Stock Market Technologies: Direct Access to the Exchange
In previous topics, we have already reviewed the general structure of the Russian stock market, talked about trading terminals that investors use, and touched on the creation of robots for automated trading thanks to the brokerage APIs . However, at a time when on the stock exchange for many traders everything is decided in a fraction of a second , the work according to the “user – brokerage system – core stock” scheme is not suitable for everyone. That is why there was a technology that allows to optimize this chain as much as possible - direct access to the exchange.

The situation on the stock exchanges around the world in recent years has been evolving according to one scenario - traders from all over the world have come together in the struggle to achieve the highest speed of trading operations. First of all, this is due to the rise of the so-called algorithmic trading in which operations are performed by special robots.
')
As a rule, robots make a huge number of such operations in one trading session (from thousands to hundreds of thousands), earning each of them is not very much, but thanks to the volume, providing a stable income for its owner. With this method of trading speed comes to the fore. If the order sent to the market by your robot lingers on the way for at least a couple of milliseconds, then you may miss profits. And just as well, if the market data will be sent to the robot with a delay, it will not be able to quickly respond to changes within the framework of a given algorithm, which is also fraught with losses.
To minimize time costs, traders resort to a whole range of measures from optimizing the code of their software to acquiring “broad” communication channels. However, the greatest gain in time can be achieved by removing the broker system from the bidding path.
Direct Access (DMA) is a technology of high-speed access to stock exchanges, in which the application is placed in the exchange trading system directly, bypassing the broker trading system. All this allows to significantly reduce the time of delivery of the application to the exchange and receiving information about its status.
With such an organization of the trading process, a trader can expect a significant time gain. For example, if you are directly connected to the stock and currency markets of the Moscow Exchange, the processing time of an application decreases to 0.5 ms , and in the FORTS and Standard markets it does not exceed 3 ms. When using the same broker system, applications are processed in a time from 5-10 ms to 150-500 ms, depending on the broker system, market type and connection method. Those. through broker systems, applications are processed 10-100 times slower than with a direct connection (although this speed suits many merchants quite well).
Naturally, the use of direct access technology is more expensive (often significantly) and is suitable only for those who perform a large number of operations per day and are willing to pay for their speed.
Despite the fact that technically, thanks to the direct access to the stock exchange, traders can perform trading operations without a broker, the “documented” access is still carried out through broker companies. That is, in order to be able to directly trade on, say, the stock market of the Moscow Stock Exchange, an investor needs to enter into an agreement with a broker and already have him purchase the service of direct access to the stock exchange.

