DES to J in a hundred lines
A week of thirty-lead on JS should be diluted with something really crazy.
I recommend reading, for example, with this series of articles or this book before reading; language dictionary here ; Nevertheless, I will try to explain in detail my actions (all explanations are hidden under spoilers, so as not to clutter up the article).
')
If you have any questions, suggestions or corrections to the code, welcome to the comments.
DES (Data Encryption Standard) is a symmetric encryption algorithm developed by IBM and approved by the US government in 1977 as the official standard (FIPS 46-3).
DES is a typical block cipher using a 56-bit key. The encryption process consists in the initial permutation of the bits of a 64-bit block, sixteen cycles of encryption, and finally, the inverse permutation of the bits.
DES uses several matrices that should be prepared ahead of time.

The pattern is visible with the naked eye: in the upper half of the matrix from top to bottom from right to left are odd numbers from 1 to 63, and each element of the lower half of the matrix is one less than the corresponding element of the top. Take advantage of this.
This matrix is related to P as follows: the 0th element of P -1 is 39, the 39th element of P is 0, and so on.
In other words, the elements of the matrix P -1 are the indices of their indices in the matrix P. It sounds confusing, but this underlies the formula of this matrix.

The 7th, 15th, and so on bits are “thrown out” from the key - they serve to control parity.
The pattern in G is not so obvious; nevertheless, it is easy to obtain the matrix G from an 8x8 matrix of consecutive numbers, from which the last column was simply thrown out.
Everything is sad here - patterns are not visible, so let's write the matrix as it is.

The first line is the indices, the second is the values. I will not stop here in detail.

This matrix is easily obtained from
Operator

Here, too, are not visible patterns. Let's go further.

It is huge, three-dimensional, and there is absolutely no regularity in it either.
We will write down this matrix as it is, and at the same time we will create a couple of verbs so that it will be easier to deal with later.
First, we compile a list of keys that we will use (we assume that the
The original 8-byte text is divided into two 32-bit parts:
Now we need to apply each of the keys to the pair L, R as follows:

To do this, create a recursive monad that accepts a box with three values at the input and returns a similar box.
And we will call it as many times as we have keys:
Swap L and R again and get the encrypted text.
Let us turn everything into a dyad, which accepts a key with the left operand, and a right-hand one with an 8-byte array:
Decryption is performed in the same way, with the only difference that the keys are applied in the reverse order.
Before applying what we have, you need to prepare the text:
in.txt:
Let's write the result to the file.
out.txt:
And try to decipher the result.
The code is entirely on the peystbin .
Thank you all for your attention!

I recommend reading, for example, with this series of articles or this book before reading; language dictionary here ; Nevertheless, I will try to explain in detail my actions (all explanations are hidden under spoilers, so as not to clutter up the article).
')
If you have any questions, suggestions or corrections to the code, welcome to the comments.
What is DES
DES (Data Encryption Standard) is a symmetric encryption algorithm developed by IBM and approved by the US government in 1977 as the official standard (FIPS 46-3).
DES is a typical block cipher using a 56-bit key. The encryption process consists in the initial permutation of the bits of a 64-bit block, sixteen cycles of encryption, and finally, the inverse permutation of the bits.
Preparing the soil
DES uses several matrices that should be prepared ahead of time.
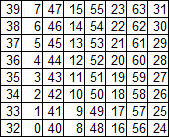
Initial permutation matrix P

