Transparent encryption of network folders in the corporate space
The wide distribution of network technologies ( LAN , CAN , VPN ) allows companies to organize fast and convenient exchange of information at various distances. Nevertheless, the protection of information in the corporate environment is a task that remains relevant today and disturbs the minds of the leaders of small, medium and large companies in the most diverse fields of activity. In addition, whatever the size of the company, for management almost always there is a need to differentiate the rights of employees to access confidential information based on the degree of its importance.

In this article, we will talk about transparent encryption as one of the most common ways to protect information in a corporate environment, consider the general encryption principles for several users (cryptography with several public keys), and also describe how to configure transparent encryption of network folders using CyberSafe Files Encryption .
')
The use of virtual cryptodisks or the full disk encryption function is justified on the user's local computer; however, in the corporate space, a more reasonable approach is to use transparent encryption , since this function provides fast and convenient work with secret files simultaneously for several users. When creating and editing files, the processes of their encryption and decryption occur automatically, on the fly. To work with protected documents, company employees do not need to have any skills in the field of cryptography, they do not need to perform any additional actions in order to decrypt or encrypt secret files.
Work with secret documents occurs in the usual mode using standard system applications. All the functions of configuring encryption and access rights can be assigned to one person, such as a system administrator.
Transparent encryption works as follows. To encrypt a file, a randomly generated symmetric session key is used, which in turn is protected by the user’s public asymmetric key. If the user accesses the file in order to make any changes to it, the transparent encryption driver decrypts the symmetric key with the help of the user's private (private) key and then, using the symmetric key, decrypts the file itself. Details on how transparent encryption works are described in the previous topic .
But what to do if there are several users and secret files are not stored on the local PC, but in a folder on a remote server? After all, the encrypted file is the same, but each user has his own unique key pair.
In this case, the so-called digital envelopes are used .
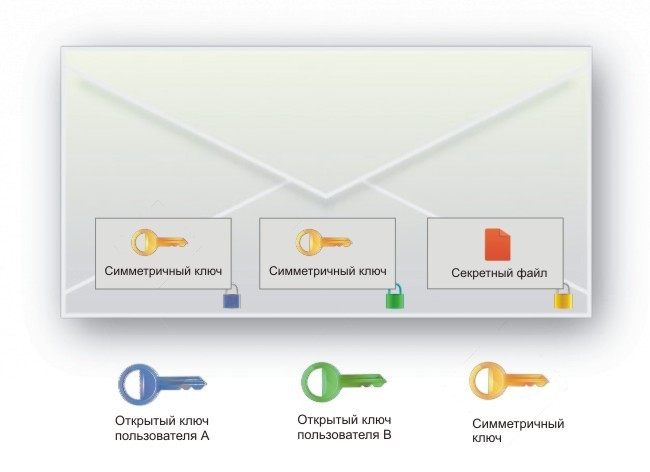
As can be seen from the figure, the digital envelope contains a file encrypted with a randomly generated symmetric key, as well as several copies of this symmetric key, protected with the public asymmetric keys of each of the users. There will be as many copies as the users are allowed to access the protected folder.
The transparent encryption driver works as follows: when a user accesses a file, he checks whether his certificate (public key) is on the list of allowed. If yes, then using that user's private key decrypts exactly that copy of the symmetric key, which was encrypted with its public key. If this user’s certificate is not listed, access will be denied.
Using CyberSafe, the system administrator will be able to set up transparent encryption of the network folder without using additional data protection protocols, such as IPSec or WebDAV, and further control user access to this or that encrypted folder.
To configure transparent encryption for each of the users who are going to allow access to confidential information, CyberSafe must be installed on the computer, a personal certificate is created, and the public key is published on the CyberSafe public key server.
Next, the sysadmin on the remote server creates a new folder, adds it to CyberSafe and assigns the keys of those users who can later work with the files in this folder. Of course, you can create as many folders as you need, store confidential information of varying degrees of importance in them, and the system administrator can at any time remove a user from having access to the folder, or add a new one.
