike air it does not contain water and oxygen, it prolongs the life of the equipment. It is non-toxic and odorless, which means it practically does not evaporate. But it is of varying effectiveness and the selection of the right mineral oil is a real art.
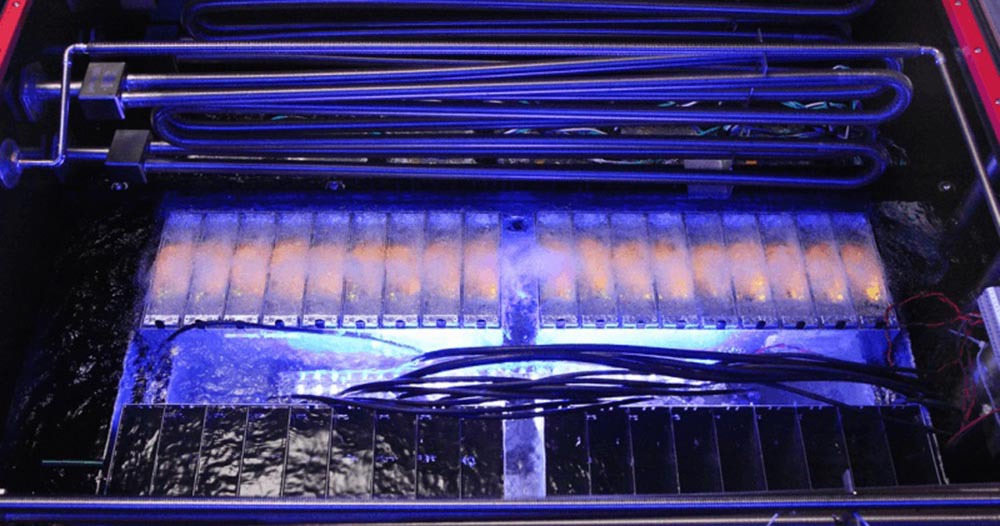

Various companies have long been closely involved in these issues and have had various successes due to the use of different mineral oils, creating their own know-how. About a month ago, Intel and SGI announced a “news” that, thanks to the use of mineral oil and its own developed cooling system based on it, which provides for the operation of servers in a liquid, can provide heat removal from the cabinet to several tens of kilowatts and even more. But they still have problems, especially in their message it is mentioned that conventional optical cables in their mineral oil will most likely not be able to work, for which reason, alas, it is not specified, apparently the oil is aggressive for them. The solution is far from commercial exploitation.
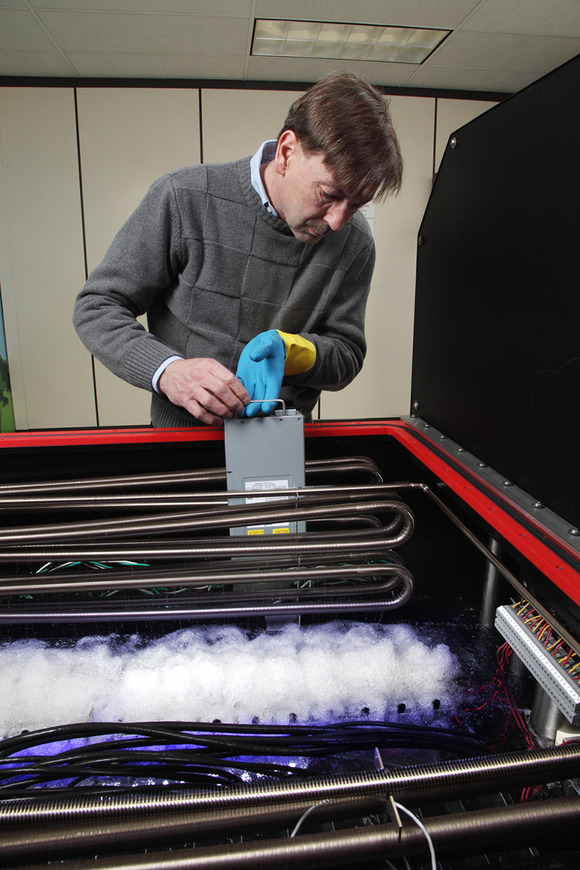

