Nokia: Connecting Planets
Elon Musk once said: " If humanity does not land on Mars during my lifetime, I am very, very upset ."
And if it happens, or rather it does not, it will not be the only one. We would also like one day the foot of a man to set foot on the surface of the “red planet”. It would seem, what have the production of mobile devices and interplanetary travel? But actually there is a connection. For example, in the ranks of our employees there is a person who participates in the development of the concept of a very real space project.

')
This man’s name is Lasse Lindquist. In the past, a student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), the developer of promising spacesuits in the NASA engineering team. Today, he works at Nokia as head of the department of brand programs and marketing analytics and is part of the team of the Finnish space Veggies space project.

Lasse Lindquist in the picture to the left.
By the way, aspiring to make the "red planet" a little greener, "Cosmo-webbing" recently won the NASA global space competition , presenting their project of the Martian greenhouse.
The Space Veggies team considered that despite the unusual habitat conditions, astronauts and cosmonauts (omitting various conventions, we will refer to them as marshonauts later in the text), especially considering the duration of Martian expeditions, will need more traditional and familiar food for an earthly person. As a result, the project participants developed a special modular design, which is called space gardens within the team. It is able to provide marsonavtov organically generated oxygen and food. However, the participants of Space Veggies were not limited to the development of a space greenhouse module, creating a common ecosystem where the Marshonauts will also be able to work and relax.

A special point in the creation of this project was to take care of the mental health of the members of the space expedition. Much attention was paid to the design of the internal space. Engineers tried to bring the format of greenhouses to the terrestrial one, as a result of which their design is distinguished by a large area of translucent surfaces, so that plants and marshavats could get access to sunlight.
“The secret of the success of our project lies in the fact that it is based on the concept of self-sustaining development ,” says Lasse Lindquist. - If humanity wants to conquer other planets and successfully exist outside the planet Earth, we must achieve a higher level of autonomous existence and sustainable development in our new habitats than the one we have today. In addition, we must be confident in our mental health in the conditions of life in space colonies. We must be sure that we will not go mad . "
The project is designed for the development of the Martian colonies, so the design of the base is scalable, and new modules can easily connect to an existing system.
According to the basic idea, the Space Veggies Martian base consists of two types of spaces:
1. A secure bunker where people can live and work most of the time.

2. The modules of greenhouses (space gardens) attached to it, which have an adequate level of protection from radiation and allow the Marshonauts to arrange short-term rest breaks “in nature”.
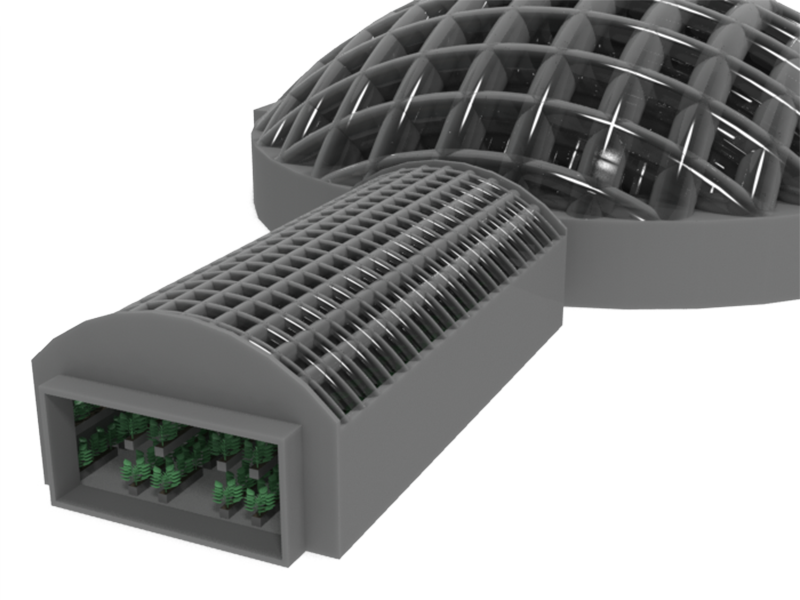
Roughly speaking, the entire Martian base of Space Veggies consists of strong “hard modules” and more open to the external influence of “soft modules”. Interestingly, to provide additional protection for “hard modules” against radiation and the fall of small space bodies, a rather non-trivial approach is used: an external coating using the surface material of Mars. The soil is blown into special external cells of the “hard module”, thereby creating an additional layer of the shell.

