Guide to designing relational databases (1-3 part of 15) [translation]
Translation cycle of 15 articles on database design.
Information is intended for beginners.
It helped me. It is possible that it will help someone else to fill in the gaps.
If you are going to create your own databases, then it would be nice to adhere to the rules of database design, as this will ensure the long-term integrity and ease of maintenance of your data. This guide will tell you what a database is and how to design a database that follows the rules for designing relational databases.
Databases are programs that allow you to save and receive large amounts of related information. Databases consist of tables that contain information . When you create a database you need to think about which tables you need to create and what relationships exist between the information in the tables. In other words, you need to think about the design of your database. A good database design, as mentioned earlier, will ensure data integrity and ease of maintenance.
')
A database is created to store information in it and retrieve this information if necessary. This means that we need to be able to insert information into the database and we want to be able to select information from the database ( SELECT ).
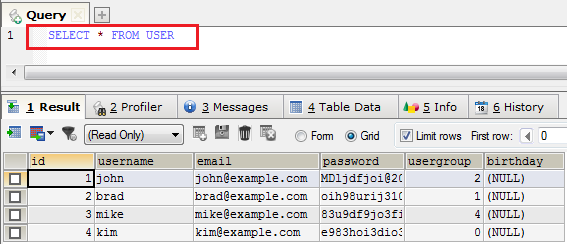
The database query language was coined for this purpose and was named Structured Query Language or SQL. INSERT and SELECT operations are part of this same language. Below is an example of a query for retrieving data and its result.
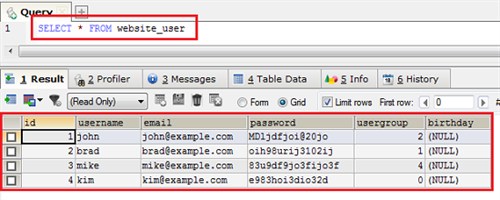
SQL is a big topic for narration and its consideration is beyond the scope of this guide. This article is strictly focused on the presentation of the database design process . Later, in a separate tutorial, I will cover the basics of SQL.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to create a relational data model. A relational model is a model that describes how to organize data in tables and how to determine the relationships between these tables.
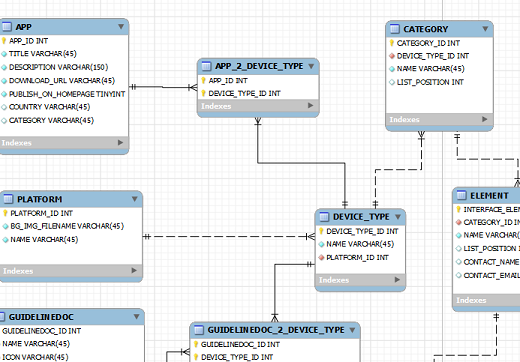
The rules of the relational model dictate how information should be organized in tables and how the tables are related to each other. Ultimately, the result can be presented in the form of a database diagram or, more precisely, an entity-relationship diagram, as in the figure (Example taken from MySQL Workbench).
As examples in the manual, I used a number of applications.
RDBMS
The RDBMS I used to create the sample tables is MySQL. MySQL is the most popular RDBMS and it is free.
Utility for database administration.
After installing MySQL, you only get the command line interface to interact with MySQL. Personally, I prefer a graphical interface for managing my databases. I often use SQLyog. This is a free GUI utility. The images of the tables in this manual are taken from there.
Visual modeling.
There is a great free MySQL Workbench application. It allows you to design your database graphically. Images of diagrams in the manual are made in this program.
It is important to know that although this guide contains examples for MySQL, database design is independent of the RDBMS. This means that the information is applicable to relational databases in general, not only to MySQL. You can apply the knowledge from this guide to any relational databases like Mysql, Postgresql, Microsoft Access, Microsoft Sql or Oracle.
In the next part, I will briefly talk about the evolution of databases. You will find out where the database and relational data model came from.
In the 1970s and 1980s, when computer scientists still wore brown tuxedos and glasses with large, square frames, the data was stored structurelessly in files that were a text document with data separated by (usually) commas or tabulations.

It looked like professionals in the field of information technology in the 70s. (Bill Gates is at the bottom left).
Even today, text files are still used to store small amounts of simple information. Comma-Separated Values (CSV) - comma-separated values are very popular and are widely supported today by various software and operating systems. Microsoft Excel is one of the examples of programs that can work with CSV files. The data stored in such a file can be read by a computer program.