Another company, GRC, has long used a much more efficient mineral oil, offers a ready-made commercial solution and does not have similar problems, has not published this for a long time as a “news”, and according to them, they are able to remove heat from the cabinet up to 100 kW and more, which means Intel has significantly exceeded its success! So you need more critical attitude to all information from the news. If one company claims “know-how,” this does not mean that the other has not thought up any better, some may just be at the beginning of their journey in a new direction for them :) As mentioned above, Intel is still very far from commercial exploitation this solution, but without it in the end, the decision of any company will not do.
On today's motherboards, the circuits are laid out at a “huge” distance from each other in order to maximize heat dissipation for use as an air cooler, which is terribly not an effective cooler. Thanks to the cooling in the liquid, you can start the production of servers with more densely packed schemes that take into account the work in the liquid and the property of heat removal by the liquid, because the liquid has not only higher thermal conductivity than air, but a much higher heat capacity. The most effective mineral oils today have a heat capacity that exceeds the heat capacity of air by more than 1200 times!

All this allows not only to remove heat much more efficiently, but also in the case of stopping the cooling system, to get much more time to repair it before the work goes to a critical state due to the rise in temperature, since the fluid properties (high heat capacity and density) allow to absorb much more heat, while the liquid does not become overheated itself, thereby moving the threshold of "critical overheating" in time.
Very great prospects are opening up for supercomputers working in liquids; saving energy and space when operating high-performance equipment is enormous.

Most likely in the future there will be no computing and server equipment that could work without immersion in a liquid. The advantages are huge, there are practically no flaws, except that the cabinets now need to be positioned not vertically, but horizontally, which is somewhat unusual. Due to this, it is possible to increase the “density” of equipment in the Data Center, as well as provide an additional level of security. If suddenly the Data Center is flooded with water as a result of a natural disaster, the water will not affect the servers, as they are already immersed in liquid, albeit with a different density, but reliably sealed in cabinets.
- there is no need to purchase expensive chillers, HVAC (heating ventilation air cooling) systems;
- there is no need for construction of cold / hot corridors, use of raised floor;
- the number of generators, batteries of uninterruptible power systems (UPS) is reduced by N units of equipment, by reducing consumption - - energy of this equipment when working in a liquid;
- infrastructure cost per Watt is lower by 73% than during the construction of an air-cooled data center, and by 55% if the data center uses the external environment for cooling;
- the cost of infrastructure per server gives a gain of 86 and 70 percent, respectively.