As a result, Russian clients can gain access mainly to the markets that make up the Moscow Exchange:
In addition, some brokers can arrange direct access to foreign exchanges, such as the London Stock Exchange (LSE), CME markets (futures and options), etc.
In general, the direct access scheme is as follows: a server with a trading robot is connected to an intermediate server, which is located as close as possible to the core of the exchange trading system. On this server, special software is installed - the so-called gateways, which are used to transfer orders and market information directly to the trading system. At the same time, various protocols and methods of connection are used to perform transactions and receive data.
The FIX (Financial Information eXchange) protocol is a financial information exchange protocol that is a global standard for exchanging data between participants in exchange trading in real time. It is supported by the world's largest exchange platforms, including the Moscow Stock Exchange.
To obtain market information (Market Data), the FAST protocol (Fix Adapted for STreaming) is used, a standard developed by the creators of the FIX protocol, which makes it possible to achieve significant data compression capabilities for transferring large amounts of market information with minimal time delays. In addition to the Moscow Stock Exchange, it is used on the NYSE, Nasdaq-OMX and many other global sites.
Also for direct connection using native protocols. These protocols emerged before the merger of the MICEX and RTS exchanges into the Moscow Exchange.
For example, in the markets related to the RTS (FORTS - futures and options, Standard ), the Plaza II protocol is used to directly perform transactions and obtain data in the connection mode.
To perform trading operations and obtain stock exchange data on the sites previously belonging to the MICEX exchange (currency and stock markets), a bi-directional MICEXBridge gateway (TEAP) is used .
Technically, connection to the Moscow Exchange is possible in several ways, such as connecting via the Internet, connecting using the universal connection scheme or using the exchange colocation.
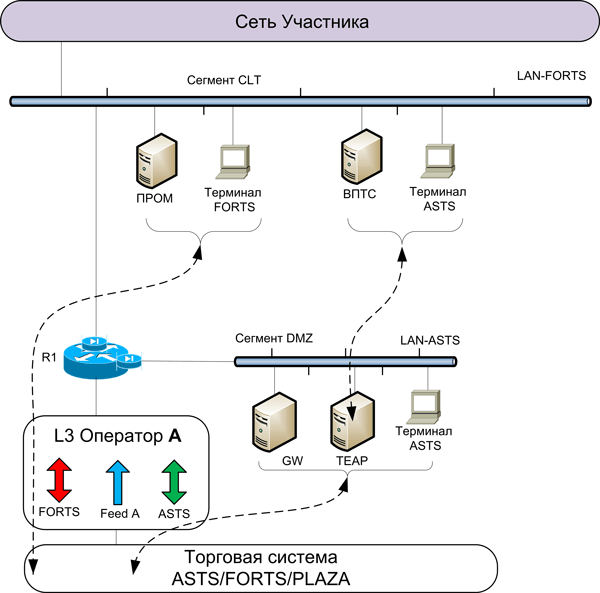
Universal wiring diagram
In more detail, the financial information transfer protocols and connection methods will be discussed in one of the following articles.
For those traders who do not use robots to trade, it is possible to trade on a direct connection using their more familiar trading terminal. However, the software that works with the brokerage trading system does not work using exchange protocols of direct connection, therefore separate programs are created for it (some of them are presented here ).
In addition, due to the fact that direct connection technologies are open, investors can independently develop software for themselves. However, since these programs ultimately have almost direct access to the core of the trading system, the exchange introduced a procedure for certifying trading solutions from third-party developers in order to rule out the likelihood of the “mad robot” putting the entire system to rest. This procedure is carried out as the development of individual investors, and software, created by special companies to order.
If you continue to move along the chain to reduce the time to perform operations, it becomes obvious that you need to place the trading robot not only logically, but also physically as close as possible to the servers with the core of the exchange trading system.
The robot can be located either on a separate server that can be rack mounted in the data center (this service is called Colocation), or on a virtual machine (Hosting), which in turn is launched along with the virtual clients of other clients on the server also installed in the data center , next to the exchange servers. Hosting services are provided, as a rule, only by large brokers who have their own counters in data centers.
Now, the Moscow Exchange trading servers are located in data center M1. Trading robots connected to exchange servers can be located in two zones - the so-called DMA-free collocation zone and the exchange's direct collocation zone.

Placing in the collocation zone of the exchange has obvious advantages: virtual machines and servers connect directly to the exchange core, while from the free zone the connection goes through the intermediate servers MICEX Gate and Plaza II. In addition, FAST data acquisition and a dedicated channel for connecting to the IOB London Stock Exchange market (Russian ADR trading in London) are available only from the exchange collocation zone.
One of the ways to significantly reduce infrastructure costs is to place the robot in a free colocation zone. The services provided in it are almost similar to the services of the exchange colocation zone. However, free cheese is only in a mousetrap, for the relative cheapness of the placement of the robot will have to "pay" a few milliseconds to increase the speed of transaction processing.
In addition, since the interfaces for creating direct connection software do not initially imply any graphical possibilities for displaying information about tenders, the ability to synchronize orders and positions, orders and positions formed on a direct connection with the broker’s real-time trading system is almost a necessary thing for control of trade operations. Therefore, many brokers try to provide their clients with such opportunities.
All this, of course, costs money and, in comparison, with the usual access to the stock exchange through brokerage systems, rather large. However, for those investors who have reached a certain level of income, such spending makes sense. According to representatives of the exchange , the owners of robots who won the Best Private Investor competition in 2011 spent on services related to direct access from 100 to 500 thousand rubles. per month. However, taking into account the fact that some merchants (although there were not so many of them) managed to reach a yield of 8000% and earn millions of rubles a month (taking into account all broker and exchange commissions), these expenses quickly paid off.
That's all for today! Thank you all for your attention, we will be happy to answer questions in the comments.

