Microsoft and Adobe released a set of updates, December 2013
The company has released a series of updates for its products, which cover 24 unique vulnerabilities (6 patches with the Critical status and 5 with the Important status). A detailed report on closed vulnerabilities, product components and their versions can be found on the corresponding page of security bulletins . This is the last patch tuesday this year, within which MS fixes vulnerabilities for products such as Internet Explorer, Windows, Office, Exchange, etc., and three updates are aimed at fixing Office products.

Update MS13-096 closes in-the-wild exploited vulnerability in Office CVE-2013-3906 (Win32 / Exploit.CVE-2013-3906.A). We wrote about it in more detail here . The attackers used specially crafted .doc files to install malicious code into the system through an exploit. Vulnerability exists in the processing code embedded in the document special image (TIFF codec). MS Word uses this component to open other objects embedded in the document, in this case TIFF images. Upgradeable are Windows Vista and Server 2008, as well as Office 2003-2007-2010. A reboot is required to apply the update.
')

The MS13-097 update closes seven vulnerabilities in all versions of Internet Explorer (6-11) for all supported operating systems, from Windows XP SP3 to Windows 8.1. Most fixable vulnerabilities are of the Remote Code Execution (RCE) type and can be used by attackers for remote code execution through a specially crafted web page. Two vulnerabilities CVE-2013-5045 and CVE-2013-5046 can be used by attackers to enhance their privileges in the system (Elevation of Privelege). Critical. Exploit code likely .
The MS13-098 update fixes the CVE-2013-3900 Remote Code Execution type vulnerability for all supported OS versions from Windows XP SP3 to Windows 8.1 / RT 8.1. The WinVerifyTrust function of the Wintrust.dll library is subject to correction. An attacker can modify a digitally signed ( Authenticode format) file to add malicious code to it, and bypass the signature verification mechanism (that is, without violating its integrity, if the integrity is checked by Windows). By modifying one of the system files in this way, an attacker can gain complete control over the system. Critical. Vulnerability is exploited in-the-wild. More details MS13-098: Update to enhance the security of Authenticode .
Update MS13-099 also fixes one RCE vulnerability CVE-2013-5056 for all supported OS versions. The Microsoft Scripting Runtime Object Library component, which is represented in the system by the Scrrun.dll library, is subject to correction. The attacker can compromise the user with malicious code through a specially prepared web page (drive-by). Use-after-free technique is used for operation. Critical. Exploit code likely.
The MS13-100 update fixes the RCE vulnerability in the Microsoft SharePoint Server product. The attacker can execute arbitrary code on the server by sending specially prepared content. Critical. Exploit code likely .
The MS13-101 update is aimed at eliminating five vulnerabilities in OS drivers. Three vulnerabilities are present in the Windows kernel-mode driver Win32k.sys (CVE-2013-3899 memory-corruption / EoP. CVE-2013-3902 use-after-free / EoP, CVE-2013-5058 integer overflow / Denial of Service) . Using these vulnerabilities, an attacker can either elevate his privileges in the system or cause it to freeze before rebooting. Another CVE-2013-3907 vulnerability is present in the Windows audio driver - portcls.sys. With its help, the attacker can also raise their privileges in the system. The fifth vulnerability CVE-2013-3903 is present in the OS kernel and can be used to provoke a system hang. This update is subject to all versions of the OS. Important.
The MS13-102 update fixes the CVE-2013-3878 Elevation of Privelege type vulnerability in the Local Remote Procedure Call (LRPC) component of the obsolete Windows XP SP3 and Windows Server 2003 SP2. An attacker can trigger a buffer overflow situation on the stack at the recipient in a specially crafted LPC message. Important. Exploit code likely .
The MS13-103 update fixes one EoP vulnerability in ASP.NET SignalR product. Important. Exploit code likely .
The MS13-104 update fixes one Information Disclosure VEVE-2013-5054 vulnerability in Office 2013-2013 RT. An error in the product is present when processing a specially prepared request to open an office file that resides on a malicious web page. At the same time, an attacker can get access to information about the current user’s access token. Important. Exploit code unlikely .
The MS13-105 update fixes four vulnerabilities in the Exchange Server 2007-2010-2013 product that can be used for remote code execution via a message with a specially prepared attachment. Critical.
Update MS13-106 fixes a flaw in the type of Security Feature Bypass for Microsoft Office 2007-2010 (hxds.dll). An attacker can bypass the limitations imposed by the ASLR when using a specially prepared web page in Internet Explorer. Thus, this vulnerability can be used in conjunction with another RCE vulnerability to execute remote code in the system. In this case, this opportunity gives the exploit code to successfully bypass the ASLR restrictions and pre-calculate the necessary address of the necessary code. The update delivers a new version of the hxds.dll library, which is compiled with support for the ASLR (/ DYNAMICBASE flag ). The flaw is exploited in-the-wild . More details MS13-106: Farewell to another ASLR bypass .
1 - Exploit code likely
The probability of exploiting the vulnerability is very high, attackers can use an exploit, for example, for remote code execution.
2 - Exploit code would be difficult to build
The exploitation probability is average, since attackers are unlikely to be able to achieve a situation of sustainable exploitation, as well as due to the technical peculiarities of vulnerability and the complexity of developing an exploit.
3 - Exploit code unlikely
The exploitation probability is minimal and attackers are unlikely to be able to develop successfully working code and take advantage of this vulnerability to conduct an attack.
We recommend our users to install updates as soon as possible and, if you have not already done so, enable automatic delivery of updates using Windows Update (by default this option is enabled).

