Arista. Acquaintance

On Habré there is not a single post about switches companies Arista Networks . At the same time there are a few comments , in my opinion, quite positive in semantic coloring.
I wanted to write about this company, their equipment, the operating system EOS and CLI .
')
Excuses
I am not a representative of the vendor and I do not have deep knowledge across the entire line. The topic is an overview and reflects my personal opinion. For the opinions of readers have comments and new topics.
Arista history
According to the book Arista Warrior and the corresponding section of the site, three key figures are guilty of the appearance of Arista Networks:
- Andy bechtolsheim
One of the founders of Sun Microsystems. In 1995, he left Sun and created Granite Systems, whose goal is to produce high-speed network switches. In 1996, Cisco buys Granite Systems. Under his leadership, Cisco creates the Catalyst 4500 series of switches. Andy leaves Cisco in 2003 and creates Kealia, a new generation server company that Sun buys in 2004.
In 2005, he became one of the founders of Arasta, who later changed its name to Arista Networks. - David Cheriton
One of the founders of Granite Systems. ASIC Chief Architect for Catalyst 4X00 on Cisco. He was also a technical consultant for Google, VMware, Tibco, Cisco, Sun and several startups. - Kenneth duda
A pioneer in high-performance networking software and a leading EOS architect at Arista. He is one of the authors of the specifications of several network protocols, for example: VXLAN and NVGRE. He was the first employee at Granite Systems and led the development of software for the Catalyst 4X00 line.
Jayshree Ullal is the CEO. She was a senior vice president at Cisco and was responsible for the Cisco Nexus 7000, Catalyst 4500, and Catalyst 6500 series. In 2005, Network World Magazine included her in the list of “50 Most Powerful People” ).
Product line.
Arista Networks offers only switches and of course related products (power cables, transceivers, service, etc.). Arista is positioning its switches for use in Data Processing Centers (DPCs).
A short free table (clickable) for some parameters from the Arista Products Quick Reference Guide (more parameters, for example, there is hardware support for VXLAN ):

The company does not manufacture routers, Wi-Fi AP, SOHO devices, firewalls and other network devices.
Merchant siliconon
Data Plane (“data transmission plane”) in Arista switches is built using special-purpose integrated circuits - ASIC .
By type of origin, ASICs are divided into:
- Custom Silicon - chips, which are usually designed and manufactured by a company that manufactures switches on these chips.
- Merchant Silicon is “commercially available” chips designed and manufactured by a company that does not manufacture switches on them.
A simple example for an analogy from the world of smartphones:
- HTC does not manufacture CPUs for its smartphones, but it assembles and sells smartphones on, for example, Qualcomm chips. This is an example of Merchant Silicon.
- Samsung company produces both an Exynos chipset and smartphones on them. In the case of Samsung, this is an example of a Custom Silicon.
Arista does not develop its own ASIC, but uses Merchant Silicon from Intel and Broadcom in its switches.
On the one hand, this is nothing unique. For example, Broadcom’s ASIC StrataXGS Trident II has built the following switches from some vendors (vendors in alphabetical order):
- Arista 7050X
- Cisco Nexus 9000
- Extreme Networks Summit X770
- Juniper QFX5100
On the other hand, with this approach, switch parameters such as:
- The quality of programming and use of ASIC resources. ASIC is not just plug and play, their resources can be managed programmatically (this is the flexibility (in a certain range) of using these chips). The switch behavior on traffic depends on the quality of the algorithms and code.
- The design is both internal (choice (for example, CPU variant, number and type of RAM) and the layout of the elements on the boards, fans, power supplies) and external (number of units, ease of port layout, etc.)
- Quality and convenience of the OS and CLI switch.
- Availability of necessary and convenient additional features implemented both on the basis of ASIC and programmatically on the RE. It should be remembered that some function can be supported in the ASIC, but not supported by the switch OS. In this case, it simply will not be available for use. Worse, when the function that performs the functions of Data Plane is implemented not in ASIC, but programmatically.
About such characteristics of Arista Networks switches as delays and work with the buffer, there are presentations, rumors and more comments on Habré .
