Detailed educational program about corporate backup, how to compare systems + a couple of practical tips
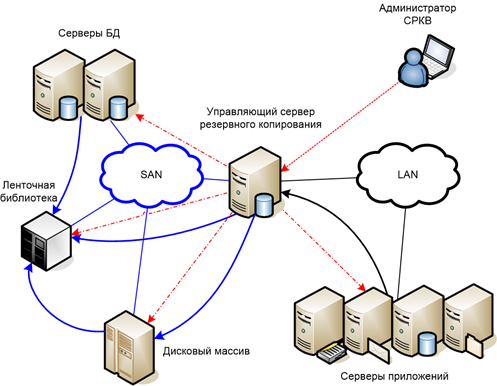
The backup system can work like this
How does a corporate backup differ from a home backup?
Scale - infrastructure to petabyte. Speed - thousands of transactions per second, so, for example, you need to be able to take a backup from the database on the fly, without stopping the recording. Zoo systems: working machines, mobile phones and tablets, profiles of people in the "cloud", copies of CRM / ERP databases, all this on different operating systems and in heavy branched systems.
Below I will talk about solutions from IBM, EMC, CommVault, Symantec, and what they give both to the business as a whole and to the IT department. Plus some of the pitfalls.
')
Let's look at these features of backup in the usual Russian companies. Including those that are backed up only in case of withdrawal of equipment.
We start the educational program. Backup is generally needed?
Usually this question is asked by people far from IT. The correct question is “what kind of backup is needed”? Earlier this year, I came across a report that, on average, in the world, data loss costs up to one third of the company's value, in the USA and Europe - up to half. Simply put, the lack of a fresh backup may in some cases mean leaving the market.
Why do I need backup?
Of course, to protect against failures, attacks and human stupidity. In general, the question is a bit naive, but still let's look at a little more.
- First, it protects data from loss. The main causes of loss are equipment failures, the fall of remote sites (for example, in case of a fire in the data center), the removal of equipment. Smaller cases - the loss of laptops and so on.
- Also backup protects the integrity of data: insures against operator errors, for example. This is the second most common reason: a person can take and "screw up" important data with the wrong team.
- Thirdly, in a corporate environment, a “hot” backup may be needed for the rapid deployment of services during an emergency, this is very important for those for whom the continuity of IT processes is particularly critical, for example, for telecom operators or banks.
How usually come to complex systems?
Everything is simple: with the growth of the company. First, simple tools are used: manual copying, then scripts according to a schedule or setting up a utility, after which a server application appears that manages this. At this stage, requirements are usually added to the level of backup from security guards or the finance department (the company’s risk manager) - and that's when the implementation begins. Each task is classified by importance and evaluated, for example, billing should roll in 5 minutes after the accident on the active backup system in another data center, and the data of the office staff - in 2 hours on previously prepared, but mothballed equipment. At this level, there is a need for tight integration with applications, and a little later - with hardware arrays for storage.
What does integration look like in practice?
As a rule, when our specialists come to install a total backup, a large company already has several backup subsystems. Most often, we are talking about already configured file backup applications and regularly taking database fingerprints (for example, nightly backup of 1C database) and storing them on a separate device. There are, of course, enchanting cases. For example, one retail chain did not make any backup bases at all about the availability of goods in a warehouse — and in the event of a failure sent people to do an inventory.
Or another example - the branch has a copy of the database, which is used only for reading. All data created on its basis is temporary. When a fall, a copy of this database is requested from the parent organization and it takes three days. People sit and wait. It is clear that the data is not lost, but if there was a correct backup, they would be able to continue working after 20 minutes.
What is most important in backup software?
Let's look at the main parameters.
Architecture
The solution architecture is undoubtedly important. Dividing the system into functional modules is common practice for all corporate backup solutions. The important point is the separation of the storage layer from the logical level of data management, as it is done, for example in CommVault Simpana - one backup task can use both a disk and a tape or even cloud storage.
