Background update data in iOS7
At the end of September, APPLE released iOS 7, one of the features of this version was improved multitasking and the ability to update data when the application is not active.
There are two options for launching the application for updating data - periodic updates and starting when you receive a special push-notification. In each of the options, the application will be launched in the background (background mode), and will be forcibly closed after 30 seconds, so there will be very little time to update.
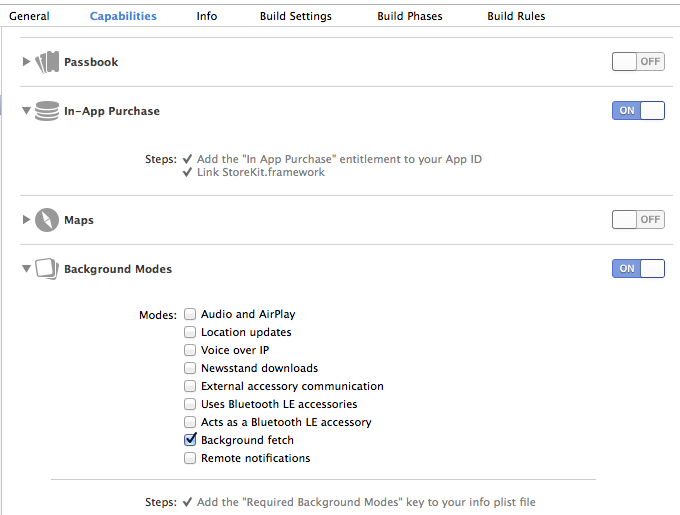
To allow the application to run in the background, you need to add the Required background modes key with the App downloads content from the network value to the application plist. This can also be done by checking the Capabilities tab.
In addition, in the method application: didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: set the minimum interval to run.
(check for version is important - in iOS 6, the application falls on this function).
Instead of a numeric value, you can use the UIApplicationBackgroundFetchIntervalMinimum variable to set the minimum possible interval, but this does not play a special role, because the minimum interval is set, not the guaranteed interval. When exactly the application will start - is unknown. It will be launched based on the statistics of the work: at what time the application usually starts, how long it usually takes in the background. The less time it takes to run the program, the more often it will run. Setting the interval is required, since by default, this value is equal to UIApplicationBackgroundFetchIntervalNever and the launch will not occur.
')
When launched, the application starts its work in the background by running the application: performFetchWithCompletionHandler method:
At the end of the method, you must call received completionHandler with the UIBackgroundFetchResultNewData parameter (variants - UIBackgroundFetchResultNoData, UIBackgroundFetchResultFailed). But in any case, after 30 seconds the application will be forcibly closed.
In addition, as with the standard launch, application: didFinishLaunchingWithOptions is called:
and if there is code in it that should not be launched in this situation (for example, UI update), in order to save processor time, it is better to disable it. When launched in this mode, I did not find additional keys in launchOptions, so I need to check the application.applicationState parameter, which will be equal to the UIApplicationStateBackground.
NB If within 30 seconds while the application is running in the background, the user starts the application via the UI, then this method will not be restarted. If necessary, the missing code can be run in the applicationWillEnterForeground method: (UIApplication *) application
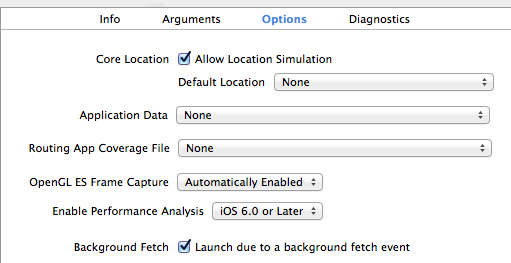
To debug the launch of the application in the background update mode in XCode, you can simulate this mode - it is enabled by ticking the scheme settings.
The second opportunity to receive content updates is to launch when receiving push notification with the content-available flag set.
I will not paint the application settings for push. I can only say that the Required background modes key with the App value is added to the plist of the application (well, or the corresponding check mark in the project settings), and the new value is added to the types of messages that the application will receive
UIRemoteNotificationTypeNewsstandContentAvailability;
When a message is received, the method runs.
to whom too
It will be given only 30 seconds and at the end of which you must call completionHandler with a parameter.
This function will be launched regardless of the state in which the application is now, even if it is in active mode.
If the application is launched in the background, then the application: didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: method will also be called, but in this case, the launchOptions will have an entry with the UIApplicationLaunchOptionsRemoteNotificationKey key.
The first pitfall - push does not come if there is nothing besides the content-available flag. If you add text or sound, then everything is fine. Since no one wants to spam the user with messages, we send an empty sound:
In principle, Apple does not limit us in choosing the method by which the update will be carried out. However, in iOS 7, a new NSURLSession class has emerged, which the company recommends using. Without delving into its description, we can say that one of its merits is the ability to download data in the background using iOS itself, even after the application is terminated.
And now a little personal experience or why all of the above didn’t work for our application (electronic newspaper on iPad). It was planned that in the morning the user will wake up, get an iPad, and the newspaper is already ready for him and is waiting to be read. But…
First, the background update does not work when the device is in sleep mode (the screen is turned off). The update will take place as soon as the screen is unlocked, which is good for the messenger, but for us it is too late.
