Methods of anonymity online. Part 3. Firefox

Hello!
Few are puzzled by the detailed setting of the browser, although the browser is the most popular program for working on the Internet. Using Firefox as an example, I will show how you can make your browser as secure as possible and a bit more “anonymous” compared to its default setting, while retaining even some functionality! :) Opera or Chrome, have similar settings, but, in my opinion, the most flexible in terms of security - yet Firefox.
The purpose of the article is not to provide a high level of anonymity, but it is effective to weed out a lot of identifying, unnecessary and even potentially dangerous data that, one way or another, are transmitted or received by the browser.
All parts here:
Part 1: Methods of anonymity online. Just about the complicated .
Part 2: Methods of anonymity online. Data leaks .
Part 3: Methods of anonymity online. Firefox .
Part 4: Methods of anonymity online. Tor & VPN. Whonix .
Cookies
Cookies are text files with some values stored by the application (often a browser) for different tasks, for example, authentication.
If you completely turn off cookies, some sites may have problems with authorization, but Firefox allows you to accept cookies and clear them after closing. The item "Accept cookies from third-party sites" is also desirable to disable, however, for example, logging in on Habré with the 3rd party cookies disabled, we will not get access to habrastorage.org, so I prefer to accept cookies from the visited sites.
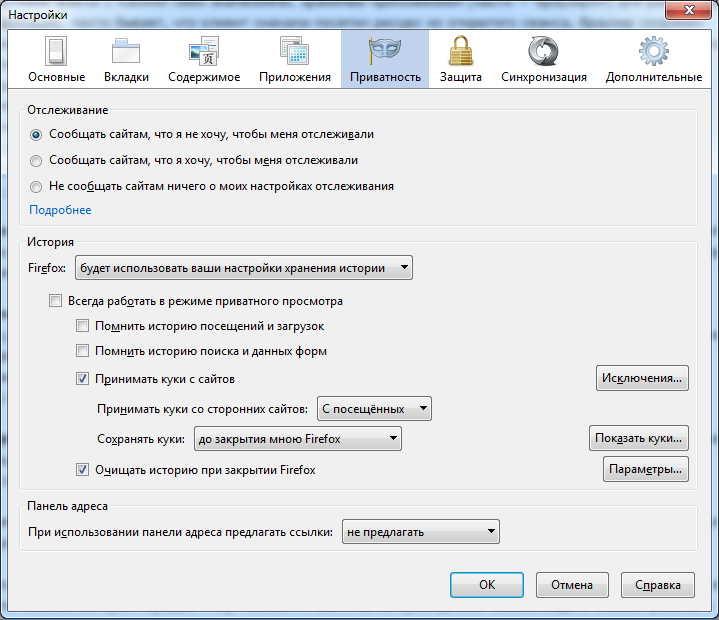
Moreover, Firefox allows you to keep a white and black list of sites with cookies.
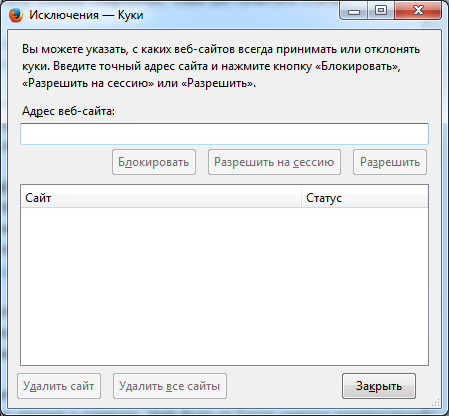
If we want privacy, then when you close Firefox, you need to clear everything. Yes, not very convenient, but no trace remains.
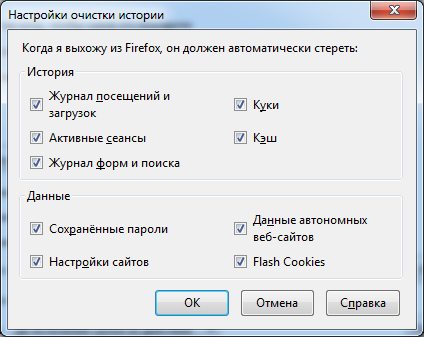
Pay attention to the tick "Flash Cookies", this is not the default tick of Firefox, we'll talk about it a little later when we touch on LSO or Flash cookies.
