Introducing Cisco TelePresence
As the languid view showed, building a network for video communication is not a trivial task: there are different solutions, interaction levels, the Internet is different everywhere, and dangerous places are above the roof. The strangest thing is that there are no Russian-speaking guides for planning, design and more fine-tuning. There is a middle, so-called. “Basic setting”, which the experienced network administrator will not be satisfied with. Depending on the situation and requirements, absolutely unexpected decisions may appear. Even for one organization with a set of requirements, finding the right solution at once will be problematic, and to be universal and to cover the full range of services provided by Cisco TelePresence equipment, you will need more than one unit. If you buy all the ciskov pieces of iron and stick everything into each other, it can turn out to be “Universal”.
There is a lot of text under the cut.

The idea of organizing all available means of information transmission, such as telephone, telegraph and communication networks, in a single network is not new, and appeared in the second half of the 20th century. This concept has reached our days under the name of ISDN, however, the development of IP networks and the emergence of new services did not give life to the proposed concept. She was replaced by solutions that were called the New Generation Network (NGN) - the network of the new generation. Using the concept of new generation networks for transmitting multimedia data, Cisco TelePresence implements its control components separately. Those. The signaling information needed to establish / disconnect the connection and determine the route of the multimedia stream is transmitted over one device. And directly multimedia data, i.e. voice and video are switched by other devices.
Videoconferencing is based on the following 5 “elephants” (I use sisko-terminology):
1. VideoNetworkServices, which control the controlplane components, are involved in call routing, incl. in “other” networks. Control signaling information;
2. Videoservices, the so-called userplane components that are directly responsible for the transfer of multimedia. The abbreviation MCU (Multipoint Control Unit) is more commonly used, based on the terminology of h.323;
3. endpoints, in Russian, end devices: maybe a TV or mobile phone, well, everything in between (iPod is not supported yet) .;
4. Managers: without them nowhere. If the camera does not work in Bugulma, the last who touched it will have to go there;
5. of course the network.
There are two types of them: call control and gateways.
• CallControl - so-called. Video Communication Server (VCS), registers endpoints (SIP and H.323), routes calls, monitors, has nothing to do with multimedia. You can collect a few pieces in a cluster, if one is hard. There are VCS Control, to connect clients from their network, and there are VCS Expressway with support for NAT, transfer firewall etc, for external connections. Expressway is located in the DMZ.
• Gateway - access to “other” networks, such as ISDN, PSTN. Business-to-Business there.

VCS Tandberg
')
Video services are optional, but are an important part of infrastructure planning for video conferencing. It is worth starting with answers to the questions: will there be conferences with more than 2 participants, is video streaming needed and is recording necessary? Accordingly, there are two types of devices:
• Conferencing - equipment for combining 3 or more participants. Provides switching and transcoding. Switching involves sending a video / audio stream from one end device to many others. Transcoding is the encoding and decoding of a media stream between endpoints. In terminology, H.323 is called MCU (MultipointControlUnit). Cisco provides its list of existing solutions: Cisco Telepresence Multipoint Switch, MCU 4000, Cisco Integrated Service Router (ISR), and cluster solutions based on MSE 8000 with several blade servers on board.

MCU 4500
• Streaming & Recording - many MCUs, in addition to conferencing, have a video broadcasting server on board. And if they are not, there are two types of glands. One, however, only records the Cisco TelePresence Recording Server. But the second and writes and broadcasts simultaneously, Cisco TelePresence Content Server. Works in Cisco Media Services Engine (MSE)
End devices can be used here:
• Software clients: LifeSize Clear C (available for Android devices), Cisco Jabber (available for iPads, Mac OS and Android). In this case, the device / codec will be the computer / tablet / phone itself;
• Personal stations: EX60, DX650, E20 - the most popular. Configured simply, web-muzzle or directly on the screen. All the terminal needs is to select a codec and give the server address. By the way, the DX650 has a VPN client on board, i.e. you can cling not to Expressway, but first into the work network, and along the tunnel to the Control;
• Meeting and conference rooms. The solutions are correctly called Collaboration Room Endpoints (MX Series and Profile Series) and Immersive TelePresence Series (TX Series). In them, the codec is a box into which screens, microphones and cameras are brought.