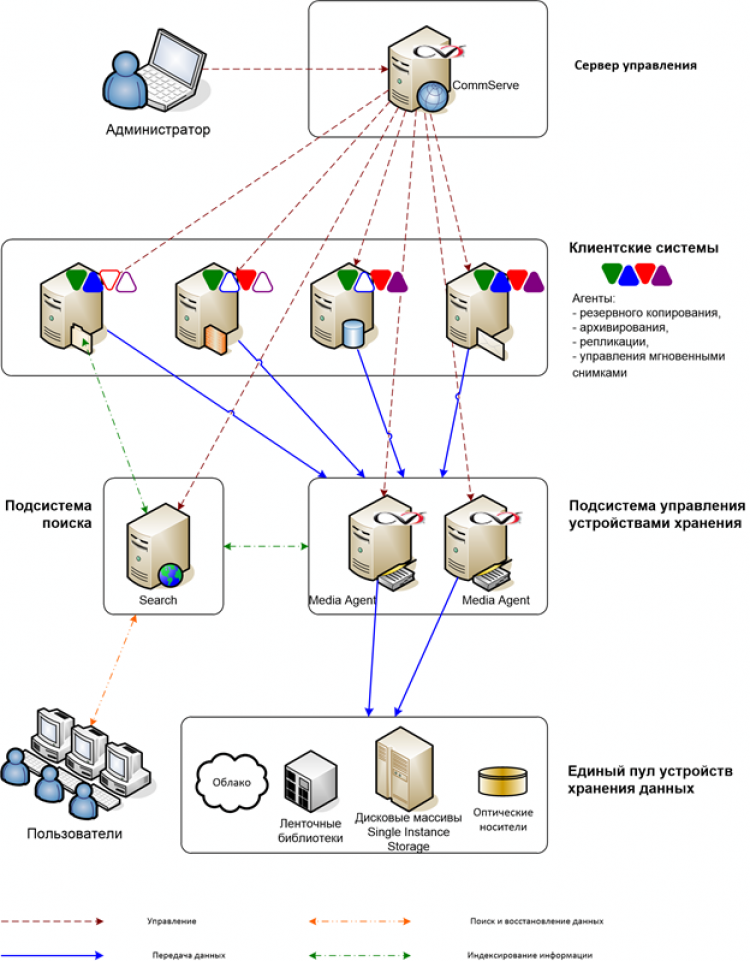
Backup Software Architecture Example (CommVault Simpana)
Functions of centralized management.
It is important to manage all operations. The backup of large systems is quite complicated, so it is important that the administrator accurately represents what is happening. With an extensive structure, for example, in a large data center with hundreds of systems, you will not “approach” each one and you will not see if it has a backup copy or not. Here you need a system that can build a report, see that all data and applications are copied or not copied, what you need to pay attention to, notify the administrator about any problems.
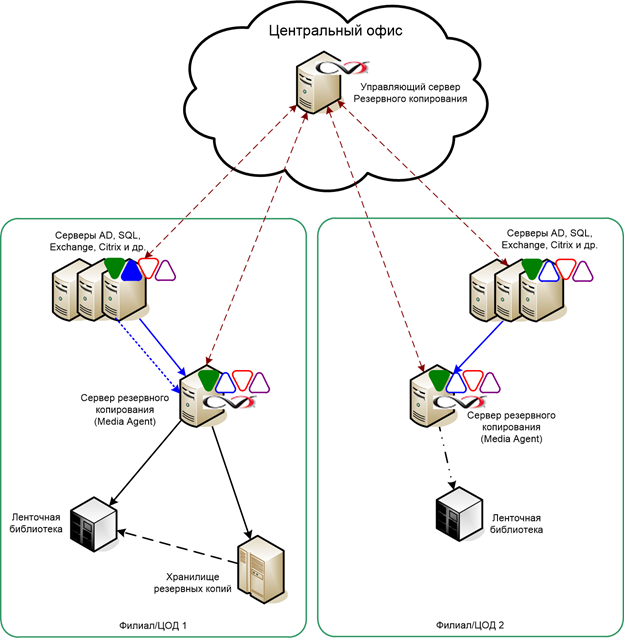
Centralized management of IBS
Market leaders have systems that allow you to see what is stored and where, what types of data, what exactly can be optimized, and so on. You can build a forecast for the year ahead.
