The history of the Eiffel Tower and ... "Descriptive Geometry"
For students of technical specialties of universities as a historical reference.
Head of the Automobile and Mechanical Department of the Lozovsky branch of the Kharkov Automobile and Road Technical School, teacher of the highest category, Cozhokaru Elena Vladimirovna
125 years ago, on March 31, 1889 , the official opening of the most recognizable architectural landmark of Paris, the Eiffel Tower, took place. Now it is known worldwide as a symbol of France.
During construction, Gustav Eifel decided to engrave under the first balcony of the tower, on all its four sides, the names of the 72 most famous French engineers, mathematicians and scientists who made a significant contribution to the history of the development of science. Moreover, there is no alphabetical or chronological order of names on the tower.
')

Eiffel Tower, Paris
On the South-Eastern side, under the number "54" is the name of Gaspard Monge (1746-1818) - the famous French mathematician, geometer, one of the founders of the famous Polytechnic School in Paris and a participant in the introduction of the metric system of weights and measures, the statesman.
Gaspard Monge was not only one of the organizers of the Polytechnic School in Paris, but also its long-term director. Monge was born in Bon Côte d'0r. Brilliantly graduated from the School of Military Engineers in Mezieres, from 1768. became a professor of mathematics, and since 1771. - also a professor of physics at this school. Since 1780 taught hydraulics at the Louvre School (Paris). Engaged in mathematical analysis, chemistry, meteorology, practical mechanics. In the period of the French bourgeois revolution, he worked in the commission to establish a new system of weights and measures, then he was the naval minister and organizer of the national defense of France. During the Directory, he became close to Napoleon Bonaparte, took part in his campaign to Egypt and founded the Egyptian Institute in Cairo (1798); was elevated to the rank of count. Gaspar Monge received worldwide recognition, creating in the 70s of the XVIII century. modern projection drawing methods and its basis - descriptive geometry. The same name was received and the main work of Monge on these issues, published in 1799.
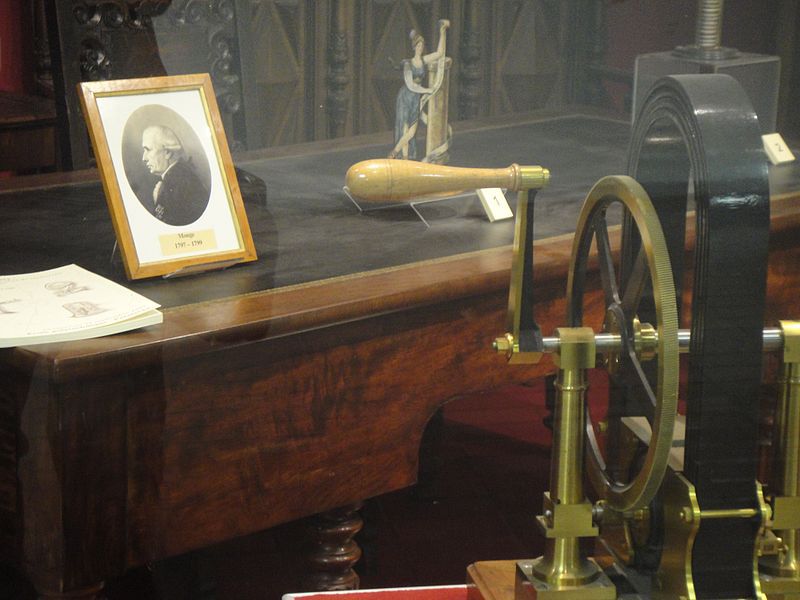

Fig. 1 Exposition dedicated to Gaspard Monge at Paris Polytechnic School
The creation of the treatise “Descriptive Geometry” (“Geometrie descriptive”) served as the beginning and the basis of the works that allowed the new Europe to master the geometric knowledge of ancient Greece.
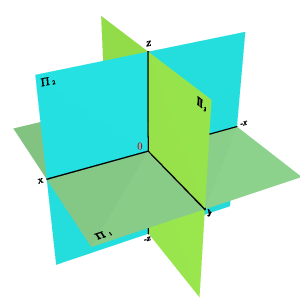
In accordance with the method proposed by Gaspard Mongem (by the method of orthogonal projection), two mutually perpendicular projection planes are considered in space. One of the planes of the projections P 1 is located horizontally (the horizontal plane of the projections), and the second P 2 is vertical (the frontal plane of the projections). The planes are endless and opaque.
The planes of the projections divide space into four dihedral angles — quarters. When considering orthogonal projections, it is assumed that the observer is in the first quarter at an infinitely large distance from them. If complete information on the distance of a point relative to the plane of projections is presented not by using numerical marks, but by using the second projection of a point built on the second plane of projections, then such a drawing is called two-image or complex.
The line of intersection of the planes of the projections is called the coordinate axis and is denoted by x 12 .
Since these planes are opaque, only those geometric objects that are located within the first quarter will be visible to the observer.
To get a flat drawing consisting of the specified projections, the plane P 1 is combined by rotating around the x axis 12 with the plane P 2 (Fig. 2). A projection drawing, in which the projection planes with everything that is depicted on them, combined in a certain way with each other, is called the Monge diagram (from French Epure, the drawing (Fig. 3) or the complex drawing.
Geometric drawing objects are divided into: linear (point, straight, plane), non-linear (curved line, surface) and composite (polyhedrons, one-dimensional and two-dimensional lines).

