Capabilities of four-processor servers on Xeon E7 v2 processors
Modern dual-processor servers are a standard workhorse in most organizations. Performance increases, memory is added, PCIe speeds up. It would seem, why in this case need multiprocessor systems?
No matter how trivial it sounds, but big data and business-critical applications. After all, servers based on the E7-4800 v2 are not only one and a half terabytes of RAM per socket, but also means of increasing reliability within one system.
')
We also did not forget to support the product.
And we will describe in more detail both the useful features of the E7 v2 platform with the Ivy Bridge-EX core and the Hyperion RS530 G4 server.
Intel itself is positioning the new processors as an alternative to RISC systems, primarily based on IBM POWER. The reason for this they have!

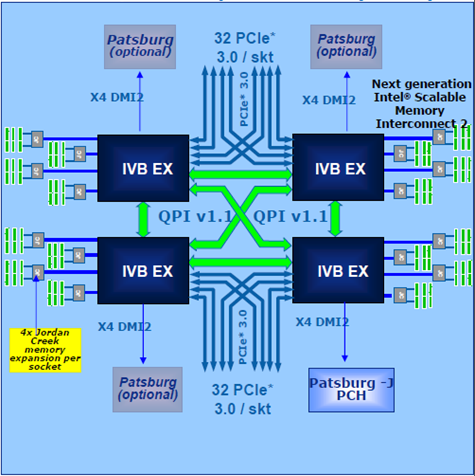
Slide taken from Intel
Let us examine each item in more detail.
Performance
The increase of this in 2 times is not just given - it is the server acceleration compared to the previous generation E7, based on Westmere-EX.
The performance of processors in the world can be measured using tests SPEC (Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation) CPU, the current version of CPU2006. Tests are divided into integer CINT and floating point CFP, but this is a single-threaded result. For comparison of multi-core processors, the rate version is used.
What does it mean?
The new four-processor server completely replaces the old eight-processor,
for example, ETegro Hyperion RS830 G3 . Consumes less power, higher performance, lower cost. Against its background, and Power looks pretty pale.
Memory
It should be noted that the E7 controller works with memory not directly, but through SMI (scalable memory interconnect) and a special buffer. What for?
The high-speed serial bus drastically simplifies motherboard routing, allowing you to remove the memory to a considerable distance from the processor and at the same time save bandwidth, since the electrical load is lowered. It also simplifies the design of memory risers that support hot swapping and adding memory “on the go.”
In the previous generation Hyperion RS530 G3 model, 64 slots were available for RAM and 2 terabytes were supported in the server.

The new processor brought a revised memory controller with support for 24 memory bars per processor (96 in the server) and a frequency of 1600 MHz (previously there was a limit of 1066 MHz).
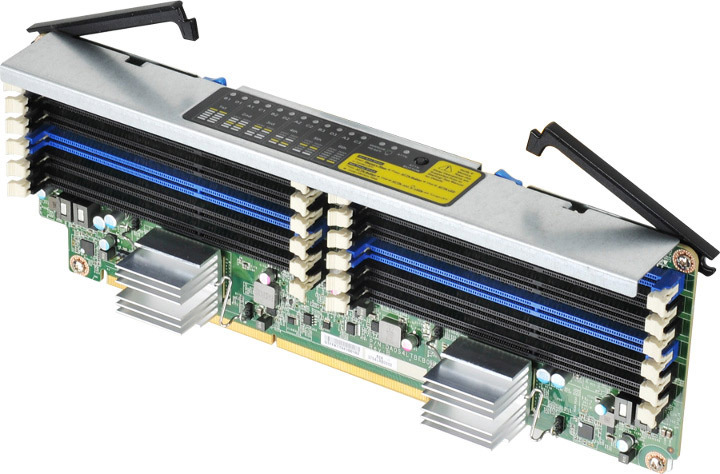

In addition to more memory, it supports switching modes of operation - Performance and
Lockstep.

