National payment system: what does it mean for you, and when exactly panic
You may have heard about the national payment system . It was originally planned that this thing will become an alternative to international payment systems. In particular, in 1998, Visa and Mastercard stopped making transfers using their cards due to the crisis - and by the way, 85% of the banking plastic market.
But in the law itself, the emphasis was ultimately made on the withdrawal of electronic payments from the shadows , which were previously not controlled in any way, and in fact providing the regulators with the ability to control banks in the field of non-cash remittances. Now we are again talking about the full creation of a national payment system, so it makes sense to wait for soon amendments regarding blocking data transmission in the United States and other relevant requirements.
To participate in all this, you need to do a really difficult job with IT and IB, and only the organization with the appropriate license can perform and verify it. We have such a license, so below I will briefly outline the main problems in this kind of work that we have already encountered.
')
An NPS is a collection of individuals who participate in remittances. The main purpose of the law is to unify approaches for the implementation of non-cash remittances.
Thanks to the adoption of this law, our government structures plan control over any non-cash remittances.
The national payment system is a combination of:
In fact, before money could appear from nowhere and disappear into nowhere. This gave rise to quite a few fraud situations that had to be manually disassembled. Therefore, the main purpose of the law is to remove illegal money transfers from the shadows.
Now, to carry out operations in the new scheme, you need to meet all sorts of requirements. And the more rights you want - the more stringent the requirements apply. Not only technical means are being introduced, but also processes that control everything.
And here, as you can imagine, there comes a drama - quite a few people perform financial transactions that require a number of protective measures, without such . This is about IT (to a greater extent), and about business processes in general. You need to quickly put software and hardware systems, protect data and do a whole lot more. And here you need someone who can do it. But about this a little later, first, let's understand a little the essence of the issue.

Now the activities of financial organizations in the field of information security is regulated by the following main documents:
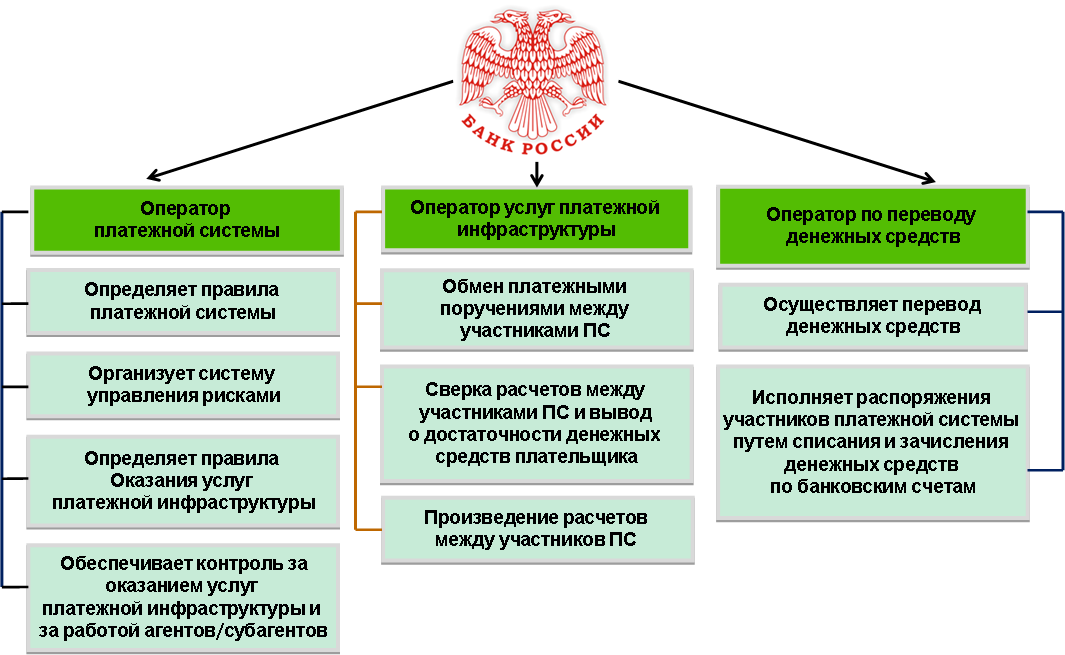
The rules of the game are as follows:

Enough raw. For example, there is a requirement to notify customers when transferring funds. But the Federal Law does not speak about the ways of notification. The bank can set an alert by phone, but then it is not clear what to do if the subscriber’s phone is turned off.
Or here is a more distant example showing a number of features of such alerts. One of the banks simply retained the paid alert service, the second began to notify free of charge (but the one-time password to the data is in the paid part of this service), the third distributed terminals for generating passwords to clients, but “moved” their cost to other services so that it now hard to find without preparation. And, in general, this is just the beginning. Who faced, knows how many unclear places there are in terms of technical and organizational regulations. Documents require a very detailed study, and this, I think, is not a matter of one month or even a year.
