How we turned the phone into a bank card

We recently invited HTC One owners to take part in testing NFC payments and now we want to thank everyone who has joined and contributed to the development of contactless payments in our country. Today, the Wallet application is already available to all HTC One and Philips Xenium W336 owners after updating the firmware, and in the near future, owners of HTC One Dual SIM, HTC One Max, HTC One SV, HTC Desire 500, HTC Desire 600 will also be able to use it and Philips Xenium W8555.
In the comments to the previous post and habrodialogues there were many questions about how Wallet works and what needs to be done to put a bank card or travel ticket in it without removing the back cover of the phone and not using double-sided tape. In this post I will try to answer these questions and tell you how it works.
How are the payment cards
A payment card (smart card) is a microprocessor placed in a piece of plastic of a standardized size that, when in contact with the reader, receives sufficient power for operation and starts the operating system with the payment application installed in it (most often Java applet in * nix-like operating system). Contactless smart cards, which have long been public transport fare cards and are rapidly becoming bank cards ( MasterCard PayPass , VISA PayWave ), work on the same principle, only they get power from the electromagnetic field of the reader at the checkout or turnstile. All contactless bank cards and the vast majority of transport combines the ISO 14443 standard .
')
A bank or transport company purchases “blanks” of cards and records its application with the client’s “payment data” on them. This process, called personalization, is carried out in the so-called perso-bureau, which can be both internal divisions of service providers and individual companies in the market. In the process of personalization, the data on the card is encrypted and locked with keys, which makes it impossible to change them. Moreover, the architecture of modern smart cards allows at the hardware level to distinguish their state before and after personalization, which completely excludes the possibility of changing (fake), for example, your billing information after the card is released.
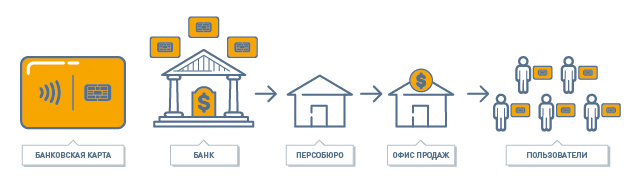
The evolution of cards from magnetic stripe ( MagStripe ) to smart cards with chip ( EMV ) and contactless interface ( RFID ) has led to the fact that the form factor of the card has ceased to matter. This makes it possible to use any object as a “carrier” of a card: a plastic card, a watch, a bracelet, a sticker, a key ring and, of course, a smartphone.
How are NFC-phones
 NFC is just a wireless data transfer technology. Same as Bluetooth or WiFi, it only works at a short distance and at a not very high frequency (13.56 MHz), which is its advantage, as it eliminates the possibility of a “random” connection.
NFC is just a wireless data transfer technology. Same as Bluetooth or WiFi, it only works at a short distance and at a not very high frequency (13.56 MHz), which is its advantage, as it eliminates the possibility of a “random” connection.At the same time, NFC is an extension of the existing standard of contactless smart cards ISO 14443, which, as we have already noted, is used in modern bank cards, passes to the office and to the parking lot, travel tickets to the metro, Troika and Podorozhniki. In other words, the NFC standard inherits the entire ISO 14443 standard, due to which 100% compatibility of NFC smartphones, contactless cards and the existing reception infrastructure is realized.
In an NFC-compatible phone, in order for it to be a full-fledged NFC device, besides the NFC antenna and the NFC controller, there must be a so-called Secure Element - a separate microprocessor, similar to that found in plastic cards. He will be responsible for the safe storage and execution of payment applications (for example, MasterCard Mobile PayPass). The Secure Element can be built-in (installed on the phone’s motherboard) or reside on a detachable module: a UICC SIM card or an SD memory card.
Write a payment card to the phone
If the NFC-enabled phone has the same microprocessor as plastic cards, the output suggests itself - you can write the same payment applications to the phone and make the same contactless payments by touching the phone to the reader.
The first attempt to put the card on the phone in the Russian Federation was made by cellular operators, for example, MTS and Russian Standard Bank , Megafon and a transport card in Yekaterinburg , Beeline and a transport card in Kazan , etc. To do this, they needed to purchase a batch of special UICC SIM-cards with a Secure Element, agree with the bank or the transport company about pre-registering a payment or transport application there, take the SIM-cards to the perso-bureau to implement the “contact personalization” process common in the industry old SIM cards for new subscribers in service centers.
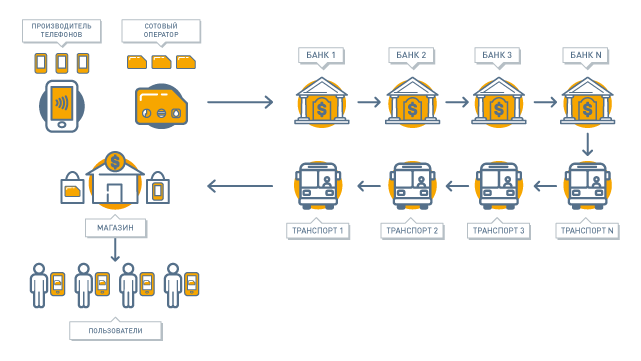
Yes, you can put the card in the phone this way, and it works. But what if you need another bank? Or a transport company in another city? Or maybe in two cities? The SIM card will have to travel in all instances before it falls into your hands, and the cellular operator will have to agree with all these companies. In this case, to reissue a bank card, for example, because of the expiration date, the operation will have to be repeated.