Adobe has also announced updates for its Adobe Flash Player and Shockwave Player products.
Updates for Flash Player close two Critical vulnerabilities CVE-2013-5331 and CVE-2013-5332, which can be used for unauthorized code execution. The company reports that CVE-2013-5331 is already being exploited by cybercriminals who send emails with an .doc file attachment. This document contains a specially shaped .swf file used to execute code. Another vulnerability CVE-2013-5332 uses a use-after-free technique to execute its code.
Versions of Flash Player are subject to correction until relevant.
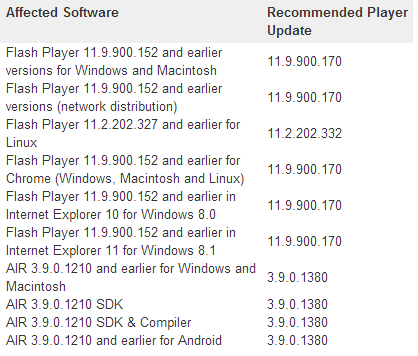
We recommend that users check the version of Flash Player used by your browser, for this you can use the official. adobe source here or here . Note that browsers such as Google Chrome and Internet Explorer 10+ are automatically updated with the release of the new version of Flash Player. You can get information on updating Flash for your browser via this link .

be secure.

Update MS13-096 closes in-the-wild exploited vulnerability in Office CVE-2013-3906 (Win32 / Exploit.CVE-2013-3906.A). We wrote about it in more detail here . The attackers used specially crafted .doc files to install malicious code into the system through an exploit. Vulnerability exists in the processing code embedded in the document special image (TIFF codec). MS Word uses this component to open other objects embedded in the document, in this case TIFF images. Upgradeable are Windows Vista and Server 2008, as well as Office 2003-2007-2010. A reboot is required to apply the update.
')