Specific arrays and DB
The first is support of arrays, sharpening for specific databases. It is necessary to obtain data from below and use them in more complex functions, such as creating hardware snapshots. Backup systems themselves are already able to perform operations with arrays to ensure data protection without affecting production systems that work with these arrays, or minimizing the load on them,
Simply put, the system should be able on the fly to make a copy of the database from which transactions are being made, and not to request this copy from the server application. That is, it should competently and imperceptibly for the application and users to take data from the disk array.
For example, CommVault or EMC systems support almost all operating systems and commercial applications on the corporate market (in particular, Oracle, Microsoft databases, CommVault still has support for PostgreSQL and MySQL, Documentum, SAP).
Deduplication - Architecture
Important competent deduplication. Good deduplication significantly reduces the price requirements for disk arrays and very tight traffic. Roughly speaking, if the first backup of user data from virtual machines was 10 Gb, then each next one, per day, maybe 50-60 Mb - due to the difference between the system casts. At the same time, the backup market leaders (about them below) for external systems have their copies visible as separate casts, that is, as if a total backup was made every time. This speeds up recovery incredibly.
I would especially note that deduplication in modern systems is done at the source, that is, on the system from which the data are being taken, which greatly reduces the load on the channels. This is very important for extensive networks that do not always have a wide enough channel through which you can transfer a full backup. The usual “serial” copy for complex systems of the SAP level is only a couple percent of the total base volume.
The deduplication subsystem, in an amicable way, should scale conveniently. Ideally, linear with the addition of storage nodes by organizing some kind of Grid or Cloud. At the same time, nodes should not be separate islands with their own data sets, but connected into a single deduplication space. And it is quite good if these nodes parallelize the load and process it in parallel. I note that now many customers are trying to measure the deduplication coefficients when comparing products. But this is not entirely correct: modern SATA drives are already 4TB in volume each. Plus or minus a couple of disks and all systems will be able to store the same amount of data - and it is better to buy one disk at the beginning than to rebuild the whole system if necessary.
Load balancing
Even in such systems there are functions to ensure the fault tolerance of the operation and load balancing, which is important in large data centers, when data volumes in one system can reach tens and hundreds of Tb. For example, a virtualization platform can have a very large amount of data and a large number of virtual machines. The system itself, in this case, should allow to build a set of servers that will transfer data, receive them from the platform and write to the storage, so that they have the opportunity to interact with each other, and in the case of increasing or decreasing the load, redistribute it automatically. The function is simple and obvious, but rather critical, because it affects the speed and efficiency of creating backup copies.
Continuity is important. In case of failure of any components, you can ensure the successful completion of tasks for the backup window (usually night). CommVault Simpana allows you to do this automatically in case of media server and deduplication database failures. Other systems have limitations or require expensive hardware solutions. In the picture you can see two servers with agents that work in conjunction and if one breaks, the other one comes into operation. At the same time, both of them write to the same disk and have a common deduplication base:

Physical storage
Most often we are talking about storage on disk arrays, where additional data protection is provided. The first layer - important data must be stored at two independent remote sites (for example, in different data centers). The second layer - this data is stored on different drives. For example, a file of 10 blocks can be recorded on 11 drives - and if any of them fails, the rest will contain enough data to restore the missing link. Here is an example of one of these systems .
Drives and tape + "cloud"
So it turns out that tape drives are still in use. Most often, the “hot” data (say, 10 percent of the most important data) is stored on disks, from where you can get them quickly, and the second level is stored on tape. It is practical and cheap, plus the tape allows you to store data for almost decades without replacing equipment, they are simply removed and put on the shelf. A frequent case is logs and other documents of banks that need to be stored for a certain period. The backup system is able to allocate such data on a disk, alienate it and archive it on a tape drive. In this case, there is always the possibility in the event of an accident to find this information and recover. By the way, you can record both full copies and deduplicated ones - if necessary, a smart system can put everything back as if the last copy was complete.