Remote personalization and TSM platform
Fortunately, unlike a plastic card, the phone is an interactive device that is always connected (be it Wi-Fi or a cellular network), which means you can write cards to it, firstly, remotely, and secondly, only those service providers that you need. To implement this function, the role of TSM ( Trusted Service Manager ) was formulated - a trusted intermediary uniting service providers (banks, transport, etc.) on the one hand, and Secure Element chips in all their forms, on the other. It is this TSM platform that we developed at i-Free and certified for compliance with all necessary standards.
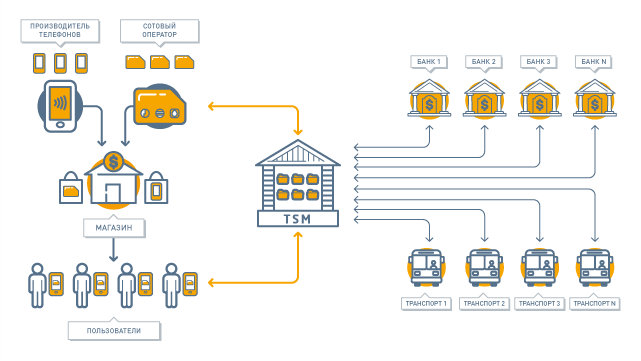
The main functions of TSM:
- Aggregation of various service providers. A bank or other service provider connects to TSM using a standard protocol and gets access to a variety of secure element, i.e. gets the opportunity to issue cards for multiple users. At the same time, he does not need to negotiate separately with each mobile operator or with each phone manufacturer. This part of TSM is called TSM Service Provider TSM.
- Aggregation of various secure element. The owner of the Secure Element (cellular operator or phone manufacturer) connects to TSM using a standard protocol and gets access to many service providers, i.e. gets the opportunity to provide its users with many services. At the same time, it does not need to negotiate separately with each service provider, it does not need to take into account the features of each service, hardware and system capabilities of different Secure Element. This part of the TSM is called the SEI TSM (Secure Element Issuer TSM).
How the TSM platform works
The TSM platform provides remote control of Secure Element chips in users' phones through a secure communication channel. At the direction of the service provider, TSM writes (or deletes, for example, in the event of a loss of a smartphone) personalization data of the card to the Secure Element of the phone, using the phone itself exclusively as a modem. In addition, the platform allows service providers to remotely “look” at the data of cards issued by them, for example, to conduct an audit or to display on the phone the actual balance on the fare payment cards or loyalty cards (if the balance is stored on the card).
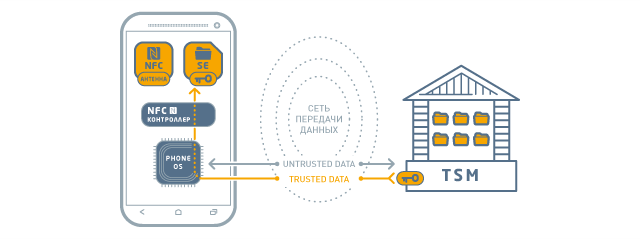
The keys to the Secure Element are stored on highly specialized HSM (Hardware Security Module) servers, which are an integral part of the TSM platform. Without the participation of the latter, it is impossible to access the chip - the plastic card industry works exactly according to this principle, only the keys are managed by the bank or the transport company that issued the card.
Which card to pay for the purchase is chosen by the user through the Wallet application, which displays cards issued and available for issue, as well as accepting applications for issuing new cards. The application is sent to the service provider, which instead of writing the billing data to a plastic card, sends this data through TSM to the Secure Element of the phone.
Custom application
 The Wallet application works in the operating system of the phone, which by definition is not secure, and, accordingly, the Wallet does not carry any security related functions. The main role of the application, in addition to the demonstration of cards issued and available for release, is to provide a communication channel between the Secure Element and TSM, as well as to provide the user with interactive interfaces to the applications (cards) loaded in the Secure Element.
The Wallet application works in the operating system of the phone, which by definition is not secure, and, accordingly, the Wallet does not carry any security related functions. The main role of the application, in addition to the demonstration of cards issued and available for release, is to provide a communication channel between the Secure Element and TSM, as well as to provide the user with interactive interfaces to the applications (cards) loaded in the Secure Element.In most cases, if the Wallet application uses the built-in Secure Element in phones, then it often does not make sense to upload it to Google.Play, since partnership with the phone manufacturers provides an important advantage: the manufacturer pre-installs the user application to the phone along with the firmware, it is not necessary promote, no need to download or install - it is already in the phone - the same native as the "Calculator".
Any card in any phone
To transform the phone into a bank card, TSM must access the Secure Element either from the manufacturer of this phone or from the owner of the SIM card (cellular operator). Since payment cards are not transferred to the phone and are not “tied” (otherwise they will be considered “duplicates”), but will be issued again, then to issue a bank card of a bank to the phone, this bank must connect to TSM.
Thus, it will not be possible to release any card to any phone, but the movement in this direction is already underway, and it is obvious to all market participants that this is a logical evolutionary step. Both phone manufacturers are interested in this (new functionality, which is more abundant than an extra megapixel in the camera), mobile operators (for about the same reason), and service providers (new audience and sales channel with interactive interaction), and users (tired of many different plastic cards).
Today in the “Wallet” you can issue a TCS Bank card, by the end of the year it will also be possible to pay transportation fees: the cities of Vologda and Cheboksary will start as a pilot zone. Next year there will be much more cards available for release. Contact you impressions!
Afterword
Many of the processes (both technological and business) described in this post are greatly simplified to facilitate understanding of the whole picture. Perhaps, in a sense, this text is even more suitable for Krestianka magazine than Habra, but this introductory material would not be enough for further publications concerning payment cards in the phone. Based on your questions and comments, we will gradually reveal certain parts of this large and hopefully interesting topic.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/202738/
All Articles