Consider a simple example:
The ABC enterprise file server stores 3 databases with confidential information of varying importance - DSP, Secret and Top Secret. It is required to provide access to: BD1 users Ivanov, Petrov, Nikiforov, to BD2 Petrov and Smirnov, to BD3 Smirnov and Ivanov.
To do this, on the file server, which can be any network resource, you will need to create three separate folders for each database and assign certificates (keys) of the corresponding users to these folders:
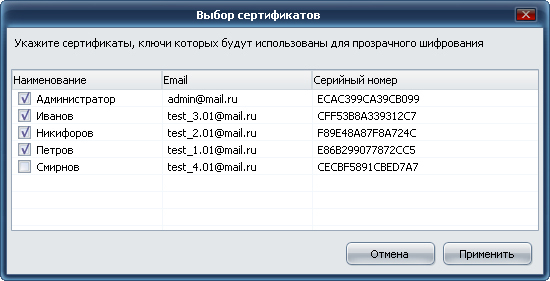
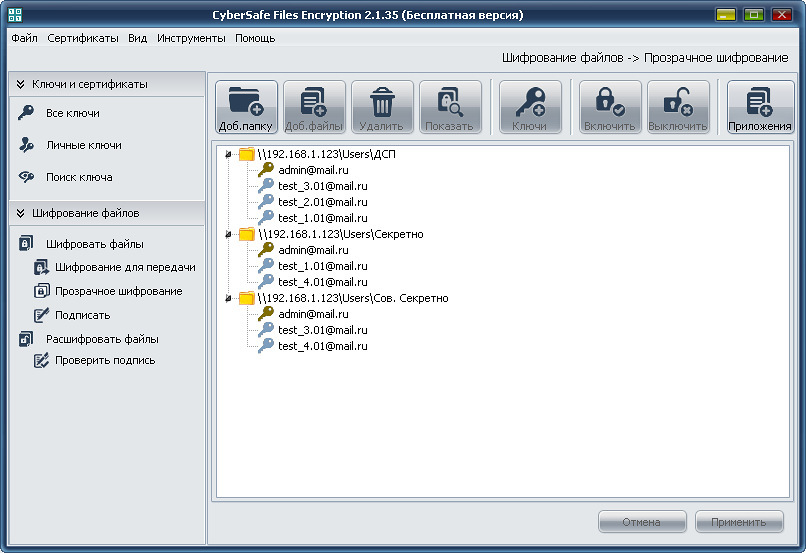
Of course, this or another similar problem with access rights can be solved using the Windows ACL . But this method can be effective only when access rights are differentiated on the computers of employees within the company. By itself, it does not protect confidential information in case of a third-party connection to the file server and the use of cryptography to protect data is simply necessary.
In addition, all file system security settings can be reset using the command line. For Windows, there is a special tool called “calcs”, which can be used to view permissions on files and folders, as well as to reset them. In Windows 7, this command is called “icacls” and is executed as follows:
It is possible that icacls will not work the first time. Then, before step 2, run the following command:
After that, the previously set permissions on files and folders will be reset.
You can create a system based on a virtual cryptodisk and ACL (for more details on such a system when using cryptodisks in organizations, it is written here .). However, such a system is also vulnerable, because to ensure constant access of employees to data on a cryptodisk, the administrator will need to keep it connected (mounted) throughout the entire working day, which compromises confidential information on the cryptodisk even without knowing the password to it, if can connect to the server.
Network drives with built-in encryption also do not solve the problem, since they protect data only when no one works with it. That is, the built-in encryption function will be able to protect confidential data from being compromised only if the disk itself is stolen.