- equipment, being in a liquid, consumes 10-20% less energy, depending on the type, due to the absence of coolers and the loss of currents from the chips, due to their presence in the insulator and ensuring their constant temperature;
- 90-95% of energy is saved due to the cooling of the servers in the liquid and the lack of large-sized cooling systems in the data center, since now the heat from the cabinet with servers in mineral oil can be effectively removed using an evaporative cooling tower (no mechanics, only water evaporation) or using a circuit with cold water;
- there are no costs associated with the depreciation of conventional cooling systems, the cost of energy supply systems are significantly reduced in terms of N units, due to the fact that you need to contain fewer UPS batteries, including;
mineral oil is almost forever, it does not need to be changed and almost does not need to be added (except in cases of leakage), unlike other coolers in the data center;
- if on average the server consumes about 230-270 watts of power and 50-170 watts for cooling, depending on the cooling method used, then cooling in a liquid reduces the average power consumption of the server to 210 watts, and the energy required for cooling it is about 10 Watt!
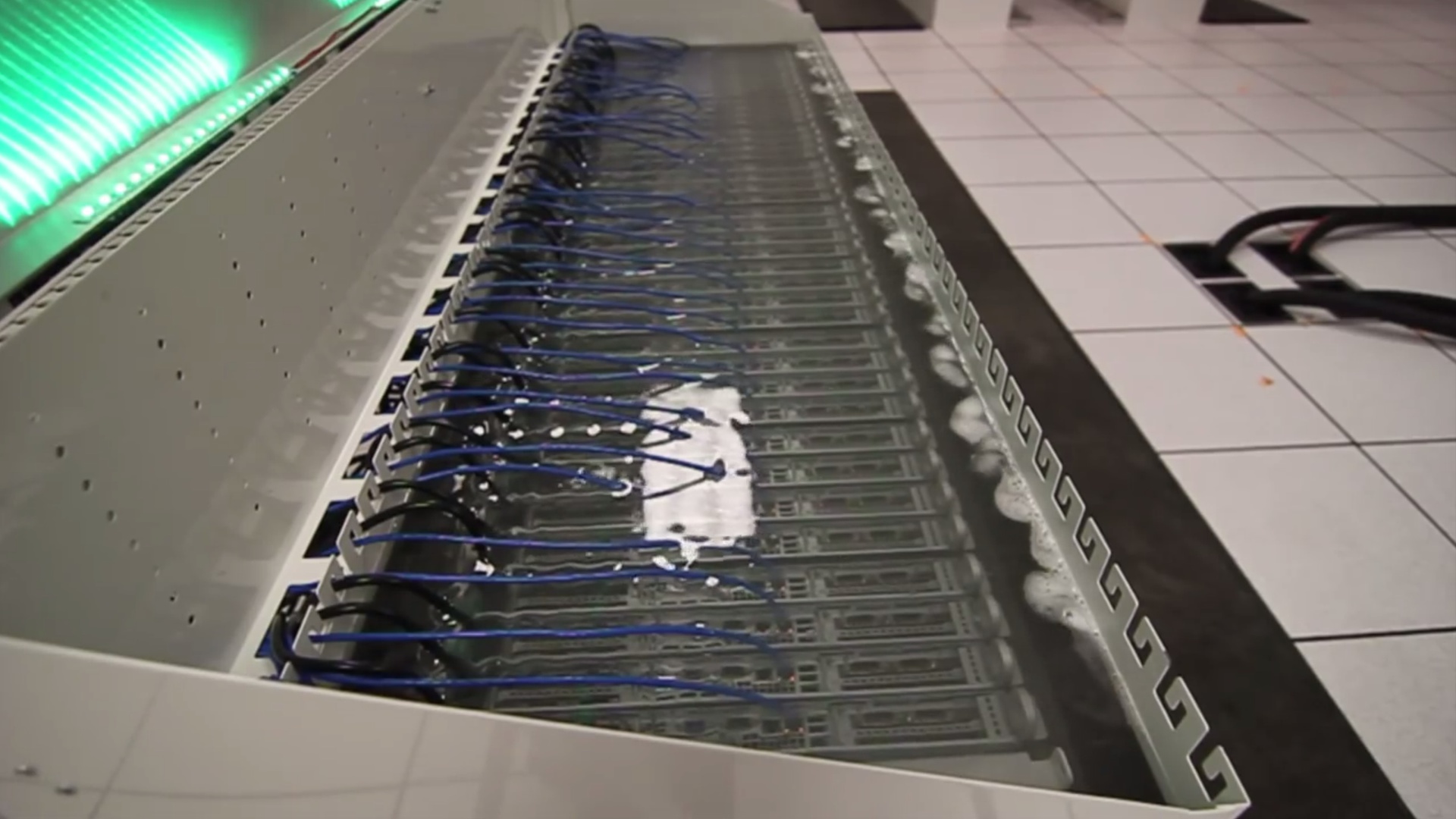

