Control of cable operator’s cable facilities
Since Soviet times, telecom operators are in charge of a kind of “legacy” - linear cable management, which connects both urban and rural facilities throughout Russia. Since the beginning of the 90s of the last century, mass thefts of copper cable and cast-iron covers of cable wells began. And the topic of protection and control of linear cable structures has become more relevant than ever. Unfortunately, it has not lost its relevance now.

Our system - APK "Tsensor-Tekhnotroniks" - began many years ago with the control of the LKS. Only a few manufacturers deal with this specificity in the world. And I will say without false modesty, Tehnotroniks is at the forefront here, which is confirmed by numerous patents .
')
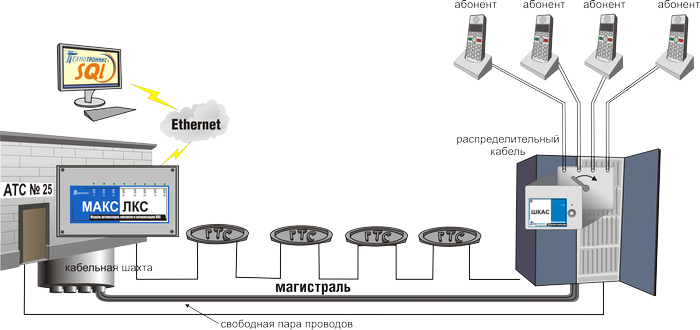
Fig. 1. The control circuit of linear cable management
In fact, LKS is the entire wired fixed-line system, which, as seen in Fig. 1, consists of:
Each of these objects can be the subject of interest of homeless people, vandals and other intruders. In addition, it is not uncommon for small telecom operators to use the infrastructure of, for example, Rostelecom. They run their cables through other people's wells, naturally, without the knowledge of the owner of the wells. Well, and, of course, it is impossible to insure against unintentional cable breakage, for example, during construction works.
All these emergencies our system allows you to track and respond to them promptly. AIC "Tsensor-Tehnotroniks" has the following functionality:
The control system of linear cable structures includes:
 MAKS LKS (Module of Authorization, Control and Signaling) - the latest generation controller for the protection of the entire spectrum of linear cable facilities.
MAKS LKS (Module of Authorization, Control and Signaling) - the latest generation controller for the protection of the entire spectrum of linear cable facilities.
According to its performance, MAKS LKS is a constructor. A controller's execution of a particular function is assigned by installing up to 8 specialized modules into it. This principle of building an LKS control system (controller + modules) makes it flexible and versatile - you can combine in this device those LKS control functions that are in demand in your enterprise, and in the required number of control points. You can also easily increase the capabilities of the system even during its operation - you just need to purchase the module you need in the plug-in and install it on a free space in the controller.
Depending on the number of plug-in modules and their functional orientation, the cost of the device ranges from 15,000 r. up to 47 500 p. VAT included.
For example, when MAKS LKS is fully loaded with the function of monitoring trunk cables (protection of 64 trunk lines), the cost of monitoring a single trunk cable is only 550 p. with VAT .
 There is a modification of the MAKS LKS controller for two plug-in modules - the MiniMAX controller . It was designed for facilities with a small number of LKS, for example, for small rural stations and "extensions" of PBXs. The development was carried out in order to reduce the cost of the solution for customers with these needs, since the MAKS LKS controller with two plug-in modules costs more than MiniMAX.
There is a modification of the MAKS LKS controller for two plug-in modules - the MiniMAX controller . It was designed for facilities with a small number of LKS, for example, for small rural stations and "extensions" of PBXs. The development was carried out in order to reduce the cost of the solution for customers with these needs, since the MAKS LKS controller with two plug-in modules costs more than MiniMAX.
Depending on the number of plug-in modules and their functional orientation, the cost of the device ranges from 8,250 p. up to 14 200 p. VAT included
 SHKAS - a device that works in conjunction with the controller MAKS LKS. ShKAS is placed in the distribution cabinet and transmits information about the breakage of the distribution cable, opening the distribution cabinet to the MAKS LKS controller, and also authorizes the access of the operating personnel to the cabinet. ShKAS is also a device-designer, in which, at the request of the customer, the corresponding functional modules are placed.
