DARPA launches 20-meter membrane telescope into geostationary orbit
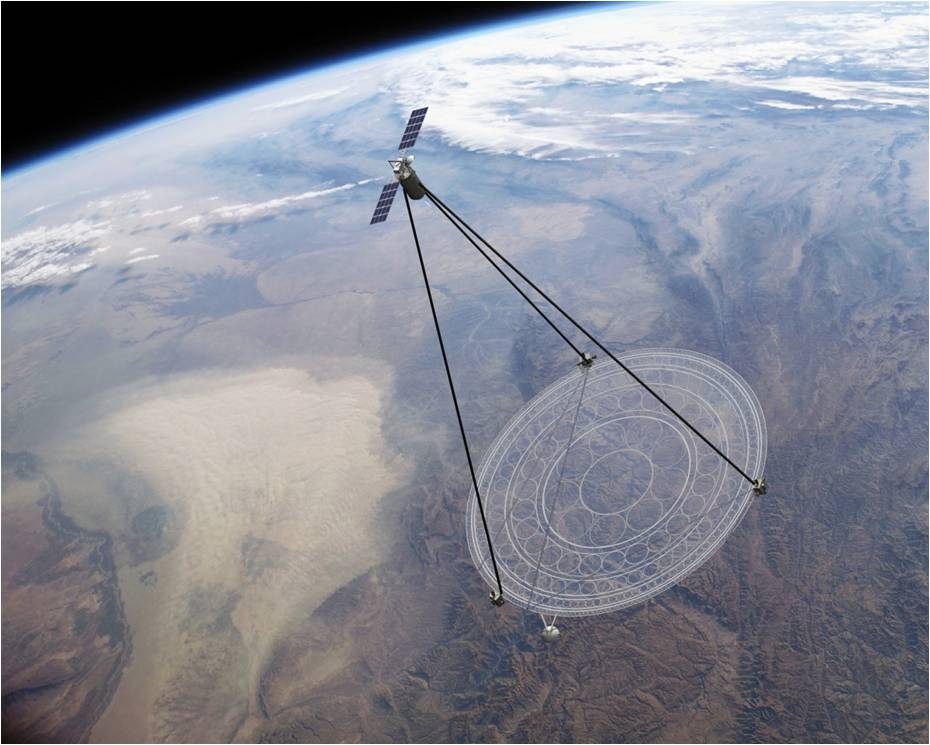

Modern military and commercial satellites engaged in photographing the Earth fly in orbits several hundred kilometers high. Moreover, their resolution reaches 50 cm per pixel. Placing in low orbits creates a mass of inconvenience - a satellite cannot conduct a continuous survey of one point, moreover, there can be no satellite at all at the right place at the right time. The geostationary orbit is devoid of these shortcomings, but from a height of 35,786 km above sea level it is impossible to obtain images of an acceptable resolution. The higher the resolution requirements, the larger must be the diameter of the lens or mirror of the telescope. So much so that to bring such a bulky telescope into a geostationary orbit is not yet economically feasible.
The DARPA MOIRE project ( Membrane Optical Imager for Real-Time Exploitation ) is designed to solve this problem with a fundamentally new telescope design. Instead of lenses or mirrors, it uses thin transparent membranes with microscopic grooves of a concentric shape that focus the light rays by diffraction. The effective diameter of such a diffractive lens will be 20 meters. When folded, the telescope is compact enough to be able to be raised into orbit by an Atlas-5 class launch vehicle. The resolution of the membrane telescope will be 2.5 meters per pixel with a field of view of 10 to 10 km. The telescope will transmit the image to the ground in real time at a frequency of 1 frame per second. It can be sent to almost any visible from orbit point of the Earth, that is, several such telescopes almost completely cover the entire surface of the planet.