EOS
EOS is a modular operating system that provides Arista switches. It is one for the entire line of switches, not only in name. Who updated at least once the IOS on the Cisco switches knows that the IOS c3550 * .bin will not work on the switch that uses the c3750 * .bin. And who worked with Juniper knows that jinstall-ex-4500 * .tgz will not replace jinstall-ex-4200 * .tgz. At Arista, it turns out to do a single OS file for the entire line. Not the main plus of EOS, but convenient.
EOS is based on Fedora . The OS runs on a separate CPU (currently x86), which allows you to separate the Control Plane (“control plane” - CPU, EOS) and Data Plane (“data transfer plane” - ASIC). All this is not new, but there are also architectural features in EOS that are not in the OS of other vendors. So, for example, the components necessary for the switch operation do not communicate with each other directly, but do it only through a special manager-base - Sysdb. Sysdb is both a common bus for communication between processes and a database for the working information of these processes. For example, a route that arrives via IGP, before it enters the ASIC, is passed by the process responsible for IGP to Sysdb; Sysdb keeps it in its bins and transfers it to the process responsible for interacting with the ASIC.
With the help of work through Sysdb it turns out to provide greater survival and stability. For example, something happened to the service responsible for SNMP (for example, the complexly formed data in the request caused a crash), and he died. The process manager (ProcMgr) automatically restarts the SNMP service. After launch, all services access Sysdb and, if their data is already there, then they restore them and continue to work with them.
In the traditional construction of the OS (including for network devices) components, services and services transfer data between themselves directly. Restarting or "dropping" the service process entails the loss of all its working data (routes, statistics and other things), and it can also affect other services with which the unlucky process worked and exchanged data: they can also "fall" or lose conditions required for operation.
The schematic structure of the "traditional OS" and Arista EOS:
 | 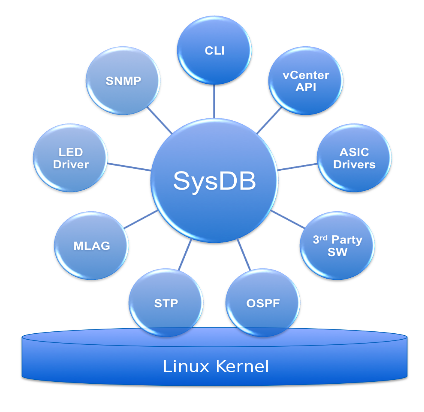 |
|---|
( Pictures from EOS Architecture Whitepaper .)
Such an EOS device does not guarantee complete stability and reliability, but it is still better than nothing. And with the help of functioning through Sysdb, ISSU services are implemented.
CLI
Cli (in EOS, all launched applications from Arista are capitalized) also works via Sysdb.
CLI commands are written in Python:
[admin@localhost ~]$ cd /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/CliPlugin/ [admin@localhost CliPlugin]$ ls -a *Cli*py AaaCli.py CliSchedulerCli.py FaultInjectionCli.py IraIpCli.py MlagShowCli.py PimCli.py RipShowTechCli.py TapAggIntfCli.py AclCli.py ClockCli.py FhrpCli.py IraIpIntfCli.py MlagTunnelCli.py PimShowTechCli.py RouteEventMonCli.py TcpdumpCli.py AclCliRules.py CpuFabricCli.py FileCli.py IraShowTechCli.py MlagWarningCli.py PmbusCli.py RouteMapCli.py TechSupportCli.py AgentCli.py DcbxCli.py FruCli.py IraVrfCli.py ModuleCli.py PortSecCli.py RoutingBgpCli.py TrackingCli.py AgentPingCli.py DebugMessageCli.py IgmpCli.py LagCli.py ModuleIntfCli.py PowerCli.py RoutingIsisCli.py UplinkFailureDetectionCli.py AgentResourceCli.py DebuggingCli.py IgmpProfileCli.py LagIntfCli.py MoreCli.py PowerDiagsCli.py