The most common mistakes in the Pivot project
Hello! More than half a year has passed since we made the pivot of our project. I will not publish the name of the project in order not to be considered as an advertising post. I would like to share with you stuffed cones. Below is an up-to-date MRR growth plate (Monthly Recurring Revenue). Everything seems to be not bad, but it could be even better.
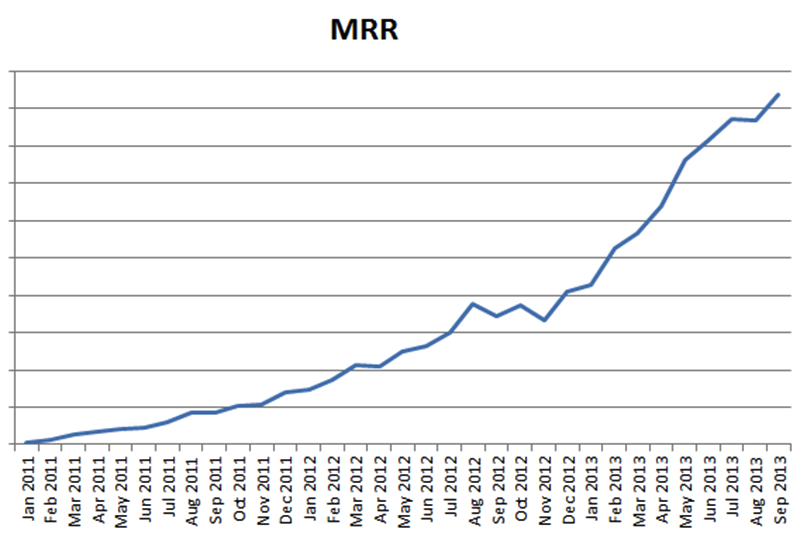
After analyzing what is happening, made conclusions and identified 3 errors that we made during the turn. We are definitely not the first and not the last who makes them. Details under the cut.
')
Before you implement something, you must conduct an experiment to test this hypothesis. The hypothesis must be clearly formulated with specific KPIs for which we will assume the hypothesis to be correct. The scan cycle usually looks like this:
After the hypothesis, we either make a Pivot or formulate a new hypothesis. And repeats everything from the beginning. I took part of the hypotheses on faith and implemented them without experiment. For example, we immediately changed the product positioning, changed the call on the website from “Build productive communication with customers” to “Organize an online customer community”, which led to a drop in conversion in registration up to 5 times.
Now we are testing all such things with at least A / B Testing. For example, now we are testing 3 landings with a different way of presenting information. The test was just launched, but now we can see from the graphs below how we made a mistake.

To eat an elephant, you need to cut it into pieces. And to concentrate at each moment of time on a specific hypothesis and its testing. In Eric Rees's Lean Startup book, 10 types of Pivot are described:
We managed to make four of them (3, 7, 8 and 9), and at the same time. Now I can say that of 4 turns, 2 were successful and 1 requires optimization and 1 was wrong. On the other hand, sometimes it is impossible to take and make a turn separately from the other. For example, you can not start selling the solution to the bank for 1000 rubles. However, by testing each pivot separately, you can greatly reduce the risks.
The implementation of paragraphs 3 and 7 allowed:
Officially, we announced a reversal after almost 3 years of the project, although we should have done it before. But better late than never. There are companies and persistent entrepreneurs who manage to make 4-5 pivots in 3 years and quite successfully. When there is no systematic approach, you can beat your head against the wall for a long time. If something does not work as it should - there is no point in pulling.
We stepped on this rake. Do not make such mistakes.

After analyzing what is happening, made conclusions and identified 3 errors that we made during the turn. We are definitely not the first and not the last who makes them. Details under the cut.
')
1. Hypothesis without testing
Before you implement something, you must conduct an experiment to test this hypothesis. The hypothesis must be clearly formulated with specific KPIs for which we will assume the hypothesis to be correct. The scan cycle usually looks like this:
- We put a hypothesis, we fix the indicators to which we aspire.
- We do an experiment.
- Analyzing the results.
- We continue until we do not know how to get closer to KPI.
After the hypothesis, we either make a Pivot or formulate a new hypothesis. And repeats everything from the beginning. I took part of the hypotheses on faith and implemented them without experiment. For example, we immediately changed the product positioning, changed the call on the website from “Build productive communication with customers” to “Organize an online customer community”, which led to a drop in conversion in registration up to 5 times.
Now we are testing all such things with at least A / B Testing. For example, now we are testing 3 landings with a different way of presenting information. The test was just launched, but now we can see from the graphs below how we made a mistake.

2. Too many turns at once.
To eat an elephant, you need to cut it into pieces. And to concentrate at each moment of time on a specific hypothesis and its testing. In Eric Rees's Lean Startup book, 10 types of Pivot are described:
- Pivot-increase: a small option in the product becomes a separate and main product.
- Pivot-reduction: one option in the product is not enough and the product is expanded by other options.
- Pivot consumer segment: changing focus from one target audience to another.
- Pivot customer needs: discard the initial customer needs in favor of another, more promising.
- Pivot platforms: move from application to platform or vice versa.
- Pivot business architecture: moving from b2b to b2c or vice versa.
- Pivot way of monetization: changes the approach to monetization of the product.
- Pivot growth mechanism: changing the approach to attracting customers.
- Pivot sales channel: the name speaks for itself.
- Pivot technology: change the technology on which the product is built.
We managed to make four of them (3, 7, 8 and 9), and at the same time. Now I can say that of 4 turns, 2 were successful and 1 requires optimization and 1 was wrong. On the other hand, sometimes it is impossible to take and make a turn separately from the other. For example, you can not start selling the solution to the bank for 1000 rubles. However, by testing each pivot separately, you can greatly reduce the risks.
The implementation of paragraphs 3 and 7 allowed:
- Increase LTV from 125,800 rubles in 2012 to 533,500 rubles in 2013 (for new customers).
- Increase ARPU from 3,500 rubles in 2012 to 13,500 rubles in 2014 (for all customers).
3. Too late.
Officially, we announced a reversal after almost 3 years of the project, although we should have done it before. But better late than never. There are companies and persistent entrepreneurs who manage to make 4-5 pivots in 3 years and quite successfully. When there is no systematic approach, you can beat your head against the wall for a long time. If something does not work as it should - there is no point in pulling.
We stepped on this rake. Do not make such mistakes.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/205676/
All Articles