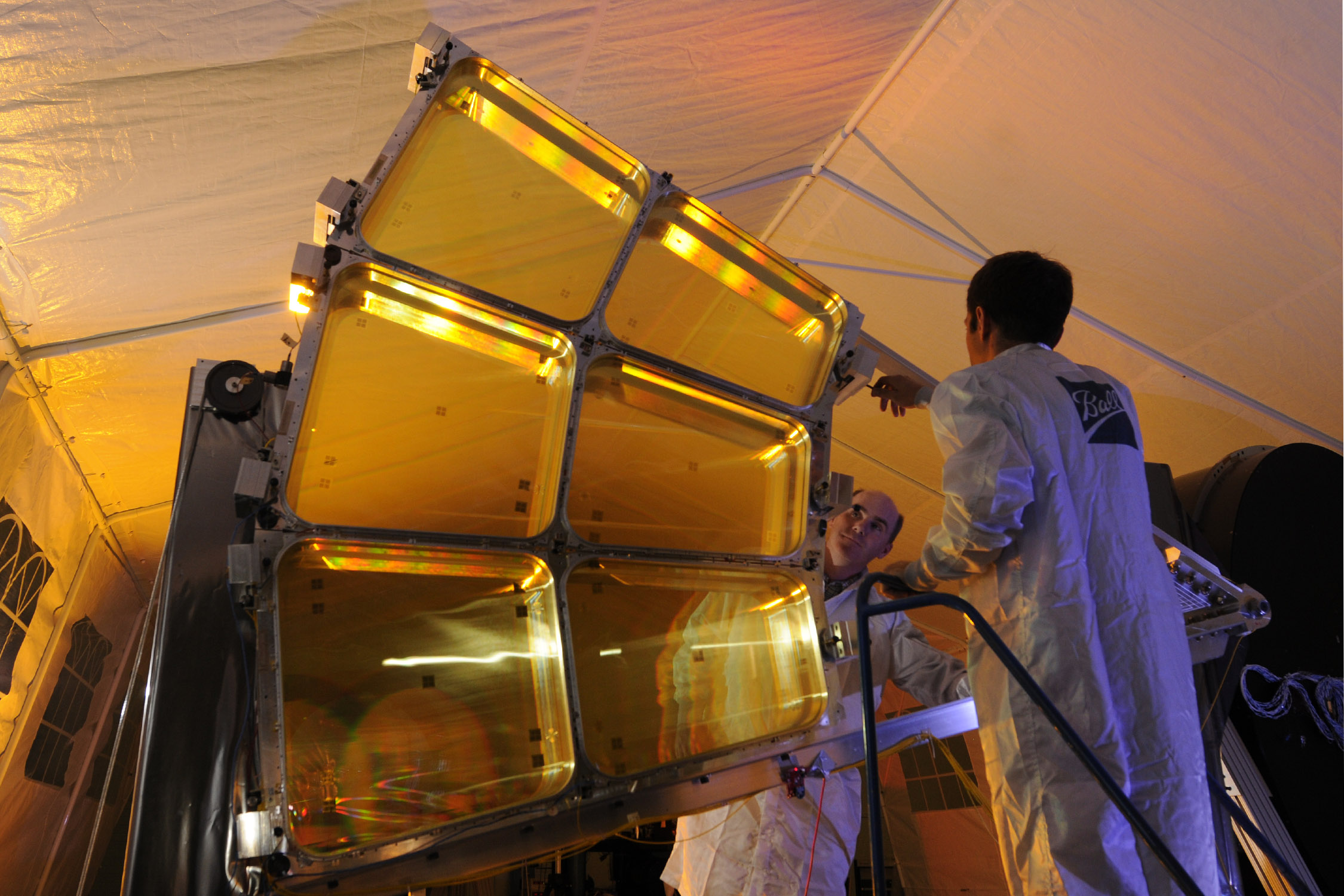

One of the sections of the MOIRE telescope prototype
')
Although the image quality of a membrane telescope is smaller than that of a refractor or reflector of the same size, this is offset by its small mass. A traditional telescope with similar characteristics would weigh about seven times more. MOIRE telescope will be the world's largest optical telescope. The diameter of the Hubble telescope is 2.4 meters, the telescope of James Webb , which is to be launched into orbit in 2015, will have a mirror diameter of 6.5 meters. Even the largest ground-based telescopes have a smaller diameter. Only in 2020 it is planned to commission the Giant Magellan telescope with a mirror diameter of 24.5 meters.
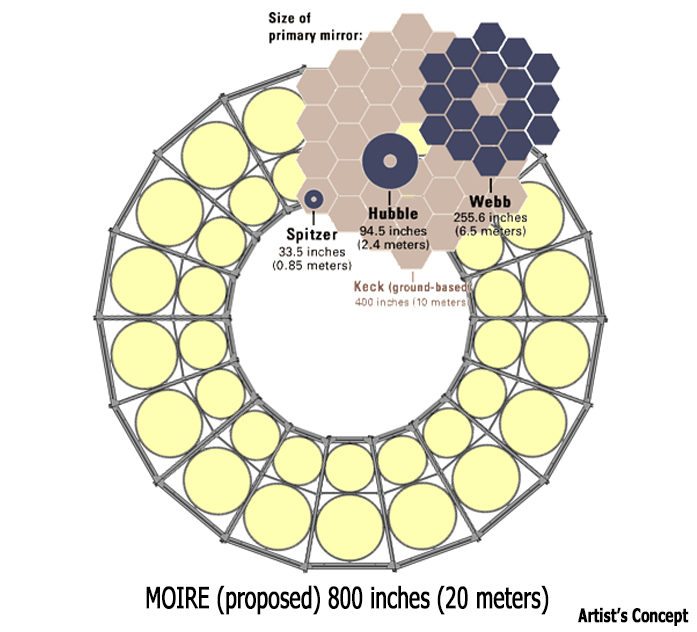
Comparing the size of MOIRE with the largest space and ground-based telescopes.
The main contractors for the MOIRE project are the US Air Force Academy and Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corporation. To date, ground tests of the 5-meter telescope prototype have successfully passed. Although the main purpose of MOIRE is military intelligence, it is possible that the experience gained from its creation will be used to build telescopes for astronomical observations, because Kepler and James Webb telescopes are also developed by Ball Aerospace & Technologies.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/205132/
All Articles