Here, in the settings, special attention should be paid to clearing the browser cache. The article: " Cookie without cookies ", justifies the need to clear the cache.
On the Firefox: about: config settings page, there is a parameter: browser.cache.disk.enable that is responsible for using the disk cache. The value "false" means that the cache will not be used at all. For the rest of browser.cache.disk settings, do not bother; after turning off the cache, they are no longer important.
A convenient and free program, CCleaner , will help you to clean out all the accumulated traces of Internet activity, stored even in the farthest corners of the hard drive.
Java, Flash, Adobe Reader ...
All of these plugins are separate applications that run on behalf of the user. They can bypass proxy settings, store their individual long-lived cookies (Flash - Local Shared Objects), etc.
All plugins should ideally be disabled or removed. Without Java and Adobe Reader in the browser it is quite possible to live, but there are situations when Flash still has to be turned on, otherwise the site simply will not work. In this case, you need to ensure regular updating of Flash and prohibition of storing Local Shared Objects (LSO) or Flash cookies.
It is also recommended to enable Flash only on request. So you are allowed to run exactly the Flash element that you really want. This can be done in the settings of the plug-ins (add-ons).

To prohibit the storage of LSO specially developed addition to Firefox, Better privacy . I prefer the tick about clearing the LSO to be added to the Firefox Erase History menu, as in the previous image.
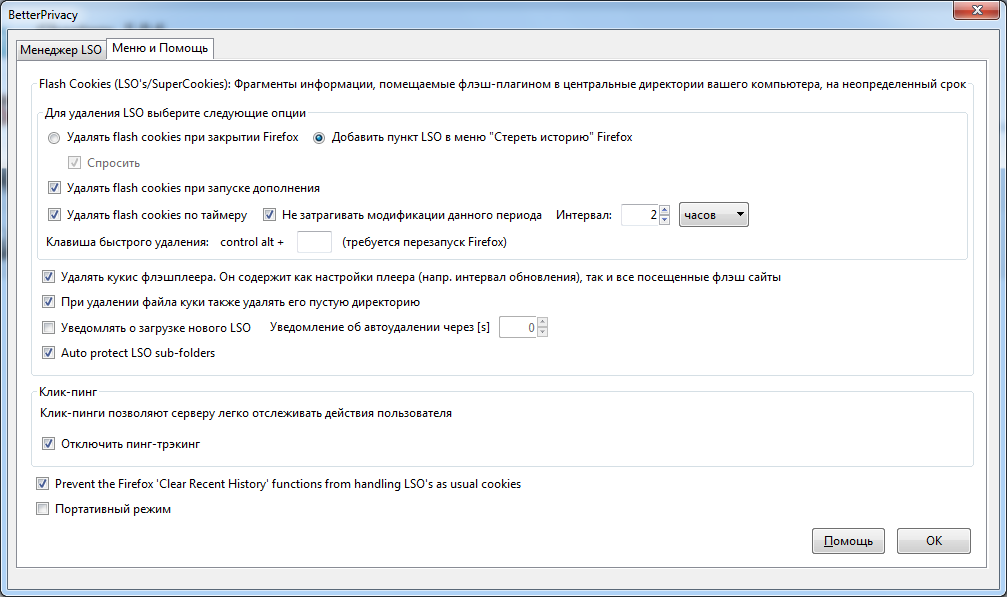
')
Browser fingerprint
The browser provides the server with dozens of data categories, including the so-called user agent . All this can form a rather unique “digital browser fingerprint”, by which it can be found among many others already in an anonymous session.
There are quite a few additions to changing the browser's user agent , I am used to using User Agent Overrider . The add-on is stable, convenient, constantly updated, available in the official Firefox repositories.
Javascript scripts
Javascript scripts executed on the client side can collect for the server many categories of identifying data. Moreover, if the visited site is subject to XSS , then the Javascript scripts included in it will help the attacker to conduct a successful attack with all the ensuing consequences.
In order to disable these scripts, the NoScript add-on is best suited.