RoutingOspf3Cli.py VersionCli.py AgentShutdownCli.py DhcpRelayHelperCli.py IgmpShowTechCli.py LagIntfMlagCli.py MrouteCli.py PsmiCli.py RoutingOspfCli.py VlanCli.py ArpEventMonCli.py DiagCli.py IgmpSnoopingCli.py LagShowTechCli.py MrouteEtbaCli.py PtpCli.py RoutingRipCli.py VlanIntfCli.py ArpIp6Cli.py DonkeyCli.py IgmpSnoopingDebugCli.py LanzCli.py MrouteEventMonCli.py QosCli.py SectionCliLib.py VmTracerCli.py ArpIpCli.py EbraEthIntfCli.py IgmpSnoopingEtbaCli.py LanzIntfCli.py MrouteShowTechCli.py RadiusCli.py SendCli.py VmTracerIntfCli.py ArpIpIntfCli.py EbraEthIntfCliModel.py IgmpSnoopingEventMonCli.py LauncherDaemonCli.py MsdpCli.py RedSupCli.py SflowCli.py VxlanCli.py BackupIntfCli.py EbraShowTechCli.py IgmpSnoopingShowTechCli.py LinkFlapCli.py NetworkCli.py RedSupCliFormatSpec.py ShellCli.py WaitForWarmupCli.py BeaconLedCli.py EbraSnmpCli.py InstallCli.py LldpConfigCli.py NetworkToolsCli.py RedSupFileCli.py SnmpCli.py WatchCli.py BfdCli.py EmailCli.py IntfCli.py LldpStatusCli.py NetworkUrlCli.py ReloadCauseCli.py StormControlCli.py XcvrCli.py BootCli.py EnvironmentCli.py IntfRangeCli.py LoggingCli.py OldDhcpRelayCli.py ReloadCli.py StpCli.py XcvrConfigCli.py BridgingCli.py ErrdisableCli.py IntfSnmpCli.py LoopbackIntfCli.py OpenFlowCli.py ReloadConfigSaveCli.py StpCliLib.py BridgingCliModel.py EthIntfCli.py Ip6NdCli.py MacEventMonCli.py PciCli.py ReloadElectionCli.py StpIntfCli.py BridgingEtbaCli.py EthShowTechCli.py IraCommonCli.py MacFlapCli.py PeerIntfCli.py ReloadFileSyncCli.py SupeSessionCli.py CliCli.py EventCli.py IraEtbaCli.py ManagementActiveIntfCli.py PfcCli.py RibIp6Cli.py SwitchIntfCli.py CliCliModel.py EventMonCli.py IraIp6Cli.py MirroringCli.py PhyCli.py RibIpCli.py SysMgrCliLib.py CliError.py ExtensionMgrCli.py IraIp6IntfCli.py MlagConfigCli.py PhyConfigCli.py RibShowTechCli.py TacacsCli.py [admin@localhost CliPlugin]$ head VlanCli.py ==> VlanCli.py <== # Copyright (c) 2006-2011 Arista Networks, Inc. All rights reserved. # Arista Networks, Inc. Confidential and Proprietary. #------------------------------------------------------------------------------- # This module implements VLAN configuration. In particular, it provides: # - the Vlan class # - the VlanSet class # - the "config-vlan" mode # - the "[no] vlan <vlan_set>" command # - the "[no] name <vlan_name>" command Users can change both built-in commands and write their own.
The very same work in the CLI is similar to the work in the Cisco IOS CLI. At first it seems that this is a copy (not like that of Huawei, but a copy). But then improvements become visible, which were very lacking in IOS.
For example, when changing the parameters of an interface group, the word “range” is not needed, and the interface numbers are displayed on the left:
localhost(config)#int e1,3,5 localhost(config-if-Et1,3,5)# localhost(config-if-Et1,3,5)#load-interval 10 Or you can see the utilization of interfaces and groups of interfaces:
localhost#sh int e3,e48 | i rate 10 seconds input rate 5.26 Gbps (53.3% with framing overhead), 433507 packets/sec 10 seconds output rate 12.2 Mbps (0.2% with framing overhead), 21824 packets/sec 10 seconds input rate 12.2 Mbps (0.2% with framing overhead), 21826 packets/sec 10 seconds output rate 5.26 Gbps (53.3% with framing overhead), 433546 packets/sec And it is absolutely not necessary to select with the cursor 3 digits per port speed in order to understand whether we are dealing with megabits or gigabits. But that's not all. EOS displays interface utilization in%.