But CommVault Simpana can also directly add a copy of the data from the corporate repository to the “cloud” (some of our customers do this with CROC's “cloud” - we even carried out certification). This additional copy can be considered by the customer as a long-term archive. For its storage it is not necessary to think about the hardware. Another copy can be used for disaster recovery systems. For example, one of the customers does this: a copy of all virtual machines is sent to our “cloud” for storage. In case of the fall of the main data center of the customer, we can run all these virtual machines on our infrastructure. At the same time, payment before the launch goes only for capacity - that is, it turns out to be very economical.
Direct work with users
If you have not encountered a corporate backup, then you may get the impression that only the IT department rolls back the data, and does it manually. But, for example, in CommVault, this is not quite the case.
In this situation, the user can himself go to the portal (in the picture below) and roll specifically his own data, if they were in a copy. Typically, such a portal also has a search engine for backups and archives (as part of user rights). The same archive can also be used to access information security staff - this will significantly reduce the number of inquiries to the IT department with questions like: “And who had this document”.
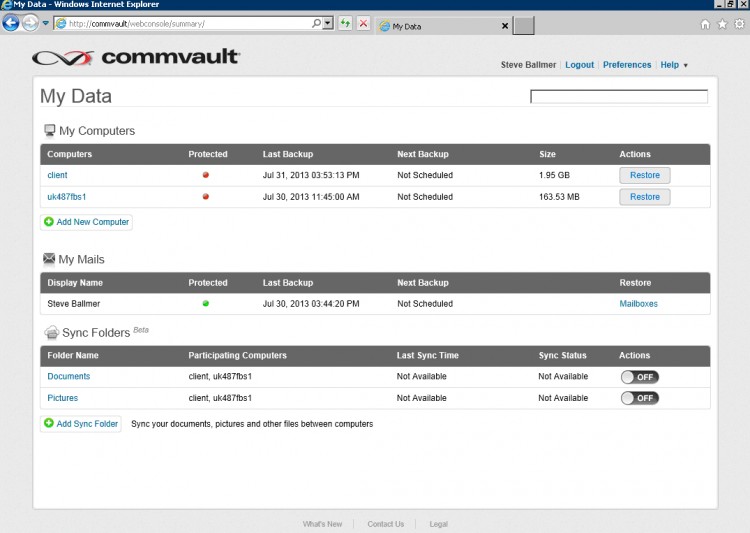
Yes, you understood correctly. If the user has lost the file, accidentally deleted the letter or wanted to find the old version of the document for comparison - he just goes and does everything himself in seconds without any complications. And he doesn't even call and write to the IT department.
We should also say about the search . All unstructured data (files, mail, SharePoint objects, etc.) that fall into the system would be good to index and organize a search engine. Simpana does it. On the one hand, via the self-service console, users can find any object themselves by keywords. On the other hand, the security service can carry out targeted measures to analyze all this information, including to search for internal threats. Well, the system can set the data retention period depending on the content of this data.

How fast can all be rolled back?
Suppose we have a complex system with an Oracle database as storage. Data is physically spread over several servers in one data center. Used by CommVault.
- The first case - the user took and deleted data from his workstation. Restores either himself or the administrator: enters the interface, selects the site. Everything else is done by the system. The user sees a beautiful web interface, the administrator can work with him or with the console.
- Now we have an Exchange mail server crashes. The script is still quite simple: again, either the user himself or the administrator determines which data needs to be restored, connects, logs in, opens the recovery console, selects the area, presses the “recover” button.
- Now we have lost data from the base of our large commercial applications for today. For example, all transactions on the sale. In this case, the backup system will knock on the RMAN mechanism that Oracle has (this is a kind of data recovery API). But since everything is already integrated with us, the administrator also only chooses what needs to be restored. Further, RMAN itself, along with the backup system, decides what to do specifically: restore the entire database or some TableSpace, i.e. a separate table, and so on.