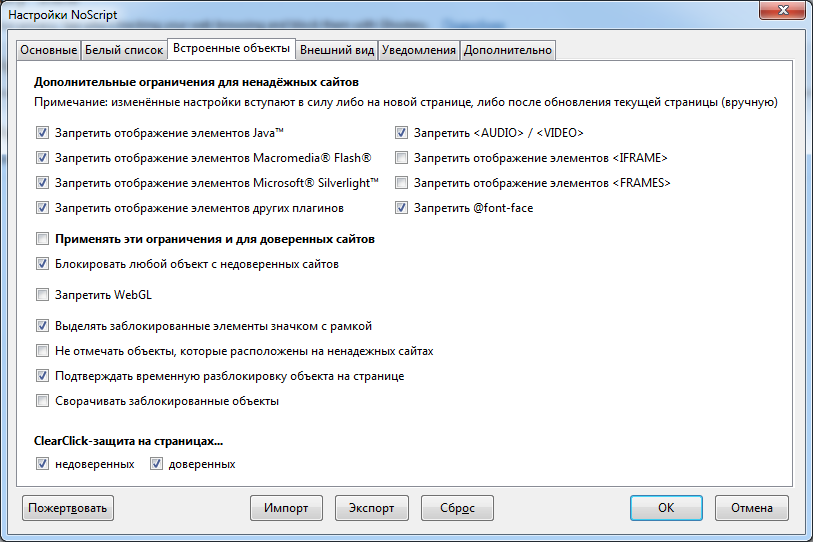
In addition to Javascript, the add-on can block many more different elements: Java, Flash, etc. The user can temporarily allow the execution of all active content on the page or do it on an ongoing basis.
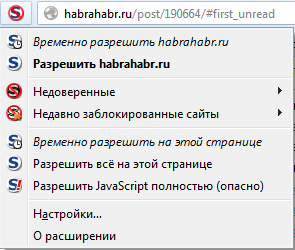
In the same section, I will describe another addon that goes side-by-side with NoScript: RequestPolicy .
The RequestPolicy addon is needed to control cross-site requests and protect against CSRF . Cross-site requests are made when you go to one site, it has already requested another site from another site, for example, a picture, and showed it to you. Such mechanisms are most often used for promotional purposes. I note that in this way malicious sites can do absolutely bad things, for example, under certain conditions, perform unauthorized actions on the third site with your remaining cookies. Imagine what that might mean.
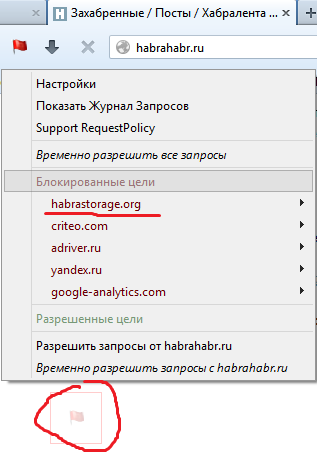
The author of RequestPolicy recommends using it in conjunction with NoScript, since each addition is sharpened to fit its goals, and together they allow you to achieve flexible and comprehensive protection. In the picture, RequestPolicy blocks the picture from habrastorage.org.
It is worth noting that some sites do not like Javascript and cross-site request blocking at all. It should take some time in the mode of "training" to form a trusted list of regularly visited resources. What to do, safety and convenience always stood on different scales.
Web bugs
Web Bugs are the invisible details of the web pages used to monitor visits to the site, they are able to additionally send the server different data about the client.
For blocking web bugs, there are two main additions: Ghostery and DoNotTrackMe .
The principle they have is similar, when I compared them, I stopped on my own subjective feelings on Ghostery, and I will describe it. It is important to note that with the default setting Ghostery does not block all the bugs and trackers, it must be done manually in its settings at the local address: resource: //firefox-at-ghostery-dot-com/ghostery/data/options.html.

When entering a site where there are similar elements, Ghostery will block them and issue the following alert.
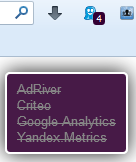
Over time, you will notice that Ghostery and RequestPolicy overlap in blocking certain elements, such as Google Analytics, Yandex.Metrics, etc.
HTTP referer
An HTTP referer is an http header with which the website can determine where the traffic is coming from. If you clicked on a link that sends an http-referer, then the site to which this link leads will be able to find out from which particular site you went to it.
