Microsoft released a set of updates, November 2013
The company has released a series of updates for its products, which cover 19 unique vulnerabilities (3 fixes with the Critical status and 5 with the Important status). A detailed report on closed vulnerabilities, product components and their versions can be found on the corresponding page of security bulletins . As part of this patch tuesday, MS releases three Critical updates and one Important for the latest browser versions and Internet Explorer 11, Windows 8.1 / RT 8.1 .

The MS13-090 update closes the cross-platform Remote Code Execution vulnerability in all versions of Windows for the icardie.dll ActiveX component (starting with Windows XP SP3 and ending with Windows 8.1). A few days ago, FireEye reported that attackers used an exploit bypassing DEP & ASLR [ msvcrt.dll ROP ] for Internet Explorer versions 7-8-9 [Windows XP and Windows 7], through which they installed malicious code (CVE- 2013-3918) aka drive-by. Despite the fact that the vulnerability is present in all versions of the OS, users using the latest versions of IE 10-11 browser on Windows 8 and 8.1 are not susceptible to exploitation, including due to the mitigation mechanisms used in these OSs. EMET users are also protected from this exploit’s destructive actions. In the morning, MS confirmed the closure of this vulnerability within patch tuesday. A reboot is required to apply fixes.
')

We have already written about the emollient technologies that Microsoft uses for its products. Using one of the latest versions of 64-bit Windows is in itself a mitigating factor, since DEP is enabled for processes there by default, regardless of whether they are compiled with its support or not (according to MS DEP applications, always enabled for 64-bit processes, but in practice, even with the Opt In mode in x64 OS, it also protects 32-bit processes, at least in Windows 8+). In contrast to 32-bit systems, in which DEP has the status of Opt In by default and requires additional configuration from the user to include applications in the list of protected ones. In addition, the use of 64-bit executables on x64 OS is an additional level of protection, as it allows the OS to create 64-bit processes that, for example, are much less sensitive to heap spray. Today, spray is the main ASLR bypass technique when performing a shell code.
You can view the status of the DEP policy on your OS by running cmd as an administrator and typing bcdedit.
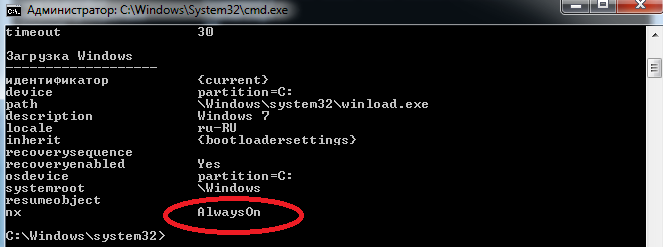
Fig. DEP settings for the system, the NX parameter is AlwaysOn (EMET is enabled in the OS).

Fig. Global DEP settings can be adjusted through the main EMET window.
Note that, for example, Internet Explorer 10+ in Enhanced Protected Mode mode uses the launch of its tabs as 64-bit processes for Windows 7 x64 as a mitigating factor. In addition, for libraries loaded into the address space of the process, ASLR (ForceASLR setup in OS for Windows 8+ and 7 with the necessary update) is forcibly included even if they are compiled without its support (/ DYNAMICBASE).