- And now our data center explodes at night. In this case, the administrator selects another data center and rolls the last copy to the “clean” equipment. The system itself collects the most recent complete copy of the deduplicated data and gives the necessary information to each subsystem and application. Regular users, most likely, do not even notice what happened. It may be that in some other data center some data is already there, replicated, or simply restored according to a schedule, then it is still easier and recovery takes place not even on a clean system.
System development from version to version
With the development of backup systems, support for new commercial applications appears. It's about standard service packs as part of support. CommVault, for example, has a good policy to release compatibility updates to the current version, rather than forcing the next release to buy: this is convenient because the company's infrastructure is constantly evolving.
In new versions of software, new features appear, such as copying in a single pass, for example, with simultaneous transfer to the archive from file servers. Or, archiving and backup operations in Exchange have recently been merged - now they are also done in a single pass. Recently, the possibility of archiving virtual machines appeared pleasant for large cloud systems: if the machine is not used for a long time or turned off, then, according to a set of rules, it can be removed from the virtualization platform, and only a backup copy will remain.
Recently, there were clients for iOS and Android for managing copies of their workstation: it’s convenient if someone leaves on a business trip and forgets a presentation, for example. Or when the laptop breaks on the road. Here, too, do not need to wake the admin in two nights: the user can do everything himself.
Vendors
According to the report Gartner - among the leaders with whom we are actively working, in particular, IBM, Symantec, EMC and CommVault.

Gartner Square: top-right leaders, niche-bottom players.
IBM Tivoli Storage Manager (TSM) is a fairly flexible product in terms of setting up and organizing a backup scheme in an enterprise. Combining the various components of TSM, the customer gets the opportunity to build the desired functionality for their tasks. But, often, this requires more time for design and implementation. TSM is often used as part of integrated solutions based on hardware and software from IBM.
EMC . Being a company that produces not only software, but also hardware, it is primarily aimed at integrating all its solutions. Therefore, if the infrastructure is more built on the Clariion storage system, VNX, data domain, you should look at the EMC backup products, which will ensure a uniform system structure. By the way, the EMC Avamar product is also a software and hardware solution.
Symantec is on the backup market with its flagship product, NetBackup, focused on the enterprise segment, and the more “lightweight” BackupExec, traditionally used in environments built primarily on Microsoft products. NetBackup is renowned for supporting a wide range of operating systems, DBMSs and business applications, including those deployed in a virtual environment. And also knows how to use advanced features of modern storage systems. NetBackup is a good choice for environments with a large share of UNIX systems. Recently, Symantec products are supplied not only as software, but also as PAK, which speeds up their deployment and configuration.
CommVault . Perhaps the most important is that it is a complete product that covers almost all potential customer needs. This is a unified platform that combines the functionality of copying, archiving and data access. Plus, traditionally good integration with virtualization platforms, deduplication and integration with cloud storage. Well, as mentioned above, the IT department is greatly relieved by a competent policy of user access rights to archive elements. According to the experience of a number of implementations, CommVault will be a good choice in the presence of a large number of heterogeneous software and hardware. In homogeneous environments based on * unix, it is probably worth thinking about other products, but in heterogeneous environments - it allows you to immediately get rid of chaos and always be sure that there is a backup, it is fresh, and quickly rolls back, if that. And this, as you probably know, is very protective of nerves.
In general, we must look, of course, in place. If you have questions about what to choose for your infrastructure, write to AlBelyaev@croc.ru, we will help you evaluate all aspects and warn about possible pitfalls.
More interesting links
- Storage virtualization : how to “smear” them across the entire data center, so that if a meteorite hits, you can continue working.
- Overview of "fast" storage used for active-active systems in the field of Big Data.
- Educational program about how to make disaster-proof solutions at home.
- About the difference in the design of data centers and the history of one accident.
- Overview of EMC backup solution : large storage in a distant data center and a small server for you, which keeps track of everything.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/196258/
All Articles