You can take more than 100 kW of heat from a 42-unit cabinet immersed in mineral oil! And also significantly reduce spending on server hardware, up to 50% for various components, and all because now the constant operating temperature is about 20 degrees lower than in the air environment, it is possible to use even dextop components without fear, since they work with much lower temperatures.
Of course, this idea has not received and will not receive such widespread use in the personal computer market, simply because the majority has long since switched to laptops and other gadgets, home workstations in the “tower” building are often used only by professionals, since they need great performance and large amount of heat. Here, for them, immersing their precious iron in a liquid can be very useful!
It turns out to implement it at home is not difficult and possible, and it was done by many lovers of moding for quite some time. Some companies even propose to purchase a ready-made solution based on the mineral oil “Crystal Plus 70T”, which is commercially available and, according to experimenters, is ideal for this task, has a heat capacity 750 times higher than that of air and a density lower than that of water.
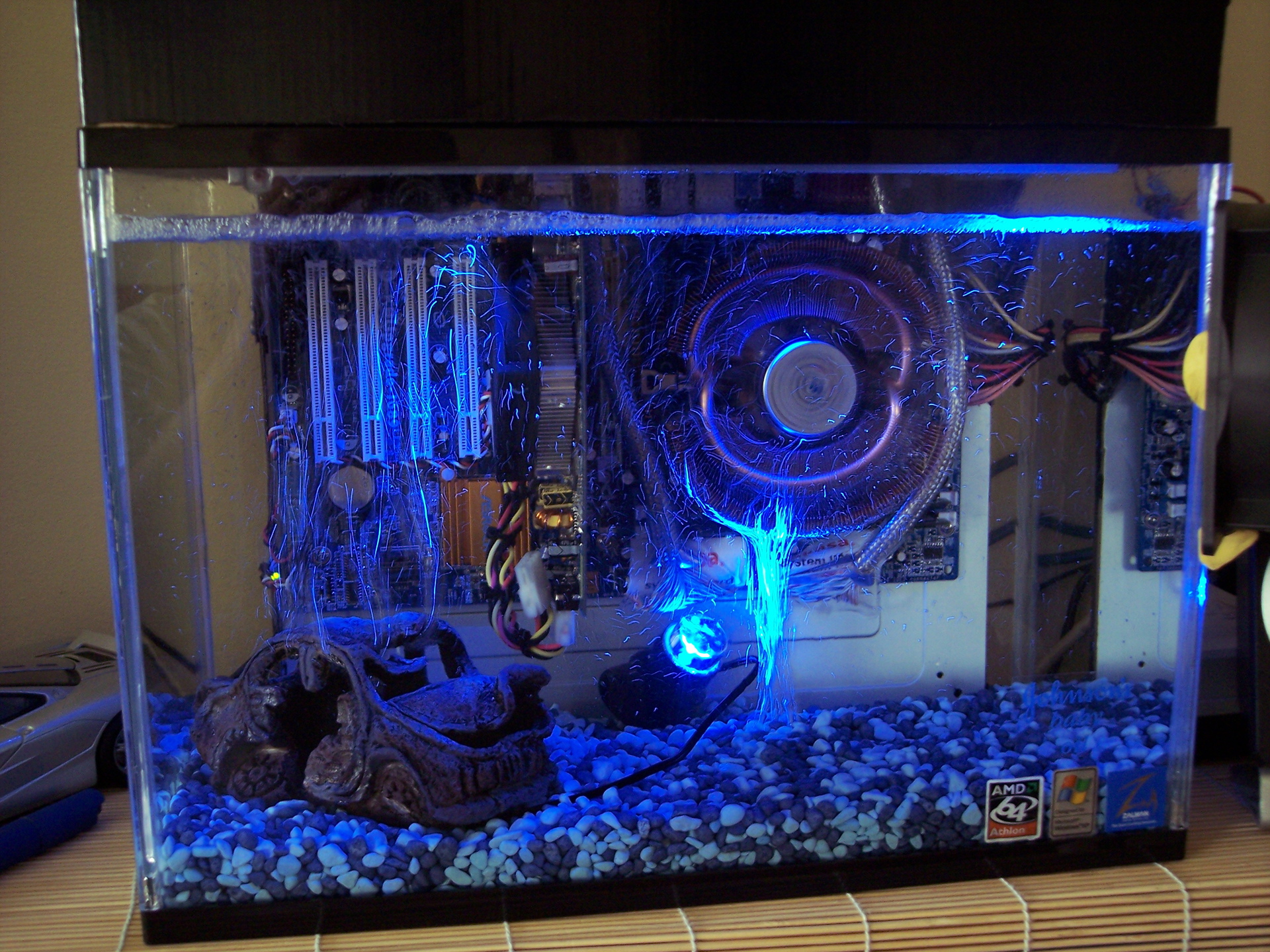