So, gradually accumulated and scattered among themselves, the rules and methods of imaging were brought to the system by the scientist and developed in his classic work. Since the publication of his “Descriptive geometry” in France by Gaspard Monge, more than two hundred years have passed. Since then, as a discipline and as a separate science, brought to life by the genius Monge, due to the urgent need to improve engineering technology, she began to spread from France to other countries with incredible speed. Nowadays, “Descriptive Geometry” has taken its rightful place among the other fundamental disciplines of the higher technical school as the main academic discipline, without the knowledge of which a complete engineering education is unthinkable.
Monge's work, originally printed as a study guide, has not lost its significance to the present day and constitutes the main part of the training course on imaging techniques . It showed the general character of the versatile activity of the great French scientist: his deep research mind, which promoted science, and tireless energy, aimed at applying theoretical calculations to the practice of engineering.
The name Gaspar Monge , immortalized on the Eiffel Tower, confirms this.
Head of the Automobile and Mechanical Department of the Lozovsky branch of the Kharkov Automobile and Road Technical School, teacher of the highest category, Cozhokaru Elena Vladimirovna
125 years ago, on March 31, 1889 , the official opening of the most recognizable architectural landmark of Paris, the Eiffel Tower, took place. Now it is known worldwide as a symbol of France.
During construction, Gustav Eifel decided to engrave under the first balcony of the tower, on all its four sides, the names of the 72 most famous French engineers, mathematicians and scientists who made a significant contribution to the history of the development of science. Moreover, there is no alphabetical or chronological order of names on the tower.
')

Eiffel Tower, Paris
On the South-Eastern side, under the number "54" is the name of Gaspard Monge (1746-1818) - the famous French mathematician, geometer, one of the founders of the famous Polytechnic School in Paris and a participant in the introduction of the metric system of weights and measures, the statesman.
Gaspard Monge was not only one of the organizers of the Polytechnic School in Paris, but also its long-term director. Monge was born in Bon Côte d'0r. Brilliantly graduated from the School of Military Engineers in Mezieres, from 1768. became a professor of mathematics, and since 1771. - also a professor of physics at this school. Since 1780 taught hydraulics at the Louvre School (Paris). Engaged in mathematical analysis, chemistry, meteorology, practical mechanics. In the period of the French bourgeois revolution, he worked in the commission to establish a new system of weights and measures, then he was the naval minister and organizer of the national defense of France. During the Directory, he became close to Napoleon Bonaparte, took part in his campaign to Egypt and founded the Egyptian Institute in Cairo (1798); was elevated to the rank of count. Gaspar Monge received worldwide recognition, creating in the 70s of the XVIII century. modern projection drawing methods and its basis - descriptive geometry. The same name was received and the main work of Monge on these issues, published in 1799.

Fig. 1 Exposition dedicated to Gaspard Monge at Paris Polytechnic School
The creation of the treatise “Descriptive Geometry” (“Geometrie descriptive”) served as the beginning and the basis of the works that allowed the new Europe to master the geometric knowledge of ancient Greece.
In accordance with the method proposed by Gaspard Mongem (by the method of orthogonal projection), two mutually perpendicular projection planes are considered in space. One of the planes of the projections P 1 is located horizontally (the horizontal plane of the projections), and the second P 2 is vertical (the frontal plane of the projections). The planes are endless and opaque.
The planes of the projections divide space into four dihedral angles — quarters. When considering orthogonal projections, it is assumed that the observer is in the first quarter at an infinitely large distance from them. If complete information on the distance of a point relative to the plane of projections is presented not by using numerical marks, but by using the second projection of a point built on the second plane of projections, then such a drawing is called two-image or complex.
The line of intersection of the planes of the projections is called the coordinate axis and is denoted by x 12 .
Since these planes are opaque, only those geometric objects that are located within the first quarter will be visible to the observer.
To get a flat drawing consisting of the specified projections, the plane P 1 is combined by rotating around the x axis 12 with the plane P 2 (Fig. 2). A projection drawing, in which the projection planes with everything that is depicted on them, combined in a certain way with each other, is called the Monge diagram (from French Epure, the drawing (Fig. 3) or the complex drawing.
Geometric drawing objects are divided into: linear (point, straight, plane), non-linear (curved line, surface) and composite (polyhedrons, one-dimensional and two-dimensional lines).


Fig. 2 System of three projection planes Fig.3 Drawing (diagram)
So, gradually accumulated and scattered among themselves, the rules and methods of imaging were brought to the system by the scientist and developed in his classic work. Since the publication of his “Descriptive geometry” in France by Gaspard Monge, more than two hundred years have passed. Since then, as a discipline and as a separate science, brought to life by the genius Monge, due to the urgent need to improve engineering technology, she began to spread from France to other countries with incredible speed. Nowadays, “Descriptive Geometry” has taken its rightful place among the other fundamental disciplines of the higher technical school as the main academic discipline, without the knowledge of which a complete engineering education is unthinkable.
Monge's work, originally printed as a study guide, has not lost its significance to the present day and constitutes the main part of the training course on imaging techniques . It showed the general character of the versatile activity of the great French scientist: his deep research mind, which promoted science, and tireless energy, aimed at applying theoretical calculations to the practice of engineering.
The name Gaspar Monge , immortalized on the Eiffel Tower, confirms this.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/217769/
All Articles