Soft-based gizmo with a huge number of functions, so far, however, is mainly used for monitoring. The fact is that almost every piece of iron has a convenient web-muzzle. The console, by the way, is also available. However, if you know how to configure Cisco switches and routers, this will not help you, the syntax is completely different. And yet, managers:
• Cisco TMS - TelePresence Management Suite. Server-based system, i.e. it needs a piece of hardware. Convenient and intuitive monitoring, mainstream - video conferencing on schedule. Those. at a certain point a call is made to all participants. Integrates into AD, in particular, the Microsoft Exchange calendar;
• Cisco TelePresence Manager and Cisco Prime Collaboration Manager - I don’t know what the real difference is from the first one. I touched only the first. But there is rial-time monitoring in the Prime Kolabourisation, for which, of course, respect.
Basically, all network requirements for streaming depend on the stream itself. For example, at least 2 Mb / s is recommended for h.264 video transmission. for one client. Delays, jitter, loss - all as in all. The most interesting question is how to connect remote clients. Whether you need a VPN, whether you need one network for all clients, or / 30 and PPTP, or NAT. Encryption implemented in Cisco TelePresence will be discussed later.
Now that we have learned a little about the functional purposes of various products (this is not all at all), we can begin to plan connection of clients, access to the network, look at the root of implementation, etc.
There are several options for establishing a call for a connection (skinny did not consider):
• h.323 - a set of protocols, users of communication cling to the gatekeeper (it is the zone controller, it is the gatekeeper, implemented in VCS) - the call handler. Gatekeeper clings to h.323 MCU;
• sip - session initialization protocol. Need a sip server (which is in VCS). It will register users, it is also SIP-proxy. It clings to the MCU (for the case of calls from 3 participants).
What sip that h.323 - equally useful. It is worth mentioning that h.323 is not a protocol, but recommendations for the protocols used. And these protocols have the character of a standard. The functions are the same. Although sip wins on the following criteria:
• more convenient to scale;
• the connection is established in 1 handshake, when in h.323 there will be 100500;
• many will notice the similarity of SIPs with the notorious HTTP protocol. True, like, understandable.
To begin with, it is important for us to determine the topology, or topologies that we want to scatter. Suppose the simplest scheme, we definitely need telepresence, video h.264 and conference SIP + h.323. A set of VCS for registration of participants and a sip server on board, an MCU for conferencing, endpoints with HD cameras and an Internet channel will cope with this.
Lyrical digression : Working with Cisco TelePresence will have to face a large number of non-tsisko devices: these include Tandberg and Codian. Cases are: once in the recent past, they were all independent of each other. Tandbert was considered the giant of video communications, and Kodian specialized in the production of MCU-nis. In 2007, the British Kordian became (for 270 million Baku) part of the giant Tandberg, and in 2010, the Tandberg became part of the giant Cisco (for 3.3 billion). Tandberg now manufactures its equipment under the TANDBERG Cisco brand, and Kodian supports and manufactures its equipment with the supply of Tsiski under the old Codian brand. Those. speaking of Kodians, etc., we mean Cisco “Om-nom-nom” corp.
The inclusion scheme will be:
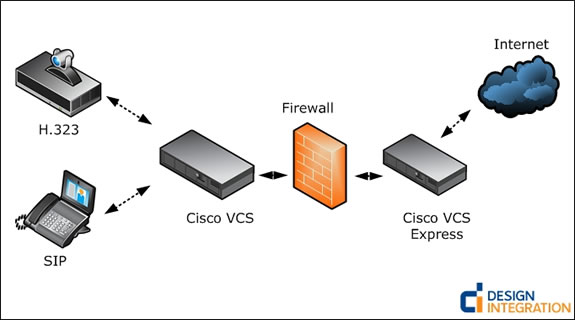
Ask a question about licensing. Since users live and are registered on VCS, and the combination of three or more clients occurs on the MCU, it is logical to assume that Cisco will unlikely give their clients unlimited possibilities for connecting conference participants. Limit the number of times, this is the maximum available number of user registrations. Initially, the machine (VCS) has the capacity for 2500 registrations (depends on the purchase configuration). You can assemble a cluster (maximum 6 devices). With the cluster, you can expand the number of MAXIMUM registrations to 10,000. Less than it should be - this is because of the reservation, i.e. if one piece of iron fails, users can be ported to the second. Limits number 2 and 3 are traversal and non-traversal calls. Traversal calls are:
• Calls from H.323 to sip (and vice versa);
• Firewall traversal call Assent;
• Firewall traversal call h.460;
• Ipv4-ipv6;
• Expressway that receives a call but does not have an extended license for local calls can use one traversal license for one call.
Non-traversal is a call inside the ipv4 network, from sip to sip, calls between VCSs, i.e. the simplest calls that do not require tricky manipulations. You can buy additional licenses for 10, 20, 50, 100, 200 and 300 pieces. By the way, if you assemble a cluster (also 6 pieces), you can get 2000 non-traversal and 400 traverse licenses. Also, many additional functions are subject to licensing for VCS, such as FindMe, Advanced Account Security, Device Provisioning and much more. Unfortunately, I didn’t find a single word by expanding the number of sip domains created (by default there are 200, but far more!).
MCU licensing is a possible number of participants in the conference. Consider the example of the Codian MCU-4210 MCU 4200 Series: it has the ability to include up to 20 participants in a video conference, has an additional 20 licenses for audio participants. For comparison, the Codian MCU-4220 can only 40 (video and add. Audio). Here 20 participants means that there are 20 virtual ports on the device that the device commutes with each other. Those. more than 20 - no way. A cluster can be assembled only if you have something from super-glands, such as the Supervisor MCU MSE 8050 stuffed with blades MCU MSE 8510 blade. By the way, there is a video broadcasting server on the same MCU-shke (4210).
We will understand what is encrypted: first alarm. It is encrypted with AES (DES, 3DES), the key is selected according to Diffie-Hellman. It is activated by pressing a button in a colorful web-muzzle. Secondly, the transmitted traffic (media data) is encrypted, by the same AES, the key for the same Diffie-Hellman. And it turns on in the same way.
