Microsoft and Adobe released a set of updates, May 2014
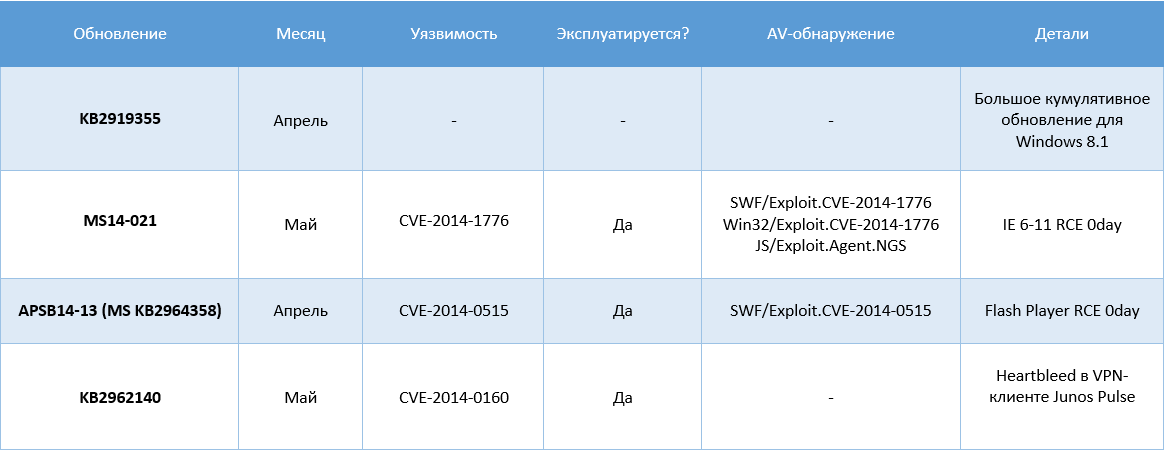
The company has released a series of updates for its products, which fix 13 unique vulnerabilities in Windows, Internet Explorer, .NET Framework, Office, and SharePoint products. Two fixes have Critical status and six Important. The critical update MS14-029 fixes two memory-corruption vulnerabilities in all versions of Internet Explorer 6-11 on all operating systems from Windows Server 2003 to Windows 8 / 8.1. Attackers can execute remote code in the browser through a specially formed web page (drive-by downloads). A reboot is required to apply the patch.