The above is an example of how such a file might look. A program reading this file must be notified that the data is separated by commas. If the program wants to select and display the category in which the Database Design Tutorial lesson is located, then it must read one line at a time until the words Database Design Tutorial are found and then it will need to read the next comma. in order to display the category Software .
Reading a file line by line is not very efficient. In a relational database, data is stored in tables. The table below contains the same data as the file. Each line or “record” contains one lesson. Each column contains some sort of lesson property. In this case, it is the title (title) and its category (category).
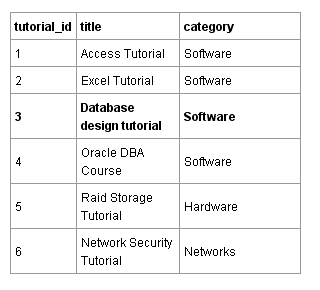
A computer program could search the tutorial_id column of this table for a specific identifier tutorial_id in order to quickly find the corresponding heading and category. This is much faster than searching the file line by line, just as a program does in a text file.
Modern relational databases are designed to allow the selection of data from specific rows, columns, and multiple tables at once, very quickly.
The relational database model was invented in the 70s by Edgar Codd (Ted Codd), a British scientist. He wanted to overcome the drawbacks of the network database model and the hierarchical model. And he was very successful at that. The relational database model is today universally accepted and is considered a powerful model for efficient data organization.
Today, a wide range of database management systems is available: from small desktop applications to multifunctional server systems with highly optimized search methods. Here are some of the most well-known relational database management systems (RDBMS):
- Oracle - used primarily for professional, large applications.
- Microsoft SQL server - Microsoft RDBMS. Available only for the Windows operating system.
- Mysql is a very popular open source RDBMS. Widely used by both professionals and beginners. What else is needed?! It is free.
- IBM - has a number of RDBMS, the most famous is DB2.
- Microsoft Access - RDBMS, which is used in the office and at home. In fact, it is more than just a database. MS Access allows you to create databases with a user interface.
In the next part, I will tell you something about the characteristics of relational databases.
Relational databases are designed to quickly store and retrieve large volumes of information. Below are some of the characteristics of relational databases and the relational data model.
Each row of data in a table is identified by a unique “key” called the primary key. Often, the primary key is an automatically incremented (auto-increment) number (1,2,3,4, etc.). Data in different tables can be linked together using keys. The primary key values of one table can be added to the rows (records) of another table, thereby linking these records together.
Using a structured query language (SQL), data from different tables that are linked by a key can be selected at one time. For example, you can create a query that selects all orders from the orders table (orders) that belong to the user with the id (id) 3 (Mike) from the users table (users). We will discuss the keys further in the following sections.
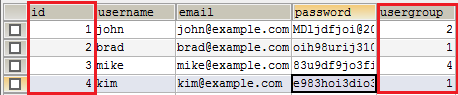
The id column in this table is the primary key. Each entry has a unique primary key, often a number. The usergroup column is a foreign key. Judging by its name, it apparently refers to a table that contains user groups.
In a database project that was created taking into account the rules of the relational data model, each piece of information, for example, the user name, is stored only in one place. This eliminates the need to work with data in several places. Data duplication is called data redundancy and this should be avoided in a good database design.
Using a relational database, you can determine what kind of data is allowed to be stored in a column. You can create a field that contains integers, decimal numbers, small fragments of text, large fragments of text, dates, etc.
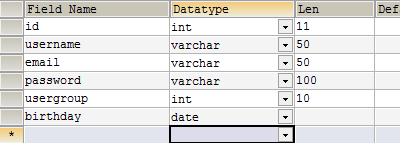
When you create a database table you provide a data type for each column. For example, varchar is a data type for small fragments of text with a maximum number of characters equal to 255, and int is numbers.
In addition to data types, RDBMS allows you to further limit the data that is available for input. For example, limit the length or force to indicate the uniqueness of the value of the entries in this column. The latter restriction is often used for fields that contain user login names (logins), or email addresses.
These restrictions give you control over the integrity of your data and prevent situations like the following:
- Enter the address (text) in the field in which you expect to see the number
- input of the region index with the length of this index itself in a hundred characters
- create users with the same name
- create users with the same email address
- Enter the weight (number) in the birthday field (date)
By adjusting the properties of the fields, linking the tables with each other and setting the limits, you can increase the reliability of your data.
Most RDBMSs offer customization of access rights, which allows you to assign certain rights to specific users. Some actions that can be allowed or denied to the user are: SELECT (select), INSERT (insert), DELETE (delete), ALTER (change), CREATE (create), etc. These are operations that can be performed using a structured query language (SQL).
In order to perform certain operations on the database, such as saving data, their selection, change, a structured query language (SQL) is used. SQL is relatively easy to understand and allows. and added samples, for example, fetching related data from multiple tables using an SQL JOIN operator. As mentioned earlier, SQL will not be discussed in this tutorial. I will focus on database design.
The way you design the database will have a direct impact on the queries that you will need to complete in order to retrieve data from the database. This is another reason why you need to think about what your base should be. With a well-designed database, your queries can be cleaner and simpler.
The relational data model is standard. By following the rules of the relational data model, you can be sure that your data can be transferred to another RDBMS relatively easily.
As mentioned earlier, designing a database is a question of identifying data, their connection and putting the results of solving this issue on paper (or in a computer program). Designing a database regardless of the RDBMS you are going to use to create it.
In the next part, we will take a closer look at the primary keys.
Information is intended for beginners.
It helped me. It is possible that it will help someone else to fill in the gaps.
Guide to database design.
1. Entry
If you are going to create your own databases, then it would be nice to adhere to the rules of database design, as this will ensure the long-term integrity and ease of maintenance of your data. This guide will tell you what a database is and how to design a database that follows the rules for designing relational databases.
Databases are programs that allow you to save and receive large amounts of related information. Databases consist of tables that contain information . When you create a database you need to think about which tables you need to create and what relationships exist between the information in the tables. In other words, you need to think about the design of your database. A good database design, as mentioned earlier, will ensure data integrity and ease of maintenance.
')
Structured Query Language (SQL).
A database is created to store information in it and retrieve this information if necessary. This means that we need to be able to insert information into the database and we want to be able to select information from the database ( SELECT ).
The database query language was coined for this purpose and was named Structured Query Language or SQL. INSERT and SELECT operations are part of this same language. Below is an example of a query for retrieving data and its result.

