Potentially inhabited sub-ice ocean found on Enceladus

More and more discoveries lead astronomers to the idea that the far corners of the solar system may be more suitable for life than previously thought. Measurements of the gravitational field of Enceladus, a small satellite of Saturn, confirmed that under the surface of the planet in the southern hemisphere is the ocean. And astronomers believe that theoretically this ocean can be inhabited.
The presence of a sub-ocean on Enceladus has long been anticipated. As early as 2005, the Cassini apparatus transmitted pictures showing powerful jets of water vapor emitted by formations called “tiger stripes” located near the ice-bound planet of the planet. By the way, similar geysers were recently discovered in Europe , another icy satellite. By themselves, these geysers do not prove the presence of liquid water under the ice. This may also be due to the occurrence of massive tectonic forces created by the gravity of Saturn and leading to the displacement of ice masses and the formation of emissions of liquid water.
')

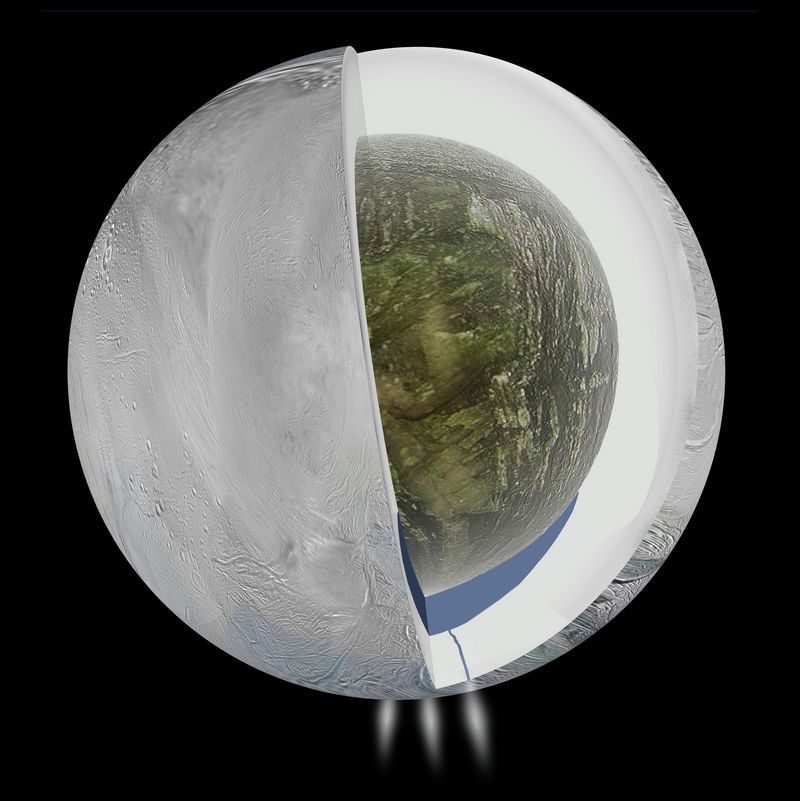
However, a number of gravitational measurements made by Cassini from 2010 to 2012, astronomers confirmed the presence of a giant reservoir of liquid water beneath the surface of the ice on Enceladus. And no less important, the heterogeneity of the structure of the planet itself was confirmed: under the ice there is a rocky core consisting of silicon compounds. Most surprisingly, a layer of silicates, covered with water, could form a habitat suitable for living. Perhaps even more suitable than in Europe.
Gravity anomaly
Geophysical data collected by Cassini, showed the presence of an anomalous change in the gravitational field of Enceladus at the south pole. Such negative anomalies occur in areas that have a mass below the calculated one. Astronomers purposefully searched for a negative gravitational anomaly in this area, since the surface of the planet was lowered here. But no one expected that the anomaly would be so great. It turned out to be significantly larger than predicted from surface measurements.

Scientists have suggested that below the surface there should be a matter with a higher density. And since water is denser than ice, the presence of a subglacial ocean was the only logical explanation.
South Tank
Unlike Europe with its entire sub-ice-covering ocean, on Enceladus the water body is located only in the south. It extends up to 50 degrees south latitude, approximately to the middle of the distance to the equator. In the region of the south pole, the ocean reaches its maximum depth.
Enceladus itself is very small, its diameter is only about 500 km. The ocean (by earthly standards this is a very large lake) lies on a rough 30-40 km. The thickness of the reservoir reaches 8-10 km. The volume of water is comparable to Lake Superior, the largest of the Great Lakes group.
The very fact that liquid water may exist on Enceladus came as a surprise. The surface temperature is about -180 degrees Celsius. Scientists assume that the source of energy for the formation of such a volume of liquid water is the gravitational field of Saturn. Or it is some kind of own energy source, the presence of which was not supposed on a small ice planet. The same Europe is much larger, almost the size of our moon.
It is not yet known why the ocean is located in the south. Probably, more intense bending and heating of ice occurs in that area. As for the geysers, it is possible that their existence is explained by tidal forces, due to which faults have formed in the ice crust.
The importance of silicon compounds for life
As mentioned, Enceladus has a rocky core of silicates, with a density of 2.4 g / cm 3 . Silicates are the source of many substances necessary for the existence of life, for example, phosphorus and sulfur compounds. Scientists have already found evidence of the presence of salts and organic molecules in the steam emitted by geysers and around the "tiger stripes". The combination of water, silicates and an energy source can lead to chemical reactions. In other words, Enceladus is now a promising place for scientists to search for extraterrestrial life.
Potentially habitable zones are found in the solar system in the most unexpected places. For example, Titan, Callisto, and Ganymede may also contain subsurface oceans (as yet unconfirmed). Peculiar potentially inhabited zones can also be on gas giants. Although the probability of intelligent life on planets so remote from the Sun is extremely low.
Next steps
Now, astronomers are going to better study the structure of Enceladus, the exact location, size and shape of the ocean. Measurements of the gravitational field will continue. In future expeditions it is supposed to conduct spectrographic studies of geysers in order to obtain more information about the composition of the water.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/218273/
All Articles