Developing a full-fledged API - application for the software package SolidWorks. Bolt model
Introduction
The previous material outlined the basic principles for developing API applications for the SolidWorks three-dimensional modeling system. In this article I would like to show the development of a real API - an application designed to improve the efficiency of the design engineer.
One of the stages of design is the development of a three-dimensional model of the product. Complex nodes use a variety of standardized and directly developed by the designer of fasteners.
Of course, an alternative option is to use configurations in SolidWorks, but if you need to use non-standardized fasteners, the engineer will not know in advance what sizes and configurations he will need. Accordingly, the process of developing and assembling complex parts will be constantly interrupted by the need to model fasteners.
As part of this work, an API was developed - an application for the automatic creation of a bolt model, with given geometrical parameters.
Targets and goals
The purpose of this work is to increase the efficiency of the labor of the engineer-designer at the stage of modeling the product being designed. In accordance with the goal, the following tasks were highlighted:
• Development of a typical bolt model;
• Creating API-application;
• Development of a library that implements the construction of the model;
Development tools
• SolidWorks;
• C #;
• WPF;
• VSTA (Visual Studio Tools for Applications);
Model development
As a result of the simulation, a three-dimensional model was obtained, shown in the figure below.
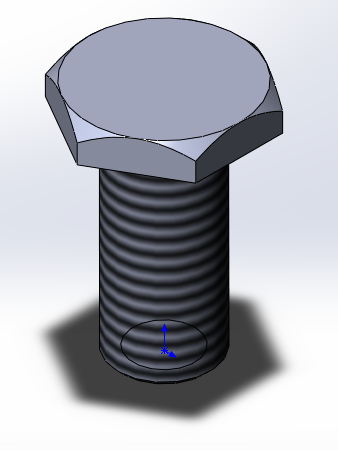
Interface development
Windows Presentation Foundation technology was chosen as an application interface development tool. XAML interface markup is shown in the listing.
<Window x:Class="APIHabr.MainWindow" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" Title="API-" Height="250" Width="375"> <Grid> <Grid.RowDefinitions> <RowDefinition Height="auto"></RowDefinition> <RowDefinition Height="auto"></RowDefinition> <RowDefinition Height="auto"></RowDefinition> <RowDefinition Height="auto"></RowDefinition> <RowDefinition Height="auto"></RowDefinition> <RowDefinition Height="auto"></RowDefinition> </Grid.RowDefinitions> <Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <ColumnDefinition Width="auto"></ColumnDefinition> <ColumnDefinition Width="auto"></ColumnDefinition> </Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <TextBlock Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0" Margin="5,5,5,5" FontSize="16" FontWeight="Bold"> :</TextBlock> <TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0" Margin="5,5,5,5" FontSize="16"> :</TextBlock> <TextBlock Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="0" Margin="5,5,5,5" FontSize="16"> :</TextBlock> <TextBlock Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="0" Margin="5,5,5,5" FontSize="16"> :</TextBlock> <TextBlock Grid.Row="4" Grid.Column="0" Margin="5,5,5,5" FontSize="16">:</TextBlock> <Button Grid.Row="5" Grid.Column="1" Width="170" Height="30" Margin="5,5,5,5" Content="" FontSize="16"></Button> <TextBox Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="1" Margin="5,5,5,5"></TextBox> <TextBox Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="2" Margin="5,5,5,5"></TextBox> <TextBox Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="3" Margin="5,5,5,5"></TextBox> <TextBox Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="4" Margin="5,5,5,5"></TextBox> </Grid> </Window> As a result, a simplified application interface has been developed, shown in the figure below.
