Creating term analysis networks based on text analysis
On behalf of the famous author Dmitry Lande (for example, “Search for knowledge on the Internet”, Internet. Navigation in complex networks: models and algorithms ) publish one of his latest works.
Currently, the tasks of building ontologies in certain areas of knowledge are relevant. Obviously, building a large sectoral ontology is a complex problem that requires large resource costs. In any case, a certain stage in the construction of general ontologies is the construction of corresponding thesauri, terminological ontologies.

This paper proposes a method for constructing a network of a natural hierarchy of terms, which can be considered as “quasiology”, the basis for the formation of a corresponding terminological ontology. The network of the natural hierarchy of terms is based on information-relevant elements of the text, supporting words and word combinations, the methodology for identifying them is given in [1, 2]. The use of such elements allows you to create search images, to cover entire areas of knowledge as the basis for the further construction of common ontologies. The reference words and phrases for the construction of natural hierarchies of terms are chosen taking into account such properties as discriminant power. At the same time, this property alone is insufficient in the construction of thesauri and ontologies. Sometimes words with low discriminant power, in particular, the most frequent words of a selected subject area (for example, the words “Information”, “Retrieval”, “Search” in the corpus of information retrieval) are important for the task that is being considered.
')
The formation of a network of natural hierarchies of terms (SEIT) is based on the content of text boxes of the corresponding directivity. The “naturalness” of the hierarchies of terms in this case is understood as a failure in the formation of a network from special methods of semantic analysis. All connections in such a network are determined by the natural use of words and phrases, which are extracted from text corpuses of statistically significant volumes. The network of natural hierarchies of terms, created fully automatically, can be considered as the basis for the further automated formation of terminological ontology.
The algorithm for forming a network of natural hierarchies of terms, which is considered in this work, involves the implementation of a sequence of steps that encompasses the preliminary processing of the source text corpus, the definition and sorting of terms, the selection of the required number of the most powerful (the largest nodes of the compactified graph of horizontal visibility [3]), the construction of the SITI and its display. Consider these steps in more detail.
1. At the first stage, the source text corpus is selected. As an example of such a corpus, an array of annotations of electronic preprints arXiv (www.arxiv.org) for 2007-2010 on the subject of information retrieval (cs.IR heading) with a volume of 550 entries is considered below.
Preliminary processing of such a text corpus provides for the selection of text parts of records, the exclusion of non-text characters, stemming.
2. At the second stage, each individual word from the text corpus is assigned an assessment of its “discriminant power”, namely TFIDF, which in canonical form is equal to the product of the frequency of this word (Term Frequency) in the text fragment by the binary logarithm of the reciprocal of the number fragments of text in which this word was found (Inverse Document Frequency) [4].
3-4. It is the same as in the previous step, only for phrases of two words (bigrams) and three words (trigrams).
5. For sequences of terms and their weights by TFIDF, compactified horizontal visibility graphs (CHVG) [1, 2] are constructed and the weighting of word weights using this algorithm is repeated. This procedure allows to take into account, in addition to terms with a large discriminant power, also high-frequency terms that are of great importance for the general subject of the text corpus. After that, all terms are sorted in descending order of the calculated weight values of the corresponding CHVG nodes.
Terms from the so-called stop dictionary are not subject to further analysis. This is usually a fixed set of official words that do not play a significant role in the content of texts.
6. The expert method determines the required volume of SEIT (number N), after which the corresponding number of single words, bigrams and trigrams (total N + N + N elements) with the largest weight values for CHVG are selected.
7. From the elements selected at the previous step, networks of natural hierarchies of terms are built, in which the terms themselves are considered nodes, and the links correspond to the occurrence of some terms in others. In fig. 1 illustrates the principle of building links of SEIT. The individual geometric shapes in this illustration correspond to single words.