Mixing the liquid can be carried out by passing air through mineral oil or even an ordinary computer cooler, which in the mineral oil rotates itself much slower than in the air, but retains its efficiency. When asked what to do with water vapor that will get into mineral oil when air is passed through for mixing, the developers answer that due to different density (greater than water), water will accumulate at the very bottom of the "aquarium" where it is not any electrical components, however, they have not yet seen that in the course of a long operation at least a tiny amount of water would appear, otherwise the reservoir would begin to resemble a “lava-lamp”.
I dare to admit that observing various FISH under water is an unforgettable pleasure. I am a diver and would not refuse a work station at home in the form of an aquarium with tropical or not-so-tropical fish.
But alas, genetic engineering still lags behind fashion in IT, fish will die if they are placed in mineral oil, it is extremely far from the necessary water for fish in its properties. Let's hope that this idea, either through the use of new technologies or through genetic engineering, will be possible for someone to implement in the future, but for now you can use robotic fish!
I will be the first to order a robotic boxfish!

Well, by itself, do not forget to support the construction of our future underwater Data Center (for which I have no idea about ideas) - order dedicated servers from us , so far in the Netherlands and the USA, and from $ 49, and in the future on the Barrier Reef!

In this article we will consider the possibility, advantages and disadvantages of placing servers in a liquid and discuss possible exploitation problems. Let us show how it all can look in practice and really work. We will also discuss the question of why fish can or cannot swim in servers :)
')
For a long time, energy loss and cooling costs during server operation did not give rest to many, including us, as the number of servers used by our subscribers is constantly growing rapidly, we are increasingly thinking about creating our own data center in the foreseeable future. And when more than half of the energy consumed by the entire data center is spent on air cooling, thanks to which it is possible to divert the released heat from the equipment with an efficiency ratio of 1.7, one wonders how to improve cooling efficiency and minimize energy losses?

It is known from the physics course that air is an extremely inefficient conductor of heat, since its thermal conductivity is 25 times lower than the thermal conductivity of water. It is more suitable for thermal insulation, rather than for heat sink. It also has a very small heat capacity, which means that it must constantly be intensively mixed and supplied with large volumes for cooling. Another thing is water and liquids. They are used in data center cooling systems in the form of a heat exchanger in order to increase the overall efficiency ratio, but they are not in direct contact with liquid servers, only through the air gap and / or radiator (for cooling the chipset, for example), which allows increasing the mechanical efficiency ratio of the cooling system ( mPUE) to 1.2 or even to 1.15 when using the external environment for cooling purposes.

But how to cool the server most efficiently? There is only one way out - to place it completely in a liquid (of course, a dielectric), preferably with the greatest possible thermal conductivity and heat capacity, which will not adversely affect the server components. And mineral oil can be such a dielectric. The idea, unfortunately and fortunately, was not new - for several years several companies have been developing and implementing it in various variations and with different efficiencies. Modern technologies allow you to build an "underwater" Data Center! But what are the advantages and disadvantages of this solution?
Advantages and disadvantages of placing servers in fluids
Cooling in a liquid now saves up to 95 percent of the electricity that is commonly used for cooling in Data Centers and, as a result, up to 50% of all energy consumed by Data Center.

The cooling system in the liquid saves up to 60% of funds during the construction of the Data Center, as there is no need to purchase expensive chillers, HVAC (heating ventilation air cooling) systems, construction of cold / hot corridors, use of raised floor, etc.

SSDs can be immersed in coolant, of course while maintaining performance :), without any modifications, as in the rest of the rest of the standard server components, with the exception of hard drives. Hard drives will require the use of additional devices, because they will not be able to rotate effectively in liquid.

