ScienceHub # 05: Biophysics of excitable systems
In the new issue of ScienceHub, we talked with Konstantin Agladze, Candidate of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Professor at the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology and Head of the Laboratory “Nanoconstruction of Membrane-Protein Complexes for Controlling Cell Physiology” at MIPT about biophysics, modern approaches to studying the heart, and how rat cells differ from human.

It is clear that this is the field of the connection of two disciplines - physics and biology, that is, when objects of biology are investigated, but by methods of physics. Konstantin Agladze prefers physicists to be involved in biophysics, rather than classical biologists, and preferably physicists who have been educated in Russia or the USSR.
What physicists can help biologists to: study the fine structures of cell interactions, cell assemblies, understand how they work using the tools of physics and mathematics.
')
Konstantin Agladze: “For example, there may be a physical approach to the population. Population dynamics is described just by nonlinear equations. This is all very well correlated. For example, the mathematical apparatus correlates well with that which is used to study, say, processes in excitable tissues (such as heart and nerve tissue. A small area in which we do this is the study of excitable systems. That is, our laboratory is called (it has historically received such a name), nanoconstructing protein complexes to control cell physiology. But in fact we simply call it the laboratory of the physics of excitable systems. ”
In the laboratory, Agladze deals specifically with heart tissue. To increase longevity and avoid heart disease, you need to understand how the heart works.
K. A .: “What happens to the heart? Waves of excitement travel along it and make a very large number of cells work as a single ensemble, pumping blood through the body. What is the result? On the one hand, this task is bionically interesting. There is a science of bionics, which originates in biological objects and thus tries to make narrow objects. This in itself is interesting. See how to pump very effectively viscous liquids, for example. But it's not that. And to see why this pumping system suddenly begins to fail? ”
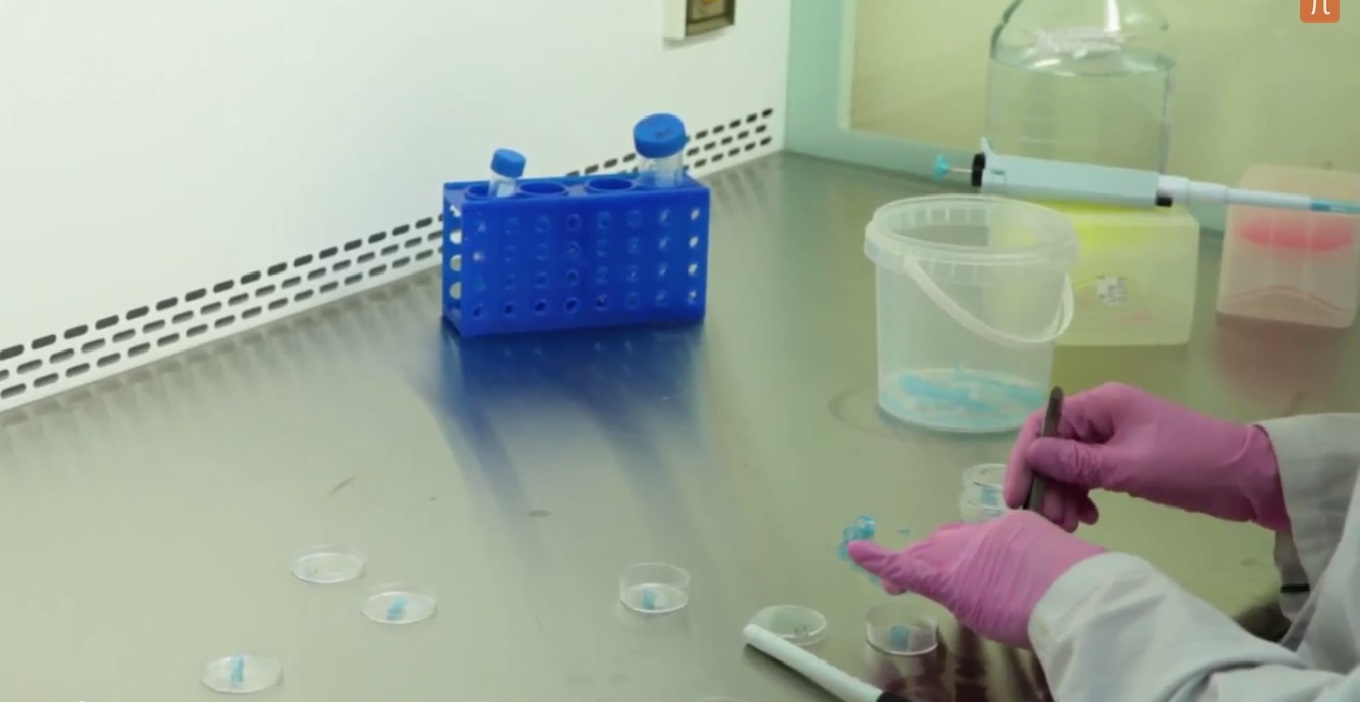