And in EOS you can make multiple pipes and use GNU / Linux programs:
sho run | grep X | grep -v Y | more It is not necessary to add “do” in the configuration mode before the command.
You can see the diff of the active and saved configuration:
localhost#sh run diffs --- flash:/startup-config +++ system:/running-config @@ -190,9 +190,10 @@ ! interface Loopback0 ipv6 enable + ipv6 address 2001:db8:ffff::ffff/128 ipv6 address 2001:db8::1/128 ip address 10.10.10.1/32 - ip address 10.255.255.1/32 secondary + ipv6 ospf priority 20 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 ! interface Management1 @@ -200,7 +201,6 @@ ! interface Vlan10 description test - shutdown mtu 9000 ip address 10.1.1.1/24 ! You can exit bash and look around:
localhost#bash Arista Networks EOS shell [admin@localhost ~]$ ls / bin dev export lib mnt opt proc sbin srv tmp var boot etc home media monitor persist root selinux sys usr [admin@localhost ~]$ sudo -s bash-4.1# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep name model name: AMD Turion(tm) II Neo N41H Dual-Core Processor model name: AMD Turion(tm) II Neo N41H Dual-Core Processor All ACLs are named. No need to remember and get confused in the rooms. For adherents of the old approach, it is possible to use numbers as names.
And so on and so forth. CLI in EOS is not just a copy, it is a self-contained shell with convenient features and far from the progenitor.
Extensible OS
The word "Extensible" in the "Extensible Operating System" is meant to indicate the extensibility of the OS functionality. This is achieved due to the possibility of installing their programs, demons, scripts on the switch. You can, for example, install and run the OpenVPN client. Or, run the script in Python, or, even ExaBGP . You can make friends with your crafts with Sysdb, and then, after collecting RPM packages, spread them across the network.
Some other features of EOS
- CloudVision allows you to connect Arista switches to the XMPP server as clients. You can write CLI commands in “chats” with them, and the switches will respond with the results of their execution. You can add multiple devices to a group chat and execute commands on all members of a group at the same time.
- Advanced Event Management is something like Cisco EEM or Junos Event Scripts: you can program actions (CLI commands, script execution) for certain events (for example: the port has dropped). Read more on the site .
- Event Monitor logs changes in MAC, ARP and routing tables on the embedded flash memory in the form of SQLite database.
- eAPI (External API) allows you to work with the switch via JSON-RPC: input and output data as JSON objects.
- Using Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP), you can automate the configuration of a new switch. The switch with default settings is loaded in ZTP mode and tries to get network settings via DHCP. Using the option bootfile-name , which can also be sent via DHCP, the switch can specify the URL to load the script (on the shell, or, for example, in the language of the embedded CLI, since it is one of the shell options). If the script is downloaded successfully, the device will execute it. In this case, automation is limited, probably, only by fantasy.
- DirectFlow allows you to set rules (such as mirroring; changing priority, VLAN, SRC / DST, etc.) applied to traffic (based on, for example, SRC / DST (IP, MAC, port) or protocol numbers, or VLAN, etc.) from the CLI (and eAPI will also go). Using such rules, you can, for example, more selectively mirror traffic for analysis, as opposed to SPAN. Or send to the cleaning system only the traffic for the desired IP, and not put this system into a gap. Such functionality is usually described as an advantage when switching switches to OpenFlow mode. DirectFlow allows you to apply rules in ASIC without OpenFlow.
Aboot
Aboot is not part of EOS, but an EOS bootloader, something like Cisco ROMmon.
I want to talk about it, because it is very simple and straightforward. Aboot is nothing more than a BusyBox . All data, including EOS images and logs, is stored on the built-in flash drive. Aboot allows you to access it (as well as access to external USB drives connected to USB ports) and restore the device to work in case of problems. Logging into Aboot is also simple: without dancing with a tambourine, without pinching buttons and sending strange codes to the console - CRTL + C.