Since the coolant is a dielectric (does not conduct electricity) - there is no need to dry the servers and drain the entire system to work in a cabinet or with a specific server. Nevertheless, this liquid should be non-toxic, odorless (with minimal evaporation) and not aggressive towards the server components, for example, do not dissolve the rubber insulation of wires, etc. Finding the right and effective mineral oil is not an easy task. Not every mineral oil is suitable for the task of cooling in a liquid. And depending on the selected oil, we will get different permissible power of the equipment in the 42-unit cabinet, the heat from which the system is able to divert.

If we talk about the effectiveness of cooling in the liquid as a whole, the system allows to achieve PUE 1.03. But how is this possible, you ask, if the use of mineral oil for cooling saves only 95% of energy? Due to what we can get additional efficiency of 2%?

The answer is simple, cooling in the liquid saves the energy consumed by the servers, due to the fact that they no longer need to install coolers for cooling, as well as due to the fact that the leakage of currents from the chips decreases, as they are reliably isolated and work at a constant temperature (a change in temperature contributes to the leakage of currents). And as a result, we save on the cooling system, as it can now occupy less volume, because it needs to remove less heat. This gives a gain of those cherished 2 percent on cooling, but we get not only that. The servers themselves begin to consume energy by 10-20 percent less than servers with different cooling. PUE total Data Center is growing.
Successes of various companies in the field of server cooling in liquid
Mineral oil is able to effectively protect against corrosion and dust, due to the fact that unlike air it does not contain water and oxygen, it prolongs the life of the equipment. It is non-toxic and odorless, which means it practically does not evaporate. But it is of varying effectiveness and the selection of the right mineral oil is a real art.

Various companies have long been closely involved in these issues and have had various successes due to the use of different mineral oils, creating their own know-how. About a month ago, Intel and SGI announced a “news” that, thanks to the use of mineral oil and its own developed cooling system based on it, which provides for the operation of servers in a liquid, can provide heat removal from the cabinet to several tens of kilowatts and even more. But they still have problems, especially in their message it is mentioned that conventional optical cables in their mineral oil will most likely not be able to work, for which reason, alas, it is not specified, apparently the oil is aggressive for them. The solution is far from commercial exploitation.

Another company, GRC, has long used a much more efficient mineral oil, offers a ready-made commercial solution and does not have similar problems, has not published this for a long time as a “news”, and according to them, they are able to remove heat from the cabinet up to 100 kW and more, which means Intel has significantly exceeded its success! So you need more critical attitude to all information from the news. If one company claims “know-how,” this does not mean that the other has not thought up any better, some may just be at the beginning of their journey in a new direction for them :) As mentioned above, Intel is still very far from commercial exploitation this solution, but without it in the end, the decision of any company will not do.
Perspectives
On today's motherboards, the circuits are laid out at a “huge” distance from each other in order to maximize heat dissipation for use as an air cooler, which is terribly not an effective cooler. Thanks to the cooling in the liquid, you can start the production of servers with more densely packed schemes that take into account the work in the liquid and the property of heat removal by the liquid, because the liquid has not only higher thermal conductivity than air, but a much higher heat capacity. The most effective mineral oils today have a heat capacity that exceeds the heat capacity of air by more than 1200 times!

All this allows not only to remove heat much more efficiently, but also in the case of stopping the cooling system, to get much more time to repair it before the work goes to a critical state due to the rise in temperature, since the fluid properties (high heat capacity and density) allow to absorb much more heat, while the liquid does not become overheated itself, thereby moving the threshold of "critical overheating" in time.
Very great prospects are opening up for supercomputers working in liquids; saving energy and space when operating high-performance equipment is enormous.