The pattern is visible with the naked eye: in the upper half of the matrix from top to bottom from right to left are odd numbers from 1 to 63, and each element of the lower half of the matrix is one less than the corresponding element of the top. Take advantage of this.
Explanations
First of all we will make the upper part.
The code runs from right to left. In order:
Get the bottom half of the matrix costs nothing:
Operator
It remains to combine this - here comes the magic of J:
The construction of the three verbs is called fork:
Thus, the construction above is equivalent to this:
The dyad performs the concatenation of arrays, and
The monadic version
|: |. 8 4 $ >: +: i.32 57 49 41 33 25 17 9 1 59 51 43 35 27 19 11 3 61 53 45 37 29 21 13 5 63 55 47 39 31 23 15 7 The code runs from right to left. In order:
i.32produces 32 consecutive numbers, starting with zero;+:doubles its operand;>:increases the operand by one;8 4 $converts the operand into an 8x4 matrix;|.inverts the main axis of the matrix, i.e. rearranges the lines in reverse order;|:transposes the matrix.
Consistently
i.32 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 +: i.32 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 52 54 56 58 60 62 >: +: i.32 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 51 53 55 57 59 61 63 8 4 $ >: +: i.32 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 51 53 55 57 59 61 63 |. 8 4 $ >: +: i.32 57 59 61 63 49 51 53 55 41 43 45 47 33 35 37 39 25 27 29 31 17 19 21 23 9 11 13 15 1 3 5 7 |: |. 8 4 $ >: +: i.32 57 49 41 33 25 17 9 1 59 51 43 35 27 19 11 3 61 53 45 37 29 21 13 5 63 55 47 39 31 23 15 7 Get the bottom half of the matrix costs nothing:
<: |: |. 8 4 $ >: +: i.32 56 48 40 32 24 16 8 0 58 50 42 34 26 18 10 2 60 52 44 36 28 20 12 4 62 54 46 38 30 22 14 6 Operator
<: decrements operand value by one.It remains to combine this - here comes the magic of J:
(] , <:) |: |. 8 4 $ >: +: i.32 57 49 41 33 25 17 9 1 59 51 43 35 27 19 11 3 61 53 45 37 29 21 13 5 63 55 47 39 31 23 15 7 56 48 40 32 24 16 8 0 58 50 42 34 26 18 10 2 60 52 44 36 28 20 12 4 62 54 46 38 30 22 14 6 The construction of the three verbs is called fork:
(fgh) y <-> (fy) g (hy)Thus, the construction above is equivalent to this:
(] |: |. 8 4 $ >: +: i.32) , (<: |: |. 8 4 $ >: +: i.32) The dyad performs the concatenation of arrays, and
] simply returns its right operand.The monadic version
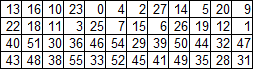
, “straightens” the matrix into an array, which we use when we obtain the final formula for the initial permutation matrix: P =: , (] , <:) |: |. 8 4 $ >: +: i.32 Reverse Rearrangement Matrix P -1

This matrix is related to P as follows: the 0th element of P -1 is 39, the 39th element of P is 0, and so on.
In other words, the elements of the matrix P -1 are the indices of their indices in the matrix P. It sounds confusing, but this underlies the formula of this matrix.
Explanations
The first step is to use the dyadic fork:
The result is a 64x64 matrix, where each row contains its number (say, i) at position P [i], and the remaining elements are filled with zeros.
In addition to the fork, adverbs
If we write
Or apply it to our matrix, adding up its lines and getting the final formula:
x (fgh) y <-> (xfy) g (xhy) (i.64) ([ * =/~) P The result is a 64x64 matrix, where each row contains its number (say, i) at position P [i], and the remaining elements are filled with zeros.
In addition to the fork, adverbs
/ and ~ are used: the first applies a verb to each element of the array, and the second changes the operands in places, soxf~ y <-> yfxIf we write
u/ y , where u is a dyadic verb, J will substitute it between all elements of y:+/ 1 2 3 <-> 1 + 2 + 3Or apply it to our matrix, adding up its lines and getting the final formula:
iP =: +/ (i.64) ([ * =/~) P Matrix initial permutation key G

