Initial setup and capabilities of FortiGate UTM devices for small businesses
Today, among the multitude of global corporate information systems, it is impossible not to note the growing number of increasingly complex network attacks, increasing the diversity of network devices and ways to access information resources of enterprises, as well as the number of applications in their environment.

Depending on the scale of enterprises, the approach to protection against such threats is divided, if large companies pay more attention to ensuring the network security of their resources, then an increasing number of threats are directed at small and medium-sized businesses. Enterprises of this segment - Small Office-Home Office (SOHO) may not have extensive infrastructure capable of withstanding modern mixed attacks, and branches / remote offices of large companies (Remote Office / Branch Office, ROBO) do not always have their own qualifications to counter such security threats. .
')
Therefore, the use of several narrowly focused solutions (usually of different manufacturers) on the perimeter of a network of small enterprises would be inexpedient in terms of time and expenses for their maintenance, implementation, and administration.
Help came from packet firewalls (which have long been insufficient) - UTM network security devices and new generation NGFW firewalls. They play a key role in the modern network security market, since they combine the many all-in-one protection services against various network attacks while having the ability to quickly deploy, easily scale and adapt to the needs of enterprises.
In this article, we look at the capabilities of Fortinet UTM devices from Fortinet, and also describe their basic configuration using the example of a model in a small form factor - FortiGate-40C, ideal for small offices with up to 25-30 users. FortiGate-40C devices offer a unified network security solution including: firewall, application control, IPS, antivirus, malware protection, antispam, VPN, web filtering, and data leakage prevention.
The difference between the approach with several narrow solutions and when using UTM FortiGate is shown schematically below:

The whole segment of SOHO / ROBO, taking into account another abbreviation - SMB (Small & Medium Business), is positioned by the manufacturer as:
- up to 100 users located in the central office;
- 5-25 remote users requiring VPN access;
- Access to resources via Ethernet and WiFi;
- The need to implement, at a minimum, anti-virus protection and web filtering;
- Part-time IT-employee;
- Fixed budget for IT security.
The entire line of FortiGate devices for the SMB / SOHO / ROBO business segment is quite extensive and is able to provide the choice of an individual solution for the specific needs and scale of the company. There can be several types of one model - with a built-in WiFi point, and with PoE ports, with optical SFPs, with ADSL on board, just look:

In addition to the above, add to the features already described the following:
- built-in wireless controller (model 40 and above) to control FortiAP “thin” access points;
- use at the same time to provide services to several customers, thanks to the support of VDOM technology (virtual domain) in models from 60C and above;
- reservation and ensuring fault tolerance / clustering (Active-Active, Active-Passive modes);
- functional load balancing (from 60C and above);
- IPSec and SSL VPN, support for PPTP, L2TP;
- static, dynamic routing RIP, OSPF, BGP, PIM;
- support for USB 3G modems;
- support for IPv6, VLAN, VoIP (SIP ALG);
- traffic shaping;
- optimization of WAN traffic;
- inspection of SSL traffic;
- identification of users and their reputation;
- user authentication and integration with Active Directory using Fortinet Single-Sign On;
- protection against DoS-attacks;
- built-in event logging;
In addition, there are opportunities for organizing centralized management of FortiGate devices using the FortiManager device, analyzing security events using FortiAnalyzer and checking the network security status using FortiScan.
Starting to configure FortiGate, in our case, the 40C model, for the beginning we will describe how to configure the device. They, as well as functions, are also quite a few:
1. A convenient web interface is available, allowing you to configure most of the required network security functions.
The very same web interface will show you a little later.
2. Management from the command line (CLI) via TELNET, SSH or via the console port (using a null modem cable that connects to the COM port) will be useful to us for more fine-tuning and configuring some functions that are only available in this way as they are not in the web interface.
3. Control FortiGlore with the FortiExplorer program installed on a PC using a USB connection through the cable provided . You do not even need to configure the network card for management and connect with something else to the device. The method is very convenient for initial configuration, as the FortiExplorer software with USB connection duplicates the functionality of both the web interface and the CLI, as well as the Setup Wizard.
Well and centralized management with FortiManager has not been canceled, but without the initial configuration of FortiGate this is impossible.
We will stop on the last version, and launch FortiExplorer, having previously connected and turned on the power of the device. When the device is fully loaded and the drivers are automatically installed on it, we will see the following:
Let's try to configure using the Setup Wizard . Select it on the left and see the first page - credentials