If the securiness seems insufficient, then it is possible to lift VPN tunnels to clients, write ACLs, configure Firewalls, etc. Turn on paranoia:
• if SIP, then SIPS (same sip, but with TLS. The address is not written as sip: <> @ ..., but sips: <> @ ...)
• if TCP / UDP, then TLS
• if RTP, then SRTP
• if the client is far away, then GRE / IPsec
• well and everything that we will think up
It is clear that this will increase the packetization time and the overall overhead.
By itself, the firmware is very convenient (X7.2.2), has a manual for itself on board, it opens with the Help button in the upper right corner. The help window that opens in the window provides background information about the subsystem in which you are now (both theoretical and practical). Input fields are also highlighted with a miniature help.
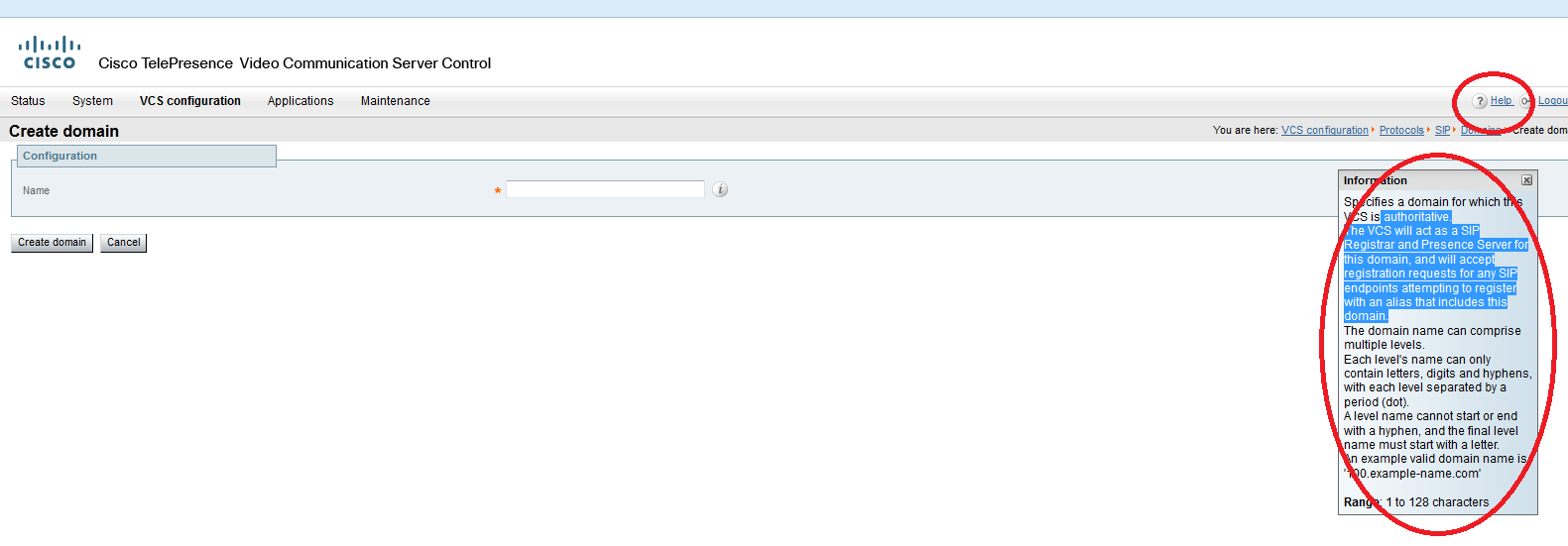
Do not worry if something is not clear, or do not remember what field to write. Help will fulfill its purpose. Softwares can be attributed to the soft set of regulars (relatively powerful within their task).
We’ll skip the basic setting, that's really something, but “how to set up VCSe + VCSc + MCU in a hurry” on the Internet is full, but the most interesting can only be found in kilometers of guides (it took me a little less than a month from “below absolute zero "). Suppose that we have performed the basic settings, set the MCU neighborhood, the Traversal zone, set the time, etc. Now let's deal with call management “like a boss”, who are these neighbors, and why do we need Traversal.
Muddy muddied start here. A zone is an abstract set of anything (domains, ip-addresses, devices, services) to which a certain set of rules apply. Zones are needed to manage bandwidth, authenticate and route calls, and this applies immediately to everything in the zone. When creating Dial-Plans, you need to specify from which zone to which call to transfer (and not to which domain). So it is easier to control everything that happens, however, setting up this outrage may seem dreary.
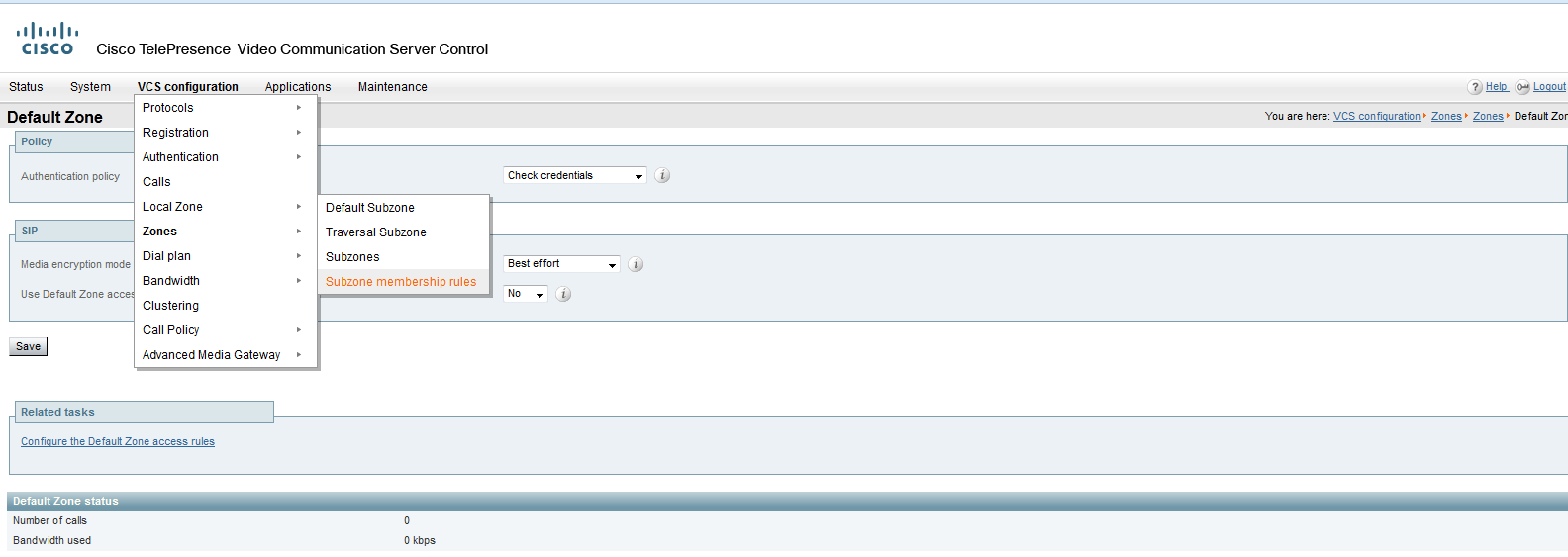
All end devices, VCS-ki and MCU-shki, in general, all your devices are included in the Local Zone ( LocalZone ). A local zone can be divided into subzones. Therefore, for management flexibility, you can create a separate subzone for a new sip domain. You can create them up to 1000. The domain that will belong to a particular subzone needs to be determined using the “Subzone membership rules”.
Zones are also neighboring ( Neighbor ), forwarding ( Traversal (client-server view)), ENUM and DNS . The last two for ENUM and DNS queries, they need to show which servers to ask for names and E.164. Traversal zone is needed for routing calls between the VCS Control and Expressway firewalls. Say, half of the customers inside will make a call through VCS Control, and half, which is located remotely, will use the Expressway tools. VCS Control– client, Expressway– server. Neighbor zone is needed, for example, to communicate with the MCU, or another VCS. Those who did not fall into any of the zones fall into DefaultZone , and work according to the rules of the default zone, which, generally speaking, you can not fill in with the rules, and everyone will just be rejected.
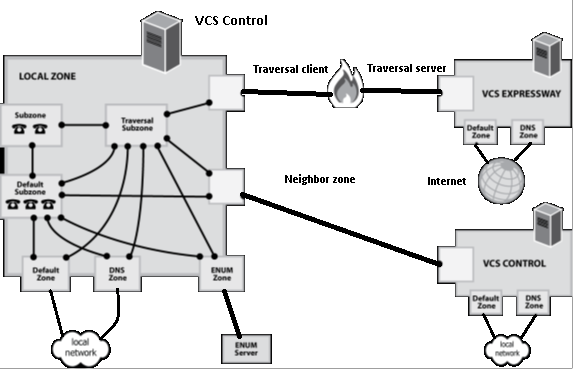
I will post screenshots in less so as not to clog the text with half-empty browser windows. Simply tell in words.
You can create Subzone (for bandwidth control, encryption and authentication) in the menu VCS Configuration -> Localzone -> Subzones . Click New , in the Policy area we allow registration Registration policy - Allow, and be sure to authorize: Authentication policy - Check Credentials. In the area of SIP Media encryption mode, you can determine the need for encryption. Bandwidth limitations are optional. This tool allows you to manage calls between zones.
Create SIP-domain ( VCS Configurations -> Protocols -> SIP -> Domains ). Click New , enter the domain name. You can create up to 200 pieces.
Creating membership rules for establishing domain membership in the subzone ( VCS Configuration -> Local zone -> Subzones membership rules ). The rule must contain the Name, priority, regular expression, under which the domain name will fall, and the subzone, the rules of which will be used in the given domain.
After the recipient and sender sabzone has been determined, call processing begins on the VCS (or VCS), according to the call policy rules ( VCS Configuration-> Call policy-> Rules ). First, we include them, secondly we write the rules. Anyone familiar with ACLs will see a lot of similarity. From where-to-policy is a simple scheme, only 3 points of the rule. The rule that is higher - it works earlier, you can change the position with the arrows up and down.
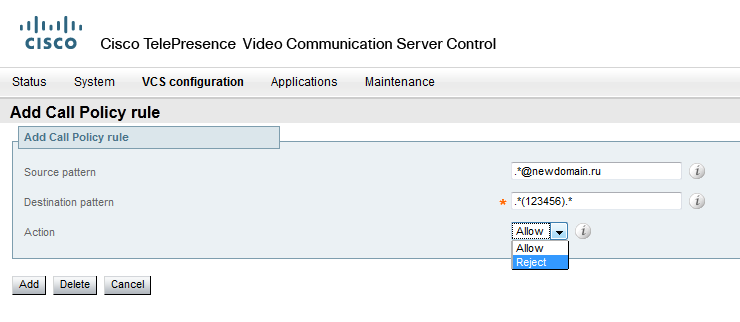
By this rule, we allow / prohibit calls to 123456 from the domain newdomain.ru, for example. There is an implicit Deny at the end or not, I, unfortunately, did not check, but just in case at the end I set the rule ". * ->. * Reject" ie block everywhere and anywhere. Naturally written earlier rules are written. Generally speaking, you can not include Call Policy, and steer calls at the level of dial-plans. But with the included rules, you will not even get to the dial-up plans, and if you have a lot of them, you do not need to run through the list of rules andfrantically search for a dial-plan under which your call falls.
Now we have come close to Dial- plans, important and necessary things, without which nothing will work. Call processing at the stage of Dial-plan-s occurs in stages. First, the rules of type “ Transform ” are triggered They allow you to do anything with addresses: cut off the domain part, add a domain part, change the name of the recipient, the sender. Let's say you want to call from the Cisco background to a thug number, “666666” for example, and get into the conference, you have rooms for you, and there is no need to create another one. So, we write the transform into the existing room and deal with it. Here is an example of how to make 639801 from 666666.