The 7th, 15th, and so on bits are “thrown out” from the key - they serve to control parity.
The pattern in G is not so obvious; nevertheless, it is easy to obtain the matrix G from an 8x8 matrix of consecutive numbers, from which the last column was simply thrown out.
Explanations
Transposing is rather a side effect, but it is in this form that we need the matrix.
Now you need to invert the lines - if you just apply to the result
Save the result in the variable
It is already clear that the first 28 elements of the matrix are exactly as we need; another 24 can be obtained by inverting the order of the rows. The remaining four elements could not be gracefully pulled out of me, so just enter them as they are:
Save the result.
}: |: i. 8 8 0 8 16 24 32 40 48 56 1 9 17 25 33 41 49 57 2 10 18 26 34 42 50 58 3 11 19 27 35 43 51 59 4 12 20 28 36 44 52 60 5 13 21 29 37 45 53 61 6 14 22 30 38 46 54 62 i. 8 8i. 8 8instead of an array of numbers immediately creates a matrix of 8x8 consecutive numbers.}:throws out the last element of the array / row of the matrix.
Transposing is rather a side effect, but it is in this form that we need the matrix.
Now you need to invert the lines - if you just apply to the result
|. then swap the whole string. In our case, you need to change the rank of the verb so that it works with each individual line: |."1 }: |: i. 8 8 56 48 40 32 24 16 8 0 57 49 41 33 25 17 9 1 58 50 42 34 26 18 10 2 59 51 43 35 27 19 11 3 60 52 44 36 28 20 12 4 61 53 45 37 29 21 13 5 62 54 46 38 30 22 14 6 " changes the rank of a verb. A rank of 0 means that the verb is applied to each element of the operand, 1 to the row and 2 to the whole matrix.Save the result in the variable
G - it will be more convenient.It is already clear that the first 28 elements of the matrix are exactly as we need; another 24 can be obtained by inverting the order of the rows. The remaining four elements could not be gracefully pulled out of me, so just enter them as they are:
4 14 $ (28 {. , G), (24 {. , |. G), (27 19 11 3) 56 48 40 32 24 16 8 0 57 49 41 33 25 17 9 1 58 50 42 34 26 18 10 2 59 51 43 35 62 54 46 38 30 22 14 6 61 53 45 37 29 21 13 5 60 52 44 36 28 20 12 4 27 19 11 3 N {. y N {. y pulls the first N elements out of y .Save the result.
G =: |."1 }: |: i. 8 8 G =: (28 {. , G), (24 {. , |. G), (27 19 11 3) KP key permutation matrix

Everything is sad here - patterns are not visible, so let's write the matrix as it is.
Shift matrix s

The first line is the indices, the second is the values. I will not stop here in detail.
s =:1, (14 $ 1, 6 $ 2), 1 Expansion matrix E

This matrix is easily obtained from
i. 8 4 i. 8 4 : the left column is cyclically shifted down and put to the matrix on the right, the right - move up and put on the left. E =: |: i. 8 4 E =: , |: (_1 |. _1 { E) , E , (1 |. 0 { E) Operator
x |. y x |. y performs a cyclic shift of the array.P2 permutation matrix (yes, there are many permutations in DES)