Standard credentials - login: " admin ", there is no password. Enter and click Next.
First of all, we have a remote control offer with FortiManager - a separate Fortinet line for centralized management and remote configuration of FortiGate, FortiWiFi and FortiCarrier devices:

Depending on the requirements, is there a place for FortiManager in the infrastructure of your network and is it necessary to hand over the reins in his hands? Select “Enable Central Management” and enter the IP or the name where our centralized manager is located. Now the next step is Next.

We see the proposal to change the default password, enter the desired one twice and click Next . Next, there will be a time zone change screen, in order not to clutter up the “air” with notarized screenshots - skip the step, since there should be no problems.
But further it is interesting, we are given the opportunity to choose the topology of connection to the Internet, one or two providers we will use, with the reservation of connection via 3G / 4G-modem or not.

One head is good, and two are better - we set up two providers, one - static wired, the second - 3G / 4G reserve.
You can choose a DHCP to the Ethernet provider - if the provider provides the address automatically, Static IP - you need to enter it manually and PPPoE - then you need only a login and access password:



Similar settings for the second “Secondary WAN” external interface, if we had chosen the item “Dual Ethernet” .
In our case, the next step is to connect a 3G / 4G modem. You must enter the phone number, login and password provider.

The next click Next and after we get to the choice of the method of balancing traffic between providers. Here to choose:
- Round Robin - does not require configuration. Balancing is carried out "in a circle", first the 1st available link, then the 2nd ... the last Nth, and back from the 1st;
- Weighted Load Balance - this parameter is assigned as “weight” (weight) for each equivalent default route to the provider, on the basis of which the traffic and its sessions are distributed as a percentage dynamically depending on the size (weight) of the route. The default value is 50% / 50%.
- Spillover - in other words, “ flipping ”. Sessions are distributed in such a way that, based on the throughput indicator (Threshold), the highest route to the provider from the routing table is used before reaching it, and when the Threshold is reached on this interface, the next route is to the corresponding provider.


Further, in both cases, with “ Dual Ethernet ”, and with “ Ethernet with 3G / 4G Backup ” we will end up with external interfaces and get to the interface settings item of the internal interface - “ LAN Settings ”, where we will be asked to enter the address and interface mask and also, if necessary, configure a DHCP server with a specific address range to automatically assign them to network devices of this interface.

After clicking Next again, another subsection of “ Security ” shines us and its first sentence in the form of setting up a schedule (Schedule) of Internet access.

Everything is very clear here - AlwaysCoca-Cola means always / everywhere / around the clock, and “ Restrict access to specified schedule ” - gives you the freedom to choose the schedule mode, except Always, but restricts access for users by weekdays (everyone or weekdays) and by time.
In the next “Internet Access Policy” menu, all the security features and the “On / Off” toggle switch for NAT address translation went off.

Unified Threat Management , the name itself says that the functions of unified threat management will soon begin to act on the perimeter guard of our local network.
- Enable Virus Detection & Removal (Email, Web Browsing, etc) is nothing more than antivirus, malware and spyware protection.
- Block Exploits and Intrusions in the network - down with exploits and intrusions, says us IPS, a system to prevent these.
- Filter SPAM and malicious (Phishing) Emails - filtering spam and other malicious mail along with the "threat of threats" UTM.
Filter User Activities - less terrible in name, but no less “secret” for the rest. Watching every one of you!
- Block Malicious Web Content - here it is, our web filtering by category, helping to prevent unwanted visits of malicious sites;
- Monitor Applications Usage and Block Unproductive Applications - the control of the applications used is also right here and is ready to block out of them, at a minimum, reducing the productivity of office workers.
The penultimate of the quick and easy settings in the face of virtual servers (Virtual Server), the holiday brings us in the form of protecting servers located inside the corporate network and providing access to their resources when connected to the external address of our FortiGate. It will help to publish web resources, such as OWA / Sharepoint, ActiveSync, Lync and many others.
Through the wizard of such servers, you can configure five and broadcast their access ports from the outside to the inside.

