The development of taxonomy of creative expression through the conceptual apparatus of mathematical game theory
This article is a logical continuation of the previous one .
The purpose of this article is to create a symbiosis of the taxonomy of creative expression and mathematical game theory. This will help develop the taxonomy proposed earlier, as well as bring it under the mathematical basis.
To disclose the conceptual apparatus and determine the point from which the development of the taxonomy presented earlier is possible, it is first necessary to answer the question “What are the signs of the game used in the mathematical theory of games?”.
Characteristic signs of such games are:
')
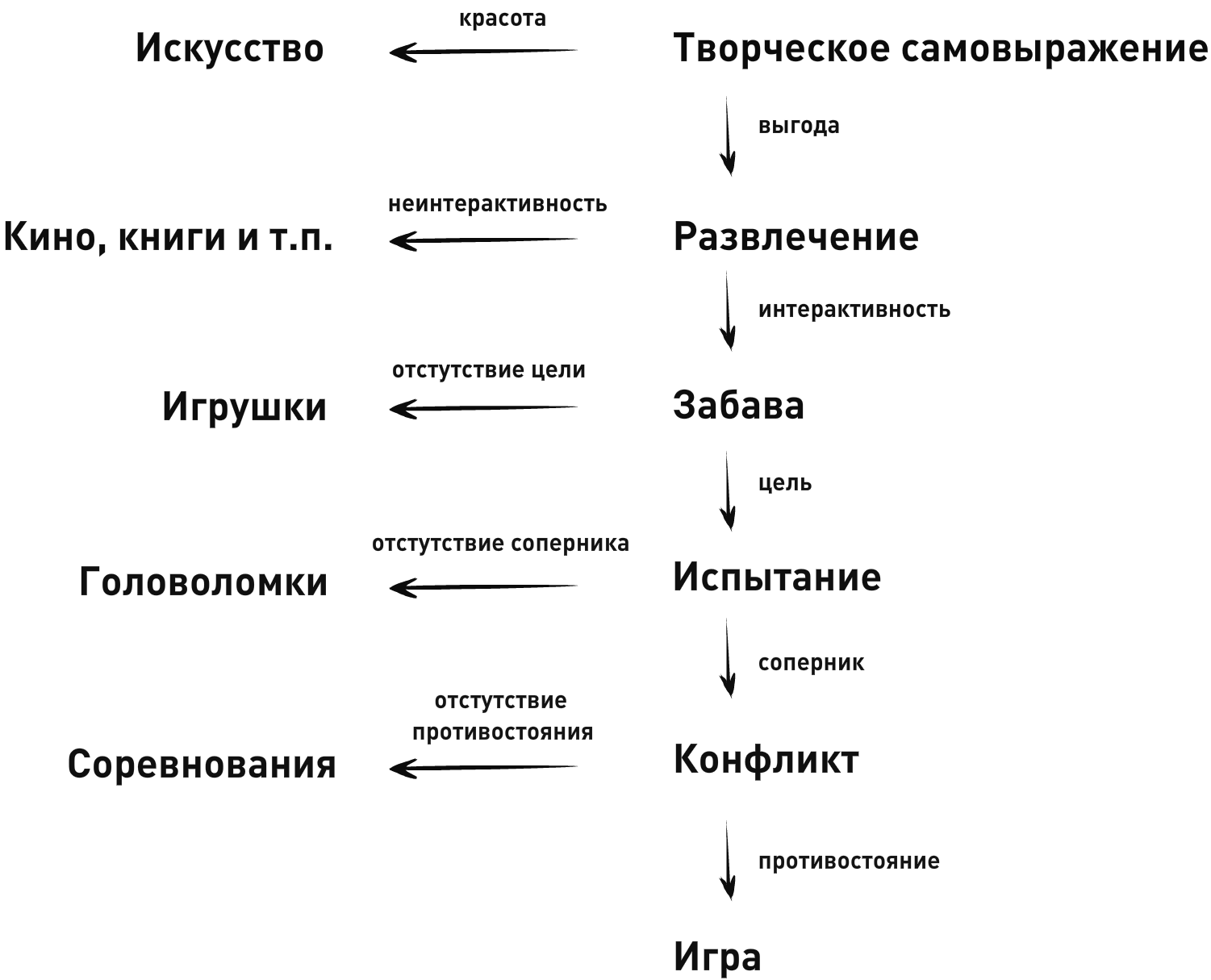
As we can see, already the first sign of the game intersects with the question-splitter of Crawford's taxonomy - “The presence of an opponent”, which brings math games to the “ Conflict ” category.
The second feature complements this conclusion by stating that the opponent must be an active agent, since artificial intelligence algorithms can be calculated sooner or later.
The third and fourth signs do not allow us to go beyond this category, because they simultaneously satisfy the requirements of the category " Competition " and the category " Game ".
The fifth sign corresponds to the category " Fun ", but since we have signs of the category of lower class " Conflict ", then we will choose it for development.
Cooperative or coalition games in game theory are games in which players can join together in groups, taking on certain obligations to other players and coordinating their actions.
Non-cooperative games are games in which each player must play for himself.