Note that a week ago, Microsoft released an unscheduled update KB2962140 for Windows 8.1 & RT 8.1, which closes the Heartbleed vulnerability (CVE-2014-0160) in the Juniper Pulse component of Juniper Networks VPN client. This VPN client is supplied by a third-party company and is used by Microsoft as part of the latest OS. This update, like all other security fixes for Windows 8.1, can be installed into the system only if the KB2919355 update is required .
')
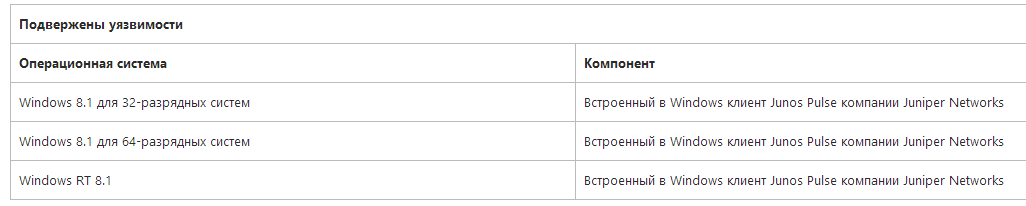
Fig. Operating systems to fix Heartbleed vulnerabilities using KB2962140. See the 2014-04 Out of Cycle Security Bulletin: Multiple products affected by the OpenSSL Heartbleed issue (CVE-2014-0160) .
In early May, the company released another unscheduled security update MS14-021 for all operating systems starting with Windows XP (no longer supported) and ending with Windows 8 / 8.1. We wrote about it in more detail here . The update closes the discovered 0day vulnerability CVE-2014-1776 (in mshtml.dll and some other files) that is present in all versions of Internet Explorer and was used by attackers in targeted attacks to install malicious code.
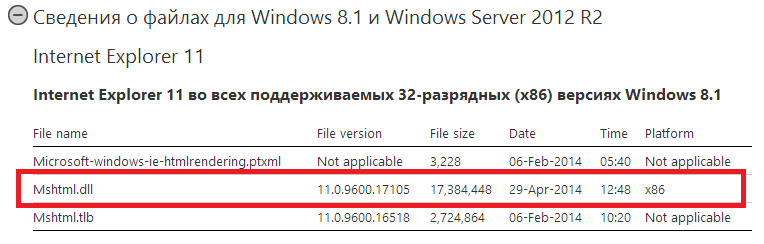
Fig. Updateable files MS14-021 for the newest Windows 8.1 & IE11, see KB2964358 section "file information".
Update MS14-029 closes two vulnerabilities in all versions of Internet Explorer: CVE-2014-0310 and CVE-2014-1815. Both vulnerabilities are of the Remote Code Execution type and can be used by attackers for remote execution of arbitrary code in the system. Vulnerability CVE-2014-1815 is exploited by hackers . Critical.
Update MS14-022 fixes three vulnerabilities in SharePoint Server 2007-2010-2013: CVE-2014-0251 (SharePoint Page Content Vulnerability), CVE-2014-1754 (SharePoint XSS Vulnerability), CVE-2014-1813 (Web Applications Page Content Vulnerability). Using these vulnerabilities, an attacker can execute arbitrary code by sending specially crafted content to a server with SharePoint. Critical. Exploit code likely .
The MS14-023 update fixes two vulnerabilities in Office 2007-2010. The RCE vulnerability CVE-2014-1756 is present in the Office 2007-2010 Chinese Chinese language checker component (Chinese Grammar Checker). Another vulnerability CVE-2014-1808 is of the Information Disclosure type and is present in some versions of Microsoft Office 2013 (MSO). Important. Exploit code likely .
The MS14-024 update fixes a flaw in the Security Feature Bypass type for Office. We already wrote earlier that attackers use Office libraries compiled without ASLR support to implement exploits. This update corrects the situation through the release of the safe versions (with ASLR support) of the mscomct2, mscomctl libraries (CVE-2014-1809), msaddndr, msstdfmt for Office 2007-2010-2013. Important. Operated in-the-wild .
Update MS14-025 fixes one vulnerability CVE-2014-1812 of type Elevation of Privilege for Windows Vista SP2 - Windows 8 / 8.1 (client versions with Remote Server Administration Tools). The vulnerability is present in the Active Directory group policy component. Important. Exploit code likely .
Update MS14-026 fixes one Elevation of Privilege vulnerability CVE-2014-1806 in all versions of the .NET Framework for all operating systems. An attacker can elevate their privileges in the system by sending a specially crafted request to a home computer or server that uses .NET Remoting . Important. Exploit code likely .
Update MS14-027 fixes one Elevation of Privilege vulnerability CVE-2014-1807 for all supported OS. The vulnerability is present in the file association mechanism (Windows Shell File Associations), and more specifically in the Windows Shell API and its ShellExecute functions. An attacker can raise their privileges in the system using a special application that calls the ShellExecute function in a special way. Important. Exploit code likely .
Update MS14-028 fixes two vulnerabilities CVE-2014-0255, CVE-2014-0256 in server editions of Windows Server 2008 & 2012. The vulnerabilities are Denial of Service and can be used by attackers to cause the target system to hang through sending a large number of specially crafted iSCSI packages. Important. Exploit code unlikely .
Unscheduled updates
EMET 5.0 TP & Attack Surface Reduction
Speaking of EMET and CVE-2014-1776, which made a lot of noise last month, it can be noted that EMET 5.0 TP (and TP2) users are protected by default from exploit actions to this vulnerability. In our recent post on the ASR (Attack Surface Reduction) option in this version of EMET, we indicated that the option blocks for Internet Explorer the download of VGX.DLL (the same library that MS recommended to manually disable before the release of MS14-021 as workaround - SA2963983 ). The vulnerability is not contained in VGX.DLL, however, disabling it helped to prevent the exploit from executing its functions.