Fig. Manually enabled EPM for Windows 7 x64 makes it possible to launch tab processes as 64-bit processes (anti-spray).
In order to enable EPM for IE, you must follow the steps. Tools -> Browser Properties -> Advanced -> Enable Extended Protected Mode.
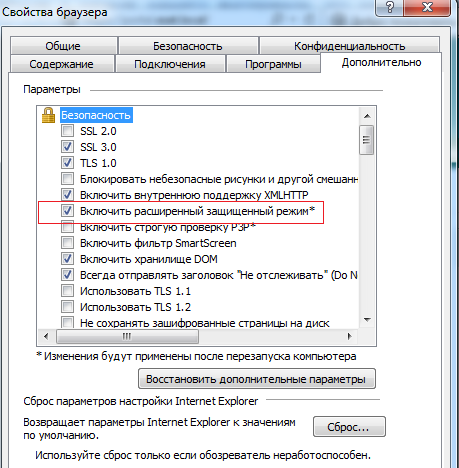
Fig. Setting the extended protected mode (aka sandboxing) for IE10 +, which is turned off by default for Windows 7 x64 (for Windows 7 x32 is a useless option). For Windows 8+ it is enabled by default and uses full tab isolation .
As for the ASLR for modules, it does not in itself have a global inclusion indicator. ASLR is included, rather than for the process, but for a specific module loaded into its address space. In case the executable image is not compiled with ASLR support, Process Explorer assigns the status to the process as missing ASLR, despite the fact that it is enabled for system libraries that work in the context of this process. In addition, the OS has a random address allocation policy for allocated memory (when using EMET, it is set via the BottomUpASLR setting).
Update MS13-088 (Critical) / Remote Code Execution: fixes ten vulnerabilities in all versions of Internet Explorer (6-11) for all Windows XP SP3 - 7 - 8.1. The attacker can execute arbitrary code in the system through a specially formed web page. Vulnerabilities are of type memory-crorruption and are associated with erroneous access of browser code to memory. Malicious attackers could exploit this vulnerability to stealthily install malicious code (drive-by). Exploit code likely .
MS13-089 (Critical) / Remote Code Execution Update: fixes one vulnerability in the GDI graphics component for all OS versions from Windows XP SP3 to 8.1. Attackers can execute remote code through a specially prepared Windows Write file for WordPad. Exploit code likely .
Update MS13-091 (Important) / Remote Code Execution: fixes three vulnerabilities in all supported versions of Microsoft Office 2003-2007-2010-2013-2013 RT. Attackers can execute remote code through a pre-prepared WordPerfect document. Exploit code likely .
Update MS13-092 (Important) / Elevation of Privilege: fixes one vulnerability in the 64-bit version of Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012. The OS code incorrectly processes the parameter when calling the Hyper-V function (hypercall), which allows an attacker to elevate their privileges in the system to the level of the system. Exploit code likely.
Update MS13-093 (Important) / Information Disclosure: fixes one vulnerability in the afd.sys kernel mode driver (Ancillary Function Driver) on all 64-bit editions of Windows except 8.1 (XP SP2 - 8-Server 2012). Vulnerability is present when data is incorrectly transferred by browser code between user mode and kernel mode memory blocks. Exploit code unlikely.
Update MS13-094 (Important) / Information Disclosure: fixes one vulnerability in all supported versions of the Microsoft Outlook email client. An attacker can use a specially prepared message (with an S / MIME certificate) to gain access to information about open ports and IP addresses of computers that work on the same network as the vulnerable system. Exploit code unlikely.
Update MS13-095 (Important) / Denial of Service: fixes one vulnerability in all supported OS versions. The vulnerability is present in the X.509 standard digital certificate processing component. An attacker could cause the web service to freeze through a specially prepared file. Exploit code unlikely.
1 - Exploit code likely
The probability of exploiting the vulnerability is very high, attackers can use an exploit, for example, for remote code execution.
2 - Exploit code would be difficult to build
The exploitation probability is average, since attackers are unlikely to be able to achieve a situation of sustainable exploitation, as well as due to the technical peculiarities of vulnerability and the complexity of developing an exploit.
3 - Exploit code unlikely
The exploitation probability is minimal and attackers are unlikely to be able to develop successfully working code and take advantage of this vulnerability to conduct an attack.
We recommend our users to install updates as soon as possible and, if you have not already done so, enable automatic delivery of updates using Windows Update (by default this option is enabled).


be secure.

The MS13-090 update closes the cross-platform Remote Code Execution vulnerability in all versions of Windows for the icardie.dll ActiveX component (starting with Windows XP SP3 and ending with Windows 8.1). A few days ago, FireEye reported that attackers used an exploit bypassing DEP & ASLR [ msvcrt.dll ROP ] for Internet Explorer versions 7-8-9 [Windows XP and Windows 7], through which they installed malicious code (CVE- 2013-3918) aka drive-by. Despite the fact that the vulnerability is present in all versions of the OS, users using the latest versions of IE 10-11 browser on Windows 8 and 8.1 are not susceptible to exploitation, including due to the mitigation mechanisms used in these OSs. EMET users are also protected from this exploit’s destructive actions. In the morning, MS confirmed the closure of this vulnerability within patch tuesday. A reboot is required to apply fixes.
')

We have already written about the emollient technologies that Microsoft uses for its products. Using one of the latest versions of 64-bit Windows is in itself a mitigating factor, since DEP is enabled for processes there by default, regardless of whether they are compiled with its support or not (according to MS DEP applications, always enabled for 64-bit processes, but in practice, even with the Opt In mode in x64 OS, it also protects 32-bit processes, at least in Windows 8+). In contrast to 32-bit systems, in which DEP has the status of Opt In by default and requires additional configuration from the user to include applications in the list of protected ones. In addition, the use of 64-bit executables on x64 OS is an additional level of protection, as it allows the OS to create 64-bit processes that, for example, are much less sensitive to heap spray. Today, spray is the main ASLR bypass technique when performing a shell code.
You can view the status of the DEP policy on your OS by running cmd as an administrator and typing bcdedit.