SHKAS - a device that works in conjunction with the controller MAKS LKS. ShKAS is placed in the distribution cabinet and transmits information about the breakage of the distribution cable, opening the distribution cabinet to the MAKS LKS controller, and also authorizes the access of the operating personnel to the cabinet. ShKAS is also a device-designer, in which, at the request of the customer, the corresponding functional modules are placed.
Depending on the number of plug-in modules and their functional orientation, the cost of the device ranges from 4300 to 7650 p. VAT included

IGD , IFD - intelligent sensors controlling access to cable sewer wells, working in conjunction with the MAKS LKS controller.
IGD cost, IFD - 1534 p. VAT included
Table 1. Quantitative and functional indicators of the monitoring system based on MAKS LKS
NOTES:
* The number of monitored highways is given for the condition that the signal line and the power line of ShKAS are supplied in different trunk cables;
** Provided controller is placed in active telecommunication cabinets;
*** The number of sensors is determined based on the required level of reliability of the route and is limited by the electrical parameters of the cable.
1. CONTROL OF MAIN CABLES: addressable, with the definition of the place of the cliff
In order to promptly react to a deliberate break in the trunk cable and detain intruders, we need information about the place of the break in the cable. Moreover, from the point of view of technology, two parameters are critical: the speed of the system’s response to a break and the accuracy of determining the accident site. Thus, MAKS LKS, even when fully loaded, polls and determines the integrity of all connected cables in a maximum of 26 seconds. And the error in determining the distance to the cable break, according to the tests, is only 1-2%. In fact, this means that on a cable length of 1 km the measurement error will be only 10-20 meters. Moreover, our system based on the MAKS LKS controller received a metrological certificate guaranteeing the compliance of measurements with a certain accuracy class.
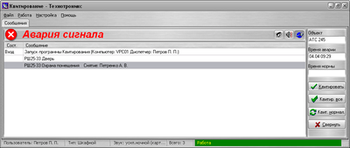
For the convenience of determining the location of a cable break in real conditions, we have provided a cartographic interface for the software "Technotronics. SQL". In the event of an accident, the dispatcher is shown a map of the area with a guideline closest to the place of cable break. This allows the dispatcher to quickly and accurately orient the task force leaving the site.

Fig. 2. A signal about a line breakage with indication of the place of a break on the map.
How is the cable break place determined? In MAKS LKS, we have implemented a patented method for determining the place of cable break, which we call capacitive. The controller continuously measures two parameters of the connected cables: resistance and capacitance - and transfers their value to the control center. In the event of a cable break, its residual capacity is calculated on the basis of which the software determines the location of the accident. However, as is well known, the cable parameters (in particular, the value of its electrical capacity) may change under the influence of seasonal and other factors. This means that the location of the cliff may not be accurately measured. To prevent such a situation and to obtain the correct results, it is important to calibrate the cable — measuring its parameters and adjusting them in software, taking into account errors. Manual cable calibration is a very time-consuming procedure: you need to go to the other end of the cable with special equipment. In our system, the automatic calibration function is implemented, when the software itself constantly re-checks the cable parameters. Due to this, the need for a time-consuming manual calibration procedure is eliminated, and the location of the cliff is calculated as quickly and accurately as possible, regardless of climatic conditions.
2. CONTROL OF DISTRIBUTION CABLES: addressable, with the definition of the place of the cliff; on free, on the pair occupied by the subscriber
Sometimes the network is organized in such a way that determining the place of a cliff is required not only on the main sections, but also on distribution ones due to their considerable length.