Fig. 1 - Formation of links in the three-level network of the natural hierarchy of terms
The first line corresponds to the selected set of single words, the second one - the set of bigrams, and the third line - the set of trigrams. If a single word enters a digram or trigram, or the digram enters a trigram, a connection is formed, which is indicated by an arrow. The set of nodes to which the terms correspond and links form a three-level network of the natural hierarchy of terms.
8. At the last stage of the development of the SEIT, it is mapped by software for analyzing and visualizing complex networks. To load networks of natural hierarchies of terms in the database, an incidence matrix of the generally accepted csv format is formed.
For the constructed networks of natural hierarchies of terms of different sizes, the distribution of outgoing degrees of nodes was determined for the selected text corpus, which turned out to be close to a power (p (k) = C * k ^ h), i.e. these networks are scale free. It turned out that the coefficient h for networks of various sizes (from 20 + 20 + 20 to 200 + 200 + 200) is from 2.1 to 2.3.
In fig. Figure 2 presents a small network of the natural hierarchy of terms of size 20 + 20 + 20, which is visualized in the form of a spiral according to the method proposed by the author.

Fig. 2 - Type SEIT size 20 + 20 + 20
In fig. Figure 3 presents a general view of the network of the natural hierarchy of terms of size 200 + 200 + 200, which is visualized by means of the Gephi system (https://gephi.org/).

Fig. 3 - CEIT visualization of 200 + 200 + 200 size using Gephi tools
In fig. 4 shows the individual fragments of the network of the natural hierarchy of terms that correspond to the selected basic terms.
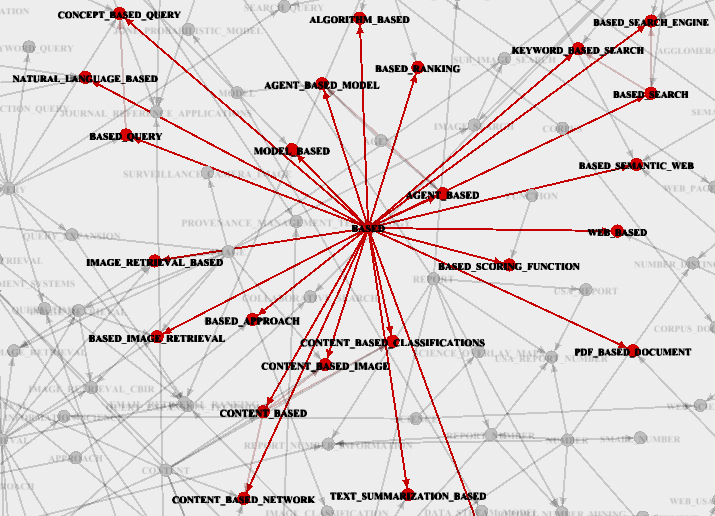

Fig. 4 - Fragments of SEIT
Thus, in the results of the research:
Currently, the tasks of building ontologies in certain areas of knowledge are relevant. Obviously, building a large sectoral ontology is a complex problem that requires large resource costs. In any case, a certain stage in the construction of general ontologies is the construction of corresponding thesauri, terminological ontologies.

This paper proposes a method for constructing a network of a natural hierarchy of terms, which can be considered as “quasiology”, the basis for the formation of a corresponding terminological ontology. The network of the natural hierarchy of terms is based on information-relevant elements of the text, supporting words and word combinations, the methodology for identifying them is given in [1, 2]. The use of such elements allows you to create search images, to cover entire areas of knowledge as the basis for the further construction of common ontologies. The reference words and phrases for the construction of natural hierarchies of terms are chosen taking into account such properties as discriminant power. At the same time, this property alone is insufficient in the construction of thesauri and ontologies. Sometimes words with low discriminant power, in particular, the most frequent words of a selected subject area (for example, the words “Information”, “Retrieval”, “Search” in the corpus of information retrieval) are important for the task that is being considered.
')
The formation of a network of natural hierarchies of terms (SEIT) is based on the content of text boxes of the corresponding directivity. The “naturalness” of the hierarchies of terms in this case is understood as a failure in the formation of a network from special methods of semantic analysis. All connections in such a network are determined by the natural use of words and phrases, which are extracted from text corpuses of statistically significant volumes. The network of natural hierarchies of terms, created fully automatically, can be considered as the basis for the further automated formation of terminological ontology.
The algorithm for forming a network of natural hierarchies of terms, which is considered in this work, involves the implementation of a sequence of steps that encompasses the preliminary processing of the source text corpus, the definition and sorting of terms, the selection of the required number of the most powerful (the largest nodes of the compactified graph of horizontal visibility [3]), the construction of the SITI and its display. Consider these steps in more detail.
1. At the first stage, the source text corpus is selected. As an example of such a corpus, an array of annotations of electronic preprints arXiv (www.arxiv.org) for 2007-2010 on the subject of information retrieval (cs.IR heading) with a volume of 550 entries is considered below.
Preliminary processing of such a text corpus provides for the selection of text parts of records, the exclusion of non-text characters, stemming.
2. At the second stage, each individual word from the text corpus is assigned an assessment of its “discriminant power”, namely TFIDF, which in canonical form is equal to the product of the frequency of this word (Term Frequency) in the text fragment by the binary logarithm of the reciprocal of the number fragments of text in which this word was found (Inverse Document Frequency) [4].
3-4. It is the same as in the previous step, only for phrases of two words (bigrams) and three words (trigrams).
5. For sequences of terms and their weights by TFIDF, compactified horizontal visibility graphs (CHVG) [1, 2] are constructed and the weighting of word weights using this algorithm is repeated. This procedure allows to take into account, in addition to terms with a large discriminant power, also high-frequency terms that are of great importance for the general subject of the text corpus. After that, all terms are sorted in descending order of the calculated weight values of the corresponding CHVG nodes.
Terms from the so-called stop dictionary are not subject to further analysis. This is usually a fixed set of official words that do not play a significant role in the content of texts.
6. The expert method determines the required volume of SEIT (number N), after which the corresponding number of single words, bigrams and trigrams (total N + N + N elements) with the largest weight values for CHVG are selected.
7. From the elements selected at the previous step, networks of natural hierarchies of terms are built, in which the terms themselves are considered nodes, and the links correspond to the occurrence of some terms in others. In fig. 1 illustrates the principle of building links of SEIT. The individual geometric shapes in this illustration correspond to single words.