Fig. DEP settings for the system, the NX parameter is AlwaysOn (EMET is enabled in the OS).

Fig. Global DEP settings can be adjusted through the main EMET window.
Note that, for example, Internet Explorer 10+ in Enhanced Protected Mode mode uses the launch of its tabs as 64-bit processes for Windows 7 x64 as a mitigating factor. In addition, for libraries loaded into the address space of the process, ASLR (ForceASLR setup in OS for Windows 8+ and 7 with the necessary update) is forcibly included even if they are compiled without its support (/ DYNAMICBASE).

Fig. Manually enabled EPM for Windows 7 x64 makes it possible to launch tab processes as 64-bit processes (anti-spray).
In order to enable EPM for IE, you must follow the steps. Tools -> Browser Properties -> Advanced -> Enable Extended Protected Mode.

Fig. Setting the extended protected mode (aka sandboxing) for IE10 +, which is turned off by default for Windows 7 x64 (for Windows 7 x32 is a useless option). For Windows 8+ it is enabled by default and uses full tab isolation .
As for the ASLR for modules, it does not in itself have a global inclusion indicator. ASLR is included, rather than for the process, but for a specific module loaded into its address space. In case the executable image is not compiled with ASLR support, Process Explorer assigns the status to the process as missing ASLR, despite the fact that it is enabled for system libraries that work in the context of this process. In addition, the OS has a random address allocation policy for allocated memory (when using EMET, it is set via the BottomUpASLR setting).
Update MS13-088 (Critical) / Remote Code Execution: fixes ten vulnerabilities in all versions of Internet Explorer (6-11) for all Windows XP SP3 - 7 - 8.1. The attacker can execute arbitrary code in the system through a specially formed web page. Vulnerabilities are of type memory-crorruption and are associated with erroneous access of browser code to memory. Malicious attackers could exploit this vulnerability to stealthily install malicious code (drive-by). Exploit code likely .
MS13-089 (Critical) / Remote Code Execution Update: fixes one vulnerability in the GDI graphics component for all OS versions from Windows XP SP3 to 8.1. Attackers can execute remote code through a specially prepared Windows Write file for WordPad. Exploit code likely .
Update MS13-091 (Important) / Remote Code Execution: fixes three vulnerabilities in all supported versions of Microsoft Office 2003-2007-2010-2013-2013 RT. Attackers can execute remote code through a pre-prepared WordPerfect document. Exploit code likely .
Update MS13-092 (Important) / Elevation of Privilege: fixes one vulnerability in the 64-bit version of Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012. The OS code incorrectly processes the parameter when calling the Hyper-V function (hypercall), which allows an attacker to elevate their privileges in the system to the level of the system. Exploit code likely.
Update MS13-093 (Important) / Information Disclosure: fixes one vulnerability in the afd.sys kernel mode driver (Ancillary Function Driver) on all 64-bit editions of Windows except 8.1 (XP SP2 - 8-Server 2012). Vulnerability is present when data is incorrectly transferred by browser code between user mode and kernel mode memory blocks. Exploit code unlikely.
Update MS13-094 (Important) / Information Disclosure: fixes one vulnerability in all supported versions of the Microsoft Outlook email client. An attacker can use a specially prepared message (with an S / MIME certificate) to gain access to information about open ports and IP addresses of computers that work on the same network as the vulnerable system. Exploit code unlikely.
Update MS13-095 (Important) / Denial of Service: fixes one vulnerability in all supported OS versions. The vulnerability is present in the X.509 standard digital certificate processing component. An attacker could cause the web service to freeze through a specially prepared file. Exploit code unlikely.
1 - Exploit code likely
The probability of exploiting the vulnerability is very high, attackers can use an exploit, for example, for remote code execution.
2 - Exploit code would be difficult to build
The exploitation probability is average, since attackers are unlikely to be able to achieve a situation of sustainable exploitation, as well as due to the technical peculiarities of vulnerability and the complexity of developing an exploit.
3 - Exploit code unlikely
The exploitation probability is minimal and attackers are unlikely to be able to develop successfully working code and take advantage of this vulnerability to conduct an attack.
We recommend our users to install updates as soon as possible and, if you have not already done so, enable automatic delivery of updates using Windows Update (by default this option is enabled).


be secure.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/201844/
All Articles