And the most pleasant thing is the mandatory use of the following (all at once) remedies:
If we talk in general - you need to revise a lot of things in IT and introduce new information security measures. But there is a nuance.
As a rule, for most organizations that are directly affected and in the most hardcore part (as a rule - banks and other large financial organizations), all this (or most) has long been implemented. Because you still need to protect information. But now you need to understand how well everything is implemented, and to what extent, that is, to receive a corresponding assessment from the results of the audit. And here we usually appear on the scene.
The following things are done:
Speaking in simpler language, we check all the requirements of the law and offer the simplest ways to solve the problem. Considering that everything in this complex of works is rather complicated and confusing, there are often “life hacks” that allow you to avoid extremely expensive options like the introduction of a fundamentally new information system from scratch. As an example - the same access to information of a certain nature. Here, for example, access control. In one of the cases, the easiest was to do it at the level of organizational measures, and not IT infrastructure - just giving the keys to the office with the necessary computers to only one person. Accordingly, the complex requirement for protection against unauthorized access immediately disappeared. Actually, it is necessary to differentiate access (at the system level using, for example, IDM), but this is no longer a stop factor for meeting the requirements of the Federal Law on NPS right now.
Thus, assessing the actual threat to information security, we build threat models that state which threats are relevant and how we are going to close them. These can be both technical measures and organizational ones; it is important that the principle of economic feasibility of choosing a particular protective measure is respected.
Our goal in carrying out such work is not to catch someone in a lie and some fraud, but to help make the processes really better, and if the Central Bank comes to you so that there are no penalties.
Some simply say, “Do us everything to score at 0.7” - and we help.
It also compiles a list of optional, but reasonable (economically sound) measures that help improve the situation with information security in general. Accordingly, it turns out two parts: how to arrive at a match quickly and cheaply and what generally needs to be done to ensure information security.
If you explain something confusedly and have questions or you just need help, ask in the comments or by mail plutsik@croc.ru .
But in the law itself, the emphasis was ultimately made on the withdrawal of electronic payments from the shadows , which were previously not controlled in any way, and in fact providing the regulators with the ability to control banks in the field of non-cash remittances. Now we are again talking about the full creation of a national payment system, so it makes sense to wait for soon amendments regarding blocking data transmission in the United States and other relevant requirements.
To participate in all this, you need to do a really difficult job with IT and IB, and only the organization with the appropriate license can perform and verify it. We have such a license, so below I will briefly outline the main problems in this kind of work that we have already encountered.
')
What is an NPC?
An NPS is a collection of individuals who participate in remittances. The main purpose of the law is to unify approaches for the implementation of non-cash remittances.
Thanks to the adoption of this law, our government structures plan control over any non-cash remittances.
What does it mean?
The national payment system is a combination of:
- money transfer operators
- bank payment agents / subagents
- payment agents
- organizations of Russian Post
- payment system operators
- payment infrastructure service operators
In fact, before money could appear from nowhere and disappear into nowhere. This gave rise to quite a few fraud situations that had to be manually disassembled. Therefore, the main purpose of the law is to remove illegal money transfers from the shadows.
How does this concern you personally?
Now, to carry out operations in the new scheme, you need to meet all sorts of requirements. And the more rights you want - the more stringent the requirements apply. Not only technical means are being introduced, but also processes that control everything.
And here, as you can imagine, there comes a drama - quite a few people perform financial transactions that require a number of protective measures, without such . This is about IT (to a greater extent), and about business processes in general. You need to quickly put software and hardware systems, protect data and do a whole lot more. And here you need someone who can do it. But about this a little later, first, let's understand a little the essence of the issue.
How is it regulated?

Now the activities of financial organizations in the field of information security is regulated by the following main documents:
- A series of standards 27 (both ISO and GOST R). Now they are recommendations, but for PP822 a decision can be made about mandatory compliance with their requirements.
- Standards of the Central Bank of Russia. The Federal Law of December 27, 2002 No. 184- “On Technical Regulation” establishes the recommendatory status of standards and other standardization documents. However, in accordance with it, when joining the standard on the voluntary decision of the organization, they become mandatory.
- Standards of international payment systems - PCI DSS. Fines for non-compliance are theoretically possible (as long as there are no cases in Russia), but there are refusals to approve projects. PCI DSS, in fact - specific technical requirements.
- The Law on Personal Data, which is naturally obligatory, sanctions are provided for by law, currently it is planned to increase sanctions and expand the number of offenses related to violations in the field of personal data processing / protection by the RKN.
- And the last one is 161 FZ “On the National Payment System”, adopted on June 27, 2011, and a group of subordinate regulatory acts adopted in accordance with it are both a Government Decree and documents of the Central Bank. It is required.