Electrophysiological study of the heart, as the direction that has emerged over 100 years ago, has now been developed and allows you to understand how the excitement spreads through the heart. This became possible only after the optical electrical determinants of the excitation waves of the heart were discovered and developed.
KA: “We put the electrode on the heart tissue, and we can see that the wave ran under the electrode. But we want to see the whole wave front. So we have to put a lot of electrodes. And if we want to see the position of the front at different points in time, then we must not only put a comb of these electrodes, but already the matrix of these electrodes. And if with good resolution, then there should be thousands of electrodes . ”
What were the breakthroughs in this area: 20 years ago dyes were developed that help track cell excitation. And in parallel, cameras have been developed that can see these fluorescents. At the same time, the former were shown to propagate an excitation wave, the emergence of vortex waves, which allows to understand that the concept of rotating vortices leads to sudden death.
K. A .: “Any attempts of multi-electrode recording needed very careful decoding, in some kind of speculation, that is, extrapolation. And there was always the question that maybe this is an extrapolator fantasy. And here it became visible. That is, it turned out possible to see it. "
The second breakthrough was when they learned how to do tissue culture and on it optical mapping. This made it possible to understand
K. A .: “There is always a question, and maybe a wave runs here in such a way that it’s a special heart, and not at all because of such pathways? Therefore, it was necessary to learn how to simplify the system. It was simplified, made from it the structure of the fabric. And they saw that there, too, one can see the spread of the waves and see why these waves lose stability under the influence of some chemicals, can break and form precursors of developing arrhythmia. Then our job was to go the other way. We began to complicate things. Then the question arises: well, after all, this heart is not isotropic, it has a fiber structure. But let us see what happens if we have not just an isotropic, but not an isotropic environment, that is, the cell comes out in one direction, what opportunities will there be for the propagation of arousal? Here we are tormented by this. This we are doing now. Plus, we can now make a controlled three-dimensional system. It is still quite thin. But still not one layer, but several layers of cells, and move in this direction. ”