Why do you need it?
The situation on the stock exchanges around the world in recent years has been evolving according to one scenario - traders from all over the world have come together in the struggle to achieve the highest speed of trading operations. First of all, this is due to the rise of the so-called algorithmic trading in which operations are performed by special robots.
')
As a rule, robots make a huge number of such operations in one trading session (from thousands to hundreds of thousands), earning each of them is not very much, but thanks to the volume, providing a stable income for its owner. With this method of trading speed comes to the fore. If the order sent to the market by your robot lingers on the way for at least a couple of milliseconds, then you may miss profits. And just as well, if the market data will be sent to the robot with a delay, it will not be able to quickly respond to changes within the framework of a given algorithm, which is also fraught with losses.
To minimize time costs, traders resort to a whole range of measures from optimizing the code of their software to acquiring “broad” communication channels. However, the greatest gain in time can be achieved by removing the broker system from the bidding path.
What is direct access to the exchange?
Direct Access (DMA) is a technology of high-speed access to stock exchanges, in which the application is placed in the exchange trading system directly, bypassing the broker trading system. All this allows to significantly reduce the time of delivery of the application to the exchange and receiving information about its status.
With such an organization of the trading process, a trader can expect a significant time gain. For example, if you are directly connected to the stock and currency markets of the Moscow Exchange, the processing time of an application decreases to 0.5 ms , and in the FORTS and Standard markets it does not exceed 3 ms. When using the same broker system, applications are processed in a time from 5-10 ms to 150-500 ms, depending on the broker system, market type and connection method. Those. through broker systems, applications are processed 10-100 times slower than with a direct connection (although this speed suits many merchants quite well).
Naturally, the use of direct access technology is more expensive (often significantly) and is suitable only for those who perform a large number of operations per day and are willing to pay for their speed.
Where is it used?
Despite the fact that technically, thanks to the direct access to the stock exchange, traders can perform trading operations without a broker, the “documented” access is still carried out through broker companies. That is, in order to be able to directly trade on, say, the stock market of the Moscow Stock Exchange, an investor needs to enter into an agreement with a broker and already have him purchase the service of direct access to the stock exchange.

As a result, Russian clients can gain access mainly to the markets that make up the Moscow Exchange:
- The stock market is the largest stock market of the CIS countries, Eastern and Central Europe. Access is provided to the “Main Market” sectors and to the Standard market sector.
- Derivatives Market (formerly FORTS) is the leading trading platform for derivatives in Russia and Eastern Europe.
- The currency and precious metals market is one of the most significant segments of the Russian financial market.
In addition, some brokers can arrange direct access to foreign exchanges, such as the London Stock Exchange (LSE), CME markets (futures and options), etc.
Types of protocols and connection methods
In general, the direct access scheme is as follows: a server with a trading robot is connected to an intermediate server, which is located as close as possible to the core of the exchange trading system. On this server, special software is installed - the so-called gateways, which are used to transfer orders and market information directly to the trading system. At the same time, various protocols and methods of connection are used to perform transactions and receive data.
The FIX (Financial Information eXchange) protocol is a financial information exchange protocol that is a global standard for exchanging data between participants in exchange trading in real time. It is supported by the world's largest exchange platforms, including the Moscow Stock Exchange.
To obtain market information (Market Data), the FAST protocol (Fix Adapted for STreaming) is used, a standard developed by the creators of the FIX protocol, which makes it possible to achieve significant data compression capabilities for transferring large amounts of market information with minimal time delays. In addition to the Moscow Stock Exchange, it is used on the NYSE, Nasdaq-OMX and many other global sites.
Also for direct connection using native protocols. These protocols emerged before the merger of the MICEX and RTS exchanges into the Moscow Exchange.
For example, in the markets related to the RTS (FORTS - futures and options, Standard ), the Plaza II protocol is used to directly perform transactions and obtain data in the connection mode.
To perform trading operations and obtain stock exchange data on the sites previously belonging to the MICEX exchange (currency and stock markets), a bi-directional MICEXBridge gateway (TEAP) is used .
Technically, connection to the Moscow Exchange is possible in several ways, such as connecting via the Internet, connecting using the universal connection scheme or using the exchange colocation.

