Top 10 Most Breakthrough Technologies of 2013 and Startups Based on Them
Retelling from www.technologyreview.com/featuredstory/513736/supergrids . MIT has published a list of the most breakthrough technologies for 2013.

"Deep-learning" - "Deep learning."
The fundamental idea of the project is the idea of creating a truly smart computer that could understand human language and draw conclusions and decisions on its own. The creator of the idea is the American inventor Ray Kurzweil, and the story of his startup begins with a meeting with Google CEO Larry Page. The purpose of their meeting was to discuss the forthcoming book of Kurzweil entitled “How to Create a Mind”. During the meeting, Kurzweil shared his desire to open a company in order to realize his concept of a “smart” computer. Of course, to implement such an idea, Google’s computational power is needed and, having heard the idea, a professional like Larry Page understood that it would be difficult for a small company with its own source of income, so he suggested R. Kurzweil to join Google. Without thinking for a long time, Kurzweil began working for Google as a technical director. One of the reasons for such quick agreement was the company's achievements in the so-called “deep learning”. The program's algorithm attempts to mimic the activity of neurons in a new cerebral cortex, in which about 80 percent of thinking occurs. Software learns, in the truest sense of the word, how to recognize patterns in sounds, images, and other data. Thus, the basic idea of deep learning is that software can imitate a large array of neocortex neurons in an artificial "neural network." Today, scientists in the field of the theory of computers and systems, programmers can simulate much more layers of virtual neurons than ever before, thanks to the continuous improvement of mathematical formulas and the increase in computer power, and research in this area continues. One of their significant achievements was noted in June of last year, when the Google system was shown 10 million frames of YouTube-video, and it recognized cats and other objects twice as efficiently as other programs. Interestingly, the technology has helped the corporation to adjust the speech recognition application for mobile phones.

')
"Temporary Social Media" - "Temporary Social Networks"
Today, an important aspect of our personal life is the ability to control the information we disclose to others. Today, every photo, any status update, any post posted on social networks is stored in the cloud. We may want to share this information with someone, but this does not mean that we want it to remain available forever. And then the question arises, what would happen if people could make their messages on the Internet the same as in everyday life: everything we published would automatically disappear and would not be “recorded” for posterity. And this service promises a Snapchat mobile phone application, and the popularity of this application has increased dramatically over the past year.
The creators of the project - Evan Speygel and Bobby Murphy, undergraduates at Stanford. The idea came to their mind two years ago. At about that time in New York, Congressman Anthony Weiner accidentally made his colorful photos, which later were posted on Twitter and he had to resign. The Snapchat program allows users to take photos and short videos, and then decide how long they will be visible to the recipient. The maximum publication time is 10 seconds, and then the images disappear forever.
Now in Snapchat, users exchange 100 million photos and videos every day. And it made the creators of Facebook nervous, who are now not indifferent to the privacy of their users, and in December launched the application - an analogue of Snapchat, called Poke.
Popularity Snapchat its creators explain the fact that people can express their opinions without worrying that what they say will be part of their digital file forever.

"Prenatal DNA Sequencing" - "Prenatal DNA Sequencing"
Last year, Illumina , the manufacturer of the widely used DNA sequencing machines in the world, agreed to pay almost half a billion dollars to a little-known startup company, Verinata , which has almost no income at all. And all because the startup is based on a technique that allows decoding the DNA of a human embryo.
The principle of technology is very simple and safe - in order to decipher the DNA, the embryo is not disturbed in any way, they simply take the maternal blood and look for embryonic DNA in it. In this way, quite serious diseases, such as Down syndrome, can already be identified before the birth of a child. This technology is a breakthrough, because in no way does it threaten the fetus of the mother, and the methods available before this created a threat of miscarriage. Illumina CEO Jay Flatley predicts that such a test will pass two million women a year.
Verinata itself is located in Redwood City, California.
"Additive Manufacturing" - "3D Printing"
General Electric (GE) will use 3D printing to manufacture parts for its jet engines. General Electric - the world's largest supplier of jet engines - is going to produce fuel injectors for a new aircraft engine using 3D printing, rather than metal casting and welding. This method, known as additive manufacturing, can completely change how GE develops and manufactures many complex parts that go in everything - from gas turbines to ultrasonic machines.
3D printing is already used to make some niche elements, such as medical implants, plastic prototypes for engineers and designers. But the decision of mass production of metal alloys to be used in thousands of jet engines is an important task for the technology.
Last fall, GE bought a couple of companies with know-how in automating precision metal fabrication, and then summarized technology into GE Aviation activities.

