"Backups" in a living organism
I decided to write this article, because in this topic shifttstas expressed interest in describing biological structures in a language understandable to programmers.
Now I will touch on the topic of saving and backing up information in DNA. For a start, a small educational program on DNA:
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a macromolecule that provides storage, transmission from generation to generation and implementation of the genetic program for the development and functioning of living organisms. DNA contains information about the structure of various types of RNA and proteins. DNA is found in all living organisms and even in those organisms the “liveliness” of which is in doubt.
DNA consists of four simple elements - nucleotides (adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine), various combinations and sequences of which provide different biological information. Here you can grasp an analogy with machine code (0; 1).
As you know, DNA is a double-stranded structure twisted into a spiral. Ever wondered why a spiral? In fact, the answer is very simple - this is the most advantageous position from an energy point of view.
')
Now let's move on to the “backups”.
From the above, we realized that DNA consists of two chains, which are interconnected and consist of separate elements - nucleotides. So, the connection is possible only between complementary nucleotides, i.e. adenine can only combine with thymine, and guanine only with cytosine.
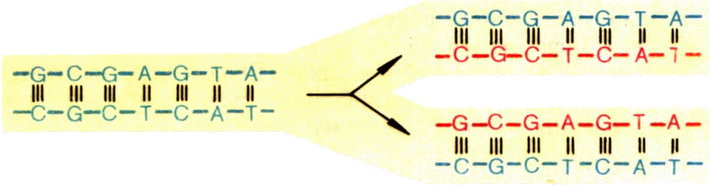
From this it follows that knowing one strand of DNA, we can recover the other. This is the use of DNA repair (recovery) systems, repairing damaged areas (by the way, there is a huge amount of them every day).
It looks like a comparison of the source code of two programs.

In DNA, according to this parameter, several types of DNA can be distinguished:
The DNA repair system can replace the damaged area with its copy, moreover, some copies are functionally active ie. with the loss of one copy, the function of the protein that they encode does not change significantly. And as a result - mutations in unique genes appear with greater frequency.
It is like creating backup copies of the parameter we need, so that in case of a failure in the program, it does not lose its value.

A person is a diploid organism, i.e. a person has 2 genes encoding the same trait (as is known, one from the mother, the other from the father). Thus, a mutation in one gene of one allele may not appear as a result, since the function of the gene paired with it will perform.

It is possible to draw an analogy with double redundancy of the system in the technique - in case of failure of one unit, another enters into operation.

Write in the comments topics of interest, I will try to clearly interpret them for you.
Thank you for attention!
Now I will touch on the topic of saving and backing up information in DNA. For a start, a small educational program on DNA:
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a macromolecule that provides storage, transmission from generation to generation and implementation of the genetic program for the development and functioning of living organisms. DNA contains information about the structure of various types of RNA and proteins. DNA is found in all living organisms and even in those organisms the “liveliness” of which is in doubt.
DNA consists of four simple elements - nucleotides (adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine), various combinations and sequences of which provide different biological information. Here you can grasp an analogy with machine code (0; 1).
As you know, DNA is a double-stranded structure twisted into a spiral. Ever wondered why a spiral? In fact, the answer is very simple - this is the most advantageous position from an energy point of view.

')
Now let's move on to the “backups”.
Backup №1 - Complementarity
From the above, we realized that DNA consists of two chains, which are interconnected and consist of separate elements - nucleotides. So, the connection is possible only between complementary nucleotides, i.e. adenine can only combine with thymine, and guanine only with cytosine.

From this it follows that knowing one strand of DNA, we can recover the other. This is the use of DNA repair (recovery) systems, repairing damaged areas (by the way, there is a huge amount of them every day).
It looks like a comparison of the source code of two programs.

Backup number 2 - Repetitions in DNA
In DNA, according to this parameter, several types of DNA can be distinguished:
- Very high repeat DNA
- Highly replicated DNA - up to 500,000 copies per genome
- Moderately repeated DNA - up to 100 copies per genome
- unique DNA
The DNA repair system can replace the damaged area with its copy, moreover, some copies are functionally active ie. with the loss of one copy, the function of the protein that they encode does not change significantly. And as a result - mutations in unique genes appear with greater frequency.
It is like creating backup copies of the parameter we need, so that in case of a failure in the program, it does not lose its value.

Backup number 3 - Allelic genes
A person is a diploid organism, i.e. a person has 2 genes encoding the same trait (as is known, one from the mother, the other from the father). Thus, a mutation in one gene of one allele may not appear as a result, since the function of the gene paired with it will perform.

It is possible to draw an analogy with double redundancy of the system in the technique - in case of failure of one unit, another enters into operation.

Write in the comments topics of interest, I will try to clearly interpret them for you.
Thank you for attention!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/203834/
All Articles