In CyberSafe, file encryption / decryption is performed not on the file server, but on the user's side . Therefore, confidential files are stored on the server only in encrypted form, which excludes the possibility of their being compromised when the attacker directly connects to the file server. All files on the server stored in a folder protected with transparent encryption are encrypted and securely protected. At the same time, users and applications see them as ordinary files: Notepad, Word, Excel, HTML, and others. Applications can read and write these files directly; the fact that they are encrypted is transparent to them.
Users without access can also see these files, but they cannot read and modify them. This means that if the system administrator does not have access to documents in one of the folders, he can still back them up. Of course, all backup files are also encrypted.
However, when a user opens any of the files to work on his computer, there is a possibility that unwanted applications will get access to him (in that case, of course, if the computer is infected). To prevent this, CyberSafe as a further security measure, there is a system of trusted applications , thanks to which the system administrator can determine the list of programs that can access files from a protected folder. All other applications that are not on the trusted list will not have access. So we will limit access to confidential information for spyware, rootkits and other malicious software.
Since all work with encrypted files is carried out on the user's side, this means that CyberSafe is not installed on the file server and, when working in the corporate space, the program can be used to protect information on network storage with the NTFS file system, such as Windows Storage Server . All confidential information in encrypted form is located in such storage, a CyberSafe is installed only on users' computers from which they access the encrypted files.

This is the advantage of CyberSafe over TrueCrypt and other encryption programs that require installation in a physical file storage location, which means that only a personal computer can be used as a server, but not a network drive. Of course, the use of network storage in companies and organizations is much more convenient and justified, rather than using a conventional computer.
Thus, using CyberSafe without any additional funds, you can organize effective protection of valuable files, ensure convenient work with encrypted network folders, as well as differentiate users' access rights to confidential information.

In this article, we will talk about transparent encryption as one of the most common ways to protect information in a corporate environment, consider the general encryption principles for several users (cryptography with several public keys), and also describe how to configure transparent encryption of network folders using CyberSafe Files Encryption .
')
What is the advantage of transparent encryption?
The use of virtual cryptodisks or the full disk encryption function is justified on the user's local computer; however, in the corporate space, a more reasonable approach is to use transparent encryption , since this function provides fast and convenient work with secret files simultaneously for several users. When creating and editing files, the processes of their encryption and decryption occur automatically, on the fly. To work with protected documents, company employees do not need to have any skills in the field of cryptography, they do not need to perform any additional actions in order to decrypt or encrypt secret files.
Work with secret documents occurs in the usual mode using standard system applications. All the functions of configuring encryption and access rights can be assigned to one person, such as a system administrator.
Multiple public key cryptography and digital envelopes
Transparent encryption works as follows. To encrypt a file, a randomly generated symmetric session key is used, which in turn is protected by the user’s public asymmetric key. If the user accesses the file in order to make any changes to it, the transparent encryption driver decrypts the symmetric key with the help of the user's private (private) key and then, using the symmetric key, decrypts the file itself. Details on how transparent encryption works are described in the previous topic .
But what to do if there are several users and secret files are not stored on the local PC, but in a folder on a remote server? After all, the encrypted file is the same, but each user has his own unique key pair.
In this case, the so-called digital envelopes are used .

As can be seen from the figure, the digital envelope contains a file encrypted with a randomly generated symmetric key, as well as several copies of this symmetric key, protected with the public asymmetric keys of each of the users. There will be as many copies as the users are allowed to access the protected folder.
The transparent encryption driver works as follows: when a user accesses a file, he checks whether his certificate (public key) is on the list of allowed. If yes, then using that user's private key decrypts exactly that copy of the symmetric key, which was encrypted with its public key. If this user’s certificate is not listed, access will be denied.
Encrypting Network Folders with CyberSafe
Using CyberSafe, the system administrator will be able to set up transparent encryption of the network folder without using additional data protection protocols, such as IPSec or WebDAV, and further control user access to this or that encrypted folder.
To configure transparent encryption for each of the users who are going to allow access to confidential information, CyberSafe must be installed on the computer, a personal certificate is created, and the public key is published on the CyberSafe public key server.
