Hardware Trojans: Now with Dope
A long time ago there were stories about spyware modules in electronic microcircuits, special codes that rendered the potential enemy's electronics unusable and other echoes of the war of the invisible front. Those tales are gone, but the problem of iron insecurity remains and is being studied in depth. A group of scientists from the USA, Switzerland and Germany proposed a special type of hardware Trojans, which are almost impossible to detect either visually or with the help of tests, or outside the laboratory.
Becker, Regazzoni, Paar and Burleson investigated the possibility and consequences of deliberate disruption of the doping process, namely the change in polarity of the dopant. In fact, only the doping mask changes, even the amount of consumable impurities can remain the same. Scientists believe that such an intervention is unnoticeable even when scanning with an electron microscope and compared with a standard (not to mention that the standard can also be “attacked”).
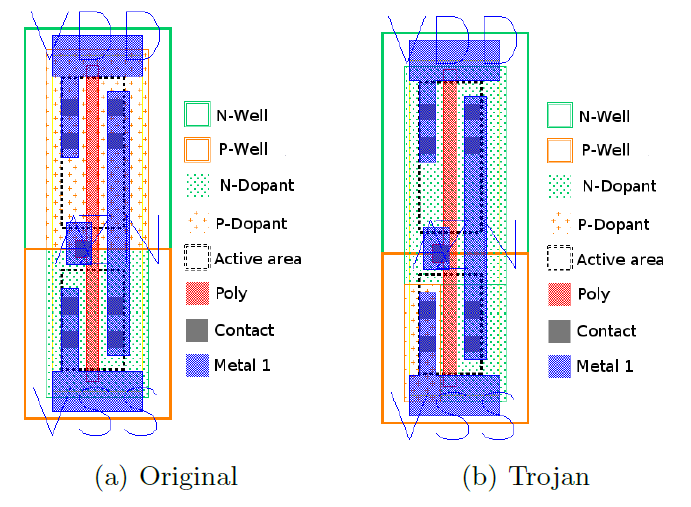
The result is a defective transistor, which can always have a fixed output voltage or create a leakage current. As an example of how such sabotage can affect security, scientists cited a random number generator at Intel's Ivy Bridge, in particular, because its design and testing method is publicly available.
')
A random number generator in Ivy Bridge stores two 128-bit constants: the key K and the state C. In normal operation, these constants are updated quite often, but by making small changes, you can achieve a fixed value for the key K and an almost fixed value for C (this is "almost "Necessary for passing internal and external tests). The difficulty of “guessing” the value of C is thus reduced to the desired number of bits; Scientists believe that 32 is enough to pass the external test NIST. Since a random number is generated by AES encrypting the state C with the key K, entropy does not suffer; cyclicity is also not observed: the state is sat quite often. The built-in test (Built-In Self-Test) checks the checksum of random numbers for the given initial parameters (the changes do not affect this area) and the entropy, so that it also does not notice forgery and at the same time remains able to report errors.
The ability to create leakage current was used in another example to determine the secret keys of an encrypted channel while maintaining the security of the channel as a whole. In fairness, it should be noted that while samples of hardware Trojans have been identified, but still ahead.
Original study
Becker, Regazzoni, Paar and Burleson investigated the possibility and consequences of deliberate disruption of the doping process, namely the change in polarity of the dopant. In fact, only the doping mask changes, even the amount of consumable impurities can remain the same. Scientists believe that such an intervention is unnoticeable even when scanning with an electron microscope and compared with a standard (not to mention that the standard can also be “attacked”).

The result is a defective transistor, which can always have a fixed output voltage or create a leakage current. As an example of how such sabotage can affect security, scientists cited a random number generator at Intel's Ivy Bridge, in particular, because its design and testing method is publicly available.
')
A random number generator in Ivy Bridge stores two 128-bit constants: the key K and the state C. In normal operation, these constants are updated quite often, but by making small changes, you can achieve a fixed value for the key K and an almost fixed value for C (this is "almost "Necessary for passing internal and external tests). The difficulty of “guessing” the value of C is thus reduced to the desired number of bits; Scientists believe that 32 is enough to pass the external test NIST. Since a random number is generated by AES encrypting the state C with the key K, entropy does not suffer; cyclicity is also not observed: the state is sat quite often. The built-in test (Built-In Self-Test) checks the checksum of random numbers for the given initial parameters (the changes do not affect this area) and the entropy, so that it also does not notice forgery and at the same time remains able to report errors.
The ability to create leakage current was used in another example to determine the secret keys of an encrypted channel while maintaining the security of the channel as a whole. In fairness, it should be noted that while samples of hardware Trojans have been identified, but still ahead.
Original study
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/193954/
All Articles