We play programming
Programmers have children. In this regard, statistics is unshakable.
And this article will be interesting to those who have a child aged 5- ~ 9 years, those who are already thinking or have already thought about the question of how to dedicate a child to the basics of programming.

If you are still thinking about this issue (I guess, no) - Programming for everyone, be creative .
You can perfectly know several programming languages, be an excellent speaker, and train dozens of juniors, but when it comes to teaching children, feel that your “terminology” is lame, and it is very difficult to find the right examples and explanations to form an understanding for the child. subject.
')
It may not be a bad idea to read Java 2 children at night instead of fairy tales as in the picture in the topic, but you probably need to be a real guru to make this interesting and exciting children's imagination, more than stories about Grandma Ezhka.
If the child is not interested - he will not listen ...
RSA Animate - Changing Education Paradigms
Children understand visual examples and tools similar to the game.
Example - Scratch, already mentioned on Habré, however, only in the framework of programming under Adruino:
But probably, the main thing is not a tool, but tasks that he can solve, tasks that can be used for game training:
Examples are given "as is", do not blame me. Further “Cat” is a visual object in the Scratch environment.
(Hello, world! Intentionally missed)
Useful rules (it seems simple, but some of these rules are difficult to follow):
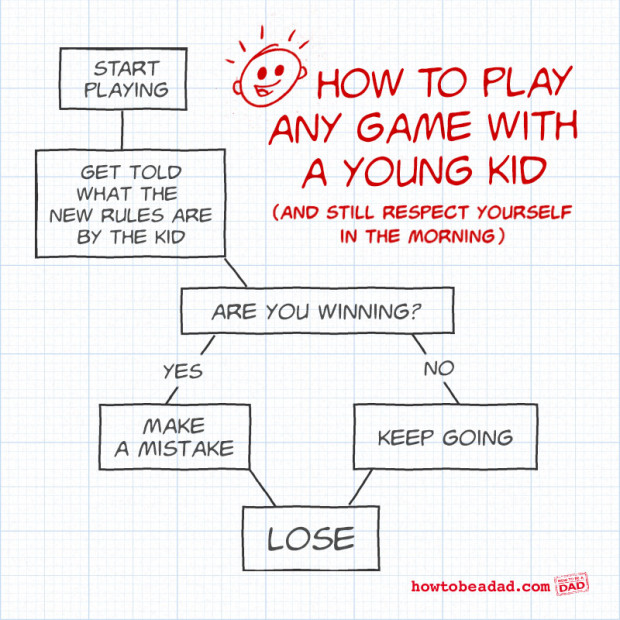
And finally, an important algorithm that I try to keep in mind.
I want to hear from habrovchan offers interesting tasks for children.
UPD: Thanks for the comments. I will try to adopt:
And this article will be interesting to those who have a child aged 5- ~ 9 years, those who are already thinking or have already thought about the question of how to dedicate a child to the basics of programming.

Why do you need it?
If you are still thinking about this issue (I guess, no) - Programming for everyone, be creative .
What is the difficulty?
You can perfectly know several programming languages, be an excellent speaker, and train dozens of juniors, but when it comes to teaching children, feel that your “terminology” is lame, and it is very difficult to find the right examples and explanations to form an understanding for the child. subject.
')
It may not be a bad idea to read Java 2 children at night instead of fairy tales as in the picture in the topic, but you probably need to be a real guru to make this interesting and exciting children's imagination, more than stories about Grandma Ezhka.
If the child is not interested - he will not listen ...
RSA Animate - Changing Education Paradigms
So where do you start?
Step 0
Familiarity with the computer, you can start with gaming programs:
- “Skhodinka to informatics” dvsvit.com.ua/cxodunku
- GCompis gcompris.net/index.html
Children understand visual examples and tools similar to the game.
Example - Scratch, already mentioned on Habré, however, only in the framework of programming under Adruino:
But probably, the main thing is not a tool, but tasks that he can solve, tasks that can be used for game training:
Challenges to start with:
Examples are given "as is", do not blame me. Further “Cat” is a visual object in the Scratch environment.
(Hello, world! Intentionally missed)
- Motion. Make the cat move around the screen
- passed N steps;
- walked over and over;
- moving from point to point.
- Riddle. The cat should make a riddle and check your answer. Example, scratch.mit.edu/projects/14709879
- Drawing:
- polygons: draw a triangle, a quadrilateral, an N-gon;
- patterns, repeating shapes, draw a house. Example, scratch.mit.edu/projects/12641639
- “Graphic editor” with a choice of color.
- Exercises with strings:
- String concatenation The cat asks the name of the boy, the name of the girl and connects them to a phrase. Example, scratch.mit.edu/projects/13642667
- Count the number of occurrences of a given letter in a word.
- Turn the word. Example scratch.mit.edu/projects/13844321
- Check the word palindrome or not.
- Multiplication Table: A cat asks for a number and tells the multiplication table for that number. Example, scratch.mit.edu/projects/14038043
- Games. The cat moves through the maze or between screens, collecting "bonuses". Example scratch.mit.edu/projects/14662137
- Clock with arrows. Example scratch.mit.edu/projects/12769526
Useful rules (it seems simple, but some of these rules are difficult to follow):
- first example;
- the child understands well if he is well explained - no need to demand much at once;
- if the child does not understand you, pause for “tomorrow” and come up with a new explanation;
- it’s necessary for the child to take time to just “play” at his own pleasure, to experiment;
- Challenging tasks (such as creating a game) are great and interesting, but for a child to learn, IMHO, simple tasks are better suited and most importantly multiple decisions / repetitions of their variations.
And finally, an important algorithm that I try to keep in mind.

I want to hear from habrovchan offers interesting tasks for children.
UPD: Thanks for the comments. I will try to adopt:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/203686/
All Articles