The MS13-097 update closes seven vulnerabilities in all versions of Internet Explorer (6-11) for all supported operating systems, from Windows XP SP3 to Windows 8.1. Most fixable vulnerabilities are of the Remote Code Execution (RCE) type and can be used by attackers for remote code execution through a specially crafted web page. Two vulnerabilities CVE-2013-5045 and CVE-2013-5046 can be used by attackers to enhance their privileges in the system (Elevation of Privelege). Critical. Exploit code likely .
The MS13-098 update fixes the CVE-2013-3900 Remote Code Execution type vulnerability for all supported OS versions from Windows XP SP3 to Windows 8.1 / RT 8.1. The WinVerifyTrust function of the Wintrust.dll library is subject to correction. An attacker can modify a digitally signed ( Authenticode format) file to add malicious code to it, and bypass the signature verification mechanism (that is, without violating its integrity, if the integrity is checked by Windows). By modifying one of the system files in this way, an attacker can gain complete control over the system. Critical. Vulnerability is exploited in-the-wild. More details MS13-098: Update to enhance the security of Authenticode .
Update MS13-099 also fixes one RCE vulnerability CVE-2013-5056 for all supported OS versions. The Microsoft Scripting Runtime Object Library component, which is represented in the system by the Scrrun.dll library, is subject to correction. The attacker can compromise the user with malicious code through a specially prepared web page (drive-by). Use-after-free technique is used for operation. Critical. Exploit code likely.
The MS13-100 update fixes the RCE vulnerability in the Microsoft SharePoint Server product. The attacker can execute arbitrary code on the server by sending specially prepared content. Critical. Exploit code likely .
The MS13-101 update is aimed at eliminating five vulnerabilities in OS drivers. Three vulnerabilities are present in the Windows kernel-mode driver Win32k.sys (CVE-2013-3899 memory-corruption / EoP. CVE-2013-3902 use-after-free / EoP, CVE-2013-5058 integer overflow / Denial of Service) . Using these vulnerabilities, an attacker can either elevate his privileges in the system or cause it to freeze before rebooting. Another CVE-2013-3907 vulnerability is present in the Windows audio driver - portcls.sys. With its help, the attacker can also raise their privileges in the system. The fifth vulnerability CVE-2013-3903 is present in the OS kernel and can be used to provoke a system hang. This update is subject to all versions of the OS. Important.
The MS13-102 update fixes the CVE-2013-3878 Elevation of Privelege type vulnerability in the Local Remote Procedure Call (LRPC) component of the obsolete Windows XP SP3 and Windows Server 2003 SP2. An attacker can trigger a buffer overflow situation on the stack at the recipient in a specially crafted LPC message. Important. Exploit code likely .
The MS13-103 update fixes one EoP vulnerability in ASP.NET SignalR product. Important. Exploit code likely .
The MS13-104 update fixes one Information Disclosure VEVE-2013-5054 vulnerability in Office 2013-2013 RT. An error in the product is present when processing a specially prepared request to open an office file that resides on a malicious web page. At the same time, an attacker can get access to information about the current user’s access token. Important. Exploit code unlikely .
The MS13-105 update fixes four vulnerabilities in the Exchange Server 2007-2010-2013 product that can be used for remote code execution via a message with a specially prepared attachment. Critical.
Update MS13-106 fixes a flaw in the type of Security Feature Bypass for Microsoft Office 2007-2010 (hxds.dll). An attacker can bypass the limitations imposed by the ASLR when using a specially prepared web page in Internet Explorer. Thus, this vulnerability can be used in conjunction with another RCE vulnerability to execute remote code in the system. In this case, this opportunity gives the exploit code to successfully bypass the ASLR restrictions and pre-calculate the necessary address of the necessary code. The update delivers a new version of the hxds.dll library, which is compiled with support for the ASLR (/ DYNAMICBASE flag ). The flaw is exploited in-the-wild . More details MS13-106: Farewell to another ASLR bypass .
1 - Exploit code likely
The probability of exploiting the vulnerability is very high, attackers can use an exploit, for example, for remote code execution.
2 - Exploit code would be difficult to build
The exploitation probability is average, since attackers are unlikely to be able to achieve a situation of sustainable exploitation, as well as due to the technical peculiarities of vulnerability and the complexity of developing an exploit.
3 - Exploit code unlikely
The exploitation probability is minimal and attackers are unlikely to be able to develop successfully working code and take advantage of this vulnerability to conduct an attack.
We recommend our users to install updates as soon as possible and, if you have not already done so, enable automatic delivery of updates using Windows Update (by default this option is enabled).

Adobe has also announced updates for its Adobe Flash Player and Shockwave Player products.
Updates for Flash Player close two Critical vulnerabilities CVE-2013-5331 and CVE-2013-5332, which can be used for unauthorized code execution. The company reports that CVE-2013-5331 is already being exploited by cybercriminals who send emails with an .doc file attachment. This document contains a specially shaped .swf file used to execute code. Another vulnerability CVE-2013-5332 uses a use-after-free technique to execute its code.
Versions of Flash Player are subject to correction until relevant.

We recommend that users check the version of Flash Player used by your browser, for this you can use the official. adobe source here or here . Note that browsers such as Google Chrome and Internet Explorer 10+ are automatically updated with the release of the new version of Flash Player. You can get information on updating Flash for your browser via this link .

be secure.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/205340/
All Articles