Prospects for research in the following - need a transition to human cells from the rat. Of course, it is impossible to simply get them, but thanks to the work of Shinya (Xinya) Yamanaka, who learned to make pluripotent cells from ordinary cells, you can make them in such quantities as to make artificial heart tissue, and see what happens in human heart tissue.
K. A .: “On the one hand, we understand that there is a lot in common between a rat heart and a human one. If this were not common, then there would be no cardiac biophysics. But the fact is that there is a big difference. And we, for example, ourselves, stumbled upon this difference. My Japanese graduate student, who did this work, used an ordinary Japanese diarrhythmic, gave him a rat heart cell culture to see what would happen, he did not see anything. And when we began to deal with this, it turned out that the very widely used third-rate diarhythmics will work only on human cells, because they have special ion channels that are blocked by these diarrhythmics. But rats do not have these ion channels. It would seem a pretty obvious thing, but she received such an unexpected confirmation. That is, if we want to develop a medicine for humans, we must use human tissues. ”
Who should do this research at all? Konstantin believes that physicists who have a good biological background are more likely, because the study of excitation waves is a very physical task.
K. A .: “Of course, the expertise of molecular biologists is extremely important. For example, for working with pluripotent cells and for routine work. Although it is a very complex and delicate process. To differentiate them into cardiac cells, competent molecular biologists are needed first and foremost. But for the next stage, the work with these heart whirls is needed by physicists.
If we talk about specialists who are trained to work in our laboratory, then this is a very difficult question. Because, if we speak specifically about, say, those guys - my graduate students, who will be the first to defend themselves at the Physics and Technology Department, these are people who are engaged in the science that maybe dozens of people in the world are doing. That is, it is not a wide audience. On the other hand, they are excellent specialists in the same fluorescence microscopy, because they had to master this at the highest level. These are people who work great with computerized information gathering systems. And these are people who, of course, routinely studied tissue engineering. Therefore, wherever specialists of such a direction are needed, they can fully work. On the other hand, I have a feeling that we will soon have to prove that our method is extremely effective in the selection of medicinal devices. And I really hope that then he will simply be in demand in most pharmaceutical companies. What is this about? To do this, look at how pharmaceutical companies work. Since the success of molecular biology was very strong and everything went down to the level of molecular machines, then in fact it all now works at the level of ion channels. Excitable cells work by working on ion channels. And when pharmacists work something out, they look at the effect of a substance on a single channel and say: “Well, we have blocked this channel. Reduce excitability. And so this medicine will work. ” This is a prospect. After this is proven in these experiments, single cells, animal experiments are conducted. ”
The main task is to understand, due to what, what happens when wave breaks occur, and how whirlwinds behave:
K. A .: “Now it is completely unknown, the whirlwinds of excitement, which ultimately cause fibrillation, to what extent these waves themselves are stable. That is, do they stabilize for homogeneity or can they stably exist on their own, reviving, multiplying and somehow supporting their existence? That is, many things related to the dynamics of these eddies are not yet known in reality. Therefore, there is still a large field for activity. ”
For lovers of video format interview Konstantin Agladze available here.

What is biophysics
It is clear that this is the field of the connection of two disciplines - physics and biology, that is, when objects of biology are investigated, but by methods of physics. Konstantin Agladze prefers physicists to be involved in biophysics, rather than classical biologists, and preferably physicists who have been educated in Russia or the USSR.
What physicists can help biologists to: study the fine structures of cell interactions, cell assemblies, understand how they work using the tools of physics and mathematics.
')
Konstantin Agladze: “For example, there may be a physical approach to the population. Population dynamics is described just by nonlinear equations. This is all very well correlated. For example, the mathematical apparatus correlates well with that which is used to study, say, processes in excitable tissues (such as heart and nerve tissue. A small area in which we do this is the study of excitable systems. That is, our laboratory is called (it has historically received such a name), nanoconstructing protein complexes to control cell physiology. But in fact we simply call it the laboratory of the physics of excitable systems. ”
In the laboratory, Agladze deals specifically with heart tissue. To increase longevity and avoid heart disease, you need to understand how the heart works.
K. A .: “What happens to the heart? Waves of excitement travel along it and make a very large number of cells work as a single ensemble, pumping blood through the body. What is the result? On the one hand, this task is bionically interesting. There is a science of bionics, which originates in biological objects and thus tries to make narrow objects. This in itself is interesting. See how to pump very effectively viscous liquids, for example. But it's not that. And to see why this pumping system suddenly begins to fail? ”

Electrophysiology
Electrophysiological study of the heart, as the direction that has emerged over 100 years ago, has now been developed and allows you to understand how the excitement spreads through the heart. This became possible only after the optical electrical determinants of the excitation waves of the heart were discovered and developed.
KA: “We put the electrode on the heart tissue, and we can see that the wave ran under the electrode. But we want to see the whole wave front. So we have to put a lot of electrodes. And if we want to see the position of the front at different points in time, then we must not only put a comb of these electrodes, but already the matrix of these electrodes. And if with good resolution, then there should be thousands of electrodes . ”
What were the breakthroughs in this area: 20 years ago dyes were developed that help track cell excitation. And in parallel, cameras have been developed that can see these fluorescents. At the same time, the former were shown to propagate an excitation wave, the emergence of vortex waves, which allows to understand that the concept of rotating vortices leads to sudden death.
K. A .: “Any attempts of multi-electrode recording needed very careful decoding, in some kind of speculation, that is, extrapolation. And there was always the question that maybe this is an extrapolator fantasy. And here it became visible. That is, it turned out possible to see it. "
The second breakthrough was when they learned how to do tissue culture and on it optical mapping. This made it possible to understand
K. A .: “There is always a question, and maybe a wave runs here in such a way that it’s a special heart, and not at all because of such pathways? Therefore, it was necessary to learn how to simplify the system. It was simplified, made from it the structure of the fabric. And they saw that there, too, one can see the spread of the waves and see why these waves lose stability under the influence of some chemicals, can break and form precursors of developing arrhythmia. Then our job was to go the other way. We began to complicate things. Then the question arises: well, after all, this heart is not isotropic, it has a fiber structure. But let us see what happens if we have not just an isotropic, but not an isotropic environment, that is, the cell comes out in one direction, what opportunities will there be for the propagation of arousal? Here we are tormented by this. This we are doing now. Plus, we can now make a controlled three-dimensional system. It is still quite thin. But still not one layer, but several layers of cells, and move in this direction. ”