Here, too, are not visible patterns. Let's go further.
S transformation matrix

It is huge, three-dimensional, and there is absolutely no regularity in it either.
We will write down this matrix as it is, and at the same time we will create a couple of verbs so that it will be easier to deal with later.
f =: dyad : '|. #: S {~ < x, ((5{y)++:0{y), (+/(2^i.4)*}:}.y)' " 0 1 fS =: monad : '}. |."1 (4 $ 1), (i.8) f 8 6 $, y' " 2 Explanations
Let's start with the second verb. This is a monad with rank 2, which converts the matrix into an 8x6 format and gives it the right operand to the first verb. The left operand is
The first verb is a dyad with the rank 0 1 (such a rank in the dyadic verb means that 0 is applied to the left operand and 1 to the right operand). This verb assumes that the right operand is an array of bits of length 6. The 0th and 5th bits define the row number in S, bits 1 through 4 define the column number, and the left operand represents the number of the submatrix. All three received numbers are pushed into the box (local analogue of the structure) and are passed to the operator input
This whole saga with inversions and adding-deleting a line of four units is needed to add leading zeros to the result lines: if they are not inverted initially, zeros are added at the end.
i.8 . Then a row of four units is added to the result, all rows of the matrix are inverted and the first row is deleted.The first verb is a dyad with the rank 0 1 (such a rank in the dyadic verb means that 0 is applied to the left operand and 1 to the right operand). This verb assumes that the right operand is an array of bits of length 6. The 0th and 5th bits define the row number in S, bits 1 through 4 define the column number, and the left operand represents the number of the submatrix. All three received numbers are pushed into the box (local analogue of the structure) and are passed to the operator input
{ - take from array by index. Operator #: translates the result into a binary numeral system, which is inverted by the next step.This whole saga with inversions and adding-deleting a line of four units is needed to add leading zeros to the result lines: if they are not inverted initially, zeros are added at the end.
Getting down to business
First, we compile a list of keys that we will use (we assume that the
key already defined):Explanations
First, we translate characters into binary representation by a samopisny monad (there will be no code in the article) and apply the initial key permutation matrix G to the result:
Then take the first 28 bits of the result and make a list of the results of the shift:
From the new in this line only adverb
Do the same with the last 28 bits:
Now we need to perform a concatenation of the corresponding strings and apply the KP key permutation matrix to each row of the result:
binkey =. chr2bin key prmkey =. G { binkey Then take the first 28 bits of the result and make a list of the results of the shift:
C =. (28 {. prmkey) |.~"1 0 +/\s From the new in this line only adverb
\ : it applies a verb to each prefix of the operand. s 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 +/\s 1 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 28 Do the same with the last 28 bits:
D =. (28 }. prmkey) |.~"1 0 +/\s N }. y N }. y drops the first N elements of y .Now we need to perform a concatenation of the corresponding strings and apply the KP key permutation matrix to each row of the result:
K =. KP {"1 C ," 1 1 D binkey =. chr2bin key prmkey =. G { binkey C =. (28 {. prmkey) |.~"1 0 +/\s D =. (28 }. prmkey) |.~"1 0 +/\s K =. KP {"1 C ," 1 1 D The original 8-byte text is divided into two 32-bit parts:
bin =. chr2bin plain prm =. P { bin L =. 32 {. prm R =. 32 }. prm Now we need to apply each of the keys to the pair L, R as follows:
To do this, create a recursive monad that accepts a box with three values at the input and returns a similar box.
Explanations
The f function in the picture above does the following:
> "Opens" the box, returning its contents. K =. > 0 { y L =. > 1 { y R =. > 2 { y The f function in the picture above does the following:
- applies the expansion matrix E to R;
- adds the result with the modulo 2 key;
- for each six-bit result block, finds the corresponding four-bit number in the S matrix;
- applies the permutation matrix P2 to this;
- adds the result to the L modulo 2;
L ~: P2 { , fS (0 { K) ~: E { R step =: monad define K =. > 0 { y L =. > 1 { y R =. > 2 { y (}. K); R ; L ~: P2 { , fS (0 { K) ~: E { R ) And we will call it as many times as we have keys:
result =. step^:(#K) K; L; R Explanations
From the new in this line only the union
u^:N , which performs the verb u N times, that is, for example,u^:4 y <-> uuuuySwap L and R again and get the encrypted text.
R =. > 1 { result L =. > 2 { result bin2chr iP { ,L,R Let us turn everything into a dyad, which accepts a key with the left operand, and a right-hand one with an 8-byte array:
Long dyad here
encode =: dyad define key =. x binkey =. chr2bin key prmkey =. G { binkey C =. (28 {. prmkey) |.~"1 0 +/\s D =. (28 }. prmkey) |.~"1 0 +/\s K =. KP {"1 C ," 1 1 D plain =. y bin =. chr2bin plain prm =. P { bin L =. 32 {. prm R =. 32 }. prm result =. step^:(#K) K; L; R R =. > 1 { result L =. > 2 { result bin2chr iP { ,L,R ) Decryption is performed in the same way, with the only difference that the keys are applied in the reverse order.
Before applying what we have, you need to prepare the text:
in.txt:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipiscing elit.Explanations
Since the algorithm works with blocks of 8 characters, it is better to fill the tail with spaces, otherwise the text will simply be repeated:
And now we will break the text into blocks of 8 characters.
1!:1 reads the contents of the file plaintext =: 1!:1 < 'in.txt' Since the algorithm works with blocks of 8 characters, it is better to fill the tail with spaces, otherwise the text will simply be repeated:
' ',~^:(8 - 8| # plaintext) plaintext And now we will break the text into blocks of 8 characters.
plaintext =: (8,~ >. 8 %~ #plaintext) $, ' ',~^:(8 - 8| # plaintext) plaintext plaintext =: 1!:1 < 'in.txt' plaintext =: (8,~ >. 8 %~ #plaintext) $, ' ',~^:(8 - 8| # plaintext) plaintext Let's write the result to the file.
Explanations
1!:21 opens the file, 1!:22 closes, and 1!:2 writes to the file out =: 1!:21 < 'out.txt' ('habrhabr' encode"1 1 plaintext) 1!:2 out 1!:22 out out.txt:
4acc c8ad 32dd 96a1 ae9c 2fdc 2025 e3d0 968c 97c0 5544 0944 2d20 2069 f943 f0d4 e98d bdea 71f9 c516 8a0a b034 5641 b0b5 53cc 2355 2fb1 4bdeAnd try to decipher the result.
cipher =: 1!:1 < 'out.txt' cipher =: (8,~ >. 8 %~ #cipher) $, cipher , 'habrhabr' decode"1 1 cipher Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipiscing elit. The code is entirely on the peystbin .
If you have any questions, suggestions or corrections to the code, welcome to the comments.
Thank you all for your attention!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/202822/
All Articles