From left to right : 1. Board game Dungeons & Dragons 2. Board game Monopoly 3. First-person shooter Halo 4. Fighting Mortal Kombat
Hybrid games are games that include elements of cooperative and non-cooperative games. In these games, players can form groups, but the game can be played in a non-cooperative style (for example, kill stealing in League of Legends ).
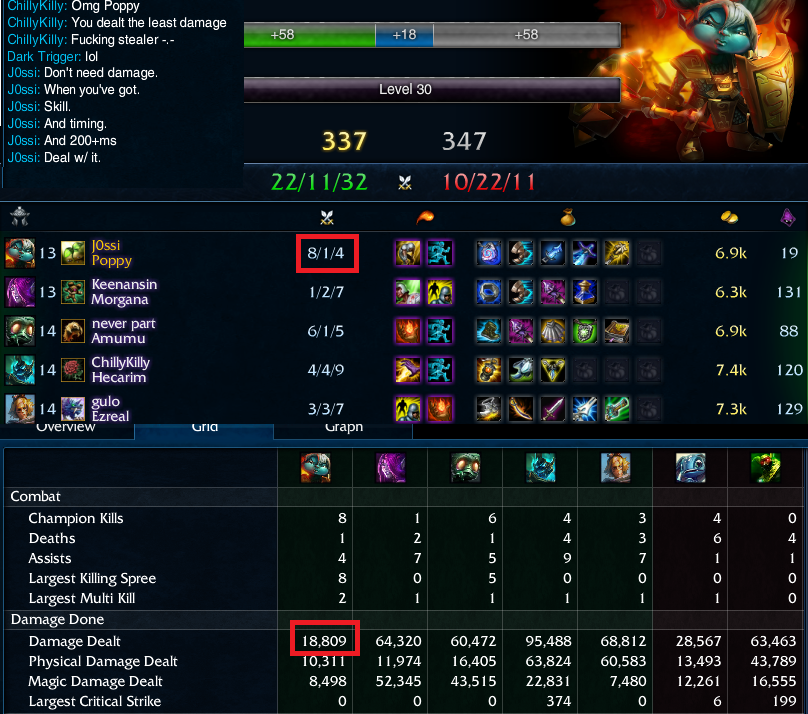
Screenshot from League of Legends game
Each player in such a game will pursue the interests of his group, at the same time trying to achieve personal gain. This behavior is called the "Tragedy of Communities".
A symmetrical game is a game in which players can change places and at the same time their winnings for the same moves will not change (the corresponding strategies of the players are equal).
An asymmetric game is a game in which the corresponding strategies of the players are not equal.

From left to right : 1. Texas Hold'em variety of card game poker 2. Economic dilemma game Ultimatum 3. Multiplayer online arena of League of Legend 4. Team online shooter Counter-strike .
From the examples of games given here, I want to tell you separately about the Ultimatum game. This game belongs to the class of games used in experimental economics. The rules are pretty simple. One of the participants must divide a certain amount of money (for clarity, we take the amount of a million euros) between himself and the second player, and he decides the size of the shares himself. The second participant must decide whether to accept the proposed amount or refuse. In case of refusal, both participants are left with nothing. In case of agreement, all remain with their shares.
It would seem that player two must agree in any case, because otherwise he gets nothing. However, experimental studies show that when a share is offered less than 30%, the second player refuses the offer.
In the next article I will discuss this game in more detail with the aim of disclosing the decision-making mechanism of the player from the perspective of neurobiology.
Zero-sum games are games in which players cannot increase or decrease the available game resources or the fund of the game. In this case, the sum of all winnings is equal to the sum of all losses in any course.
Non-zero-sum games are games in which players can increase the fund of a game. It also includes games in which winning one player does not necessarily mean losing another, and vice versa.

From left to right : 1. Blackjack card game 2. Scrabble board game 3. Fighting Tekken 4. Action Castle crashers
Parallel games are games in which players play at the same time, or at least they are not aware of the choice of other players until everyone makes their move.
Sequential or dynamic games are games in which participants can make moves in a predetermined or random order, but at the same time receive some information about the previous actions of others.