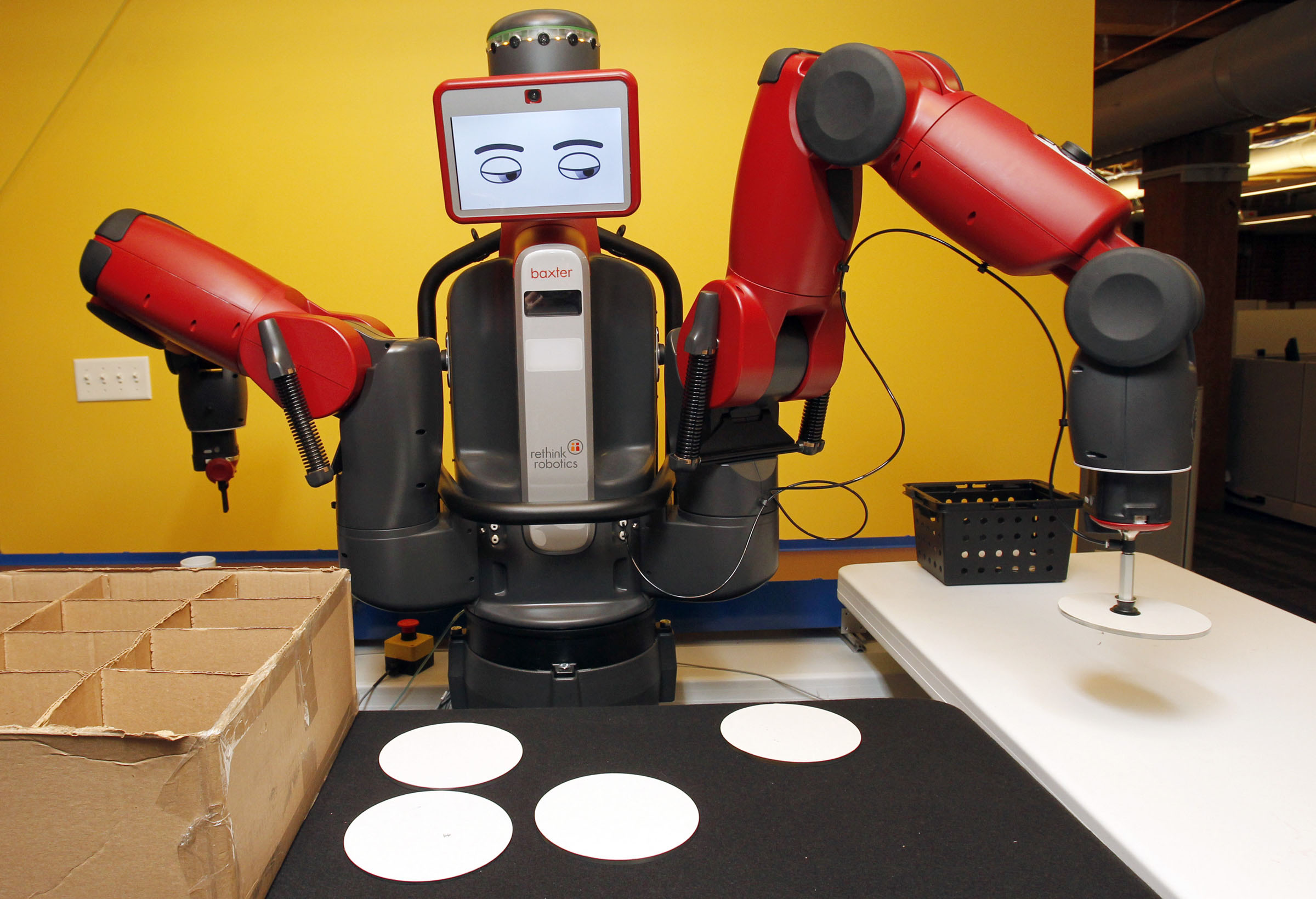
"Baxter: The Blue-Collar Robot" - "Baxter: Robot, Production Worker"
Robot Baxter was developed by the American company Rethink Robotics . The robot was created as a production worker, it is adaptive, it contains cameras, sensors and sophisticated software that allow it to “see” objects, “feel” force and “understand” its tasks. As a result, the company made a robot that automatically adapts to changing conditions, it does what is expected of it. His face, moving eyes, flexibility of movements, versatility in application distinguish him from an ordinary industrial robot, while ordinary robots can perform only certain tasks, Baxter only needs to select the desired grips and show what to do. The price of such pleasure is $ 25,000, for an industrial enterprise the amount is not large in relation to other costs when hiring an employee. In general, Rethink Robotics works on the basis of the affordability of their products and safety during operation and workflow.