To solve this task, the ShKAS controller is used in conjunction with the MAKS LKS controller, which is located in the distribution cabinet and allows you to organize the control of the distribution cable with the location of the break, according to the same principle that is used to control highways. At the same time, ShKAS can control distributions not only for a free pair, but also for a pair occupied by a subscriber. The need for this arises because distribution cables rarely have a stock in the form of service free pairs, because for the operator this means an unused commercial resource. The choice of the control method of the distribution cable is carried out by installing the appropriate modules in HACS. As a result, ShKAS can control up to 16 distribution cables on a free pair or up to 8 distributions on a busy pair, or up to 8 distributions on a free pair and up to 4 on a busy pair at the same time.
3. DISTRIBUTION CABINET CONTROL WITH AUTHORIZATION
In addition to controlling distribution cables, ShKAS monitors the opening of the distribution cabinet and authorizes access for the installer with the help of a chip-key. First, it is a handy tool for tracking unauthorized opening of the cabinet. Secondly, it allows you to dramatically reduce the load on the dispatcher. The system will automatically inform the dispatcher about the key code with the full name of the specialist. Without this tool, the dispatcher would have to receive calls from the installers who opened the distribution cabinet. In addition, thanks to the SHKAS installed in the distribution cabinet, you can, if you wish, control the time that the specialist works on the site.
And another thing: on the basis of the MAKS LKS device, we have developed a solution that allows you to transfer authorization data in a switchboard via a dedicated pair of trunk cable, which is at the same time control, which saves this resource.
Fig. 3. Signal about successful authorization
4. CONTROL OF WELLS: ease of installation on highways with any topology
Control of wells KKS - the most difficult task faced by our company in solving operational problems of telecom operators. The environment of the well, with its temperature variations, humidity and flooding, is extremely aggressive for electronics. Over the years we have studied, tested, rejected and made a huge number of options for decisions. As a result, a variant was chosen as the main one, based on specially developed intelligent sensors that meet the criteria of tightness, reliability, speed of action and others.
Intelligent sensors mounted on the covers of wells, provide targeted control of opening wells. When opened, the smart sensor instantly transmits information about its condition and a unique number to the control center, where an alarm is displayed and the opening is determined on a map of the area. The advantages of intelligent sensors are: instant fixation of the fact of opening; resistance to interference, lightning and internal short circuits; work at low and high temperatures (from -40 to + 50), complete tightness and much more.
The main advantage of the technology based on intelligent sensors is the speed and ease of installation of systems with any even difficult branched topology: it is enough to send only one pair of wires over the wells and in parallel connect our intelligent sensors to it. Moreover, their installation is carried out on the basis of cold sealing methods (3M technology).
The allowable number of intelligent sensors IGD on one line - at least 64 pieces. The number of sensors is determined based on the required level of reliability of the route and is limited by the electrical parameters of the cable.
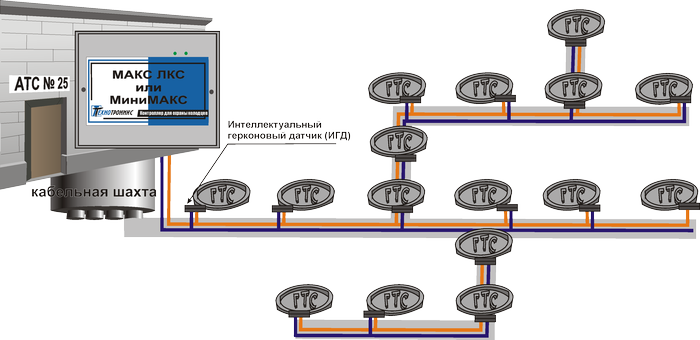
Fig. 4. Scheme of well monitoring based on smart sensors.
 There are several types of smart sensors in our nomenclature:
There are several types of smart sensors in our nomenclature:
- The intelligent reed sensor IGD is a “reed magnet” sensor, which has all the advantages listed above.
- Intellectual reed sensor IGD-R is a modification of the sensor IGD, which allows, in addition to the main functionality, to indicate the part of the route where a short circuit occurred.
 - Intelligent Photo-Sensor IFD - a unique sensor that works on a photo-principle. IFD responds instantly to light that falls into the well when it is opened, even at night.
- Intelligent Photo-Sensor IFD - a unique sensor that works on a photo-principle. IFD responds instantly to light that falls into the well when it is opened, even at night.