Fig. Mitigating factors exploiting vulnerabilities, for example CVE-2014-1776. EMET 5.0 EAF + blocks access to the page with the export of ntdll.dll from the ActionScript code, this feature is absent in EAF (allows access to the page with the export to the code of the ocx module). See more here .
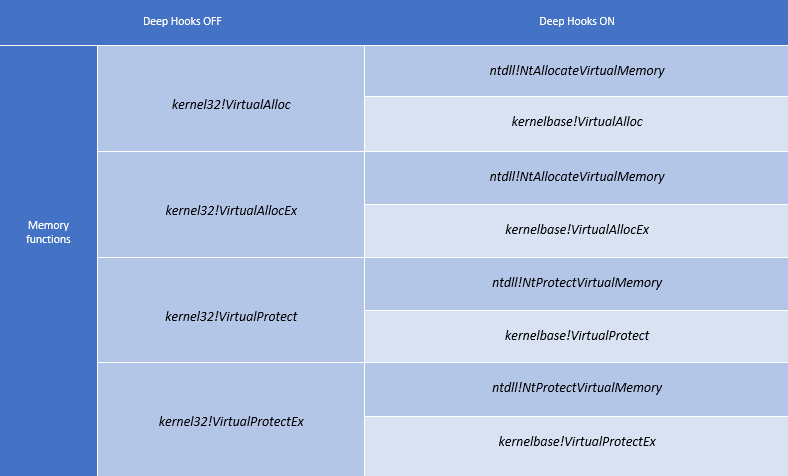
Fig. EMET uses the Deep Hooks option to control the underlying kernel32.dll libraries (using memory functions as an example). APIs are controlled to block their calling from the ROP code. With this option turned on, calls of kernel32, kernelbase and ntdll are controlled. Actual for CVE-2014-1776.
1 - Exploit code likely
The probability of exploiting the vulnerability is very high, attackers can use an exploit, for example, for remote code execution.
2 - Exploit code would be difficult to build
The exploitation probability is average, since attackers are unlikely to be able to achieve a situation of sustainable exploitation, as well as due to the technical peculiarities of vulnerability and the complexity of developing an exploit.
3 - Exploit code unlikely
The exploitation probability is minimal and attackers are unlikely to be able to develop successfully working code and take advantage of this vulnerability to conduct an attack.
We recommend our users to install updates as soon as possible and, if you have not already done so, enable automatic delivery of updates using Windows Update (by default this option is enabled).
Adobe has also released the APSB14-15 hotfix for its Reader and Acrobat products. A total of 11 vulnerabilities have been fixed. Nine of the eleven vulnerabilities are of the Remote Code Execution type and can be used by attackers to execute their code in the system: CVE-2014-0511, CVE-2014-0522, CVE-2014-0523, CVE-2014-0524, CVE-2014- 0526, CVE-2014-0525, CVE-2014-0527, CVE-2014-0528, CVE-2014-0529.
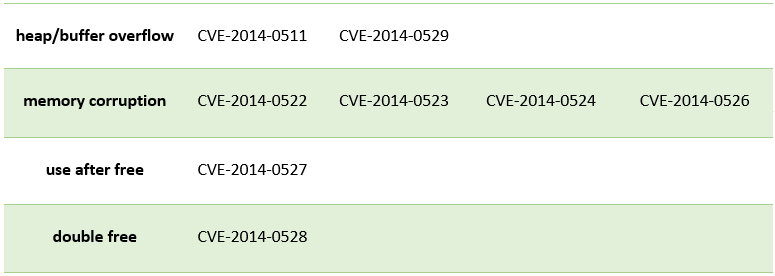
Fig. RCE vulnerabilities fixed by APSB14-15.

Fig. Actual versions of Adobe Reader & Acrobat.
Vulnerability CVE-2014-0511 and CVE-2014-0512 were discovered by the VUPEN team at Pwn2Own 2014 .
Users can update specified products through the built-in update checking engine (Adobe Updater).

be secure.

Note that a week ago, Microsoft released an unscheduled update KB2962140 for Windows 8.1 & RT 8.1, which closes the Heartbleed vulnerability (CVE-2014-0160) in the Juniper Pulse component of Juniper Networks VPN client. This VPN client is supplied by a third-party company and is used by Microsoft as part of the latest OS. This update, like all other security fixes for Windows 8.1, can be installed into the system only if the KB2919355 update is required .
')

Fig. Operating systems to fix Heartbleed vulnerabilities using KB2962140. See the 2014-04 Out of Cycle Security Bulletin: Multiple products affected by the OpenSSL Heartbleed issue (CVE-2014-0160) .
In early May, the company released another unscheduled security update MS14-021 for all operating systems starting with Windows XP (no longer supported) and ending with Windows 8 / 8.1. We wrote about it in more detail here . The update closes the discovered 0day vulnerability CVE-2014-1776 (in mshtml.dll and some other files) that is present in all versions of Internet Explorer and was used by attackers in targeted attacks to install malicious code.