SQL is a big topic for narration and its consideration is beyond the scope of this guide. This article is strictly focused on the presentation of the database design process . Later, in a separate tutorial, I will cover the basics of SQL.
Relational model.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to create a relational data model. A relational model is a model that describes how to organize data in tables and how to determine the relationships between these tables.

The rules of the relational model dictate how information should be organized in tables and how the tables are related to each other. Ultimately, the result can be presented in the form of a database diagram or, more precisely, an entity-relationship diagram, as in the figure (Example taken from MySQL Workbench).
Examples
As examples in the manual, I used a number of applications.
RDBMS
The RDBMS I used to create the sample tables is MySQL. MySQL is the most popular RDBMS and it is free.
Utility for database administration.
After installing MySQL, you only get the command line interface to interact with MySQL. Personally, I prefer a graphical interface for managing my databases. I often use SQLyog. This is a free GUI utility. The images of the tables in this manual are taken from there.
Visual modeling.
There is a great free MySQL Workbench application. It allows you to design your database graphically. Images of diagrams in the manual are made in this program.
Design independent of RDBMS.
It is important to know that although this guide contains examples for MySQL, database design is independent of the RDBMS. This means that the information is applicable to relational databases in general, not only to MySQL. You can apply the knowledge from this guide to any relational databases like Mysql, Postgresql, Microsoft Access, Microsoft Sql or Oracle.
In the next part, I will briefly talk about the evolution of databases. You will find out where the database and relational data model came from.
2. History.
In the 1970s and 1980s, when computer scientists still wore brown tuxedos and glasses with large, square frames, the data was stored structurelessly in files that were a text document with data separated by (usually) commas or tabulations.

It looked like professionals in the field of information technology in the 70s. (Bill Gates is at the bottom left).
Even today, text files are still used to store small amounts of simple information. Comma-Separated Values (CSV) - comma-separated values are very popular and are widely supported today by various software and operating systems. Microsoft Excel is one of the examples of programs that can work with CSV files. The data stored in such a file can be read by a computer program.

The above is an example of how such a file might look. A program reading this file must be notified that the data is separated by commas. If the program wants to select and display the category in which the Database Design Tutorial lesson is located, then it must read one line at a time until the words Database Design Tutorial are found and then it will need to read the next comma. in order to display the category Software .
Database tables.
Reading a file line by line is not very efficient. In a relational database, data is stored in tables. The table below contains the same data as the file. Each line or “record” contains one lesson. Each column contains some sort of lesson property. In this case, it is the title (title) and its category (category).