- Intelligent Photo-Sensor IFD-R is a modification of the IFD sensor, which allows, in addition to the main functionality, to indicate the part of the route where a short circuit occurred.
Conveniently, all types of smart sensors are fully compatible with each other and can be used in any combination.
I will not dwell on the intelligent sensors in this review article. These devices, without doubt, deserve a separate post, which I will prepare in the near future.
5. LOCK-UP DEVICES WITH SIGNALING: enhanced well protection measures
Equipping wells with a “clean” alarm system is a kind of “catching live bait”, just the same as putting an alarm in a car without locks. There is too little time for prompt response to the fact of opening without such protection; the efforts made by intruders to penetrate are minimal. Therefore, it is ideal to combine the alarm with an obstacle for intruders. For these reasons, we propose 4 options for locking devices for wells.
ZUS, locking device with alarm , is made on the basis of a standard KKS metal bottom cover, contains a bolt, a locking bolt, and an alarm sensor that is well hidden. To penetrate the well, it is necessary to unscrew the locking bolt completely with a specialized key. The whole operation takes at least a minute, and the alarm is generated in advance, in the process of unscrewing the bolt, which gives a "head start" to the protection. Cost 5 900 with VAT.
PL-1, the locking device has a simpler lock mechanism. Sensor alarm type "reed magnet" is easily placed on it using conventional screws. By itself, a PCS plastic is of no interest to intruders. It has a significant advantage in price. The fact of opening is fixed at the time of opening the sensors (opening the well).
PL-2, the locking device is a polymer hatch with two covers. It allows you to completely replace the classic cast-iron hatch and is absolutely not valued by the plunderers. To protect the cable, the bottom cover is protected with special locks; when it is opened, the system signals penetration into the well.
UZKL, the device locking the hatch covers - a screw mechanism with adjustable stops - hooks. Designed to protect the upper cast iron cover. The system responds to opening the top cover at the beginning of unlocking the locking device.
The introductory review is complete. The following posts I plan to delve into the topic of control LKS. At once I will make a reservation that there is a separate solution for those interested in monitoring the cable of the FTTB cabinet.
And finally, as a small entertainment, I publish a small excerpt from a comic book, which we did 3-4 years ago. Just on the lit topic ...

Our system - APK "Tsensor-Tekhnotroniks" - began many years ago with the control of the LKS. Only a few manufacturers deal with this specificity in the world. And I will say without false modesty, Tehnotroniks is at the forefront here, which is confirmed by numerous patents .
')
What is linear cable facilities (LKS)?

Fig. 1. The control circuit of linear cable management
In fact, LKS is the entire wired fixed-line system, which, as seen in Fig. 1, consists of:
- from the trunk cable , laid in most cases under the ground from the PBX to the distribution cabinet;
- from cable sewer wells through which access to the trunk cable is provided;
- from distribution cabinets , where the trunk is embroiled in the so-called distribution (distribution cable);
- from the distribution cable that goes directly to the subscribers.
Each of these objects can be the subject of interest of homeless people, vandals and other intruders. In addition, it is not uncommon for small telecom operators to use the infrastructure of, for example, Rostelecom. They run their cables through other people's wells, naturally, without the knowledge of the owner of the wells. Well, and, of course, it is impossible to insure against unintentional cable breakage, for example, during construction works.
All these emergencies our system allows you to track and respond to them promptly. AIC "Tsensor-Tehnotroniks" has the following functionality:
- monitoring the integrity of trunk cables with the definition of the place of the break,
- control of distribution cables with the definition of the place of the cliff on both the occupied and the free pair,
- control of access to distribution cabinets, including authorization,
- access control to cable decks;
Structure of the control system LKS
The control system of linear cable structures includes:
- MAKS LKS controller located on PBX;
- The ShKAS cabinet controller located in the distribution cabinet;
- Sensors placed on the objects of control: in wells (IHD, IFD), distribution cabinets;
- ON "Tehnotroniks.SQL";
- Ethernet communication channel.