"Memory Implants" - "Memory Implants"
Theodore Berger, a biomedical engineer and neuroscientist at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles, envisions a day in the not too distant future when a patient with severe memory loss can receive help from an electronic implant. In people whose brain has been damaged by Alzheimer's disease, a stroke or some kind of injury, as a result of which neural networks are disturbed and long-term memories no longer form. For more than two decades, Berger worked to develop silicon chips that simulate signal processing that neurons reproduce when they function properly, allowing us to recall our experience and knowledge. Ultimately, Berger wants to restore the ability to create long-term memories by implanting chips into the brain. The device is a tiny chip with electrodes and is implanted in the area of the brain that is responsible for the transition of short-term memory to long-term (hippocampus), then records the signals - short-term memories. After that, the signals are sent to the computer, where they are mathematically transformed into long-term memories; and then sent to the second set of electrodes, which stimulates another part of the hippocampus.
The goal of the device is not to identify individual memories, but to study how they are transformed into long-term ones.
Berger's team tested devices on rats trained in a simple memorization task. Each rat with an implant was placed in a chamber with two levers. At first she was shown one lever on one side, and the rat pressed it. After a short wait, two levers appeared on both sides, and if the rat pressed the second lever, it received a sip of water. Successful execution of this task required memorization from the rat, which lever she pressed first.
To test the work of memory prostheses, the researchers injected some substance into the rats that violated the natural work of memory and repeated the experiment with levers. The rats were still able to properly use the levers - and this meant that they were still able to form new memories. In other words, rat implants memorized information for them.
“Big Data from Cheap Phones” - “Big Data from Cheap Phones”
The essence of the technology is that information collected from simple cell phones, and subsequently analyzed, can provide scientists and researchers with an opportunity to get to the essence of where, how and in what quantity people move and put together a picture of their behavior. These data are useful in dealing with the most crisis situations — and can even help you understand the spread of certain diseases and help prevent their spread.
A renowned epidemiologist at the Harvard School of Public Health in Boston, Caroline Buke, points to her computer on a map of the highlands of western Kenya, which represents one of the thousands of national cell phone towers. Bouquet deals with the fight against malaria and explains that the data transmitted from this tower near the city of Keriho can be worth its weight in gold.
When she and her colleagues studied the data transmitted from this tower, she found that people making telephone inquiries or sending text messages passing through the Keriho tower made 16 times more trips away from the region than the average for the region. Moreover, they three times more than others visited the territory to the northeast of Lake Victoria, which, according to the records of the Ministry of Health, was identified as a hot spot for malaria. Thus, the signal radius of the tower covers a significant area for transmission of malaria, which can be transmitted from person to person through mosquito bites. Satellite images showed the likely culprit of the epidemic — a tea plantation that was most likely full of migrant workers. And Caroline Bouquet made it clear that there would be a ton of infected people.
Now Bouquet is building new predictive models for the spread of malaria, the fact that Lake Victoria is a major center of malaria has been identified for a long time, but before that there was no information about how many people come and go in this area when they come and go, what specific the places they go, and which of the available places attract people the most.
Existing and quite common ways of obtaining such information include interviews by nurses of people affected by malaria about where they have been lately, sometimes public health workers literally count people in transportation hubs.
Intelligent analysis of data obtained from cell phones can help in the adoption of new measures to combat malaria, for example, to understand in what places it is necessary first of all to intensify the fight against mosquitoes. Analyzing this data shows how it can be used to create tools that health workers, governments, and others can use to identify and monitor the epidemic, manage disasters, and optimize the transportation system.

“Supergrids” - “Super Networks”
Supergrids (English) - super-high voltage networks. High-voltage DC power lines can efficiently transport electricity over distances of thousands of kilometers and long distances under water, ahead of the AC lines that currently dominate transmission networks. But they prevailed over the course of a century, because the high DC voltage could only be used for point-to-point transmission; it was impossible to form the integrated grid networks necessary for a stable system of electricity.
ABB, a Swiss conglomerate, has solved a major technical obstacle to such networks. They developed a “DC breaker” that disconnects parts of the grid where there is a problem, allowing others to continue to work. These networks will be more efficient when connecting remote sources of renewable energy.