A computer program could search the tutorial_id column of this table for a specific identifier tutorial_id in order to quickly find the corresponding heading and category. This is much faster than searching the file line by line, just as a program does in a text file.
Modern relational databases are designed to allow the selection of data from specific rows, columns, and multiple tables at once, very quickly.
The history of the relational model.
The relational database model was invented in the 70s by Edgar Codd (Ted Codd), a British scientist. He wanted to overcome the drawbacks of the network database model and the hierarchical model. And he was very successful at that. The relational database model is today universally accepted and is considered a powerful model for efficient data organization.
Today, a wide range of database management systems is available: from small desktop applications to multifunctional server systems with highly optimized search methods. Here are some of the most well-known relational database management systems (RDBMS):
- Oracle - used primarily for professional, large applications.
- Microsoft SQL server - Microsoft RDBMS. Available only for the Windows operating system.
- Mysql is a very popular open source RDBMS. Widely used by both professionals and beginners. What else is needed?! It is free.
- IBM - has a number of RDBMS, the most famous is DB2.
- Microsoft Access - RDBMS, which is used in the office and at home. In fact, it is more than just a database. MS Access allows you to create databases with a user interface.
In the next part, I will tell you something about the characteristics of relational databases.
3. Characteristics of relational databases.
Relational databases are designed to quickly store and retrieve large volumes of information. Below are some of the characteristics of relational databases and the relational data model.
Using keys.
Each row of data in a table is identified by a unique “key” called the primary key. Often, the primary key is an automatically incremented (auto-increment) number (1,2,3,4, etc.). Data in different tables can be linked together using keys. The primary key values of one table can be added to the rows (records) of another table, thereby linking these records together.
Using a structured query language (SQL), data from different tables that are linked by a key can be selected at one time. For example, you can create a query that selects all orders from the orders table (orders) that belong to the user with the id (id) 3 (Mike) from the users table (users). We will discuss the keys further in the following sections.

The id column in this table is the primary key. Each entry has a unique primary key, often a number. The usergroup column is a foreign key. Judging by its name, it apparently refers to a table that contains user groups.
No data redundancy.
In a database project that was created taking into account the rules of the relational data model, each piece of information, for example, the user name, is stored only in one place. This eliminates the need to work with data in several places. Data duplication is called data redundancy and this should be avoided in a good database design.
Input Restriction.
Using a relational database, you can determine what kind of data is allowed to be stored in a column. You can create a field that contains integers, decimal numbers, small fragments of text, large fragments of text, dates, etc.

When you create a database table you provide a data type for each column. For example, varchar is a data type for small fragments of text with a maximum number of characters equal to 255, and int is numbers.
In addition to data types, RDBMS allows you to further limit the data that is available for input. For example, limit the length or force to indicate the uniqueness of the value of the entries in this column. The latter restriction is often used for fields that contain user login names (logins), or email addresses.
These restrictions give you control over the integrity of your data and prevent situations like the following:
- Enter the address (text) in the field in which you expect to see the number
- input of the region index with the length of this index itself in a hundred characters
- create users with the same name
- create users with the same email address
- Enter the weight (number) in the birthday field (date)
Maintain data integrity.
By adjusting the properties of the fields, linking the tables with each other and setting the limits, you can increase the reliability of your data.
Assignment of rights.
Most RDBMSs offer customization of access rights, which allows you to assign certain rights to specific users. Some actions that can be allowed or denied to the user are: SELECT (select), INSERT (insert), DELETE (delete), ALTER (change), CREATE (create), etc. These are operations that can be performed using a structured query language (SQL).
Structured Query Language (SQL).
In order to perform certain operations on the database, such as saving data, their selection, change, a structured query language (SQL) is used. SQL is relatively easy to understand and allows. and added samples, for example, fetching related data from multiple tables using an SQL JOIN operator. As mentioned earlier, SQL will not be discussed in this tutorial. I will focus on database design.
The way you design the database will have a direct impact on the queries that you will need to complete in order to retrieve data from the database. This is another reason why you need to think about what your base should be. With a well-designed database, your queries can be cleaner and simpler.

Portability
The relational data model is standard. By following the rules of the relational data model, you can be sure that your data can be transferred to another RDBMS relatively easily.
As mentioned earlier, designing a database is a question of identifying data, their connection and putting the results of solving this issue on paper (or in a computer program). Designing a database regardless of the RDBMS you are going to use to create it.
In the next part, we will take a closer look at the primary keys.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/193136/
All Articles