After the transform is completed and the transform rules applicable to the call have run out, processing begins according to the rules of the Search rules . Create a Search Rule for dial plans, for routing search requests to specific zones ( VCSConfiguration -> Dial-Plan -> SearchRules ). An example of the rule for the subzone domain is below.
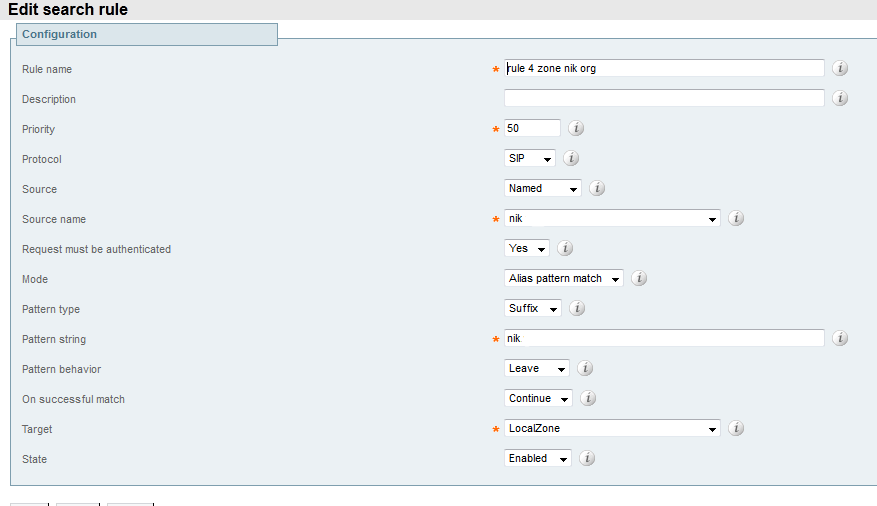
Please note that the rule created for the outgoing zone specified in the Source name searches for the Pattern string in the request, specified as the recipient suffix ( Suffix ) of the URI "nik". In other words, if from a zone nik a call has a destination address nik, then you need to look for this address in the local zone ( Local Zone ). The rule in the drop-down field State is turned on in the Enable position.
Now a couple of words Pattern matching variables . Yes, yes, and the most pleasant thing - these things work in general everywhere, if there is a regular search, suffix or prefix in the search. These are variables of the type% pattern%, which are used in regular programs, Search Rules, and generally everywhere where you work with ip-addresses or sip-domains.
A brief but useful list of variables:
% localdomains% - all local sip domains
% ip% - all ipv4 and ipv6 addresses
% ipv4%,% ipv6% the same, but separately
% localdomain1% - sip domain with index 1 (varies from 1 to 200)
% systemname% - systemname
The question is - who will call? There are several ways to create a sip user. The first obvious one is to create a local user directly in VCS (VCS Configuration -> Authentication -> Devices -> Local Database ). The second option is to create a user in TMS (we still have a manager). To create users of end devices (registered with devices) go to the menu System -> Regulation -> Users . On the left in the Create Group and Users menu ( Add Group , Add users ). In the same menu on the left, below, select the Configuration Template and create a template for the group. There is a reservation that for different terminal devices the patterns will be different, but, in fact, with the same set of options. For example, the domain, the address of the SIP server, the address of the phone book, etc. ... A set of schemes is downloaded to TMS, all schemes are filled by the administrator. Filling the template is intuitively understandable, but the schemes of this template for end devices (be it a jabber client, or an E20 terminal) must first be downloaded from the site
It is possible to perform authentication after integration into AD or LDAP, but we did not have to.
Now Expressway. Create a SIP domain in the same way as in Control-e. Since TMS and Expressway are in different networks and are separated by an ACL, the user also needs to be created in the Local Database (Similarly, create a sub-zone and a membership Rule for membership in the sub-zone). To enable authentication, enable Search Rule using the SIP protocol, with the DefaultZone source, you need to search by the following regular schedule ^ (. +) @ Domain \ .ru $ , and send it to the Traversal Zone for VCS Control. For what and why - it turned out only empirically: before registration, since it is NOT control, no one gets under "his" network, the user is not in the domain, he is not in the subband, i.e. all non-registered individuals fall into DefaultZone.
You can create 2 universal rules, Call's to Traversal zone and Call's from Traversal zone for calls between VCS-kami (we can now operate with such concepts?). It is not difficult to guess what kind they will be, but if you do not need to allow end-to-end calls, it is better not to write such a general rule, but to do it for each domain separately.
Briefly about the MCU. Actually, the Conference itself, as we remember, is organized at the MCU. The management of conferences is simple, we set up the h.323 VCS connection with the MCU (car and cart guides on the Internet on this topic) and create the conference itself. The features of the MCU help are the same as on VCS, but still: a conference is created in the Conference tab with the button “ Add a new conference ”. When you create a conference, most of the fields will be filled out of a template (previously configured), you only need to fill in the following fields:
• Name - Sign Identifier
• Digital ID — numbers added to the prefix for registration
• PIN if necessary
• Guest Aidish
• Guest PIN.
Templates provide automatic filling of some fields, you can change them in the menu Home -> Conferences -> Templates . In addition to the basic settings, a custom layout will be available for configuration ( Main page: -> Conferences -> Conference “name” -> Custom layout ). It defines the location of video conferencing participants on the screen.
So from scratch, you can configure a conference dialer from a pile of expensive pieces of iron. Thank you for living to the end and happy new year to you!
Sources
habrahabr.ru
www.cisco.com
www.anticisco.ru
linkmeup.ru
mcu.dc.codian.com
There is a lot of text under the cut.