The rules of the game are as follows:


How raw are the documents?
Enough raw. For example, there is a requirement to notify customers when transferring funds. But the Federal Law does not speak about the ways of notification. The bank can set an alert by phone, but then it is not clear what to do if the subscriber’s phone is turned off.
Or here is a more distant example showing a number of features of such alerts. One of the banks simply retained the paid alert service, the second began to notify free of charge (but the one-time password to the data is in the paid part of this service), the third distributed terminals for generating passwords to clients, but “moved” their cost to other services so that it now hard to find without preparation. And, in general, this is just the beginning. Who faced, knows how many unclear places there are in terms of technical and organizational regulations. Documents require a very detailed study, and this, I think, is not a matter of one month or even a year.
What is important to know if you are a potential NPS participant
- NPS members are required to protect information
- Government of the Russian Federation sets information security requirements
- Requirements for the protection of information and monitoring their implementation also establishes the Bank of Russia, while in fact it is the only regulator
- A risk management system is introduced to reduce the likelihood of interruptions in PS operations.
- The key purpose of protecting information in the software is ensuring uninterrupted operation of the software
- In case of theft of funds from the client’s account, the bank is obliged, under certain conditions, to refund the full amount of the stolen funds.
And now all the future problems of organizations in one list
- New requirements have arisen for the protection of information in the NPC from unauthorized access, destruction, modification, blocking, copying, distribution, and others. To respect the confidentiality of information and to exercise the right of access to information. They need to follow.
- It is necessary in principle to have an information security service.
- It is important to determine the order of access to the facilities of the PS infrastructure
- It is necessary to include in the duties of employees the fulfillment of the requirements of information security,
- Be sure to identify security threats and vulnerabilities
- It is necessary to analyze the risks of information security and start managing them
- It is necessary to constantly detect security incidents and react to them, and accordingly report to the Central Bank on a monthly basis.
- It is necessary to ensure the protection of information when using the Internet, etc.
- It is necessary to develop and implement a system for protecting information in information systems.
- To organize and carry out measures for monitoring and evaluating compliance at least once every 2 years and again report back to the Central Bank about this.
And the most pleasant thing is the mandatory use of the following (all at once) remedies:
- SKZI
- SZI from NSD
- Antivirus
- Firewall
- IDS / IPS
- Security Analysis Tool
What to do, doctor?
If we talk in general - you need to revise a lot of things in IT and introduce new information security measures. But there is a nuance.
And if I already have everything?
As a rule, for most organizations that are directly affected and in the most hardcore part (as a rule - banks and other large financial organizations), all this (or most) has long been implemented. Because you still need to protect information. But now you need to understand how well everything is implemented, and to what extent, that is, to receive a corresponding assessment from the results of the audit. And here we usually appear on the scene.
The following things are done:
- Evaluation of compliance with information security requirements for 161-FZ
- Development of recommendations for bringing the ISIB into conformity with the requirements of 161-FZ
- Development and improvement of the existing IS for ensuring information security
- Inventory of information assets, analysis and description of business processes
- Carry out an IS risk assessment
- Technical design of the information security system
- Introduction of technical means of information protection
- Information systems security analysis and penetration testing
- Raising awareness on security issues
- Building incident management processes.
Speaking in simpler language, we check all the requirements of the law and offer the simplest ways to solve the problem. Considering that everything in this complex of works is rather complicated and confusing, there are often “life hacks” that allow you to avoid extremely expensive options like the introduction of a fundamentally new information system from scratch. As an example - the same access to information of a certain nature. Here, for example, access control. In one of the cases, the easiest was to do it at the level of organizational measures, and not IT infrastructure - just giving the keys to the office with the necessary computers to only one person. Accordingly, the complex requirement for protection against unauthorized access immediately disappeared. Actually, it is necessary to differentiate access (at the system level using, for example, IDM), but this is no longer a stop factor for meeting the requirements of the Federal Law on NPS right now.
Thus, assessing the actual threat to information security, we build threat models that state which threats are relevant and how we are going to close them. These can be both technical measures and organizational ones; it is important that the principle of economic feasibility of choosing a particular protective measure is respected.
Our goal in carrying out such work is not to catch someone in a lie and some fraud, but to help make the processes really better, and if the Central Bank comes to you so that there are no penalties.
Some simply say, “Do us everything to score at 0.7” - and we help.
It also compiles a list of optional, but reasonable (economically sound) measures that help improve the situation with information security in general. Accordingly, it turns out two parts: how to arrive at a match quickly and cheaply and what generally needs to be done to ensure information security.
If you explain something confusedly and have questions or you just need help, ask in the comments or by mail plutsik@croc.ru .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/217419/
All Articles