Since the modular structure of the base is flexible and scalable, its inhabitants at any time can turn any “soft module” into “hard”: the outer shell of all station modules is identical and has special cells, so the “soft module” is just enough to fill with soil. Such multi-functionality of the modules will be useful, for example, as a temporary solution when expanding the composition of the participants of the Martian expedition.
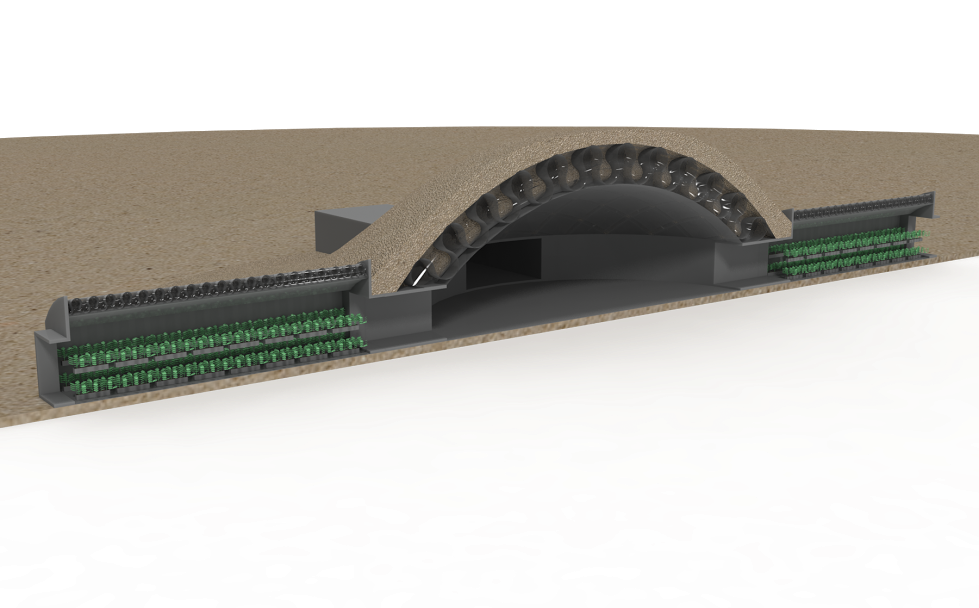

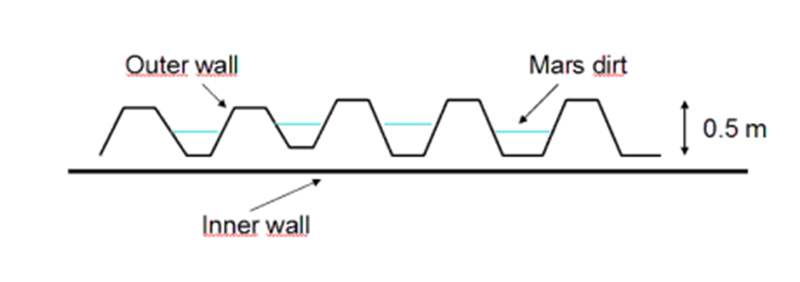
The shell of the greenhouse in the cut
In addition, this technology will not only expand the workspace of the station, but also protect it in the event that the station suffered minor damage: it is enough to cover the damaged section of the module with soil. If the situation cannot be corrected, then a special design of doors-locks, which isolate the damaged segment from the entire station, will come to the rescue.

It is noteworthy that the main material were selected panels of flexible PVC with a UV protected coating. The minimum tensile strength of PVC is 6 MPa, while the maximum difference between the static pressure inside and outside is only 0.05 MPa, which indicates the correctness of the choice of this material from a security point of view. If we consider any abnormal situations like Martian storms, then according to preliminary calculations, the dynamic pressure in such situations will not exceed 100 N / m², which is completely offset by the construction of the walls of the Martian base. And it, by the way, has a sandwich structure consisting of two layers: the upper more durable layer with special cells to hold the soil and the inner layer. This design is designed to compensate for internal and external pressure: the pressure inside the station is planned to be set at 0.5 atmospheres for a comfortable life for the inhabitants of the station.

The team chose a nuclear reactor designed using the advanced technology SAIRS (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0149197004800118) as the main source of energy. Since the project developers rely only on those energy sources to which fuel delivery is not required, it is planned to use solar batteries, heat generators and, possibly, wind generators as additional and reserve sources of electricity.
As for growing plants, the creators of Space Veggies plan to use greenhouse systems based on aeroponic technology and later plant growing using organic soil. Since the atmosphere of Mars consists of 95% of carbon dioxide with impurities of nitrogen, argon, oxygen and other gases, they are also planned to be used with special need. As mentioned above, the modules of the greenhouse have translucent segments, which will help partially compensate for the necessary need for sunlight to grow and maintain plant life. In addition to this, economical LED lamps will be installed in greenhouses.

“ Mobile technologies are very much similar to space ones, from the point of view that both of them constantly face certain challenges ,” says Lasse Lindquist. “ How to place the most modern technologies in a small space, reduce energy costs, and, more precisely, extract they are more useful, to create a complex interface simple and user-friendly? These and other questions have to be answered constantly by engineers in both fields . ”
And if it happens, or rather it does not, it will not be the only one. We would also like one day the foot of a man to set foot on the surface of the “red planet”. It would seem, what have the production of mobile devices and interplanetary travel? But actually there is a connection. For example, in the ranks of our employees there is a person who participates in the development of the concept of a very real space project.