Firefox has an interesting setting in about: config: network.http.sendRefererHeader . This item determines when an HTTP referer will be sent. There are three options:
- 0 - never send HTTP referer
- 1 - send only by clicked links
- 2 - send for links and pictures (by default)
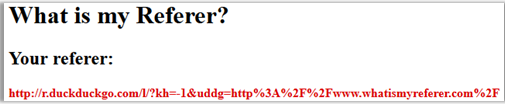
Let's do an experiment. There is a website: www.whatismyreferer.com , the purpose of which is to show our HTTP referer.
Use the default value of network.http.sendRefererHeader = 2 .
We click on the link: www.whatismyreferer.com , we see our referrer highlighted in red (in your case it will be slightly different):

Do the same: www.whatismyreferer.com , but with network.http.sendRefererHeader = 0 . Oops!

Set network.http.sendRefererHeader = 0 , and the referrer will not be transmitted.
In the settings there is another similar parameter, network.http.sendSecureXSiteReferrer , it is responsible for transferring the referrer between two https sites. However, do not bother, it does not work after disabling the previous setting.
By the way everyone heard about the search engine DuckDuckGo ? The fact that he does not send referrers, I was sure. But clicking the left mouse button on the first link (after the advertisement) in its search results for the query: duckduckgo.com/?q=www.whatismyreferer.com with the network.http.sendRefererHeader = 2 set , I saw the following:
If you click the middle mouse button (open a new tab), then everything is OK, the referrer really does not show.
Be careful : referrers are used in the work of many Internet resources, their disconnection can lead to the most unexpected consequences, for example, after turning off the referrer, I was not allowed to log in to TM ID.
Other
It would be completely superfluous to send any service information to Mozilla.
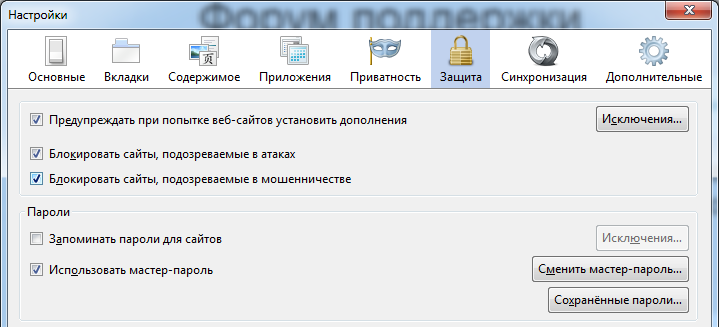
For greater anonymity, I would advise not to store passwords at all, although Firefox has the ability to use a master password with which all other passwords are encrypted, so you cannot pull them out in the clear.
HTTPS Everywhere
This addon is needed in order to force the use of only https-connection for sites that support it.

Adblock plus
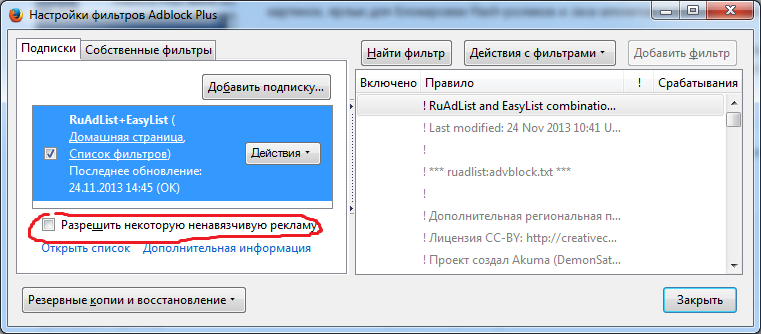
Not as safe as simply useful. Adblock Plus is needed to block all possible advertising while it has a regularly updated list of filters. I’ll note that there is a tick in the settings: “Allow some unobtrusive advertising”, which can be removed if desired.
The last tip for those who actively use SOCKS when surfing the web. The network.proxy.socks_remote_dns setting determines where DNS queries will be performed when using SOCKS5. The value “true” establishes that they will be executed via SOCKS proxy, and not on the client itself. So we will defend against DNS-leaks .
More details about each setting from about: config Firefox can be read here . And on this link, part of them is painted in Russian.
Ufff, like everything! I myself use the described configuration of Firefox. At first it was necessary to get used a little, but I understand why all this is needed.
Thank! Ready to answer all questions.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/203680/
All Articles