I think this will help present the simplicity and capabilities of aboot:
Aboot 2.0.5-430838 Press Control-C now to enter Aboot shell ^CWelcome to Aboot. Aboot# echo $SHELL /bin/sh Aboot# arp devmem initblockdev overcast-lcd swiinfo ash df initnetdev ping switch_root autoboot dirname insmod ping6 switchroot base64 dmesg iostat pmap sync basename dosfsck ip poweroff sysinit blockdev dropbearmulti ipcalc powertop tail boardinit du kexec ps tar boot echo kill pwd tee bootchartd egrep ln readlink telnet bunzip2 env login realpath tftp burnK7 expr losetup reboot time burnMMX false ls recover touch burnP6 fdisk lsmod reset tr busybox fgconsole lspci rev traceroute bzcat fgrep lsusb rm traceroute6 cat find md5sum rmdir true checkpass flashrom mdev rmmod udhcpc chgrp flock mkdir route umount chmod free mkdosfs rx uname chown fsck.msdos mkfs.vfat scp unxz chroot fsck.vfat mknod sed unzip clear fullrecover mktemp setpci vi cmp grep modinfo sh vmcore-dmesg cp gunzip more sha1sum wget cpio halt mount sleep which cut head mpstat smemcap xz date help mv ssh xzcat dbclient hexdump nbd-client stat yes dd ifconfig netconf stty zcat devio init nvramtool sum Aboot# exit Restarting system. Even ipcalc is for convenience.
Application
As mentioned earlier, Arista Networks targets its equipment in data centers and offers the following options for optimal use:
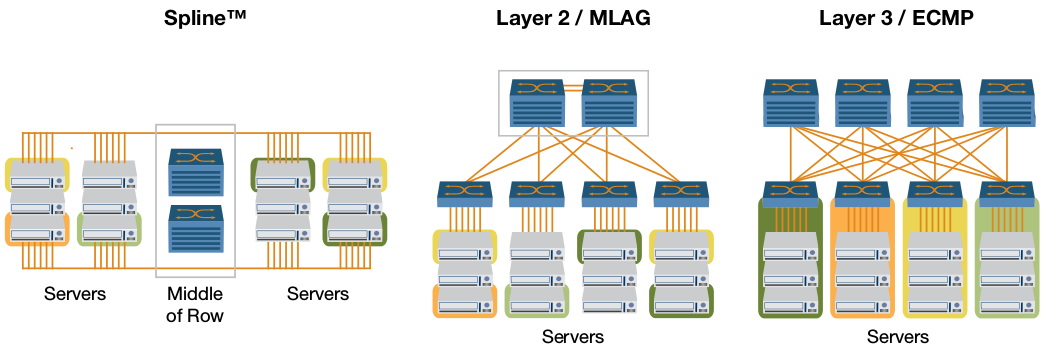
- Single-Tier "Spline" - a hybrid of Leaf ("list") and Spine ("root") - "Spline". It is proposed to put two redundant switches in the center of the row. Using, for example, 7316X switches, from its 512 40 Gbit / s ports, you can make 2048 ports 10 Gbit / s speed using a special QSFP-SFP + splitter (adapter from QSFP to 4 SFP +). From 7250QX-64 we get 256 SFP + interfaces at just 2 U. As can be seen from the switch characteristics table, switching will be without oversubscription. The name is pure marketing, but with the right calculation and approach, implementation can be very cost-effective, easy to build and maintain. For example, in the past, to connect 240 copper ports without redundancy, you needed 5 boards of 48 ports on the Cisco Catalyst 6506.
- Layer 2 / MLAG - already become “classic” Leaf and Spine, built on MLAG (also known as MC-LAG). The MC-LAG is a Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation Group , that is, a LAG built from two devices (in this case, switches) to a third device (switch or server), while the third device assumes it is connected to one device. Thus, it is possible to do without STP and, importantly, both channels will be active (active / active).
- Layer 3 / ECMP is a variation of the “classic” Leaf and Spine, but with all the links between all the devices on L3 (IPv4 and / or IPv6). Due to the absence of restrictions on more than two devices in the nodes, this scheme has better scalability than the previous one. All connections also work in active mode, no STP. Protection against banding traffic is based on routing protocols. Balanced traffic using ECMP .
Nothing prevents to assemble a ring or mixed topology using STP and its more advanced options, including PVST. But it will have a negative effect on the inefficiency, scaling and ease of use.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/211869/
All Articles