 MAKS LKS (Module of Authorization, Control and Signaling) - the latest generation controller for the protection of the entire spectrum of linear cable facilities.
MAKS LKS (Module of Authorization, Control and Signaling) - the latest generation controller for the protection of the entire spectrum of linear cable facilities.According to its performance, MAKS LKS is a constructor. A controller's execution of a particular function is assigned by installing up to 8 specialized modules into it. This principle of building an LKS control system (controller + modules) makes it flexible and versatile - you can combine in this device those LKS control functions that are in demand in your enterprise, and in the required number of control points. You can also easily increase the capabilities of the system even during its operation - you just need to purchase the module you need in the plug-in and install it on a free space in the controller.
Depending on the number of plug-in modules and their functional orientation, the cost of the device ranges from 15,000 r. up to 47 500 p. VAT included.
For example, when MAKS LKS is fully loaded with the function of monitoring trunk cables (protection of 64 trunk lines), the cost of monitoring a single trunk cable is only 550 p. with VAT .
 There is a modification of the MAKS LKS controller for two plug-in modules - the MiniMAX controller . It was designed for facilities with a small number of LKS, for example, for small rural stations and "extensions" of PBXs. The development was carried out in order to reduce the cost of the solution for customers with these needs, since the MAKS LKS controller with two plug-in modules costs more than MiniMAX.
There is a modification of the MAKS LKS controller for two plug-in modules - the MiniMAX controller . It was designed for facilities with a small number of LKS, for example, for small rural stations and "extensions" of PBXs. The development was carried out in order to reduce the cost of the solution for customers with these needs, since the MAKS LKS controller with two plug-in modules costs more than MiniMAX.Depending on the number of plug-in modules and their functional orientation, the cost of the device ranges from 8,250 p. up to 14 200 p. VAT included
 SHKAS - a device that works in conjunction with the controller MAKS LKS. ShKAS is placed in the distribution cabinet and transmits information about the breakage of the distribution cable, opening the distribution cabinet to the MAKS LKS controller, and also authorizes the access of the operating personnel to the cabinet. ShKAS is also a device-designer, in which, at the request of the customer, the corresponding functional modules are placed.
SHKAS - a device that works in conjunction with the controller MAKS LKS. ShKAS is placed in the distribution cabinet and transmits information about the breakage of the distribution cable, opening the distribution cabinet to the MAKS LKS controller, and also authorizes the access of the operating personnel to the cabinet. ShKAS is also a device-designer, in which, at the request of the customer, the corresponding functional modules are placed.Depending on the number of plug-in modules and their functional orientation, the cost of the device ranges from 4300 to 7650 p. VAT included

IGD , IFD - intelligent sensors controlling access to cable sewer wells, working in conjunction with the MAKS LKS controller.
IGD cost, IFD - 1534 p. VAT included
Table 1. Quantitative and functional indicators of the monitoring system based on MAKS LKS
| Control functions | Number of control points when fully loaded with this function | |
| MAX LKS (without ShKAS) | MAKS LKS with ShKAS | |
| 1. Monitoring the main cable with the definition of the place of break | 64 pairs | 64 * pairs |
| 2. Control distribution cable with the definition of the place of breakage on a free pair | 64 ** pairs | 1024 couples |
| 3. Control distribution cable with the definition of the place of breakage on a busy pair | - | 512 pairs |
| 4. Control and security of KKS wells based on smart sensors | more than 512 *** wells | - |
| 5. Control of distribution cabinets (RS) for opening | 64 RS | 64 RS |
| 6. Control of distribution cabinets (RS) with authorization | - | 64 RS |
NOTES:
* The number of monitored highways is given for the condition that the signal line and the power line of ShKAS are supplied in different trunk cables;
** Provided controller is placed in active telecommunication cabinets;
*** The number of sensors is determined based on the required level of reliability of the route and is limited by the electrical parameters of the cable.
