Pwn2Own 2014: results
The second day of Pwn2Own ended, which resulted in pwned all of these browsers on up-to-date OS, including Apple Safari (on OS X Mavericks), Mozilla Firefox (on Windows 8.1 x64), and Google Chrome (on Windows 8.1 x64 ) and MS Internet Explorer (Windows 8.1 x64). For both days of the competition, only the Oracle Java plugin resisted. Recently, we wrote about the initiative of the organizers to include in the contest so-called. "Exploit Unicorn" with a record fee of $ 150K. As a result, no one got the reward, since no one demonstrated any attempts to remotely execute code in this system configuration: Internet Explorer 11 x64 on Windows 8.1 x64 + EMET. In the stated requirements of the organizers, the exploit should use two vulnerabilities RCE + LPE for successful remote execution of the code with the subsequent elevation of its privileges to the maximum possible level (SYSTEM) and overcoming sandboxing restrictions (user-mode restriction).
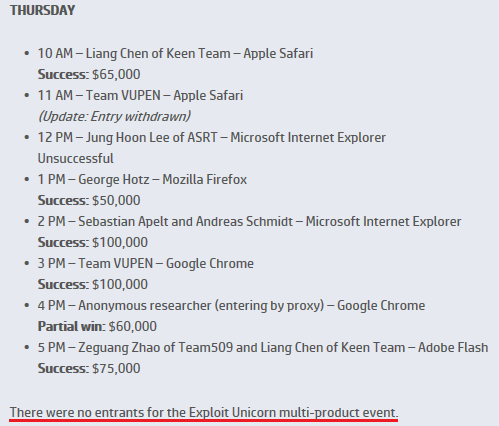
pwned times:
')
= $ 850K cash.
It is interesting to note that the VUPEN researchers demonstrated remote code execution in Google Chrome, bypassing sandbox restrictions without a Local Privilege Escalation (LPE) vulnerability, only due to a use-after-free vulnerability in the Blink browser engine. We have previously indicated that Chrome uses the special features of Windows, which allow you to limit the processes of browser tabs from performing system and other functions.

Chrome sandboxing:

Fig. Sandboxing mode as implemented in Google Chrome. Almost all security identifiers of users of SID groups in the access token have Deny status, which prohibits the process from performing important system functions allowed for these groups.

Fig. Chrome uses a special job object to include all browser processes. The object allows you to limit the application's actions in relation to the resources of the OS, preventing exploitation of the browser by attackers.

pwned times:
')
- Mozilla Firefox x 4 = $ 200K
- MS Internet Explorer x 2 = $ 200K
- Google Chrome x 2 (partial) = $ 160K
- Apple Safari x 1 = $ 65K
- Adobe Flash Player x 2 = $ 150K
- Adobe Reader x 1 = $ 75K
= $ 850K cash.
It is interesting to note that the VUPEN researchers demonstrated remote code execution in Google Chrome, bypassing sandbox restrictions without a Local Privilege Escalation (LPE) vulnerability, only due to a use-after-free vulnerability in the Blink browser engine. We have previously indicated that Chrome uses the special features of Windows, which allow you to limit the processes of browser tabs from performing system and other functions.

Chrome sandboxing:

Fig. Sandboxing mode as implemented in Google Chrome. Almost all security identifiers of users of SID groups in the access token have Deny status, which prohibits the process from performing important system functions allowed for these groups.

Fig. Chrome uses a special job object to include all browser processes. The object allows you to limit the application's actions in relation to the resources of the OS, preventing exploitation of the browser by attackers.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/215831/
All Articles