The crown of creation (we will not be afraid of this word) of the Setup Wizardand All Russia is the remote access of users via VPN. There are IPSec and SSL VPN to choose from, where you can immediately add three users to the local database to authenticate by login / password, PSK (Pre-shared Key) for IPSec SSL, or up to five SSL VPN Bookmarks to access the necessary servers from the web. SSL portal.


The “Setup Wizard” FortiGate, saying goodbye to you, will display for your convenience the statistical summary “Summary” where you can verify the settings you just made and return before it is too late.

We observe again a pleasant “ Device configuration completed ” eye, and this is exactly what we were seeking.
Now, from the web interface, we can check what the Wizard has configured for us, and for access, in the left FortiExplorer column, we can select “ Web-Based Manager ” or immediately connect to the internal interface and go to the address we configured in the “ LAN Settings ” section Wizard'a.
Out of the box, the device has an address of 192.168.1.99/24, which, we make a reservation, has not changed. You can connect to FortiGate-40C, since it has a hardware switch (Internal) in any of its Internal interfaces ( 1-5 ), as shown below:

After connecting, if it was done from a PC, you need to check whether the built-in DHCP server gave us the address. The result should be something like this:

So, if everything is OK, enter in the browser, https: // 192.168.1.99, accept the certificate, log in and see the start page:

Immediately, we can see that from the start you can see which security functions are already included. But to test this, we need to look into security policies. The policies that are in effect and created on the device are found in the menu Policy -> Policy -> Policy, as if three times it sounds strange. See below policy:
1. Access from the internal interface Internal to the external interface Modem
2. Access from the internal interface Internal to the external Wan1 for IPSec VPN connections of remote users.
3. Access from the internal interface Internal to the external Wan1 for all users to access the Internet from the local network.
4. Access from the external interface Wan1 to the internal interface Internal for access from the Internet to the virtual server wizard_vip_1 , created from the wizard “Setup Wizard”.
5. The default policy ( Implicit ) prohibits any other connections, except those described in the policies above.
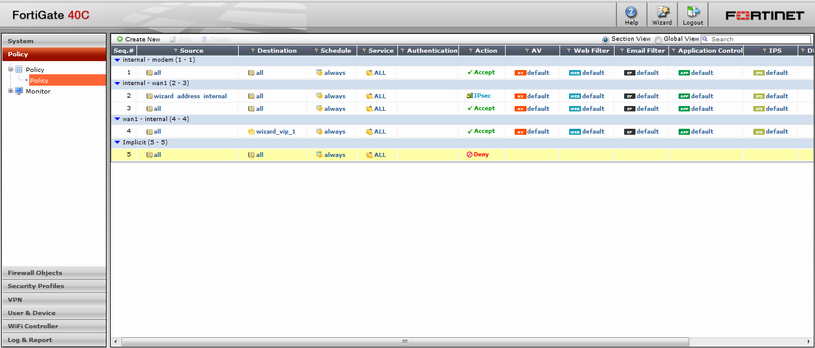
After viewing the picture, it should be noted that the policies are applied on a “top-down” basis. The first approaching is applied to this type of traffic and, depending on the action, allows or denies the passage of traffic. And in order to see the order of policing, you need to change the view mode from Section View to Global View and you’ll get this:

Also note the AV , WebFilter , EmailFilter , Aplication Control, and IPS columns . For each of the created policies, standard (default) protection profiles of the anti-virus, web filtering, anti-spam, application control and IPS security functions are applied.
All these profiles are customizable and can be changed in the web interface section of the Security Profiles menu in the web interface.
Antivirus profile:

Web filtering profile:

Application control sensor:

IPS Intrusion Prevention System Sensor:

Email Filtering Profile:

DLP data leakage prevention module sensor:

VoIP profile:

Customer reputation level settings page:

The presence of the profiles themselves in absolutely correctly created policies at the start of the device after the automatic Configuration Wizard symbolizes only its (Master) adequacy and the manufacturer’s concern for the safety of UTM FortiGate users practically out of the box.
Summing up, I just want to note that the care is not completely free: both for the device and for the single (in the SMB / SOHO / ROBO devices segment) the subscription to it for updating the actual signatures of the numerous threat protection functions will have to be given their blood.
But without BUT:
If protection and care is fully justified by the low price in the market, plus the high status of Fortinet as a five-year leader of UTM devices in Gartner square (Gartner), high reliability and performance, a wide range of products for any scale of enterprises. This is all not to mention the speed and ease of configuration, as we were able to verify this article together.
Authorized Fortinet Training Courses
MUK-Service - all types of IT repair: warranty, non-warranty repair, sale of spare parts, contract service

Depending on the scale of enterprises, the approach to protection against such threats is divided, if large companies pay more attention to ensuring the network security of their resources, then an increasing number of threats are directed at small and medium-sized businesses. Enterprises of this segment - Small Office-Home Office (SOHO) may not have extensive infrastructure capable of withstanding modern mixed attacks, and branches / remote offices of large companies (Remote Office / Branch Office, ROBO) do not always have their own qualifications to counter such security threats. .
')
Therefore, the use of several narrowly focused solutions (usually of different manufacturers) on the perimeter of a network of small enterprises would be inexpedient in terms of time and expenses for their maintenance, implementation, and administration.
Help came from packet firewalls (which have long been insufficient) - UTM network security devices and new generation NGFW firewalls. They play a key role in the modern network security market, since they combine the many all-in-one protection services against various network attacks while having the ability to quickly deploy, easily scale and adapt to the needs of enterprises.
In this article, we look at the capabilities of Fortinet UTM devices from Fortinet, and also describe their basic configuration using the example of a model in a small form factor - FortiGate-40C, ideal for small offices with up to 25-30 users. FortiGate-40C devices offer a unified network security solution including: firewall, application control, IPS, antivirus, malware protection, antispam, VPN, web filtering, and data leakage prevention.
The difference between the approach with several narrow solutions and when using UTM FortiGate is shown schematically below:

The whole segment of SOHO / ROBO, taking into account another abbreviation - SMB (Small & Medium Business), is positioned by the manufacturer as:
- up to 100 users located in the central office;
- 5-25 remote users requiring VPN access;
- Access to resources via Ethernet and WiFi;
- The need to implement, at a minimum, anti-virus protection and web filtering;
- Part-time IT-employee;
- Fixed budget for IT security.
The entire line of FortiGate devices for the SMB / SOHO / ROBO business segment is quite extensive and is able to provide the choice of an individual solution for the specific needs and scale of the company. There can be several types of one model - with a built-in WiFi point, and with PoE ports, with optical SFPs, with ADSL on board, just look:

In addition to the above, add to the features already described the following:
- built-in wireless controller (model 40 and above) to control FortiAP “thin” access points;
- use at the same time to provide services to several customers, thanks to the support of VDOM technology (virtual domain) in models from 60C and above;
- reservation and ensuring fault tolerance / clustering (Active-Active, Active-Passive modes);
- functional load balancing (from 60C and above);
- IPSec and SSL VPN, support for PPTP, L2TP;
- static, dynamic routing RIP, OSPF, BGP, PIM;
- support for USB 3G modems;
- support for IPv6, VLAN, VoIP (SIP ALG);
- traffic shaping;
- optimization of WAN traffic;
- inspection of SSL traffic;
- identification of users and their reputation;
- user authentication and integration with Active Directory using Fortinet Single-Sign On;
- protection against DoS-attacks;
- built-in event logging;
In addition, there are opportunities for organizing centralized management of FortiGate devices using the FortiManager device, analyzing security events using FortiAnalyzer and checking the network security status using FortiScan.
Starting to configure FortiGate, in our case, the 40C model, for the beginning we will describe how to configure the device. They, as well as functions, are also quite a few:
1. A convenient web interface is available, allowing you to configure most of the required network security functions.
The very same web interface will show you a little later.
2. Management from the command line (CLI) via TELNET, SSH or via the console port (using a null modem cable that connects to the COM port) will be useful to us for more fine-tuning and configuring some functions that are only available in this way as they are not in the web interface.
3. Control FortiGlore with the FortiExplorer program installed on a PC using a USB connection through the cable provided . You do not even need to configure the network card for management and connect with something else to the device. The method is very convenient for initial configuration, as the FortiExplorer software with USB connection duplicates the functionality of both the web interface and the CLI, as well as the Setup Wizard.
Well and centralized management with FortiManager has not been canceled, but without the initial configuration of FortiGate this is impossible.
We will stop on the last version, and launch FortiExplorer, having previously connected and turned on the power of the device. When the device is fully loaded and the drivers are automatically installed on it, we will see the following:
Let's try to configure using the Setup Wizard . Select it on the left and see the first page - credentials

