Power supply of a private house

In this article I want to begin the description of the concept of smart home in my understanding and consider some aspects of its implementation. At once I will make a reservation that I practically do not see the application of the concept of “Smart Home” to an apartment, since there are practically no systems in it that require automation. Quite another thing - a private house. It contains many systems that can and should be automated - from water supply to garden lighting. So my definition. Smart home is a set of automatic systems that operate with minimal participation of its inhabitants, while providing maximum comfort, safety and energy saving. However, the implementation should be as simple and accessible as possible.
I will start with the implementation of the energy supply at home.
Backup power home
Unlike an apartment, the house is much more dependent on the availability of electricity, because in its absence, we automatically lose almost all systems - lighting, heating, ventilation, hot water, and often water supply in general, if a pumping station is used. Therefore, as part of the comfort of a smart home, it is necessary to provide backup power supply. The simplest solution is to use a standalone generator. But it still needs to be properly connected so that when the power supply is restored, nothing burns, to choose its power so as not to overload and decide on its launch. Of course, you can install a power plant with a capacity of 10 kW or more, with automatic start-up and with matching circuits with the power grid, but its price is prohibitively high. That and install it is not so easy. Well, the question remains, when to start it - immediately after a power outage, after half an hour or manually. After all, walking with a flashlight while waiting for a launch is somehow not very comfortable, and instant start-up is often inconvenient, especially at night or with a 15-minute shutdown. So the easiest option is expensive and not very convenient. This led to a search for a more rational solution.
I will describe briefly the main idea. It consists of several solutions:
')
- Power supply of all home lighting via UPS. This will allow you to always have lighting for several hours, depending on the battery, time of day, the number and type of lamps included.
- The presence of additional wiring for sockets with backup power. This will provide backup power for critical systems with a minimum power generator. Without the need to disconnect all consumers from the sockets, so as not to overload the generator. Sockets should preferably be made in a different color so that they can be easily identified.
- The presence of a circuit that automatically connects the generator to the network, in case of its absence and disconnecting the generator from the network when the power supply is restored.
- Run the generator. This can be solved by choice - automatically, by timer, manually. I prefer the manual launch.
- Automatic jamming of the generator.
Implementation details
All the same, a power outage is an extraordinary situation; there is no point in spending money on a completely autonomous system. Therefore, we divide consumers into groups. These are lighting, critical systems (boiler, pump), non-critical systems (refrigerator, ventilation, TV). What causes the greatest discomfort when turning off the power? Usually - this is the lack of lighting. Without lighting is difficult to do, well, it consumes a little. Therefore we reserve it first of all, with the help of the UPS. A specific model must be selected on the basis of several conditions - the number and type of lamps, the type and capacity of the battery. In most cases, a conventional computer UPS, worth $ 200, is sufficient. It connects to the shield, in the gap line lighting. The battery life should be at least 30 minutes to cover short-term outages and give time to start the generator, if necessary. Sound alarm is desirable to disable, so as not to wake the house at night.
The next question is the choice of generator power. Usually 2500 watts is more than enough. And this is a common consumer model, worth about $ 400. This is enough to provide power to the boiler and well pumps, lighting, refrigerator and computer. Powered by batteries, just like lighting, is extremely disadvantageous. Firstly, a large output power of the inverter is needed, secondly, a large capacity of batteries and the high cost of replacing them, thirdly, the inverter must output the correct sine wave, as some motors and modulated boiler burners are sensitive to its shape. The generator produces a pure sine wave, autonomous for at least 15 hours at one gas station, cheap. Also, it is most often completed with a starter and its own battery, which allows, if desired, to realize autostart.
Next - power wiring with redundancy from the generator. Pumps and a boiler are connected to it. It is necessary to provide at least one outlet in each room. This will allow you to connect at will the rest of household appliances.
Well and the last - connection.