From left to right : 1. Rock-paper-scissors game ( Rock-paper-scissors) 2. Jenga board game 3. Starcraft 2 real-time strategy game network mode 4. Step-by-step strategy Heroes of Might and Magic 3
Games with full information - games in which players know all the moves made up to the present moment, as well as possible strategies of opponents.
Games with incomplete information - games in which players do not know information about all the moves of the opponent.

From left to right : 1. Family version of Agricola board game 2. Prisoner's dilemma dilemma game ( Prisoner's dilemma) 3. Pure Chess computer logic game 4. Online first-person shooter game Quake 3 Arena
By analogy with the game Ultimatum , I want to separately consider the game-problem The prisoner's dilemma . A small introduction: in all judicial systems, the punishment for banditry (committing crimes in an organized group) is much harder than for the same crimes committed alone.
The wording of the game is as follows:
“ Two criminals, A and B, got caught at similar crimes on the same time. There is reason to believe that they acted in collusion, and the police, isolating them from each other, offered them the same deal: if one testifies against the other, but the latter keeps silence, the first is released for helping the investigation, and the second receives the maximum term of imprisonment (10 years). If both are silent, their act is carried out under a lighter article and each of them is sentenced to 0.5 years If both testify against each other, they get t is the minimum term (2 years). Each prisoner chooses to keep silent or testify against another. However, none of them knows exactly what the other will do. What will happen? "
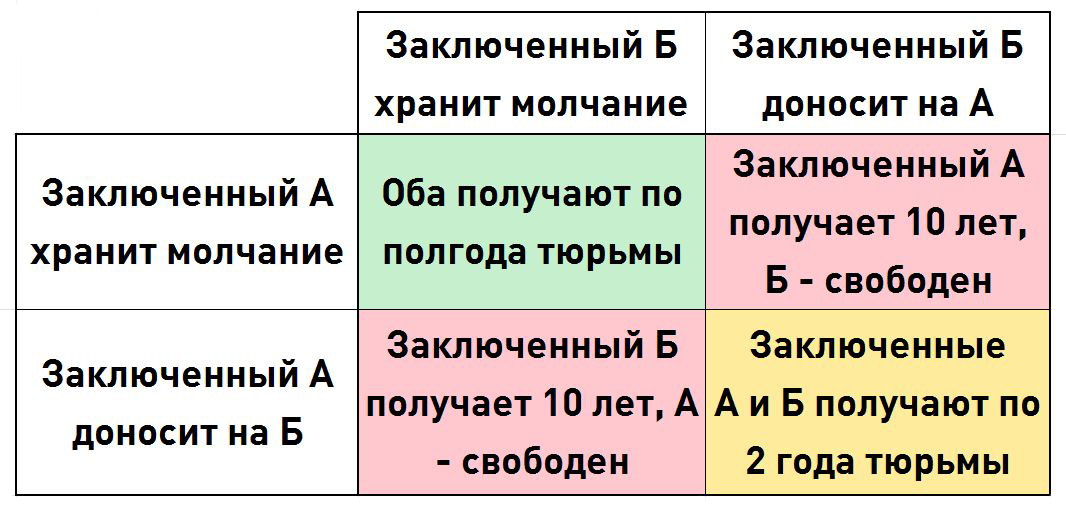
Matrix of the Prisoner's dilemma game ( Prisoner's dilemma)
The problem is that if players seek to maximize their winnings, they will come to a non-optimal solution, while cooperation would be beneficial to both players.
Despite this, it is the most rational way out for the player in this game to get across to the second player, because no matter what the other player chooses, everyone wins more if he betrays.
If you argue from the prisoner, “If the second is silent, then you can bring it to him and immediately go free, or sit down for six months. If the second pawns me, then I can either sit down for 10 years , or for 2 years. ”
Endless games are games that can last indefinitely, and the winner and his winnings are not determined until the end of all moves.
Discrete games - games that have a finite number of players, moves, events, outcomes, etc.