Introduction
The idea of organizing all available means of information transmission, such as telephone, telegraph and communication networks, in a single network is not new, and appeared in the second half of the 20th century. This concept has reached our days under the name of ISDN, however, the development of IP networks and the emergence of new services did not give life to the proposed concept. She was replaced by solutions that were called the New Generation Network (NGN) - the network of the new generation. Using the concept of new generation networks for transmitting multimedia data, Cisco TelePresence implements its control components separately. Those. The signaling information needed to establish / disconnect the connection and determine the route of the multimedia stream is transmitted over one device. And directly multimedia data, i.e. voice and video are switched by other devices.
Videoconferencing is based on the following 5 “elephants” (I use sisko-terminology):
1. VideoNetworkServices, which control the controlplane components, are involved in call routing, incl. in “other” networks. Control signaling information;
2. Videoservices, the so-called userplane components that are directly responsible for the transfer of multimedia. The abbreviation MCU (Multipoint Control Unit) is more commonly used, based on the terminology of h.323;
3. endpoints, in Russian, end devices: maybe a TV or mobile phone, well, everything in between (iPod is not supported yet) .;
4. Managers: without them nowhere. If the camera does not work in Bugulma, the last who touched it will have to go there;
5. of course the network.
VideoNetworkServices
There are two types of them: call control and gateways.
• CallControl - so-called. Video Communication Server (VCS), registers endpoints (SIP and H.323), routes calls, monitors, has nothing to do with multimedia. You can collect a few pieces in a cluster, if one is hard. There are VCS Control, to connect clients from their network, and there are VCS Expressway with support for NAT, transfer firewall etc, for external connections. Expressway is located in the DMZ.
• Gateway - access to “other” networks, such as ISDN, PSTN. Business-to-Business there.