"Deep-learning" - "Deep learning."
The fundamental idea of the project is the idea of creating a truly smart computer that could understand human language and draw conclusions and decisions on its own. The creator of the idea is the American inventor Ray Kurzweil, and the story of his startup begins with a meeting with Google CEO Larry Page. The purpose of their meeting was to discuss the forthcoming book of Kurzweil entitled “How to Create a Mind”. During the meeting, Kurzweil shared his desire to open a company in order to realize his concept of a “smart” computer. Of course, to implement such an idea, Google’s computational power is needed and, having heard the idea, a professional like Larry Page understood that it would be difficult for a small company with its own source of income, so he suggested R. Kurzweil to join Google. Without thinking for a long time, Kurzweil began working for Google as a technical director. One of the reasons for such quick agreement was the company's achievements in the so-called “deep learning”. The program's algorithm attempts to mimic the activity of neurons in a new cerebral cortex, in which about 80 percent of thinking occurs. Software learns, in the truest sense of the word, how to recognize patterns in sounds, images, and other data. Thus, the basic idea of deep learning is that software can imitate a large array of neocortex neurons in an artificial "neural network." Today, scientists in the field of the theory of computers and systems, programmers can simulate much more layers of virtual neurons than ever before, thanks to the continuous improvement of mathematical formulas and the increase in computer power, and research in this area continues. One of their significant achievements was noted in June of last year, when the Google system was shown 10 million frames of YouTube-video, and it recognized cats and other objects twice as efficiently as other programs. Interestingly, the technology has helped the corporation to adjust the speech recognition application for mobile phones.

')
"Temporary Social Media" - "Temporary Social Networks"
Today, an important aspect of our personal life is the ability to control the information we disclose to others. Today, every photo, any status update, any post posted on social networks is stored in the cloud. We may want to share this information with someone, but this does not mean that we want it to remain available forever. And then the question arises, what would happen if people could make their messages on the Internet the same as in everyday life: everything we published would automatically disappear and would not be “recorded” for posterity. And this service promises a Snapchat mobile phone application, and the popularity of this application has increased dramatically over the past year.
The creators of the project - Evan Speygel and Bobby Murphy, undergraduates at Stanford. The idea came to their mind two years ago. At about that time in New York, Congressman Anthony Weiner accidentally made his colorful photos, which later were posted on Twitter and he had to resign. The Snapchat program allows users to take photos and short videos, and then decide how long they will be visible to the recipient. The maximum publication time is 10 seconds, and then the images disappear forever.
Now in Snapchat, users exchange 100 million photos and videos every day. And it made the creators of Facebook nervous, who are now not indifferent to the privacy of their users, and in December launched the application - an analogue of Snapchat, called Poke.
Popularity Snapchat its creators explain the fact that people can express their opinions without worrying that what they say will be part of their digital file forever.

"Prenatal DNA Sequencing" - "Prenatal DNA Sequencing"
Last year, Illumina , the manufacturer of the widely used DNA sequencing machines in the world, agreed to pay almost half a billion dollars to a little-known startup company, Verinata , which has almost no income at all. And all because the startup is based on a technique that allows decoding the DNA of a human embryo.
The principle of technology is very simple and safe - in order to decipher the DNA, the embryo is not disturbed in any way, they simply take the maternal blood and look for embryonic DNA in it. In this way, quite serious diseases, such as Down syndrome, can already be identified before the birth of a child. This technology is a breakthrough, because in no way does it threaten the fetus of the mother, and the methods available before this created a threat of miscarriage. Illumina CEO Jay Flatley predicts that such a test will pass two million women a year.
Verinata itself is located in Redwood City, California.

"Additive Manufacturing" - "3D Printing"
General Electric (GE) will use 3D printing to manufacture parts for its jet engines. General Electric - the world's largest supplier of jet engines - is going to produce fuel injectors for a new aircraft engine using 3D printing, rather than metal casting and welding. This method, known as additive manufacturing, can completely change how GE develops and manufactures many complex parts that go in everything - from gas turbines to ultrasonic machines.
3D printing is already used to make some niche elements, such as medical implants, plastic prototypes for engineers and designers. But the decision of mass production of metal alloys to be used in thousands of jet engines is an important task for the technology.
Last fall, GE bought a couple of companies with know-how in automating precision metal fabrication, and then summarized technology into GE Aviation activities.

"Baxter: The Blue-Collar Robot" - "Baxter: Robot, Production Worker"
Robot Baxter was developed by the American company Rethink Robotics . The robot was created as a production worker, it is adaptive, it contains cameras, sensors and sophisticated software that allow it to “see” objects, “feel” force and “understand” its tasks. As a result, the company made a robot that automatically adapts to changing conditions, it does what is expected of it. His face, moving eyes, flexibility of movements, versatility in application distinguish him from an ordinary industrial robot, while ordinary robots can perform only certain tasks, Baxter only needs to select the desired grips and show what to do. The price of such pleasure is $ 25,000, for an industrial enterprise the amount is not large in relation to other costs when hiring an employee. In general, Rethink Robotics works on the basis of the affordability of their products and safety during operation and workflow.