From left to right : 1. Online MMORPG Dream Of Mirror Online 2. Board game Uno 3. PVP server online MMORPG World of Warcraft 4. Board card game Magic: The Gathering
As a result, we get the following scheme of disclosure of the taxonomy of creative expression.
The purpose of this article is to create a symbiosis of the taxonomy of creative expression and mathematical game theory. This will help develop the taxonomy proposed earlier, as well as bring it under the mathematical basis.
To disclose the conceptual apparatus and determine the point from which the development of the taxonomy presented earlier is possible, it is first necessary to answer the question “What are the signs of the game used in the mathematical theory of games?”.
Characteristic signs of such games are:
')
- The presence of several participants in the game.
- Uncertainty of the participants' behavior due to the presence of several options for each of them.
- Distinction (mismatch) of interests of participants
- The interconnected behavior of participants, since the result obtained by each of them depends on the behavior of all participants.
- The presence of rules of conduct, known to all participants.
As we can see, already the first sign of the game intersects with the question-splitter of Crawford's taxonomy - “The presence of an opponent”, which brings math games to the “ Conflict ” category.
The second feature complements this conclusion by stating that the opponent must be an active agent, since artificial intelligence algorithms can be calculated sooner or later.
The third and fourth signs do not allow us to go beyond this category, because they simultaneously satisfy the requirements of the category " Competition " and the category " Game ".
The fifth sign corresponds to the category " Fun ", but since we have signs of the category of lower class " Conflict ", then we will choose it for development.
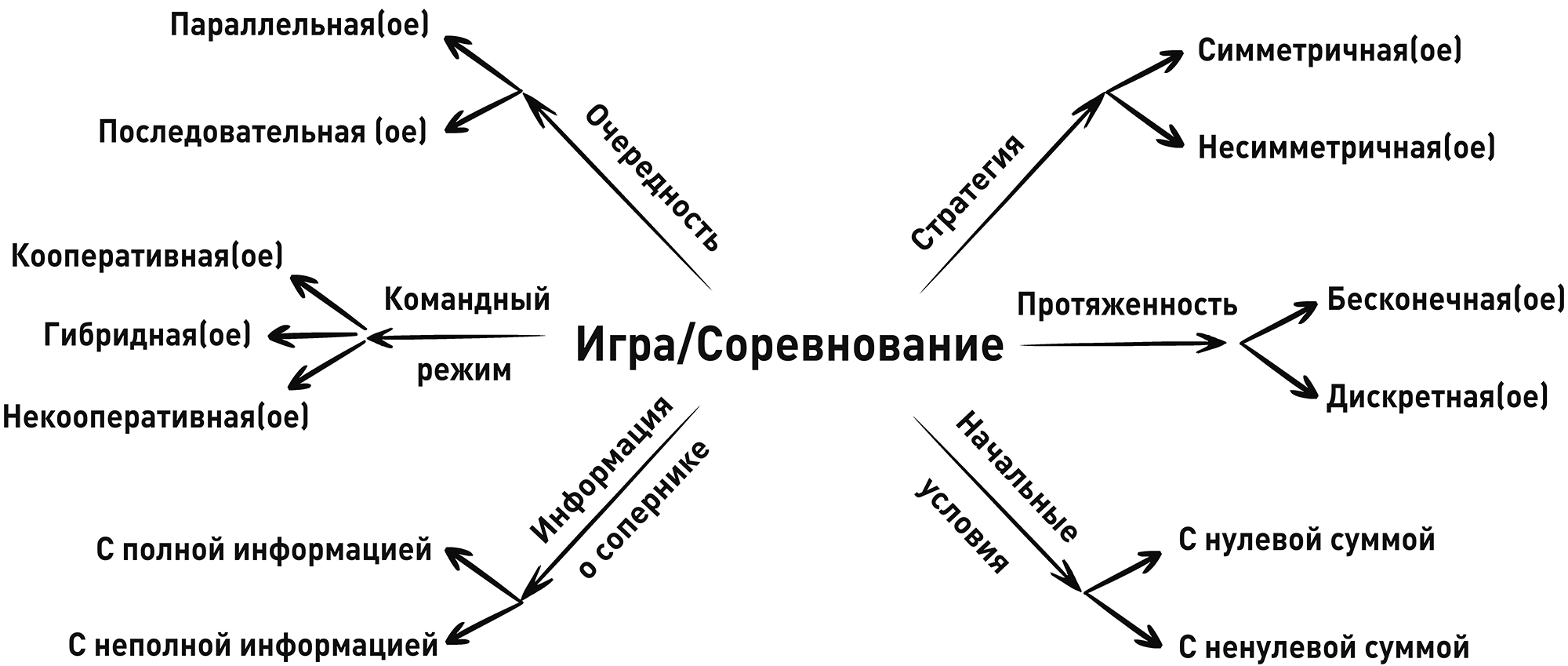
Types of games in the mathematical theory of games
- Cooperative, non-cooperative and hybrid games
Cooperative or coalition games in game theory are games in which players can join together in groups, taking on certain obligations to other players and coordinating their actions.
Non-cooperative games are games in which each player must play for himself.

From left to right : 1. Board game Dungeons & Dragons 2. Board game Monopoly 3. First-person shooter Halo 4. Fighting Mortal Kombat
Hybrid games are games that include elements of cooperative and non-cooperative games. In these games, players can form groups, but the game can be played in a non-cooperative style (for example, kill stealing in League of Legends ).