Universal wiring diagram
In more detail, the financial information transfer protocols and connection methods will be discussed in one of the following articles.
Soft
For those traders who do not use robots to trade, it is possible to trade on a direct connection using their more familiar trading terminal. However, the software that works with the brokerage trading system does not work using exchange protocols of direct connection, therefore separate programs are created for it (some of them are presented here ).
In addition, due to the fact that direct connection technologies are open, investors can independently develop software for themselves. However, since these programs ultimately have almost direct access to the core of the trading system, the exchange introduced a procedure for certifying trading solutions from third-party developers in order to rule out the likelihood of the “mad robot” putting the entire system to rest. This procedure is carried out as the development of individual investors, and software, created by special companies to order.
What else?
If you continue to move along the chain to reduce the time to perform operations, it becomes obvious that you need to place the trading robot not only logically, but also physically as close as possible to the servers with the core of the exchange trading system.
The robot can be located either on a separate server that can be rack mounted in the data center (this service is called Colocation), or on a virtual machine (Hosting), which in turn is launched along with the virtual clients of other clients on the server also installed in the data center , next to the exchange servers. Hosting services are provided, as a rule, only by large brokers who have their own counters in data centers.
Now, the Moscow Exchange trading servers are located in data center M1. Trading robots connected to exchange servers can be located in two zones - the so-called DMA-free collocation zone and the exchange's direct collocation zone.

Placing in the collocation zone of the exchange has obvious advantages: virtual machines and servers connect directly to the exchange core, while from the free zone the connection goes through the intermediate servers MICEX Gate and Plaza II. In addition, FAST data acquisition and a dedicated channel for connecting to the IOB London Stock Exchange market (Russian ADR trading in London) are available only from the exchange collocation zone.
One of the ways to significantly reduce infrastructure costs is to place the robot in a free colocation zone. The services provided in it are almost similar to the services of the exchange colocation zone. However, free cheese is only in a mousetrap, for the relative cheapness of the placement of the robot will have to "pay" a few milliseconds to increase the speed of transaction processing.
In addition, since the interfaces for creating direct connection software do not initially imply any graphical possibilities for displaying information about tenders, the ability to synchronize orders and positions, orders and positions formed on a direct connection with the broker’s real-time trading system is almost a necessary thing for control of trade operations. Therefore, many brokers try to provide their clients with such opportunities.
All this, of course, costs money and, in comparison, with the usual access to the stock exchange through brokerage systems, rather large. However, for those investors who have reached a certain level of income, such spending makes sense. According to representatives of the exchange , the owners of robots who won the Best Private Investor competition in 2011 spent on services related to direct access from 100 to 500 thousand rubles. per month. However, taking into account the fact that some merchants (although there were not so many of them) managed to reach a yield of 8000% and earn millions of rubles a month (taking into account all broker and exchange commissions), these expenses quickly paid off.
That's all for today! Thank you all for your attention, we will be happy to answer questions in the comments.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/204620/
All Articles