Fig. Updateable files MS14-021 for the newest Windows 8.1 & IE11, see KB2964358 section "file information".
Update MS14-029 closes two vulnerabilities in all versions of Internet Explorer: CVE-2014-0310 and CVE-2014-1815. Both vulnerabilities are of the Remote Code Execution type and can be used by attackers for remote execution of arbitrary code in the system. Vulnerability CVE-2014-1815 is exploited by hackers . Critical.
Update MS14-022 fixes three vulnerabilities in SharePoint Server 2007-2010-2013: CVE-2014-0251 (SharePoint Page Content Vulnerability), CVE-2014-1754 (SharePoint XSS Vulnerability), CVE-2014-1813 (Web Applications Page Content Vulnerability). Using these vulnerabilities, an attacker can execute arbitrary code by sending specially crafted content to a server with SharePoint. Critical. Exploit code likely .
The MS14-023 update fixes two vulnerabilities in Office 2007-2010. The RCE vulnerability CVE-2014-1756 is present in the Office 2007-2010 Chinese Chinese language checker component (Chinese Grammar Checker). Another vulnerability CVE-2014-1808 is of the Information Disclosure type and is present in some versions of Microsoft Office 2013 (MSO). Important. Exploit code likely .
The MS14-024 update fixes a flaw in the Security Feature Bypass type for Office. We already wrote earlier that attackers use Office libraries compiled without ASLR support to implement exploits. This update corrects the situation through the release of the safe versions (with ASLR support) of the mscomct2, mscomctl libraries (CVE-2014-1809), msaddndr, msstdfmt for Office 2007-2010-2013. Important. Operated in-the-wild .
Update MS14-025 fixes one vulnerability CVE-2014-1812 of type Elevation of Privilege for Windows Vista SP2 - Windows 8 / 8.1 (client versions with Remote Server Administration Tools). The vulnerability is present in the Active Directory group policy component. Important. Exploit code likely .
Update MS14-026 fixes one Elevation of Privilege vulnerability CVE-2014-1806 in all versions of the .NET Framework for all operating systems. An attacker can elevate their privileges in the system by sending a specially crafted request to a home computer or server that uses .NET Remoting . Important. Exploit code likely .
Update MS14-027 fixes one Elevation of Privilege vulnerability CVE-2014-1807 for all supported OS. The vulnerability is present in the file association mechanism (Windows Shell File Associations), and more specifically in the Windows Shell API and its ShellExecute functions. An attacker can raise their privileges in the system using a special application that calls the ShellExecute function in a special way. Important. Exploit code likely .
Update MS14-028 fixes two vulnerabilities CVE-2014-0255, CVE-2014-0256 in server editions of Windows Server 2008 & 2012. The vulnerabilities are Denial of Service and can be used by attackers to cause the target system to hang through sending a large number of specially crafted iSCSI packages. Important. Exploit code unlikely .
Unscheduled updates

EMET 5.0 TP & Attack Surface Reduction
Speaking of EMET and CVE-2014-1776, which made a lot of noise last month, it can be noted that EMET 5.0 TP (and TP2) users are protected by default from exploit actions to this vulnerability. In our recent post on the ASR (Attack Surface Reduction) option in this version of EMET, we indicated that the option blocks for Internet Explorer the download of VGX.DLL (the same library that MS recommended to manually disable before the release of MS14-021 as workaround - SA2963983 ). The vulnerability is not contained in VGX.DLL, however, disabling it helped to prevent the exploit from executing its functions.

Fig. Mitigating factors exploiting vulnerabilities, for example CVE-2014-1776. EMET 5.0 EAF + blocks access to the page with the export of ntdll.dll from the ActionScript code, this feature is absent in EAF (allows access to the page with the export to the code of the ocx module). See more here .

Fig. EMET uses the Deep Hooks option to control the underlying kernel32.dll libraries (using memory functions as an example). APIs are controlled to block their calling from the ROP code. With this option turned on, calls of kernel32, kernelbase and ntdll are controlled. Actual for CVE-2014-1776.
1 - Exploit code likely
The probability of exploiting the vulnerability is very high, attackers can use an exploit, for example, for remote code execution.
2 - Exploit code would be difficult to build
The exploitation probability is average, since attackers are unlikely to be able to achieve a situation of sustainable exploitation, as well as due to the technical peculiarities of vulnerability and the complexity of developing an exploit.
3 - Exploit code unlikely
The exploitation probability is minimal and attackers are unlikely to be able to develop successfully working code and take advantage of this vulnerability to conduct an attack.
We recommend our users to install updates as soon as possible and, if you have not already done so, enable automatic delivery of updates using Windows Update (by default this option is enabled).

Adobe has also released the APSB14-15 hotfix for its Reader and Acrobat products. A total of 11 vulnerabilities have been fixed. Nine of the eleven vulnerabilities are of the Remote Code Execution type and can be used by attackers to execute their code in the system: CVE-2014-0511, CVE-2014-0522, CVE-2014-0523, CVE-2014-0524, CVE-2014- 0526, CVE-2014-0525, CVE-2014-0527, CVE-2014-0528, CVE-2014-0529.

Fig. RCE vulnerabilities fixed by APSB14-15.

Fig. Actual versions of Adobe Reader & Acrobat.
Vulnerability CVE-2014-0511 and CVE-2014-0512 were discovered by the VUPEN team at Pwn2Own 2014 .
Users can update specified products through the built-in update checking engine (Adobe Updater).

be secure.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/222367/
All Articles