Standard credentials - login: " admin ", there is no password. Enter and click Next.
First of all, we have a remote control offer with FortiManager - a separate Fortinet line for centralized management and remote configuration of FortiGate, FortiWiFi and FortiCarrier devices:

Depending on the requirements, is there a place for FortiManager in the infrastructure of your network and is it necessary to hand over the reins in his hands? Select “Enable Central Management” and enter the IP or the name where our centralized manager is located. Now the next step is Next.

We see the proposal to change the default password, enter the desired one twice and click Next . Next, there will be a time zone change screen, in order not to clutter up the “air” with notarized screenshots - skip the step, since there should be no problems.
But further it is interesting, we are given the opportunity to choose the topology of connection to the Internet, one or two providers we will use, with the reservation of connection via 3G / 4G-modem or not.

One head is good, and two are better - we set up two providers, one - static wired, the second - 3G / 4G reserve.
You can choose a DHCP to the Ethernet provider - if the provider provides the address automatically, Static IP - you need to enter it manually and PPPoE - then you need only a login and access password:



Similar settings for the second “Secondary WAN” external interface, if we had chosen the item “Dual Ethernet” .
In our case, the next step is to connect a 3G / 4G modem. You must enter the phone number, login and password provider.

The next click Next and after we get to the choice of the method of balancing traffic between providers. Here to choose:
- Round Robin - does not require configuration. Balancing is carried out "in a circle", first the 1st available link, then the 2nd ... the last Nth, and back from the 1st;
- Weighted Load Balance - this parameter is assigned as “weight” (weight) for each equivalent default route to the provider, on the basis of which the traffic and its sessions are distributed as a percentage dynamically depending on the size (weight) of the route. The default value is 50% / 50%.
- Spillover - in other words, “ flipping ”. Sessions are distributed in such a way that, based on the throughput indicator (Threshold), the highest route to the provider from the routing table is used before reaching it, and when the Threshold is reached on this interface, the next route is to the corresponding provider.


Further, in both cases, with “ Dual Ethernet ”, and with “ Ethernet with 3G / 4G Backup ” we will end up with external interfaces and get to the interface settings item of the internal interface - “ LAN Settings ”, where we will be asked to enter the address and interface mask and also, if necessary, configure a DHCP server with a specific address range to automatically assign them to network devices of this interface.

After clicking Next again, another subsection of “ Security ” shines us and its first sentence in the form of setting up a schedule (Schedule) of Internet access.

Everything is very clear here - Always
In the next “Internet Access Policy” menu, all the security features and the “On / Off” toggle switch for NAT address translation went off.