VCS Tandberg
')
Videoservices
Video services are optional, but are an important part of infrastructure planning for video conferencing. It is worth starting with answers to the questions: will there be conferences with more than 2 participants, is video streaming needed and is recording necessary? Accordingly, there are two types of devices:
• Conferencing - equipment for combining 3 or more participants. Provides switching and transcoding. Switching involves sending a video / audio stream from one end device to many others. Transcoding is the encoding and decoding of a media stream between endpoints. In terminology, H.323 is called MCU (MultipointControlUnit). Cisco provides its list of existing solutions: Cisco Telepresence Multipoint Switch, MCU 4000, Cisco Integrated Service Router (ISR), and cluster solutions based on MSE 8000 with several blade servers on board.

MCU 4500
• Streaming & Recording - many MCUs, in addition to conferencing, have a video broadcasting server on board. And if they are not, there are two types of glands. One, however, only records the Cisco TelePresence Recording Server. But the second and writes and broadcasts simultaneously, Cisco TelePresence Content Server. Works in Cisco Media Services Engine (MSE)
Endpoints
End devices can be used here:
• Software clients: LifeSize Clear C (available for Android devices), Cisco Jabber (available for iPads, Mac OS and Android). In this case, the device / codec will be the computer / tablet / phone itself;
• Personal stations: EX60, DX650, E20 - the most popular. Configured simply, web-muzzle or directly on the screen. All the terminal needs is to select a codec and give the server address. By the way, the DX650 has a VPN client on board, i.e. you can cling not to Expressway, but first into the work network, and along the tunnel to the Control;
• Meeting and conference rooms. The solutions are correctly called Collaboration Room Endpoints (MX Series and Profile Series) and Immersive TelePresence Series (TX Series). In them, the codec is a box into which screens, microphones and cameras are brought.


Management
Soft-based gizmo with a huge number of functions, so far, however, is mainly used for monitoring. The fact is that almost every piece of iron has a convenient web-muzzle. The console, by the way, is also available. However, if you know how to configure Cisco switches and routers, this will not help you, the syntax is completely different. And yet, managers:
• Cisco TMS - TelePresence Management Suite. Server-based system, i.e. it needs a piece of hardware. Convenient and intuitive monitoring, mainstream - video conferencing on schedule. Those. at a certain point a call is made to all participants. Integrates into AD, in particular, the Microsoft Exchange calendar;
• Cisco TelePresence Manager and Cisco Prime Collaboration Manager - I don’t know what the real difference is from the first one. I touched only the first. But there is rial-time monitoring in the Prime Kolabourisation, for which, of course, respect.
Network
Basically, all network requirements for streaming depend on the stream itself. For example, at least 2 Mb / s is recommended for h.264 video transmission. for one client. Delays, jitter, loss - all as in all. The most interesting question is how to connect remote clients. Whether you need a VPN, whether you need one network for all clients, or / 30 and PPTP, or NAT. Encryption implemented in Cisco TelePresence will be discussed later.
Now that we have learned a little about the functional purposes of various products (this is not all at all), we can begin to plan connection of clients, access to the network, look at the root of implementation, etc.
There are several options for establishing a call for a connection (skinny did not consider):
• h.323 - a set of protocols, users of communication cling to the gatekeeper (it is the zone controller, it is the gatekeeper, implemented in VCS) - the call handler. Gatekeeper clings to h.323 MCU;
• sip - session initialization protocol. Need a sip server (which is in VCS). It will register users, it is also SIP-proxy. It clings to the MCU (for the case of calls from 3 participants).
You can quote from the Cisco Video and TelePresence Architecture Design Guide:
SIP (SIP) is a protocol for communication and signaling. SCP and H.323 are purely telecommunications protocols. It is not necessary to understand or support. On occasion, however, this strength becomes one of the disadvantages because it complicates interoperation between vendors. Furthermore, SIP is less detailed in SCCP or H.323 specification, vendor interoperation is somewhat challenging at times. For example, in SIP there is more than one way to implement some features. If you are incompatible.
What sip that h.323 - equally useful. It is worth mentioning that h.323 is not a protocol, but recommendations for the protocols used. And these protocols have the character of a standard. The functions are the same. Although sip wins on the following criteria:
• more convenient to scale;
• the connection is established in 1 handshake, when in h.323 there will be 100500;
• many will notice the similarity of SIPs with the notorious HTTP protocol. True, like, understandable.
To begin with, it is important for us to determine the topology, or topologies that we want to scatter. Suppose the simplest scheme, we definitely need telepresence, video h.264 and conference SIP + h.323. A set of VCS for registration of participants and a sip server on board, an MCU for conferencing, endpoints with HD cameras and an Internet channel will cope with this.
Lyrical digression : Working with Cisco TelePresence will have to face a large number of non-tsisko devices: these include Tandberg and Codian. Cases are: once in the recent past, they were all independent of each other. Tandbert was considered the giant of video communications, and Kodian specialized in the production of MCU-nis. In 2007, the British Kordian became (for 270 million Baku) part of the giant Tandberg, and in 2010, the Tandberg became part of the giant Cisco (for 3.3 billion). Tandberg now manufactures its equipment under the TANDBERG Cisco brand, and Kodian supports and manufactures its equipment with the supply of Tsiski under the old Codian brand. Those. speaking of Kodians, etc., we mean Cisco “Om-nom-nom” corp.
The inclusion scheme will be:

Licensing
Ask a question about licensing. Since users live and are registered on VCS, and the combination of three or more clients occurs on the MCU, it is logical to assume that Cisco will unlikely give their clients unlimited possibilities for connecting conference participants. Limit the number of times, this is the maximum available number of user registrations. Initially, the machine (VCS) has the capacity for 2500 registrations (depends on the purchase configuration). You can assemble a cluster (maximum 6 devices). With the cluster, you can expand the number of MAXIMUM registrations to 10,000. Less than it should be - this is because of the reservation, i.e. if one piece of iron fails, users can be ported to the second. Limits number 2 and 3 are traversal and non-traversal calls. Traversal calls are:
• Calls from H.323 to sip (and vice versa);
• Firewall traversal call Assent;
• Firewall traversal call h.460;
• Ipv4-ipv6;
• Expressway that receives a call but does not have an extended license for local calls can use one traversal license for one call.
Non-traversal is a call inside the ipv4 network, from sip to sip, calls between VCSs, i.e. the simplest calls that do not require tricky manipulations. You can buy additional licenses for 10, 20, 50, 100, 200 and 300 pieces. By the way, if you assemble a cluster (also 6 pieces), you can get 2000 non-traversal and 400 traverse licenses. Also, many additional functions are subject to licensing for VCS, such as FindMe, Advanced Account Security, Device Provisioning and much more. Unfortunately, I didn’t find a single word by expanding the number of sip domains created (by default there are 200, but far more!).
MCU licensing is a possible number of participants in the conference. Consider the example of the Codian MCU-4210 MCU 4200 Series: it has the ability to include up to 20 participants in a video conference, has an additional 20 licenses for audio participants. For comparison, the Codian MCU-4220 can only 40 (video and add. Audio). Here 20 participants means that there are 20 virtual ports on the device that the device commutes with each other. Those. more than 20 - no way. A cluster can be assembled only if you have something from super-glands, such as the Supervisor MCU MSE 8050 stuffed with blades MCU MSE 8510 blade. By the way, there is a video broadcasting server on the same MCU-shke (4210).
Encryption
We will understand what is encrypted: first alarm. It is encrypted with AES (DES, 3DES), the key is selected according to Diffie-Hellman. It is activated by pressing a button in a colorful web-muzzle. Secondly, the transmitted traffic (media data) is encrypted, by the same AES, the key for the same Diffie-Hellman. And it turns on in the same way.
If the securiness seems insufficient, then it is possible to lift VPN tunnels to clients, write ACLs, configure Firewalls, etc. Turn on paranoia:
• if SIP, then SIPS (same sip, but with TLS. The address is not written as sip: <> @ ..., but sips: <> @ ...)
• if TCP / UDP, then TLS
• if RTP, then SRTP
• if the client is far away, then GRE / IPsec
• well and everything that we will think up
It is clear that this will increase the packetization time and the overall overhead.
VCS Software Overview
By itself, the firmware is very convenient (X7.2.2), has a manual for itself on board, it opens with the Help button in the upper right corner. The help window that opens in the window provides background information about the subsystem in which you are now (both theoretical and practical). Input fields are also highlighted with a miniature help.

Do not worry if something is not clear, or do not remember what field to write. Help will fulfill its purpose. Softwares can be attributed to the soft set of regulars (relatively powerful within their task).
Customization
We’ll skip the basic setting, that's really something, but “how to set up VCSe + VCSc + MCU in a hurry” on the Internet is full, but the most interesting can only be found in kilometers of guides (it took me a little less than a month from “below absolute zero "). Suppose that we have performed the basic settings, set the MCU neighborhood, the Traversal zone, set the time, etc. Now let's deal with call management “like a boss”, who are these neighbors, and why do we need Traversal.
Zones
Muddy muddied start here. A zone is an abstract set of anything (domains, ip-addresses, devices, services) to which a certain set of rules apply. Zones are needed to manage bandwidth, authenticate and route calls, and this applies immediately to everything in the zone. When creating Dial-Plans, you need to specify from which zone to which call to transfer (and not to which domain). So it is easier to control everything that happens, however, setting up this outrage may seem dreary.
All end devices, VCS-ki and MCU-shki, in general, all your devices are included in the Local Zone ( LocalZone ). A local zone can be divided into subzones. Therefore, for management flexibility, you can create a separate subzone for a new sip domain. You can create them up to 1000. The domain that will belong to a particular subzone needs to be determined using the “Subzone membership rules”.
Zones are also neighboring ( Neighbor ), forwarding ( Traversal (client-server view)), ENUM and DNS . The last two for ENUM and DNS queries, they need to show which servers to ask for names and E.164. Traversal zone is needed for routing calls between the VCS Control and Expressway firewalls. Say, half of the customers inside will make a call through VCS Control, and half, which is located remotely, will use the Expressway tools. VCS Control– client, Expressway– server. Neighbor zone is needed, for example, to communicate with the MCU, or another VCS. Those who did not fall into any of the zones fall into DefaultZone , and work according to the rules of the default zone, which, generally speaking, you can not fill in with the rules, and everyone will just be rejected.

I will post screenshots in less so as not to clog the text with half-empty browser windows. Simply tell in words.
You can create Subzone (for bandwidth control, encryption and authentication) in the menu VCS Configuration -> Localzone -> Subzones . Click New , in the Policy area we allow registration Registration policy - Allow, and be sure to authorize: Authentication policy - Check Credentials. In the area of SIP Media encryption mode, you can determine the need for encryption. Bandwidth limitations are optional. This tool allows you to manage calls between zones.
Create SIP-domain ( VCS Configurations -> Protocols -> SIP -> Domains ). Click New , enter the domain name. You can create up to 200 pieces.
Creating membership rules for establishing domain membership in the subzone ( VCS Configuration -> Local zone -> Subzones membership rules ). The rule must contain the Name, priority, regular expression, under which the domain name will fall, and the subzone, the rules of which will be used in the given domain.