Secondly, despite the fact that the documentation says “If your app is suspended or not running, push will not launch the app, if it is in the “not running” state. This means that if the user himself deleted the application from the task list or the system unloaded it, then push comes, but the application does not start. It is not clear whether this is a bug or not, but what it is, that is. Alas.
PS In order for the application to start, you must also allow the ability to run in the device settings (or rather, do not deny it, because by default it is enabled for new programs). You can check this from the application by checking the [[UIApplication sharedApplication] backgroundRefreshStatus] value.
There are two options for launching the application for updating data - periodic updates and starting when you receive a special push-notification. In each of the options, the application will be launched in the background (background mode), and will be forcibly closed after 30 seconds, so there will be very little time to update.
Periodic data update (Background fetch)
To allow the application to run in the background, you need to add the Required background modes key with the App downloads content from the network value to the application plist. This can also be done by checking the Capabilities tab.

In addition, in the method application: didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: set the minimum interval to run.
If([[[UIDevice currentDevice] systemVersion] floatValue] >=7.0){ [[UIApplication sharedApplication] setMinimumBackgroundFetchInterval:600]; } (check for version is important - in iOS 6, the application falls on this function).
Instead of a numeric value, you can use the UIApplicationBackgroundFetchIntervalMinimum variable to set the minimum possible interval, but this does not play a special role, because the minimum interval is set, not the guaranteed interval. When exactly the application will start - is unknown. It will be launched based on the statistics of the work: at what time the application usually starts, how long it usually takes in the background. The less time it takes to run the program, the more often it will run. Setting the interval is required, since by default, this value is equal to UIApplicationBackgroundFetchIntervalNever and the launch will not occur.
')
When launched, the application starts its work in the background by running the application: performFetchWithCompletionHandler method:
-(void)application:(UIApplication *)application performFetchWithCompletionHandler:(void (^)(UIBackgroundFetchResult))completionHandler{ //DO SOMETHING completionHandler(UIBackgroundFetchResultNewData); } At the end of the method, you must call received completionHandler with the UIBackgroundFetchResultNewData parameter (variants - UIBackgroundFetchResultNoData, UIBackgroundFetchResultFailed). But in any case, after 30 seconds the application will be forcibly closed.
In addition, as with the standard launch, application: didFinishLaunchingWithOptions is called:
and if there is code in it that should not be launched in this situation (for example, UI update), in order to save processor time, it is better to disable it. When launched in this mode, I did not find additional keys in launchOptions, so I need to check the application.applicationState parameter, which will be equal to the UIApplicationStateBackground.
NB If within 30 seconds while the application is running in the background, the user starts the application via the UI, then this method will not be restarted. If necessary, the missing code can be run in the applicationWillEnterForeground method: (UIApplication *) application
To debug the launch of the application in the background update mode in XCode, you can simulate this mode - it is enabled by ticking the scheme settings.

Run from push message.
The second opportunity to receive content updates is to launch when receiving push notification with the content-available flag set.
I will not paint the application settings for push. I can only say that the Required background modes key with the App value is added to the plist of the application (well, or the corresponding check mark in the project settings), and the new value is added to the types of messages that the application will receive
UIRemoteNotificationTypeNewsstandContentAvailability;
UIRemoteNotificationType myTypes = UIRemoteNotificationTypeBadge | UIRemoteNotificationTypeAlert|UIRemoteNotificationTypeSound|UIRemoteNotificationTypeNewsstandContentAvailability; [application registerForRemoteNotificationTypes:myTypes]; When a message is received, the method runs.
-(void) application:(UIApplication *)application performFetchWithCompletionHandler:(void (^)(UIBackgroundFetchResult))completionHandler{ //DO SOMETHING completionHandler(UIBackgroundFetchResultNewData); } to whom too
It will be given only 30 seconds and at the end of which you must call completionHandler with a parameter.
This function will be launched regardless of the state in which the application is now, even if it is in active mode.
If the application is launched in the background, then the application: didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: method will also be called, but in this case, the launchOptions will have an entry with the UIApplicationLaunchOptionsRemoteNotificationKey key.
The first pitfall - push does not come if there is nothing besides the content-available flag. If you add text or sound, then everything is fine. Since no one wants to spam the user with messages, we send an empty sound:
aps = { "content-available" = 1; sound = ""; }; What can be done in 30 seconds?
In principle, Apple does not limit us in choosing the method by which the update will be carried out. However, in iOS 7, a new NSURLSession class has emerged, which the company recommends using. Without delving into its description, we can say that one of its merits is the ability to download data in the background using iOS itself, even after the application is terminated.
A spoon of tar
And now a little personal experience or why all of the above didn’t work for our application (electronic newspaper on iPad). It was planned that in the morning the user will wake up, get an iPad, and the newspaper is already ready for him and is waiting to be read. But…
First, the background update does not work when the device is in sleep mode (the screen is turned off). The update will take place as soon as the screen is unlocked, which is good for the messenger, but for us it is too late.
Secondly, despite the fact that the documentation says “If your app is suspended or not running, push will not launch the app, if it is in the “not running” state. This means that if the user himself deleted the application from the task list or the system unloaded it, then push comes, but the application does not start. It is not clear whether this is a bug or not, but what it is, that is. Alas.
PS In order for the application to start, you must also allow the ability to run in the device settings (or rather, do not deny it, because by default it is enabled for new programs). You can check this from the application by checking the [[UIApplication sharedApplication] backgroundRefreshStatus] value.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/208434/
All Articles