Screenshot from League of Legends game
Each player in such a game will pursue the interests of his group, at the same time trying to achieve personal gain. This behavior is called the "Tragedy of Communities".
- Symmetric and asymmetric games
A symmetrical game is a game in which players can change places and at the same time their winnings for the same moves will not change (the corresponding strategies of the players are equal).
An asymmetric game is a game in which the corresponding strategies of the players are not equal.

From left to right : 1. Texas Hold'em variety of card game poker 2. Economic dilemma game Ultimatum 3. Multiplayer online arena of League of Legend 4. Team online shooter Counter-strike .
From the examples of games given here, I want to tell you separately about the Ultimatum game. This game belongs to the class of games used in experimental economics. The rules are pretty simple. One of the participants must divide a certain amount of money (for clarity, we take the amount of a million euros) between himself and the second player, and he decides the size of the shares himself. The second participant must decide whether to accept the proposed amount or refuse. In case of refusal, both participants are left with nothing. In case of agreement, all remain with their shares.
It would seem that player two must agree in any case, because otherwise he gets nothing. However, experimental studies show that when a share is offered less than 30%, the second player refuses the offer.
In the next article I will discuss this game in more detail with the aim of disclosing the decision-making mechanism of the player from the perspective of neurobiology.
- Games with zero and non-zero amount
Zero-sum games are games in which players cannot increase or decrease the available game resources or the fund of the game. In this case, the sum of all winnings is equal to the sum of all losses in any course.
Non-zero-sum games are games in which players can increase the fund of a game. It also includes games in which winning one player does not necessarily mean losing another, and vice versa.

From left to right : 1. Blackjack card game 2. Scrabble board game 3. Fighting Tekken 4. Action Castle crashers
- Parallel and sequential games
Parallel games are games in which players play at the same time, or at least they are not aware of the choice of other players until everyone makes their move.
Sequential or dynamic games are games in which participants can make moves in a predetermined or random order, but at the same time receive some information about the previous actions of others.

From left to right : 1. Rock-paper-scissors game ( Rock-paper-scissors) 2. Jenga board game 3. Starcraft 2 real-time strategy game network mode 4. Step-by-step strategy Heroes of Might and Magic 3
- Games with complete and incomplete information
Games with full information - games in which players know all the moves made up to the present moment, as well as possible strategies of opponents.
Games with incomplete information - games in which players do not know information about all the moves of the opponent.

From left to right : 1. Family version of Agricola board game 2. Prisoner's dilemma dilemma game ( Prisoner's dilemma) 3. Pure Chess computer logic game 4. Online first-person shooter game Quake 3 Arena
By analogy with the game Ultimatum , I want to separately consider the game-problem The prisoner's dilemma . A small introduction: in all judicial systems, the punishment for banditry (committing crimes in an organized group) is much harder than for the same crimes committed alone.
The wording of the game is as follows:
“ Two criminals, A and B, got caught at similar crimes on the same time. There is reason to believe that they acted in collusion, and the police, isolating them from each other, offered them the same deal: if one testifies against the other, but the latter keeps silence, the first is released for helping the investigation, and the second receives the maximum term of imprisonment (10 years). If both are silent, their act is carried out under a lighter article and each of them is sentenced to 0.5 years If both testify against each other, they get t is the minimum term (2 years). Each prisoner chooses to keep silent or testify against another. However, none of them knows exactly what the other will do. What will happen? "

Matrix of the Prisoner's dilemma game ( Prisoner's dilemma)
The problem is that if players seek to maximize their winnings, they will come to a non-optimal solution, while cooperation would be beneficial to both players.
Despite this, it is the most rational way out for the player in this game to get across to the second player, because no matter what the other player chooses, everyone wins more if he betrays.
If you argue from the prisoner, “If the second is silent, then you can bring it to him and immediately go free, or sit down for six months. If the second pawns me, then I can either sit down for 10 years , or for 2 years. ”
- Infinite and discrete games
Endless games are games that can last indefinitely, and the winner and his winnings are not determined until the end of all moves.
Discrete games - games that have a finite number of players, moves, events, outcomes, etc.

From left to right : 1. Online MMORPG Dream Of Mirror Online 2. Board game Uno 3. PVP server online MMORPG World of Warcraft 4. Board card game Magic: The Gathering
As a result, we get the following scheme of disclosure of the taxonomy of creative expression.
Taxonomy Disclosure
Original taxonomy of creative expression

Taxonomy disclosure through the conceptual apparatus of mathematical game theory

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/195882/
All Articles