Cryptolocker 2.0 or fake?
In a previous post on ransomware (ransomware), we pointed to the activation of the FileCoder family, which is used by cybercriminals to encrypt user files with the subsequent demand for ransom for decryption. Already since July 2013, attackers have redoubled their efforts to spread this type of malware. In addition, during this period of time, the appearance of a new modification of Win32 / Filecoder.BQ , which is better known as Cryptolocker and is the most dangerous variant of the cryptographer, was recorded. When infecting Cryptolocker, the user either loses his data or is forced to pay attackers for decryption.

As can be seen in the statistics below, Cryptolocker is most active in the United States. Obviously, this region is the most attractive for attackers due to the sufficient user consistency. It is easier for attackers to make a profit this way, because many users are willing to pay the required amount only to regain access to the original files. Not only Cryptolocker, but also such well-known banking malware tools as Zeus or SpyEye were also focused in their time primarily on the United States because of the most monetization.
')
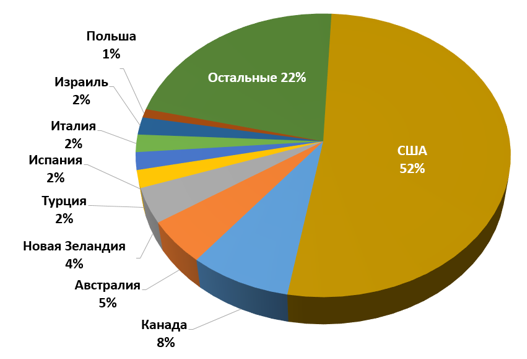
Fig. Geography of distribution Cryptolocker.
Last month, we discovered another Filecoder family that caught our attention because the name Cryptolocker 2.0 was present in the modification code. This modification was added by our analysts like MSIL / Filecoder.D and MSIL / Filecoder.E .
Analysis of the new version shows that both modifications (regular Cryptolocker and Cryptolocker 2.0) work in the same way. After infecting the system, they search for certain file types (by extension) in the file system, encrypt them, and display a message to the user about the need to pay the ransom for decryption. Both modifications use the RSA public key algorithm for encryption. At the same time, there are certain differences between the two families.


There are three visible differences between these families. The first version uses RSA-2048, while the new version claims the use of a more robust RSA-4096 (although in fact it uses RSA-1024). Another difference is that Cryptolocker 2.0 displays the amount of time left before the proposed deletion of the RSA private key (with which you can decrypt the key unique for each AES file, through which you can decrypt the file itself). In addition, version 2.0 accepts ransom only in bitcoins , while the first version also accepts MoneyPak and Ukash.
There are other differences between these families, which were identified after the analysis of malicious code. The most obvious is the programming language that the attackers used to develop these modifications. A regular Cryptolocker is written in C ++, and a new one in C #. The files and registry keys used by these modifications also differ, and the number of file extensions to be encrypted has also been increased in the new version; now it is also aimed at audio / video files and image files: .mp3, .mp4, .jpg, .png,. avi, .mpg.
When the malware is launched on the system, it contacts the C & C server manager and requests the unique RSA public key from there. Then each file matching the encryption criterion is encrypted using a unique 3DES key, which is then in turn encrypted using an RSA public key that was received from the server. This encrypted key will be written into the body of the auxiliary file, which will have the same name as the original one, but one more extension “.k” (% filename%.% Fileext% .k) will be added to it.
Thus, files can be decrypted if the RSA private key is known, which will help to decrypt the 3DES keys (AES in the case of the first version). Another difference between the versions is that the first Cryptolocker stores the encrypted key at the end of the encrypted file, and not in a separate file.

In addition to Cryptolocker's main feature - file encryption, it contains additional features, for example, it displays windows on the desktop that mimic “activators” or shareware hackers software: Microsoft Windows, Office, Team Viewer, Adobe Photoshop or even ESET Smart Security.


Cryptolocker chooses which window to display to the user, depending on the name of the executable file from which it was launched. Once launched, it is installed on the system and then begins to encrypt files. This method of masking allows you to put down the vigilance of users who resort to the help of various hackers and use similar software to violate the integrity of proprietary programs.
We note that Cryptolocker 2.0 has the ability to spread through removable media, overwriting the contents of the executable file on your body. The new version also features the ability to steal Bitcoin wallets files, launch a legitimate BFGMiner Bitcoin generation application without the user's knowledge, or use the compromised system as a bot to organize DDoS attacks against certain servers.
findings
Taking into account all the above-mentioned differences between Cryptolocker and Cryptolocker 2.0, we cannot conclude that this is indeed a new version of this malicious program. The attacker's move from C ++ to C # is a rather unexpected solution, but at the same time, none of the key differences can be considered a significant improvement in the capabilities of the malicious program.
The malicious software Cryptolocker 2.0, which shows up as MSIL / Filecoder.D and MSIL / Filecoder.E, is really dangerous and can cause a lot of harm to users who do not back up their data. In the case of Cryptolocker, backing up data is one of the best defenses against its destructive actions.
We also recommend using the seventh version of ESET Smart Security and ESET NOD32 AV products, as they contain the special feature of extended memory scanning. It helps improve the detection of already known or as yet unknown modifications of malicious programs, including Filecoder.