After the recipient and sender sabzone has been determined, call processing begins on the VCS (or VCS), according to the call policy rules ( VCS Configuration-> Call policy-> Rules ). First, we include them, secondly we write the rules. Anyone familiar with ACLs will see a lot of similarity. From where-to-policy is a simple scheme, only 3 points of the rule. The rule that is higher - it works earlier, you can change the position with the arrows up and down.

By this rule, we allow / prohibit calls to 123456 from the domain newdomain.ru, for example. There is an implicit Deny at the end or not, I, unfortunately, did not check, but just in case at the end I set the rule ". * ->. * Reject" ie block everywhere and anywhere. Naturally written earlier rules are written. Generally speaking, you can not include Call Policy, and steer calls at the level of dial-plans. But with the included rules, you will not even get to the dial-up plans, and if you have a lot of them, you do not need to run through the list of rules and
Now we have come close to Dial- plans, important and necessary things, without which nothing will work. Call processing at the stage of Dial-plan-s occurs in stages. First, the rules of type “ Transform ” are triggered They allow you to do anything with addresses: cut off the domain part, add a domain part, change the name of the recipient, the sender. Let's say you want to call from the Cisco background to a thug number, “666666” for example, and get into the conference, you have rooms for you, and there is no need to create another one. So, we write the transform into the existing room and deal with it. Here is an example of how to make 639801 from 666666.

After the transform is completed and the transform rules applicable to the call have run out, processing begins according to the rules of the Search rules . Create a Search Rule for dial plans, for routing search requests to specific zones ( VCSConfiguration -> Dial-Plan -> SearchRules ). An example of the rule for the subzone domain is below.

Please note that the rule created for the outgoing zone specified in the Source name searches for the Pattern string in the request, specified as the recipient suffix ( Suffix ) of the URI "nik". In other words, if from a zone nik a call has a destination address nik, then you need to look for this address in the local zone ( Local Zone ). The rule in the drop-down field State is turned on in the Enable position.
Now a couple of words Pattern matching variables . Yes, yes, and the most pleasant thing - these things work in general everywhere, if there is a regular search, suffix or prefix in the search. These are variables of the type% pattern%, which are used in regular programs, Search Rules, and generally everywhere where you work with ip-addresses or sip-domains.
A brief but useful list of variables:
% localdomains% - all local sip domains
% ip% - all ipv4 and ipv6 addresses
% ipv4%,% ipv6% the same, but separately
% localdomain1% - sip domain with index 1 (varies from 1 to 200)
% systemname% - systemname
The question is - who will call? There are several ways to create a sip user. The first obvious one is to create a local user directly in VCS (VCS Configuration -> Authentication -> Devices -> Local Database ). The second option is to create a user in TMS (we still have a manager). To create users of end devices (registered with devices) go to the menu System -> Regulation -> Users . On the left in the Create Group and Users menu ( Add Group , Add users ). In the same menu on the left, below, select the Configuration Template and create a template for the group. There is a reservation that for different terminal devices the patterns will be different, but, in fact, with the same set of options. For example, the domain, the address of the SIP server, the address of the phone book, etc. ... A set of schemes is downloaded to TMS, all schemes are filled by the administrator. Filling the template is intuitively understandable, but the schemes of this template for end devices (be it a jabber client, or an E20 terminal) must first be downloaded from the site

It is possible to perform authentication after integration into AD or LDAP, but we did not have to.
Now Expressway. Create a SIP domain in the same way as in Control-e. Since TMS and Expressway are in different networks and are separated by an ACL, the user also needs to be created in the Local Database (Similarly, create a sub-zone and a membership Rule for membership in the sub-zone). To enable authentication, enable Search Rule using the SIP protocol, with the DefaultZone source, you need to search by the following regular schedule ^ (. +) @ Domain \ .ru $ , and send it to the Traversal Zone for VCS Control. For what and why - it turned out only empirically: before registration, since it is NOT control, no one gets under "his" network, the user is not in the domain, he is not in the subband, i.e. all non-registered individuals fall into DefaultZone.
You can create 2 universal rules, Call's to Traversal zone and Call's from Traversal zone for calls between VCS-kami (we can now operate with such concepts?). It is not difficult to guess what kind they will be, but if you do not need to allow end-to-end calls, it is better not to write such a general rule, but to do it for each domain separately.
Briefly about the MCU. Actually, the Conference itself, as we remember, is organized at the MCU. The management of conferences is simple, we set up the h.323 VCS connection with the MCU (car and cart guides on the Internet on this topic) and create the conference itself. The features of the MCU help are the same as on VCS, but still: a conference is created in the Conference tab with the button “ Add a new conference ”. When you create a conference, most of the fields will be filled out of a template (previously configured), you only need to fill in the following fields:
• Name - Sign Identifier
• Digital ID — numbers added to the prefix for registration
• PIN if necessary
• Guest Aidish
• Guest PIN.
Templates provide automatic filling of some fields, you can change them in the menu Home -> Conferences -> Templates . In addition to the basic settings, a custom layout will be available for configuration ( Main page: -> Conferences -> Conference “name” -> Custom layout ). It defines the location of video conferencing participants on the screen.
So from scratch, you can configure a conference dialer from a pile of expensive pieces of iron. Thank you for living to the end and happy new year to you!
Sources
habrahabr.ru
www.cisco.com
www.anticisco.ru
linkmeup.ru
mcu.dc.codian.com
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/208106/
All Articles