The default is Performance mode, which sets SMI performance to 2667MT / s and works with eight DDR channels per processor. The total is 340 gigabytes per second of memory bandwidth per four processors. Great result! In the STREAM Triad test, it turned out to reach 244GB / s, which is 2.4 times more than 101GB / s for a system with E7 v1.
Lockstep mode allows you to work with DDR3 1600, but at the same time, the performance of the SMI channel is limited to 1600MT / s. Supports mirroring and memory rank sparing. When operating the Lockstep mode, you need to take into account a number of nuances:
Mirroring reduces the amount of memory available to the system by half. Memory rank sparing reserves one rank per channel, more memory is available, but reliability is not as high as that of a mirror.
Input Output
The previous generation E7 v1 relied on the capabilities of the 7500 chipset, which had 32 PCIe 2.0 lines. In the Hyperion RS530 G3 there were two such chips, which made it possible to remove 64 lines to the server.
E7 v2 got an integrated PCIe 3.0 controller with 32 two lines. Somewhat less than the E5-2600 (40 lines per processor), but there are four of them. 128 lines, each of which is about twice as fast as PCIe 2.0 - that’s four times on the slide and ran over.
Reliability
The easiest way to describe the pivot table is where Romley is E5-4600; Boxboro EX - E7 v1, Brickland - E7 v2.
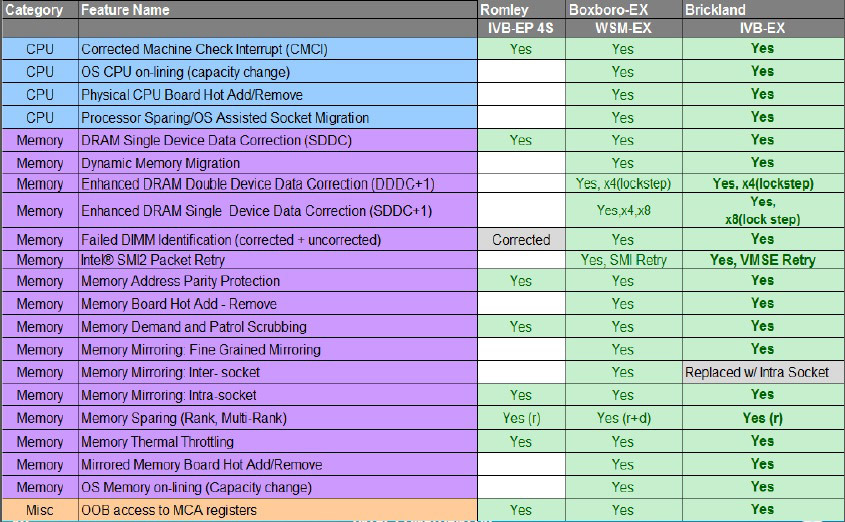
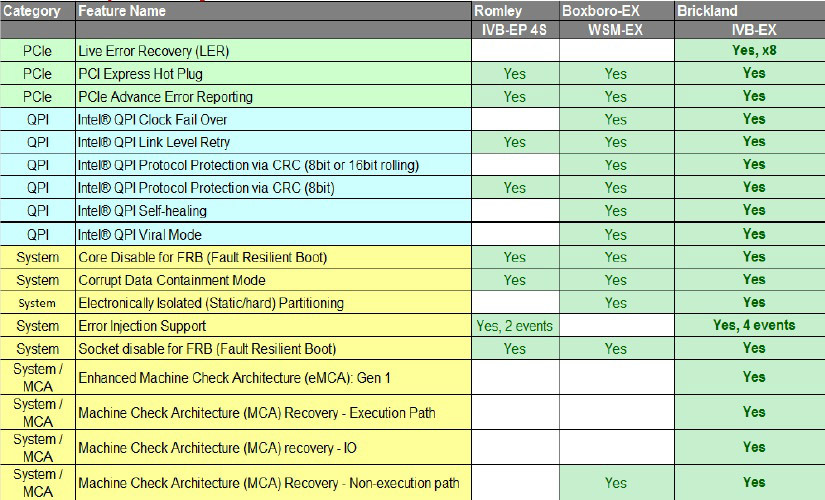
We will not paint every technology, but as a result, five nines are typed, only 5 minutes of inactivity per year.
Now about us and the current server


Beauty!
We will not write specifications for a long and hard time, they are on the site . It is better to show the most pleasant chips on a live product :)
Hot add memory
If not all memory raisers are filled - you can safely add more without stopping the server:
Intel threatens to finish the code for hot swap memory (it will work only in the mirroring mode, it worked in RS530 G3), then it will be possible to change the bad bars on the go.
PCIe hot plug
Has the network controller flown off? FC card left the roof? Want to add another PCIe flash? Do not turn off the server:
NVMe in practice
In our previous drive article, we mentioned the NVMe SSD and support for this model, here’s how it was implemented:

As we already mentioned, the NVMe connector is made compatible with SAS, so the backplane has pins for connecting a regular SAS controller.

Backplane drives
A live test machine with the E7-4880 v2 is in our laboratory and is available for testing.
PS Together with the announcement of the new generation, we offer 2 Hyperion RS530 G3 systems with four Xeon E7-8837 processors, an LSI 9260-8i controller and 8 memory raisers with a modest 50% discount.
No matter how trivial it sounds, but big data and business-critical applications. After all, servers based on the E7-4800 v2 are not only one and a half terabytes of RAM per socket, but also means of increasing reliability within one system.