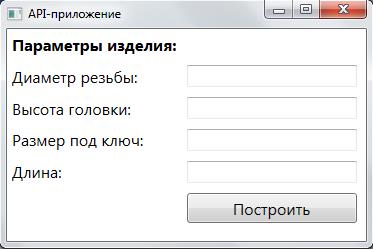
Software implementation
public partial class MainWindow : Window { public MainWindow() { InitializeComponent(); } public SldWorks swApp; void Button_Click_1(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { ModelDoc2 swDoc = null; PartDoc swPart = null; DrawingDoc swDrawing = null; AssemblyDoc swAssembly = null; bool boolstatus = false; int longstatus = 0; int longwarnings = 0; swDoc = ((ModelDoc2)(swApp.ActiveDoc)); OpenDoc(ref swDoc, ref longstatus, ref longwarnings); swApp.ActivateDoc2("", false, ref longstatus); swDoc = ((ModelDoc2)(swApp.ActiveDoc)); ModelView myModelView = null; boolstatus = GrooveDiameter(swDoc, boolstatus); boolstatus = SetBoltHeadHeight(swDoc, boolstatus); boolstatus = SetDimensionUnderKey(swDoc, boolstatus); boolstatus = SetLength(swDoc, boolstatus); } // static bool SetLength(ModelDoc2 swDoc, bool boolstatus) { boolstatus = swDoc.Extension.SelectByID2("", "FACE", 0.011912467420266637, 0.01846469011343288, 0.0037872311733622155, false, 0, null, 0); boolstatus = swDoc.Extension.SelectByID2("D1@1@.SLDPRT", "DIMENSION", 0.047351053302585169, 0.019301296053367275, 0.0028786441805853363, true, 0, null, 0); boolstatus = swDoc.EditRebuild3(); swDoc.ClearSelection2(true); return boolstatus; } // static bool SetDimensionUnderKey(ModelDoc2 swDoc, bool boolstatus) { boolstatus = swDoc.Extension.SelectByID2("", "FACE", -0.00036826155354674484, 0.051999999999850388, -0.0013844273092900039, false, 0, null, 0); boolstatus = swDoc.Extension.SelectByID2("D4@1@.SLDPRT", "DIMENSION", 0.0079871009577274082, 0.035833016414888383, -0.013439947146820423, true, 0, null, 0); boolstatus = swDoc.EditRebuild3(); swDoc.ClearSelection2(true); return boolstatus; } // static bool SetBoltHeadHeight(ModelDoc2 swDoc, bool boolstatus) { boolstatus = swDoc.Extension.SelectByID2("", "FACE", 0.0025916945023696791, 0.022486595775220126, 0.012228373547031879, false, 0, null, 0); boolstatus = swDoc.Extension.SelectByID2("D2@1@.SLDPRT", "DIMENSION", 0.032400529167230879, 0.043963039647934993, 0, true, 0, null, 0); boolstatus = swDoc.EditRebuild3(); swDoc.ClearSelection2(true); return boolstatus; } // static bool GrooveDiameter(ModelDoc2 swDoc, bool boolstatus) { boolstatus = swDoc.Extension.SelectByID2("", "FACE", -0.00081167638456329516, 0.026711469979688613, 0.0089633242408808655, false, 0, null, 0); boolstatus = swDoc.Extension.SelectByID2("D3@1@.SLDPRT", "DIMENSION", 0.0056429925389302749, 0.040324953527420437, 0, true, 0, null, 0); boolstatus = swDoc.EditRebuild3(); swDoc.ClearSelection2(true); return boolstatus; } // void OpenDoc(ref ModelDoc2 swDoc, ref int longstatus, ref int longwarnings) { swDoc = ((ModelDoc2)(swApp.OpenDoc6("D:\\\\Item2\\.SLDPRT", 1, 0, "", ref longstatus, ref longwarnings))); } } Conclusion
The main goal of such API-applications is to automate the process of creating a model. As part of this work, only automation of fastener modeling (bolts) was considered. In the following, the following automation issues will be considered:
• API - an application for assembling a model of typical structures in the software package SolidWorks;
• API - an application to automate the development of design documentation;
• API - an application for modeling complex products.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/204098/
All Articles