Unified Threat Management , the name itself says that the functions of unified threat management will soon begin to act on the perimeter guard of our local network.
- Enable Virus Detection & Removal (Email, Web Browsing, etc) is nothing more than antivirus, malware and spyware protection.
- Block Exploits and Intrusions in the network - down with exploits and intrusions, says us IPS, a system to prevent these.
- Filter SPAM and malicious (Phishing) Emails - filtering spam and other malicious mail along with the "threat of threats" UTM.
Filter User Activities - less terrible in name, but no less “secret” for the rest. Watching every one of you!
- Block Malicious Web Content - here it is, our web filtering by category, helping to prevent unwanted visits of malicious sites;
- Monitor Applications Usage and Block Unproductive Applications - the control of the applications used is also right here and is ready to block out of them, at a minimum, reducing the productivity of office workers.
The penultimate of the quick and easy settings in the face of virtual servers (Virtual Server), the holiday brings us in the form of protecting servers located inside the corporate network and providing access to their resources when connected to the external address of our FortiGate. It will help to publish web resources, such as OWA / Sharepoint, ActiveSync, Lync and many others.
Through the wizard of such servers, you can configure five and broadcast their access ports from the outside to the inside.

The crown of creation (we will not be afraid of this word) of the Setup Wizard


The “Setup Wizard” FortiGate, saying goodbye to you, will display for your convenience the statistical summary “Summary” where you can verify the settings you just made and return before it is too late.

We observe again a pleasant “ Device configuration completed ” eye, and this is exactly what we were seeking.
Now, from the web interface, we can check what the Wizard has configured for us, and for access, in the left FortiExplorer column, we can select “ Web-Based Manager ” or immediately connect to the internal interface and go to the address we configured in the “ LAN Settings ” section Wizard'a.
Out of the box, the device has an address of 192.168.1.99/24, which, we make a reservation, has not changed. You can connect to FortiGate-40C, since it has a hardware switch (Internal) in any of its Internal interfaces ( 1-5 ), as shown below:

After connecting, if it was done from a PC, you need to check whether the built-in DHCP server gave us the address. The result should be something like this:

So, if everything is OK, enter in the browser, https: // 192.168.1.99, accept the certificate, log in and see the start page:

Immediately, we can see that from the start you can see which security functions are already included. But to test this, we need to look into security policies. The policies that are in effect and created on the device are found in the menu Policy -> Policy -> Policy, as if three times it sounds strange. See below policy:
1. Access from the internal interface Internal to the external interface Modem
2. Access from the internal interface Internal to the external Wan1 for IPSec VPN connections of remote users.
3. Access from the internal interface Internal to the external Wan1 for all users to access the Internet from the local network.
4. Access from the external interface Wan1 to the internal interface Internal for access from the Internet to the virtual server wizard_vip_1 , created from the wizard “Setup Wizard”.
5. The default policy ( Implicit ) prohibits any other connections, except those described in the policies above.

After viewing the picture, it should be noted that the policies are applied on a “top-down” basis. The first approaching is applied to this type of traffic and, depending on the action, allows or denies the passage of traffic. And in order to see the order of policing, you need to change the view mode from Section View to Global View and you’ll get this:

Also note the AV , WebFilter , EmailFilter , Aplication Control, and IPS columns . For each of the created policies, standard (default) protection profiles of the anti-virus, web filtering, anti-spam, application control and IPS security functions are applied.
All these profiles are customizable and can be changed in the web interface section of the Security Profiles menu in the web interface.
Antivirus profile:

Web filtering profile:

Application control sensor:

IPS Intrusion Prevention System Sensor:

Email Filtering Profile:

DLP data leakage prevention module sensor:

VoIP profile:

Customer reputation level settings page:

The presence of the profiles themselves in absolutely correctly created policies at the start of the device after the automatic Configuration Wizard symbolizes only its (Master) adequacy and the manufacturer’s concern for the safety of UTM FortiGate users practically out of the box.
Summing up, I just want to note that the care is not completely free: both for the device and for the single (in the SMB / SOHO / ROBO devices segment) the subscription to it for updating the actual signatures of the numerous threat protection functions will have to be given their blood.
But without BUT:
If protection and care is fully justified by the low price in the market, plus the high status of Fortinet as a five-year leader of UTM devices in Gartner square (Gartner), high reliability and performance, a wide range of products for any scale of enterprises. This is all not to mention the speed and ease of configuration, as we were able to verify this article together.
Authorized Fortinet Training Courses
MUK-Service - all types of IT repair: warranty, non-warranty repair, sale of spare parts, contract service
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/209690/
All Articles