The future in the laboratory "Nanoconstruction of membrane-protein complexes to control cell physiology"
Prospects for research in the following - need a transition to human cells from the rat. Of course, it is impossible to simply get them, but thanks to the work of Shinya (Xinya) Yamanaka, who learned to make pluripotent cells from ordinary cells, you can make them in such quantities as to make artificial heart tissue, and see what happens in human heart tissue.
K. A .: “On the one hand, we understand that there is a lot in common between a rat heart and a human one. If this were not common, then there would be no cardiac biophysics. But the fact is that there is a big difference. And we, for example, ourselves, stumbled upon this difference. My Japanese graduate student, who did this work, used an ordinary Japanese diarrhythmic, gave him a rat heart cell culture to see what would happen, he did not see anything. And when we began to deal with this, it turned out that the very widely used third-rate diarhythmics will work only on human cells, because they have special ion channels that are blocked by these diarrhythmics. But rats do not have these ion channels. It would seem a pretty obvious thing, but she received such an unexpected confirmation. That is, if we want to develop a medicine for humans, we must use human tissues. ”

New specialists. Who is it?
Who should do this research at all? Konstantin believes that physicists who have a good biological background are more likely, because the study of excitation waves is a very physical task.
K. A .: “Of course, the expertise of molecular biologists is extremely important. For example, for working with pluripotent cells and for routine work. Although it is a very complex and delicate process. To differentiate them into cardiac cells, competent molecular biologists are needed first and foremost. But for the next stage, the work with these heart whirls is needed by physicists.
If we talk about specialists who are trained to work in our laboratory, then this is a very difficult question. Because, if we speak specifically about, say, those guys - my graduate students, who will be the first to defend themselves at the Physics and Technology Department, these are people who are engaged in the science that maybe dozens of people in the world are doing. That is, it is not a wide audience. On the other hand, they are excellent specialists in the same fluorescence microscopy, because they had to master this at the highest level. These are people who work great with computerized information gathering systems. And these are people who, of course, routinely studied tissue engineering. Therefore, wherever specialists of such a direction are needed, they can fully work. On the other hand, I have a feeling that we will soon have to prove that our method is extremely effective in the selection of medicinal devices. And I really hope that then he will simply be in demand in most pharmaceutical companies. What is this about? To do this, look at how pharmaceutical companies work. Since the success of molecular biology was very strong and everything went down to the level of molecular machines, then in fact it all now works at the level of ion channels. Excitable cells work by working on ion channels. And when pharmacists work something out, they look at the effect of a substance on a single channel and say: “Well, we have blocked this channel. Reduce excitability. And so this medicine will work. ” This is a prospect. After this is proven in these experiments, single cells, animal experiments are conducted. ”
Unsolved issues:
The main task is to understand, due to what, what happens when wave breaks occur, and how whirlwinds behave:
K. A .: “Now it is completely unknown, the whirlwinds of excitement, which ultimately cause fibrillation, to what extent these waves themselves are stable. That is, do they stabilize for homogeneity or can they stably exist on their own, reviving, multiplying and somehow supporting their existence? That is, many things related to the dynamics of these eddies are not yet known in reality. Therefore, there is still a large field for activity. ”
For lovers of video format interview Konstantin Agladze available here.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/202024/
All Articles