Stock market: How are exchanges organized and why are they needed?

The opinion of a large number of people about the stock market, often comes down to the fact that this is just a platform for speculation and making money from the air. Especially often similar reasonings can be heard in discussions of derivatives (futures, options). But is it really?
The stock exchange we are used to is essentially a secondary securities market, where rights to the ownership or debts of companies issuing securities are redistributed. Due to this, the companies entering the stock exchange do not receive any financing - when they say that as a result of a fall in stocks, the company lost so many millions, then these are nothing more than beautiful words, because in fact, there are no losses other than image ones.
')
Mechanisms of organized trading of the secondary market serve for the redistribution of securities between large primary investors (underwriters and investment consortia) and smaller investment companies and private investors. The main turnover of securities occurs precisely in the secondary market. Without the existence of this secondary market, the normal functioning of the primary will not be possible.
Due to the secondary market, individuals become direct or indirect owners of securities (with the help of investment banks and funds). The presence of a sufficient number of private investors allows the economy to function effectively, attracting huge amounts of money to solve their immediate problems.
The secondary securities market is of two types - exchange and over-the-counter (more here ), while the first place, of course, is central to the entire stock market. When working on the stock exchange, the investor does not see his counterparty in the transaction, and its execution is guaranteed by the exchange. On the over-the-counter market, transactions are made directly between two counterparties (respectively, they also bear all the risks), and various low-liquid securities are traded there, the demand for which is not so great that the issuing company “bother” with the listing on the stock exchange.
How does the exchange
The Exchange is the most convenient place for conducting operations with securities. On the infrastructure of the domestic securities market, we have repeatedly written on Habré ( one , two ), and now we’ll discuss in more detail, in fact, the exchange as a separate unit of the market.

Its functions include the organization of trading in securities - now almost all the exchanges are electronic, that is, applications for trading come in through closed electronic communication systems, rather than the method of shouting, and immediately find their way into the trading system.
The exchange should be composed of:
- The trading system , where buy and sell orders are accumulated, is “mated” in the event of a price match, i.e. registration of transactions with various instruments and records in the relevant accounting registers (eg).
- The clearing house , which keeps records of participants ’funds, delivers money for each transaction to paper sellers and deducts money from buyers’ accounts, and carries out external and internal cash transfers.
- The Depositary Center , which, similarly to the Clearing House, keeps records of securities of participants in trades, delivers securities to buyers 'accounts, writes off securities from sellers' accounts, clears securities according to the results of trading in authorized depositories.
All these operations are performed automatically.
Another important role played by an organized exchange platform is to ensure the liquidity of securities.
Liquidity is the ability to quickly or without significant overhead costs to sell or buy a security.
Due to the large number of bidders and a large number of securities sold and bought at the same time, liquidity can be quite high. The exchange provides conditions for the liquidity of each specific paper in two ways: a reasonable pricing policy that attracts private investors, and the creation of an institution of market makers.
A market maker is a bidder who, by agreement with the exchange, is obliged to maintain the difference between purchase and sale prices within certain limits. For this, he receives certain benefits from the stock exchange - for example, the ability to conduct operations with securities that the market maker supports with reduced commissions or without them at all.

Another interesting point concerning the role of stock exchanges in the stock market. Since the exchange activity is licensed and regulated by the state, not only the organizer of the auction, but also certain regulatory functions are assigned to the exchange. For example, the exchange is obliged to monitor the market in order to suppress price manipulations, frauds in securities and violations of the rules for the implementation of brokerage activities.
Why do you need it
Securities are a form of capital existence and are traded on the stock market. All this carries a number of functions.
First, securities redistribute cash:
- Between countries and territories.
- Between industries and sectors of the economy.
- Between individual enterprises within the same sector.
It is necessary to understand that the market is arranged in such a way that money flows to where it can bring the greatest effect from its use. This principle is manifested in the redistribution of capital, always and everywhere - no matter whether we are talking about private companies or entire countries.
Secondly, thanks to the securities, there is a redistribution of investments in each specific enterprise between large, medium and small investors. This process affects almost every citizen of the country, even if he is not aware of this. Thus, a conditional man in the street who has a deposit in a bank may not know and not think that a bank, using its money, could buy, for example, corporate bonds - this is how a particular person, unaware of it, becomes a source of development funds specific enterprise and the economy as a whole.
The third important function of securities is that they serve to fix the rights of the owners to a share of the debt or ownership of enterprises (in the case of company securities) or on the share of debt of the whole state (in the case of government securities).
Depending on the type of securities and the specific issuer, the income that the securities bring may vary from the loss itself to astronomical amounts. Naturally, there is always a risk of losing money - for example, in the event of the bankruptcy of an enterprise that issued securities, but on large time horizons - from 15 to 30 years on average - securities generate income corresponding to or exceeding economic growth.
At the same time, it is important to understand that the laws of physics do not apply in the stock market - in particular, the force of gravity. Often, many believe that once stocks have grown significantly in a short period of time, they will certainly be waiting for a fall. This is not entirely true.
Example : Over the course of 10 years, Berkshire Hathaway’s shares rose from $ 6,000 to $ 10,000. At this point, many decided that growth was already quite significant, and missed the opportunity to earn huge money on a price that in the following 6 years rose to $ 70,000 and even higher.
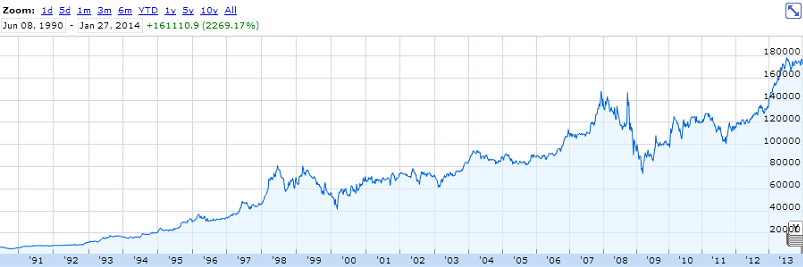
As a risk payment that carries such financing of the economy, the owners of securities receive additional income: coupons, interest payments in the case of debt securities, dividends and a rise in the market value in the case of equity securities.
Example : Dow Jones Index. At the beginning of 1950, the value of this index was 201 points, and by the beginning of 2000, already 10,940. It turns out that over 50 years the index has grown more than 50 times. If someone invested $ 1,000 in 1950, by the end of 2000 the amount would have increased to $ 50,000.
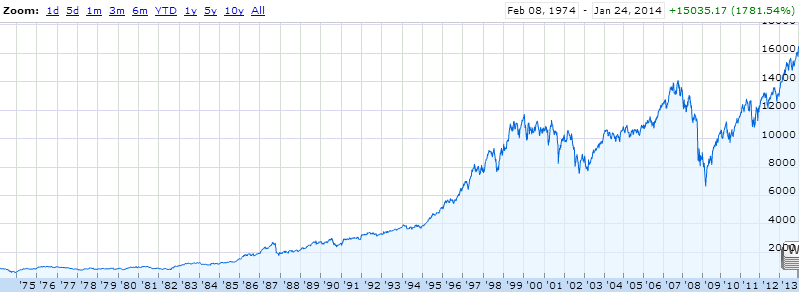
Growth from 74 to the present is also impressive.
Thus, the role of the stock market as a place where securities are traded and the redistribution of capital between countries, sectors of the economy and enterprises, on the one hand, and various groups of investors, on the other. Without the stock market, it would have been impossible for the economy to develop effectively and meet the needs of every member of society.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/210570/
All Articles