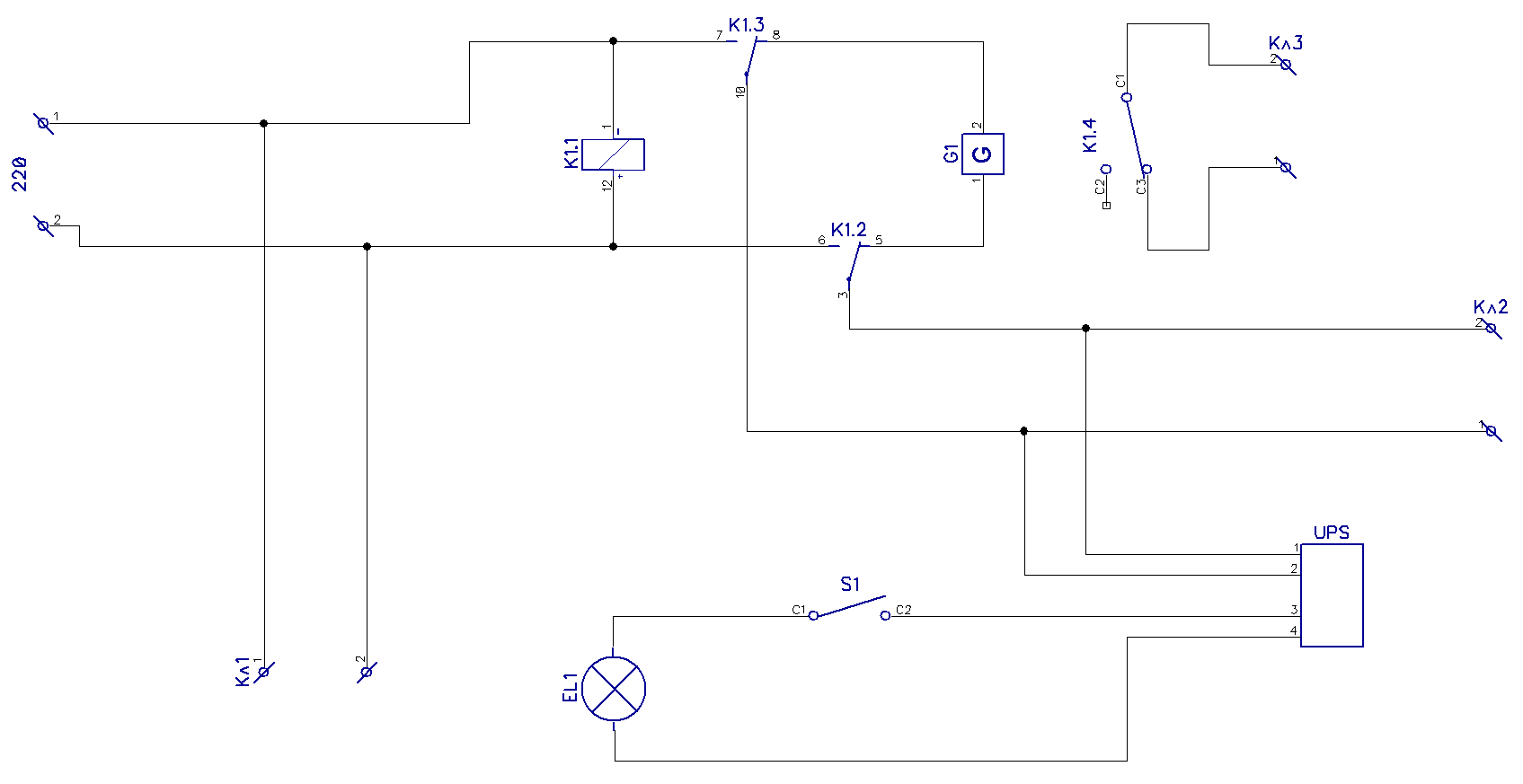
Connection scheme of backup power systems.
In the diagram:
EL1 - lighting in the house,
CL1 - connection terminal for non-reserved outlets
CL2 - connection terminal to reserved outlets
Kl3 - terminal included in the generator ignition break.
K1 - relay controlling contact group K1.2, K1.3, K1.4
G - generator
UPS - uninterruptible power supply
When there is mains voltage, the relay coil is energized and power is supplied directly to the mains. In the event of a power failure, the contacts will move to the initial position indicated in the diagram and connect a generator to the network. The lighting will continue to be powered by the UPS for some time. If necessary, the generator can be started, which will provide power to the lighting and backup sockets connected to terminal CL2. When external power is restored, relay K1 will work, disconnecting the generator from the mains and breaking the generator ignition circuit, thereby shutting it down. The system will return to its original state. The wiring diagram is only a demonstration of the idea, and not a schematic diagram.
As a result, the cost of the entire system is about $ 600 + work on the laying of wires. But in some cases, you can use the existing wiring, if it is correctly displayed on the shield.
Afterword
The article describes the basic scheme. If desired, it can and should be improved. Especially when it becomes possible to integrate with remote control, monitoring and other things. At least in the future, you can add an alert about power outages, remote start and shutdown of the generator, etc. Also, together with the lighting, you can provide backup power through the UPS alarm system, router and server, but usually this is not required. Since they are most often equipped with their own backup power sources. It is enough to plug them into an outlet connected to the power line from the generator. Also, I did not consider connecting solar panels and wind turbines. It is expensive and poorly suited for backup power. They provide low power throughout their entire service life, and backup power requires relatively high power for a short period — several tens of hours per year.
UPD: Considering this, preference is given not only to the comfort of the solution, and also to respect for the balance of price-benefit. This problem can be solved in a mass of ways. This solution seems to me the most balanced. A further increase in comfort is accompanied by a significant increase in cost, which is not always acceptable.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/221829/
All Articles