Next, the sysadmin on the remote server creates a new folder, adds it to CyberSafe and assigns the keys of those users who can later work with the files in this folder. Of course, you can create as many folders as you need, store confidential information of varying degrees of importance in them, and the system administrator can at any time remove a user from having access to the folder, or add a new one.
Consider a simple example:
The ABC enterprise file server stores 3 databases with confidential information of varying importance - DSP, Secret and Top Secret. It is required to provide access to: BD1 users Ivanov, Petrov, Nikiforov, to BD2 Petrov and Smirnov, to BD3 Smirnov and Ivanov.
To do this, on the file server, which can be any network resource, you will need to create three separate folders for each database and assign certificates (keys) of the corresponding users to these folders:


Of course, this or another similar problem with access rights can be solved using the Windows ACL . But this method can be effective only when access rights are differentiated on the computers of employees within the company. By itself, it does not protect confidential information in case of a third-party connection to the file server and the use of cryptography to protect data is simply necessary.
In addition, all file system security settings can be reset using the command line. For Windows, there is a special tool called “calcs”, which can be used to view permissions on files and folders, as well as to reset them. In Windows 7, this command is called “icacls” and is executed as follows:
1. In the command line with administrator rights, enter: cmd
2. Go to the disk or partition, for example: CD / DD:
3. To reset all permissions, enter: icacls * / T / Q / C / RESET
It is possible that icacls will not work the first time. Then, before step 2, run the following command:
takeown / r / f *
After that, the previously set permissions on files and folders will be reset.
You can create a system based on a virtual cryptodisk and ACL (for more details on such a system when using cryptodisks in organizations, it is written here .). However, such a system is also vulnerable, because to ensure constant access of employees to data on a cryptodisk, the administrator will need to keep it connected (mounted) throughout the entire working day, which compromises confidential information on the cryptodisk even without knowing the password to it, if can connect to the server.
Network drives with built-in encryption also do not solve the problem, since they protect data only when no one works with it. That is, the built-in encryption function will be able to protect confidential data from being compromised only if the disk itself is stolen.
In CyberSafe, file encryption / decryption is performed not on the file server, but on the user's side . Therefore, confidential files are stored on the server only in encrypted form, which excludes the possibility of their being compromised when the attacker directly connects to the file server. All files on the server stored in a folder protected with transparent encryption are encrypted and securely protected. At the same time, users and applications see them as ordinary files: Notepad, Word, Excel, HTML, and others. Applications can read and write these files directly; the fact that they are encrypted is transparent to them.
Users without access can also see these files, but they cannot read and modify them. This means that if the system administrator does not have access to documents in one of the folders, he can still back them up. Of course, all backup files are also encrypted.
However, when a user opens any of the files to work on his computer, there is a possibility that unwanted applications will get access to him (in that case, of course, if the computer is infected). To prevent this, CyberSafe as a further security measure, there is a system of trusted applications , thanks to which the system administrator can determine the list of programs that can access files from a protected folder. All other applications that are not on the trusted list will not have access. So we will limit access to confidential information for spyware, rootkits and other malicious software.
Since all work with encrypted files is carried out on the user's side, this means that CyberSafe is not installed on the file server and, when working in the corporate space, the program can be used to protect information on network storage with the NTFS file system, such as Windows Storage Server . All confidential information in encrypted form is located in such storage, a CyberSafe is installed only on users' computers from which they access the encrypted files.

This is the advantage of CyberSafe over TrueCrypt and other encryption programs that require installation in a physical file storage location, which means that only a personal computer can be used as a server, but not a network drive. Of course, the use of network storage in companies and organizations is much more convenient and justified, rather than using a conventional computer.
Thus, using CyberSafe without any additional funds, you can organize effective protection of valuable files, ensure convenient work with encrypted network folders, as well as differentiate users' access rights to confidential information.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/211012/
All Articles