')
This man’s name is Lasse Lindquist. In the past, a student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), the developer of promising spacesuits in the NASA engineering team. Today, he works at Nokia as head of the department of brand programs and marketing analytics and is part of the team of the Finnish space Veggies space project.

Lasse Lindquist in the picture to the left.
By the way, aspiring to make the "red planet" a little greener, "Cosmo-webbing" recently won the NASA global space competition , presenting their project of the Martian greenhouse.
Concept
The Space Veggies team considered that despite the unusual habitat conditions, astronauts and cosmonauts (omitting various conventions, we will refer to them as marshonauts later in the text), especially considering the duration of Martian expeditions, will need more traditional and familiar food for an earthly person. As a result, the project participants developed a special modular design, which is called space gardens within the team. It is able to provide marsonavtov organically generated oxygen and food. However, the participants of Space Veggies were not limited to the development of a space greenhouse module, creating a common ecosystem where the Marshonauts will also be able to work and relax.

A special point in the creation of this project was to take care of the mental health of the members of the space expedition. Much attention was paid to the design of the internal space. Engineers tried to bring the format of greenhouses to the terrestrial one, as a result of which their design is distinguished by a large area of translucent surfaces, so that plants and marshavats could get access to sunlight.
“The secret of the success of our project lies in the fact that it is based on the concept of self-sustaining development ,” says Lasse Lindquist. - If humanity wants to conquer other planets and successfully exist outside the planet Earth, we must achieve a higher level of autonomous existence and sustainable development in our new habitats than the one we have today. In addition, we must be confident in our mental health in the conditions of life in space colonies. We must be sure that we will not go mad . "
The project is designed for the development of the Martian colonies, so the design of the base is scalable, and new modules can easily connect to an existing system.
Technical side
According to the basic idea, the Space Veggies Martian base consists of two types of spaces:
1. A secure bunker where people can live and work most of the time.

2. The modules of greenhouses (space gardens) attached to it, which have an adequate level of protection from radiation and allow the Marshonauts to arrange short-term rest breaks “in nature”.

Roughly speaking, the entire Martian base of Space Veggies consists of strong “hard modules” and more open to the external influence of “soft modules”. Interestingly, to provide additional protection for “hard modules” against radiation and the fall of small space bodies, a rather non-trivial approach is used: an external coating using the surface material of Mars. The soil is blown into special external cells of the “hard module”, thereby creating an additional layer of the shell.

Since the modular structure of the base is flexible and scalable, its inhabitants at any time can turn any “soft module” into “hard”: the outer shell of all station modules is identical and has special cells, so the “soft module” is just enough to fill with soil. Such multi-functionality of the modules will be useful, for example, as a temporary solution when expanding the composition of the participants of the Martian expedition.


The shell of the greenhouse in the cut
In addition, this technology will not only expand the workspace of the station, but also protect it in the event that the station suffered minor damage: it is enough to cover the damaged section of the module with soil. If the situation cannot be corrected, then a special design of doors-locks, which isolate the damaged segment from the entire station, will come to the rescue.

It is noteworthy that the main material were selected panels of flexible PVC with a UV protected coating. The minimum tensile strength of PVC is 6 MPa, while the maximum difference between the static pressure inside and outside is only 0.05 MPa, which indicates the correctness of the choice of this material from a security point of view. If we consider any abnormal situations like Martian storms, then according to preliminary calculations, the dynamic pressure in such situations will not exceed 100 N / m², which is completely offset by the construction of the walls of the Martian base. And it, by the way, has a sandwich structure consisting of two layers: the upper more durable layer with special cells to hold the soil and the inner layer. This design is designed to compensate for internal and external pressure: the pressure inside the station is planned to be set at 0.5 atmospheres for a comfortable life for the inhabitants of the station.

The team chose a nuclear reactor designed using the advanced technology SAIRS (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0149197004800118) as the main source of energy. Since the project developers rely only on those energy sources to which fuel delivery is not required, it is planned to use solar batteries, heat generators and, possibly, wind generators as additional and reserve sources of electricity.
As for growing plants, the creators of Space Veggies plan to use greenhouse systems based on aeroponic technology and later plant growing using organic soil. Since the atmosphere of Mars consists of 95% of carbon dioxide with impurities of nitrogen, argon, oxygen and other gases, they are also planned to be used with special need. As mentioned above, the modules of the greenhouse have translucent segments, which will help partially compensate for the necessary need for sunlight to grow and maintain plant life. In addition to this, economical LED lamps will be installed in greenhouses.

“ Mobile technologies are very much similar to space ones, from the point of view that both of them constantly face certain challenges ,” says Lasse Lindquist. “ How to place the most modern technologies in a small space, reduce energy costs, and, more precisely, extract they are more useful, to create a complex interface simple and user-friendly? These and other questions have to be answered constantly by engineers in both fields . ”
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/204226/
All Articles