Most likely in the future there will be no computing and server equipment that could work without immersion in a liquid. The advantages are huge, there are practically no flaws, except that the cabinets now need to be positioned not vertically, but horizontally, which is somewhat unusual. Due to this, it is possible to increase the “density” of equipment in the Data Center, as well as provide an additional level of security. If suddenly the Data Center is flooded with water as a result of a natural disaster, the water will not affect the servers, as they are already immersed in liquid, albeit with a different density, but reliably sealed in cabinets.
Liquid cooling in numbers
Savings of over 60% of funds during construction:
- there is no need to purchase expensive chillers, HVAC (heating ventilation air cooling) systems;
- there is no need for construction of cold / hot corridors, use of raised floor;
- the number of generators, batteries of uninterruptible power systems (UPS) is reduced by N units of equipment, by reducing consumption - - energy of this equipment when working in a liquid;
- infrastructure cost per Watt is lower by 73% than during the construction of an air-cooled data center, and by 55% if the data center uses the external environment for cooling;
- the cost of infrastructure per server gives a gain of 86 and 70 percent, respectively.

Savings over 50% of operating costs:
- equipment, being in a liquid, consumes 10-20% less energy, depending on the type, due to the absence of coolers and the loss of currents from the chips, due to their presence in the insulator and ensuring their constant temperature;
- 90-95% of energy is saved due to the cooling of the servers in the liquid and the lack of large-sized cooling systems in the data center, since now the heat from the cabinet with servers in mineral oil can be effectively removed using an evaporative cooling tower (no mechanics, only water evaporation) or using a circuit with cold water;
- there are no costs associated with the depreciation of conventional cooling systems, the cost of energy supply systems are significantly reduced in terms of N units, due to the fact that you need to contain fewer UPS batteries, including;
mineral oil is almost forever, it does not need to be changed and almost does not need to be added (except in cases of leakage), unlike other coolers in the data center;
- if on average the server consumes about 230-270 watts of power and 50-170 watts for cooling, depending on the cooling method used, then cooling in a liquid reduces the average power consumption of the server to 210 watts, and the energy required for cooling it is about 10 Watt!

You can take more than 100 kW of heat from a 42-unit cabinet immersed in mineral oil! And also significantly reduce spending on server hardware, up to 50% for various components, and all because now the constant operating temperature is about 20 degrees lower than in the air environment, it is possible to use even dextop components without fear, since they work with much lower temperatures.
From “underwater” servers to liquid cooled PCs or how to create a workstation in a liquid at home
Of course, this idea has not received and will not receive such widespread use in the personal computer market, simply because the majority has long since switched to laptops and other gadgets, home workstations in the “tower” building are often used only by professionals, since they need great performance and large amount of heat. Here, for them, immersing their precious iron in a liquid can be very useful!
It turns out to implement it at home is not difficult and possible, and it was done by many lovers of moding for quite some time. Some companies even propose to purchase a ready-made solution based on the mineral oil “Crystal Plus 70T”, which is commercially available and, according to experimenters, is ideal for this task, has a heat capacity 750 times higher than that of air and a density lower than that of water.

Mixing the liquid can be carried out by passing air through mineral oil or even an ordinary computer cooler, which in the mineral oil rotates itself much slower than in the air, but retains its efficiency. When asked what to do with water vapor that will get into mineral oil when air is passed through for mixing, the developers answer that due to different density (greater than water), water will accumulate at the very bottom of the "aquarium" where it is not any electrical components, however, they have not yet seen that in the course of a long operation at least a tiny amount of water would appear, otherwise the reservoir would begin to resemble a “lava-lamp”.
I want fish to swim in the servers! Throw in there fishes!
I dare to admit that observing various FISH under water is an unforgettable pleasure. I am a diver and would not refuse a work station at home in the form of an aquarium with tropical or not-so-tropical fish.
But alas, genetic engineering still lags behind fashion in IT, fish will die if they are placed in mineral oil, it is extremely far from the necessary water for fish in its properties. Let's hope that this idea, either through the use of new technologies or through genetic engineering, will be possible for someone to implement in the future, but for now you can use robotic fish!
I will be the first to order a robotic boxfish!

Well, by itself, do not forget to support the construction of our future underwater Data Center (for which I have no idea about ideas) - order dedicated servers from us , so far in the Netherlands and the USA, and from $ 49, and in the future on the Barrier Reef!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/222669/
All Articles