Identification based on movement data (tracking)
Identification based on movement data
Not so long ago, I came across an interesting article on the network - an analytical report on how you can identify the user of a mobile device with a 95% guarantee, knowing only 4 points (in fact, base stations) through which he got in touch at certain intervals time (1.5-2 hours). What was the essence of it ...
Among the scientific studies in the field of access control based on location data, the work of a group of American and British researchers [1], who conducted a detailed analysis of movement data of approximately 1.5 million cellular network subscribers for more than a year and a half, is particularly worth noting. The task of the analysis was to identify how unique the routes of movement of subscribers are and whether it is possible, having only data on the subscriber's stay at certain points for some time, it is sufficient to accurately identify his personality. The result of the study was the conclusion that, knowing only 4 space-time points, you can identify a person with 95% probability.
According to researchers, data on the movement of subscribers has long been closely interested in various commercial organizations [1] and are trying to get them in all possible ways [2]. Table 4 provides an overview of location methods and their accuracy.
Table 4
Location methods and their accuracy
')

As already noted, the study used a sample of data on the observation of movements of 1.5 million subscribers for 15 months [1], which guaranteed the presence of a representative sample. On average, as noted, data from each subscriber was transmitted on average through 6500 antennas, the phone was used by subscribers on average 114 times per month (calls and SMS transmissions). The accuracy of location measurement varied from 0.15 km2 in cities to 15 km2 in rural areas.
Figure 1 shows the main results of the study in the form of a graph of the dependence of the unique route on the number of space-time points. As can be seen from the graph, with two space-time points, the uniqueness of the route (the columns of the green diagram, where) is approximately 50%, i.e. identify by two points of the subscriber is almost impossible. When choosing 4 or more points, the uniqueness of the routes is already more than 95%
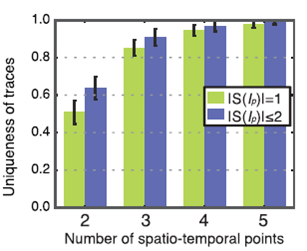
Figure 1 - The dependence of the unique route on the number
space-time points
In addition to the dependence of the uniqueness of the routes on the number of space-time points, the dependence on the accuracy of measurements in time and location data was also investigated. The results of the research are presented in Fig. 2. In particular, diagrams A (for 4 space-time points) and D (for 10 space-time points) of Fig. 2 show the dependences of the route uniqueness on time intervals of measurements of location data and the number of hundreds of base stations of a mobile station. communication network.
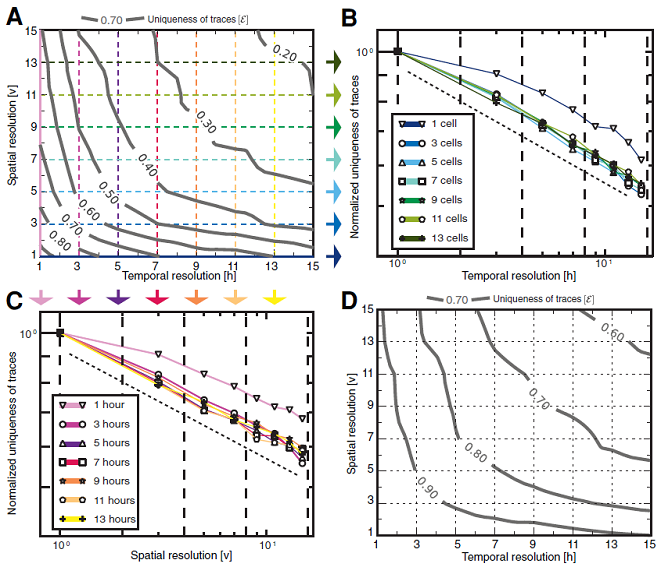
Figure 2 - The dependence of the unique route from time (figure B) and
spatial (diagram C) resolution (measurement accuracy)
The general conclusion of this work is that the routes of movement of subscribers are highly unique and with their help it is possible to identify the person. Thus, the movements of subscribers to some extent are personal data, respectively, this conclusion implies certain consequences regarding the confidentiality of personal data and, in particular, the protection of data on the location of users.
Sources:
1. Jakob, EB Context-Aware User Authentication - Supporting Proximity-Based Login in Pervasive Computing / Jakob E. Bardram, Rasmus E. Kjaer, Michael F. Pedersen, - Berlin: UbiComp, LNCS2864. - № 2003. - P. 107-123.
2. Ilyin S. Navigation without GPS. How to determine your coordinates by IP, GSM / UMTS and Wi-Fi / Stepin Ilyin, - Hacker, 2009. - № 4. - p. 124.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/207922/
All Articles