Fig. 1 - Formation of links in the three-level network of the natural hierarchy of terms
The first line corresponds to the selected set of single words, the second one - the set of bigrams, and the third line - the set of trigrams. If a single word enters a digram or trigram, or the digram enters a trigram, a connection is formed, which is indicated by an arrow. The set of nodes to which the terms correspond and links form a three-level network of the natural hierarchy of terms.
8. At the last stage of the development of the SEIT, it is mapped by software for analyzing and visualizing complex networks. To load networks of natural hierarchies of terms in the database, an incidence matrix of the generally accepted csv format is formed.
For the constructed networks of natural hierarchies of terms of different sizes, the distribution of outgoing degrees of nodes was determined for the selected text corpus, which turned out to be close to a power (p (k) = C * k ^ h), i.e. these networks are scale free. It turned out that the coefficient h for networks of various sizes (from 20 + 20 + 20 to 200 + 200 + 200) is from 2.1 to 2.3.
In fig. Figure 2 presents a small network of the natural hierarchy of terms of size 20 + 20 + 20, which is visualized in the form of a spiral according to the method proposed by the author.

Fig. 2 - Type SEIT size 20 + 20 + 20
In fig. Figure 3 presents a general view of the network of the natural hierarchy of terms of size 200 + 200 + 200, which is visualized by means of the Gephi system (https://gephi.org/).

Fig. 3 - CEIT visualization of 200 + 200 + 200 size using Gephi tools
In fig. 4 shows the individual fragments of the network of the natural hierarchy of terms that correspond to the selected basic terms.


Fig. 4 - Fragments of SEIT
Thus, in the results of the research:
- An algorithm for constructing networks of natural hierarchies of terms based on text corpus analysis is proposed.
- Based on this algorithm, a network of a natural hierarchy of terms is built on the text body.
- The properties of the network of natural hierarchies of terms, which turned out to be scaled by outgoing links, were investigated.
- Selected web visualization tools for natural term hierarchies.
- The language network built using the proposed methodology can be used as a basis for building a general ontology (in the example considered, on the subject of information retrieval), used in practice as a ready-to-use navigation tool in databases of relevant subjects, as well as for organizing contextual prompts users of information retrieval systems.
Literature
- Lande DV, Snarskii AA, Yagunova EV, Pronoza EV, that -2 an 12 12/12/15.
- Lande DV, Snarskii AA Compactified Horizontal Visibility Graph for the Language Network // Preprint Arxiv (1302.4619)
- Luque, V., Lacasa, L., Ballesteros, F., Luque J. Horizontal visibility graphs: Exact results for the random time series // Physical Review E, 2009. - P. 046103-1 - 046103-11.
- Salton G., McGill MJ - New York: McGraw-Hill, 1983. - 448 p.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/219243/
All Articles