"Memory Implants" - "Memory Implants"
Theodore Berger, a biomedical engineer and neuroscientist at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles, envisions a day in the not too distant future when a patient with severe memory loss can receive help from an electronic implant. In people whose brain has been damaged by Alzheimer's disease, a stroke or some kind of injury, as a result of which neural networks are disturbed and long-term memories no longer form. For more than two decades, Berger worked to develop silicon chips that simulate signal processing that neurons reproduce when they function properly, allowing us to recall our experience and knowledge. Ultimately, Berger wants to restore the ability to create long-term memories by implanting chips into the brain. The device is a tiny chip with electrodes and is implanted in the area of the brain that is responsible for the transition of short-term memory to long-term (hippocampus), then records the signals - short-term memories. After that, the signals are sent to the computer, where they are mathematically transformed into long-term memories; and then sent to the second set of electrodes, which stimulates another part of the hippocampus.
The goal of the device is not to identify individual memories, but to study how they are transformed into long-term ones.
Berger's team tested devices on rats trained in a simple memorization task. Each rat with an implant was placed in a chamber with two levers. At first she was shown one lever on one side, and the rat pressed it. After a short wait, two levers appeared on both sides, and if the rat pressed the second lever, it received a sip of water. Successful execution of this task required memorization from the rat, which lever she pressed first.
To test the work of memory prostheses, the researchers injected some substance into the rats that violated the natural work of memory and repeated the experiment with levers. The rats were still able to properly use the levers - and this meant that they were still able to form new memories. In other words, rat implants memorized information for them.

“Big Data from Cheap Phones” - “Big Data from Cheap Phones”
The essence of the technology is that information collected from simple cell phones, and subsequently analyzed, can provide scientists and researchers with an opportunity to get to the essence of where, how and in what quantity people move and put together a picture of their behavior. These data are useful in dealing with the most crisis situations — and can even help you understand the spread of certain diseases and help prevent their spread.
A renowned epidemiologist at the Harvard School of Public Health in Boston, Caroline Buke, points to her computer on a map of the highlands of western Kenya, which represents one of the thousands of national cell phone towers. Bouquet deals with the fight against malaria and explains that the data transmitted from this tower near the city of Keriho can be worth its weight in gold.
When she and her colleagues studied the data transmitted from this tower, she found that people making telephone inquiries or sending text messages passing through the Keriho tower made 16 times more trips away from the region than the average for the region. Moreover, they three times more than others visited the territory to the northeast of Lake Victoria, which, according to the records of the Ministry of Health, was identified as a hot spot for malaria. Thus, the signal radius of the tower covers a significant area for transmission of malaria, which can be transmitted from person to person through mosquito bites. Satellite images showed the likely culprit of the epidemic — a tea plantation that was most likely full of migrant workers. And Caroline Bouquet made it clear that there would be a ton of infected people.
Now Bouquet is building new predictive models for the spread of malaria, the fact that Lake Victoria is a major center of malaria has been identified for a long time, but before that there was no information about how many people come and go in this area when they come and go, what specific the places they go, and which of the available places attract people the most.
Existing and quite common ways of obtaining such information include interviews by nurses of people affected by malaria about where they have been lately, sometimes public health workers literally count people in transportation hubs.
Intelligent analysis of data obtained from cell phones can help in the adoption of new measures to combat malaria, for example, to understand in what places it is necessary first of all to intensify the fight against mosquitoes. Analyzing this data shows how it can be used to create tools that health workers, governments, and others can use to identify and monitor the epidemic, manage disasters, and optimize the transportation system.

“Supergrids” - “Super Networks”
Supergrids (English) - super-high voltage networks. High-voltage DC power lines can efficiently transport electricity over distances of thousands of kilometers and long distances under water, ahead of the AC lines that currently dominate transmission networks. But they prevailed over the course of a century, because the high DC voltage could only be used for point-to-point transmission; it was impossible to form the integrated grid networks necessary for a stable system of electricity.
ABB, a Swiss conglomerate, has solved a major technical obstacle to such networks. They developed a “DC breaker” that disconnects parts of the grid where there is a problem, allowing others to continue to work. These networks will be more efficient when connecting remote sources of renewable energy.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/212797/
All Articles