As can be seen in the statistics below, Cryptolocker is most active in the United States. Obviously, this region is the most attractive for attackers due to the sufficient user consistency. It is easier for attackers to make a profit this way, because many users are willing to pay the required amount only to regain access to the original files. Not only Cryptolocker, but also such well-known banking malware tools as Zeus or SpyEye were also focused in their time primarily on the United States because of the most monetization.
')

Fig. Geography of distribution Cryptolocker.
Last month, we discovered another Filecoder family that caught our attention because the name Cryptolocker 2.0 was present in the modification code. This modification was added by our analysts like MSIL / Filecoder.D and MSIL / Filecoder.E .
Analysis of the new version shows that both modifications (regular Cryptolocker and Cryptolocker 2.0) work in the same way. After infecting the system, they search for certain file types (by extension) in the file system, encrypt them, and display a message to the user about the need to pay the ransom for decryption. Both modifications use the RSA public key algorithm for encryption. At the same time, there are certain differences between the two families.


There are three visible differences between these families. The first version uses RSA-2048, while the new version claims the use of a more robust RSA-4096 (although in fact it uses RSA-1024). Another difference is that Cryptolocker 2.0 displays the amount of time left before the proposed deletion of the RSA private key (with which you can decrypt the key unique for each AES file, through which you can decrypt the file itself). In addition, version 2.0 accepts ransom only in bitcoins , while the first version also accepts MoneyPak and Ukash.
There are other differences between these families, which were identified after the analysis of malicious code. The most obvious is the programming language that the attackers used to develop these modifications. A regular Cryptolocker is written in C ++, and a new one in C #. The files and registry keys used by these modifications also differ, and the number of file extensions to be encrypted has also been increased in the new version; now it is also aimed at audio / video files and image files: .mp3, .mp4, .jpg, .png,. avi, .mpg.
When the malware is launched on the system, it contacts the C & C server manager and requests the unique RSA public key from there. Then each file matching the encryption criterion is encrypted using a unique 3DES key, which is then in turn encrypted using an RSA public key that was received from the server. This encrypted key will be written into the body of the auxiliary file, which will have the same name as the original one, but one more extension “.k” (% filename%.% Fileext% .k) will be added to it.
Thus, files can be decrypted if the RSA private key is known, which will help to decrypt the 3DES keys (AES in the case of the first version). Another difference between the versions is that the first Cryptolocker stores the encrypted key at the end of the encrypted file, and not in a separate file.

In addition to Cryptolocker's main feature - file encryption, it contains additional features, for example, it displays windows on the desktop that mimic “activators” or shareware hackers software: Microsoft Windows, Office, Team Viewer, Adobe Photoshop or even ESET Smart Security.


Cryptolocker chooses which window to display to the user, depending on the name of the executable file from which it was launched. Once launched, it is installed on the system and then begins to encrypt files. This method of masking allows you to put down the vigilance of users who resort to the help of various hackers and use similar software to violate the integrity of proprietary programs.
We note that Cryptolocker 2.0 has the ability to spread through removable media, overwriting the contents of the executable file on your body. The new version also features the ability to steal Bitcoin wallets files, launch a legitimate BFGMiner Bitcoin generation application without the user's knowledge, or use the compromised system as a bot to organize DDoS attacks against certain servers.
findings
Taking into account all the above-mentioned differences between Cryptolocker and Cryptolocker 2.0, we cannot conclude that this is indeed a new version of this malicious program. The attacker's move from C ++ to C # is a rather unexpected solution, but at the same time, none of the key differences can be considered a significant improvement in the capabilities of the malicious program.
The malicious software Cryptolocker 2.0, which shows up as MSIL / Filecoder.D and MSIL / Filecoder.E, is really dangerous and can cause a lot of harm to users who do not back up their data. In the case of Cryptolocker, backing up data is one of the best defenses against its destructive actions.
We also recommend using the seventh version of ESET Smart Security and ESET NOD32 AV products, as they contain the special feature of extended memory scanning. It helps improve the detection of already known or as yet unknown modifications of malicious programs, including Filecoder.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/207532/
All Articles