NASA is testing an inflatable aerodynamic brake for landing humans on Mars
The landing of the rover Curiosity called "7 minutes of horror" - this was the most critical area of the entire Martian mission. First, the capsule with the device extinguished the speed of the atmosphere of Mars, then continued braking with the help of a parachute and, finally, carefully lowered to the surface with the help of a “sky crane” - a platform with rocket engines. The mass of the rover - a little less than a ton. Carefully landing a larger load on Mars is a task even more difficult than overcoming the “7 minutes of horror”. In a rarefied Martian atmosphere, parachutes are much less efficient than on Earth, where they can even land a tank smoothly. Therefore, NASA is developing an additional system of aerodynamic braking, which will allow you to land a larger load on Mars with greater accuracy.
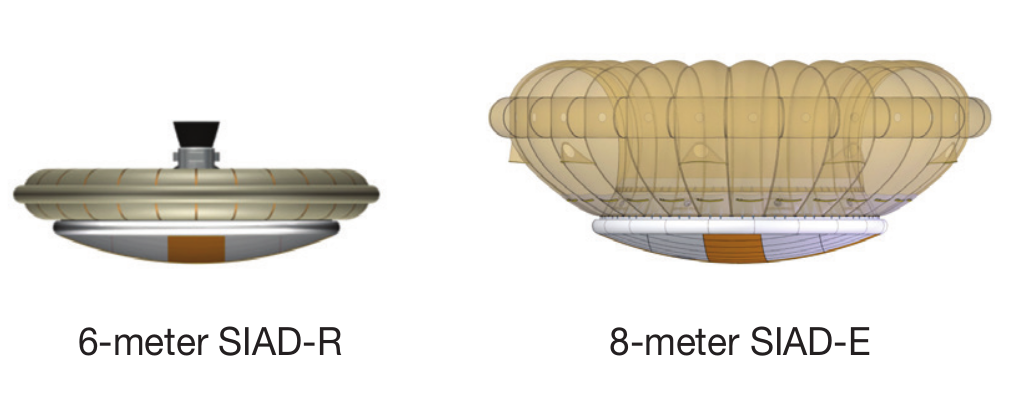
Now, in the framework of the Low Density Supersonic Decelerator or LDSD program, the development is going in three directions. One of them is a giant 33-meter parachute of conventional design. About his tests recently wrote on Habré. The other two devices, called "Supersonic Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerators - SIAD), are much more unusual. They are an inflatable "skirt", which significantly increases the aerodynamic resistance of the descent vehicle. The first version has a diameter of 6 meters and is inflated with a gas cylinder. It is designed for planting autonomous vehicles like the Curiosity. The second option, with a diameter of 8 meters, is inflated with a stream of incoming air and is designed for heavier loads, including even landing gears with people on board. Both versions of the inflatable brake begin to work at a speed of 3.5 speeds of sound and slow down the device to 2 speeds of sound when the parachute can be used safely.
With the help of the new landing system, you can increase the maximum weight of the descent cargo from the current 1.5 to 3 tons, improve the accuracy of landing from 10 to 3 km and significantly expand the geography, or rather areography, of possible landing sites, since you can land on platforms 2 - 3 kilometers higher - earlier they were inaccessible due to the fact that when landing on high ground the thickness of the atmosphere was not enough to slow down.
')

Field tests of inflatable braking systems will be held in 2014-2015 in Hawaii according to a rather interesting pattern. The descent vehicle will be raised to a height of 37 kilometers using a helium balloon. Then, using rocket engines, it will be thrown higher - up to 55 km and accelerated to supersonic speeds, after which the inflatable brake will come into action, and then the parachute. Since 2012, SIAD has been tested in a wind tunnel and on a rocket rail platform, known to many on the TV show "MythBusters":


Now, in the framework of the Low Density Supersonic Decelerator or LDSD program, the development is going in three directions. One of them is a giant 33-meter parachute of conventional design. About his tests recently wrote on Habré. The other two devices, called "Supersonic Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerators - SIAD), are much more unusual. They are an inflatable "skirt", which significantly increases the aerodynamic resistance of the descent vehicle. The first version has a diameter of 6 meters and is inflated with a gas cylinder. It is designed for planting autonomous vehicles like the Curiosity. The second option, with a diameter of 8 meters, is inflated with a stream of incoming air and is designed for heavier loads, including even landing gears with people on board. Both versions of the inflatable brake begin to work at a speed of 3.5 speeds of sound and slow down the device to 2 speeds of sound when the parachute can be used safely.
With the help of the new landing system, you can increase the maximum weight of the descent cargo from the current 1.5 to 3 tons, improve the accuracy of landing from 10 to 3 km and significantly expand the geography, or rather areography, of possible landing sites, since you can land on platforms 2 - 3 kilometers higher - earlier they were inaccessible due to the fact that when landing on high ground the thickness of the atmosphere was not enough to slow down.
')

Field tests of inflatable braking systems will be held in 2014-2015 in Hawaii according to a rather interesting pattern. The descent vehicle will be raised to a height of 37 kilometers using a helium balloon. Then, using rocket engines, it will be thrown higher - up to 55 km and accelerated to supersonic speeds, after which the inflatable brake will come into action, and then the parachute. Since 2012, SIAD has been tested in a wind tunnel and on a rocket rail platform, known to many on the TV show "MythBusters":

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/219847/
All Articles