Functional control system LKS
1. CONTROL OF MAIN CABLES: addressable, with the definition of the place of the cliff
In order to promptly react to a deliberate break in the trunk cable and detain intruders, we need information about the place of the break in the cable. Moreover, from the point of view of technology, two parameters are critical: the speed of the system’s response to a break and the accuracy of determining the accident site. Thus, MAKS LKS, even when fully loaded, polls and determines the integrity of all connected cables in a maximum of 26 seconds. And the error in determining the distance to the cable break, according to the tests, is only 1-2%. In fact, this means that on a cable length of 1 km the measurement error will be only 10-20 meters. Moreover, our system based on the MAKS LKS controller received a metrological certificate guaranteeing the compliance of measurements with a certain accuracy class.
For the convenience of determining the location of a cable break in real conditions, we have provided a cartographic interface for the software "Technotronics. SQL". In the event of an accident, the dispatcher is shown a map of the area with a guideline closest to the place of cable break. This allows the dispatcher to quickly and accurately orient the task force leaving the site.

Fig. 2. A signal about a line breakage with indication of the place of a break on the map.
How is the cable break place determined? In MAKS LKS, we have implemented a patented method for determining the place of cable break, which we call capacitive. The controller continuously measures two parameters of the connected cables: resistance and capacitance - and transfers their value to the control center. In the event of a cable break, its residual capacity is calculated on the basis of which the software determines the location of the accident. However, as is well known, the cable parameters (in particular, the value of its electrical capacity) may change under the influence of seasonal and other factors. This means that the location of the cliff may not be accurately measured. To prevent such a situation and to obtain the correct results, it is important to calibrate the cable — measuring its parameters and adjusting them in software, taking into account errors. Manual cable calibration is a very time-consuming procedure: you need to go to the other end of the cable with special equipment. In our system, the automatic calibration function is implemented, when the software itself constantly re-checks the cable parameters. Due to this, the need for a time-consuming manual calibration procedure is eliminated, and the location of the cliff is calculated as quickly and accurately as possible, regardless of climatic conditions.
2. CONTROL OF DISTRIBUTION CABLES: addressable, with the definition of the place of the cliff; on free, on the pair occupied by the subscriber
Sometimes the network is organized in such a way that determining the place of a cliff is required not only on the main sections, but also on distribution ones due to their considerable length.
To solve this task, the ShKAS controller is used in conjunction with the MAKS LKS controller, which is located in the distribution cabinet and allows you to organize the control of the distribution cable with the location of the break, according to the same principle that is used to control highways. At the same time, ShKAS can control distributions not only for a free pair, but also for a pair occupied by a subscriber. The need for this arises because distribution cables rarely have a stock in the form of service free pairs, because for the operator this means an unused commercial resource. The choice of the control method of the distribution cable is carried out by installing the appropriate modules in HACS. As a result, ShKAS can control up to 16 distribution cables on a free pair or up to 8 distributions on a busy pair, or up to 8 distributions on a free pair and up to 4 on a busy pair at the same time.
3. DISTRIBUTION CABINET CONTROL WITH AUTHORIZATION
In addition to controlling distribution cables, ShKAS monitors the opening of the distribution cabinet and authorizes access for the installer with the help of a chip-key. First, it is a handy tool for tracking unauthorized opening of the cabinet. Secondly, it allows you to dramatically reduce the load on the dispatcher. The system will automatically inform the dispatcher about the key code with the full name of the specialist. Without this tool, the dispatcher would have to receive calls from the installers who opened the distribution cabinet. In addition, thanks to the SHKAS installed in the distribution cabinet, you can, if you wish, control the time that the specialist works on the site.
And another thing: on the basis of the MAKS LKS device, we have developed a solution that allows you to transfer authorization data in a switchboard via a dedicated pair of trunk cable, which is at the same time control, which saves this resource.
Fig. 3. Signal about successful authorization
4. CONTROL OF WELLS: ease of installation on highways with any topology
Control of wells KKS - the most difficult task faced by our company in solving operational problems of telecom operators. The environment of the well, with its temperature variations, humidity and flooding, is extremely aggressive for electronics. Over the years we have studied, tested, rejected and made a huge number of options for decisions. As a result, a variant was chosen as the main one, based on specially developed intelligent sensors that meet the criteria of tightness, reliability, speed of action and others.
