Startup step by step: first business model
We continue the series of articles on how to build a startup - we talk about each step with our own example. We have already described how to come up with an idea and how to assemble a team , now let's talk about the business model.
In the previous article, we mentioned lean startup (“a thrifty startup”) - a common approach that we use. The brief point is that you do not need to do a product or service completely, but you must do it step by step, checking the effectiveness of each step on the real audience.
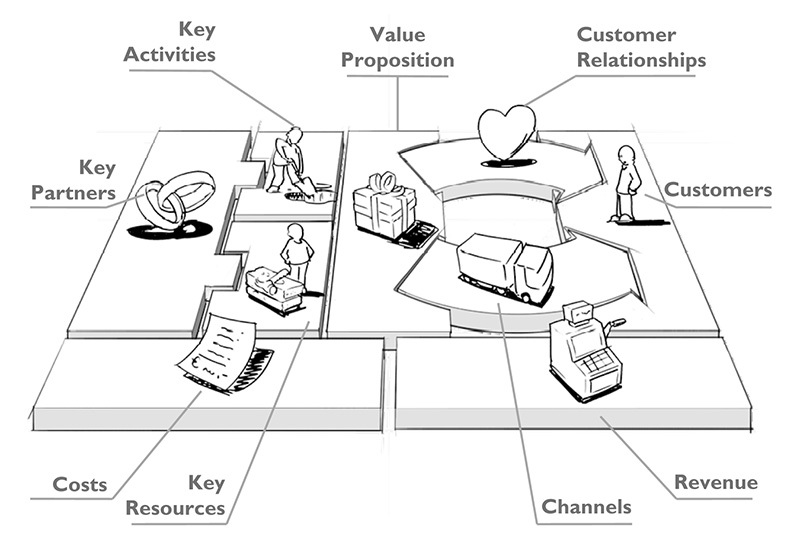
In lean startup, a business model canvas is used , as well as an alternative option - lean canvas. This is a visual scheme of the business, showing the key components and processes. Whatever version of the canvas you choose, to compile a model, you need to answer a few basic questions:
')
- What is the uniqueness of the product / service?
- What problems / needs does he solve?
- What resources are needed for implementation?
- Who will be key partners?
- What are the channels for promotion and distribution?
- What are the costs?
- How do you plan to earn?
- Where and when to take investments?
- Who is the target audience?
We speculate on the answers to our example. Recall that our project - Learzing - is an educational platform with learning applications / games and a social component.
Problem -> idea -> solution

The situation in the online education market leaves much to be desired. In our opinion (and not only), online courses are often boring and ineffective. [1] This is a problem that we want to solve, we push off from it in order to come up with an idea for our service.
We are sure that the future is interactive learning. Add to this the game and the social component, as well as humor, and get the next level of online education. People should enjoy learning, combine business with pleasure. This is a general idea ; we make a start from it in order to come to a decision.
The platform, which contains educational applications and games on various topics, giving the opportunity to study with friends, entertaining the user with game mechanics, allows you to involve the user more in the learning process, thereby increasing its effectiveness. [2] These are the components that together make our solution unique. The uniqueness here is not a big word, it is just the difference between the product and the existing solutions.
Read more about how we came to our idea, as well as our reasoning about online education in our first article .
Resources, partners and channels

One of the key resources , and perhaps the most important is the team. This is more than a part of a business model, since a good team will not fall apart after a failure, but will switch to another idea / model and continue on. More about the team - in our second article .
Our key partners are teachers, educational institutions. Through teachers we can learn their own wishes and needs of students. Having learned the wishes and needs, we make an application prototype based on them. We test it together with teachers and students, make changes, test again, etc., as a result we get a ready-made application. And also potential customers. Thus, teachers are not only partners, but also channels for feedback, creating and promoting a product at the same time.
Since the platform involves a fairly large number of applications, and it is difficult to write a lot of good applications on our own, we need to look for partnerships with the developers of educational applications and games - this is another category of partners.
To encourage users to learn, they can be awarded bonuses. For example, a student receives not only experience / achievements for passing a level, but also something that will be useful to him in real life - for example, exclusive discounts, gift certificates, coupons, etc. Hence another category of partners - companies that will these bonuses provide.
Expenses, incomes and investments

One of the pleasant moments in a startup is a team of enthusiasts who work enthusiastically, believing in the success of the project. That is, there are no salaries, and all expenses at the first stage are directly related to the creation and operation of the product: trips to hackathons (we will especially note JetBrains EdTech Hackathon and HackDay ), collaboration tools (we use Redbooth and Google Docs), hosting for the site, private a repository on GitHub, buying devices for testing (for example, iPhone 4 as the minimum technical requirement for a product), etc.
When studying the market, we found a successful and close in spirit project with games for brain development - Lumosity . In order not to reinvent the wheel, we decided to focus on this project in many aspects, including the monetization model. Lumosity allows you to play for free the first 30 days, and then becomes paid - you can pay every month or pay immediately a year in advance. At the moment we are focusing on this model of monetization .
For third-party investments , we concluded that it is better to look for investors not at the stage when there is a business model or prototype, but at the stage when everything is already working and generating income. That is, in fact, when an investor is not really needed, or rather, it is needed in order for a startup to grow much faster than if you do it yourself.
At this stage, several models have already been tried, an effective one has been found, so it turns out that the funding received will go exactly where it is needed and will not be wasted. This is beneficial for both start-up and investor. If everything is already working and profitable, more options appear. You can negotiate with different investors, the investment will be greater, and the share of business that is given in exchange for investment will be smaller.
That is, at the start we try different models at our own expense ( bootstrapping ), and when everything turned out already, you can attract investors to scale the business.
Another channel, crowdfunding, is unique in that it can be used simultaneously for receiving feedback, promoting and financing a product.
The target audience

The first comment we heard from our mentor when we talked about our idea is to determine the target audience, now you have it too broad and blurred.
Well, we still have not decided. Children, teenagers, students, young people and people of middle and old age - among all these strata there are quite a few curious people who want to learn something new, learn something. Perhaps these will be companies interested in training their employees. Maybe our platform will be for several target audiences at once?
We decided that we would define Central Asia in the process of developing the first applications and from surveys in the course of development.
useful links
It will be useful to anyone who is not indifferent to "lean" startups:- Service to build lean canvas - Lean Stack .
- Step-by-step instructions on how to create an Internet startup from lean startup guru Steve Blanca.
- Handbook startups - Running Lean .
Theory and practice
Our first business model is, of course, approximate and theoretical. The question is whether the compiled model works and how effective it is. You can say for sure - very rarely something works exactly as planned. But you need to start somewhere, and step by step the model is checked and refined. Each of the points should be considered an assumption and checked in practice. We are sure that the model will change more than once, and perhaps it will become completely different.Links
[1] Sebastian Thrun, Godfather Of Free Online Education, Changes Course[2] Do Serious Games Work? Results from Three Studies
All articles of the series
- Startup step by step: the future of online education
- Startup step by step: team and mentors
- Startup step by step: first business model
- How we made the educational platform: first design, landing page and logo
- How we made the educational platform: the first application
- Making an HTML5 Quest: Using the MVC Pattern in Construct 2
- Making an HTML5 quest: creating a character and basic animation
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/215863/
All Articles