')
We also did not forget to support the product.
And we will describe in more detail both the useful features of the E7 v2 platform with the Ivy Bridge-EX core and the Hyperion RS530 G4 server.
Intel itself is positioning the new processors as an alternative to RISC systems, primarily based on IBM POWER. The reason for this they have!

Slide taken from Intel
Let us examine each item in more detail.
Performance
The increase of this in 2 times is not just given - it is the server acceleration compared to the previous generation E7, based on Westmere-EX.
The performance of processors in the world can be measured using tests SPEC (Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation) CPU, the current version of CPU2006. Tests are divided into integer CINT and floating point CFP, but this is a single-threaded result. For comparison of multi-core processors, the rate version is used.
| CPU | SPECint_rate_base2006 | SPECfp_rate_base2006 |
| 4x E7-4890 v2 | 2340 | 1730 |
| 4x E7-4870 | 1080 | 698 |
| 8x E7-8870 | 1930 | 1280 |
| IBM Power 750 Express (4.0 GHz, 32 core, SLES) | 1230 | 1050 |
What does it mean?
The new four-processor server completely replaces the old eight-processor,
for example, ETegro Hyperion RS830 G3 . Consumes less power, higher performance, lower cost. Against its background, and Power looks pretty pale.
Memory
It should be noted that the E7 controller works with memory not directly, but through SMI (scalable memory interconnect) and a special buffer. What for?
The high-speed serial bus drastically simplifies motherboard routing, allowing you to remove the memory to a considerable distance from the processor and at the same time save bandwidth, since the electrical load is lowered. It also simplifies the design of memory risers that support hot swapping and adding memory “on the go.”
In the previous generation Hyperion RS530 G3 model, 64 slots were available for RAM and 2 terabytes were supported in the server.

The new processor brought a revised memory controller with support for 24 memory bars per processor (96 in the server) and a frequency of 1600 MHz (previously there was a limit of 1066 MHz).

In addition to more memory, it supports switching modes of operation - Performance and
Lockstep.

The default is Performance mode, which sets SMI performance to 2667MT / s and works with eight DDR channels per processor. The total is 340 gigabytes per second of memory bandwidth per four processors. Great result! In the STREAM Triad test, it turned out to reach 244GB / s, which is 2.4 times more than 101GB / s for a system with E7 v1.
Lockstep mode allows you to work with DDR3 1600, but at the same time, the performance of the SMI channel is limited to 1600MT / s. Supports mirroring and memory rank sparing. When operating the Lockstep mode, you need to take into account a number of nuances:
- The maximum number of RAS features is available.
- Modules must be installed in identical pairs (two in each of the two channels).
- Full system memory available.
Mirroring reduces the amount of memory available to the system by half. Memory rank sparing reserves one rank per channel, more memory is available, but reliability is not as high as that of a mirror.
Input Output
The previous generation E7 v1 relied on the capabilities of the 7500 chipset, which had 32 PCIe 2.0 lines. In the Hyperion RS530 G3 there were two such chips, which made it possible to remove 64 lines to the server.
E7 v2 got an integrated PCIe 3.0 controller with 32 two lines. Somewhat less than the E5-2600 (40 lines per processor), but there are four of them. 128 lines, each of which is about twice as fast as PCIe 2.0 - that’s four times on the slide and ran over.
Reliability
The easiest way to describe the pivot table is where Romley is E5-4600; Boxboro EX - E7 v1, Brickland - E7 v2.


We will not paint every technology, but as a result, five nines are typed, only 5 minutes of inactivity per year.
Now about us and the current server


Beauty!
We will not write specifications for a long and hard time, they are on the site . It is better to show the most pleasant chips on a live product :)
Hot add memory
If not all memory raisers are filled - you can safely add more without stopping the server:
Intel threatens to finish the code for hot swap memory (it will work only in the mirroring mode, it worked in RS530 G3), then it will be possible to change the bad bars on the go.
PCIe hot plug
Has the network controller flown off? FC card left the roof? Want to add another PCIe flash? Do not turn off the server:
NVMe in practice
In our previous drive article, we mentioned the NVMe SSD and support for this model, here’s how it was implemented:

As we already mentioned, the NVMe connector is made compatible with SAS, so the backplane has pins for connecting a regular SAS controller.

Backplane drives
A live test machine with the E7-4880 v2 is in our laboratory and is available for testing.
PS Together with the announcement of the new generation, we offer 2 Hyperion RS530 G3 systems with four Xeon E7-8837 processors, an LSI 9260-8i controller and 8 memory raisers with a modest 50% discount.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/220483/
All Articles