Intelligent sensors mounted on the covers of wells, provide targeted control of opening wells. When opened, the smart sensor instantly transmits information about its condition and a unique number to the control center, where an alarm is displayed and the opening is determined on a map of the area. The advantages of intelligent sensors are: instant fixation of the fact of opening; resistance to interference, lightning and internal short circuits; work at low and high temperatures (from -40 to + 50), complete tightness and much more.
The main advantage of the technology based on intelligent sensors is the speed and ease of installation of systems with any even difficult branched topology: it is enough to send only one pair of wires over the wells and in parallel connect our intelligent sensors to it. Moreover, their installation is carried out on the basis of cold sealing methods (3M technology).
The allowable number of intelligent sensors IGD on one line - at least 64 pieces. The number of sensors is determined based on the required level of reliability of the route and is limited by the electrical parameters of the cable.

Fig. 4. Scheme of well monitoring based on smart sensors.
 There are several types of smart sensors in our nomenclature:
There are several types of smart sensors in our nomenclature:- The intelligent reed sensor IGD is a “reed magnet” sensor, which has all the advantages listed above.
- Intellectual reed sensor IGD-R is a modification of the sensor IGD, which allows, in addition to the main functionality, to indicate the part of the route where a short circuit occurred.
 - Intelligent Photo-Sensor IFD - a unique sensor that works on a photo-principle. IFD responds instantly to light that falls into the well when it is opened, even at night.
- Intelligent Photo-Sensor IFD - a unique sensor that works on a photo-principle. IFD responds instantly to light that falls into the well when it is opened, even at night.- Intelligent Photo-Sensor IFD-R is a modification of the IFD sensor, which allows, in addition to the main functionality, to indicate the part of the route where a short circuit occurred.
Conveniently, all types of smart sensors are fully compatible with each other and can be used in any combination.
I will not dwell on the intelligent sensors in this review article. These devices, without doubt, deserve a separate post, which I will prepare in the near future.
5. LOCK-UP DEVICES WITH SIGNALING: enhanced well protection measures
Equipping wells with a “clean” alarm system is a kind of “catching live bait”, just the same as putting an alarm in a car without locks. There is too little time for prompt response to the fact of opening without such protection; the efforts made by intruders to penetrate are minimal. Therefore, it is ideal to combine the alarm with an obstacle for intruders. For these reasons, we propose 4 options for locking devices for wells.
ZUS, locking device with alarm , is made on the basis of a standard KKS metal bottom cover, contains a bolt, a locking bolt, and an alarm sensor that is well hidden. To penetrate the well, it is necessary to unscrew the locking bolt completely with a specialized key. The whole operation takes at least a minute, and the alarm is generated in advance, in the process of unscrewing the bolt, which gives a "head start" to the protection. Cost 5 900 with VAT.
PL-1, the locking device has a simpler lock mechanism. Sensor alarm type "reed magnet" is easily placed on it using conventional screws. By itself, a PCS plastic is of no interest to intruders. It has a significant advantage in price. The fact of opening is fixed at the time of opening the sensors (opening the well).
PL-2, the locking device is a polymer hatch with two covers. It allows you to completely replace the classic cast-iron hatch and is absolutely not valued by the plunderers. To protect the cable, the bottom cover is protected with special locks; when it is opened, the system signals penetration into the well.
UZKL, the device locking the hatch covers - a screw mechanism with adjustable stops - hooks. Designed to protect the upper cast iron cover. The system responds to opening the top cover at the beginning of unlocking the locking device.
The introductory review is complete. The following posts I plan to delve into the topic of control LKS. At once I will make a reservation that there is a separate solution for those interested in monitoring the cable of the FTTB cabinet.
And finally, as a small entertainment, I publish a small excerpt from a comic book, which we did 3-4 years ago. Just on the lit topic ...
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/209160/
All Articles