Prototype housing for electronics: grow or mill?

Our previous article about making a working prototype of an electronic device caused a lot of questions and discussions in the comments, so we decided to continue this topic and focus on creating prototype housings and mechanisms for electronics, to make it easier for you to navigate in various materials and prototyping technologies offered by modern manufacturers .
As always, we will pay attention to the most pressing issues and give useful tips based on our practice:
- What materials is used to make a prototype case for electronic devices?
- Overview of modern prototyping technologies: what to choose? Here we look at different 3D-printers and compare them with milling technology on CNC machines.
- How to choose a manufacturer of the prototype, what documents to provide the contractor?
1. What is the prototype case for electronic devices made of?
Optimal materials for the electronics housing are selected taking into account the requirements of the design, the purpose of the device (working conditions), the preferences of the customer and the price category of development. Modern technologies allow the use of the following materials for the manufacture of prototypes:
- Various types of plastic: ABS, PC, PA, PP, etc. For shells that require increased impact resistance or resistance to aggressive media, polyamides and polyformaldehydes (PA, POM) are used.
- Metals: aluminum, various grades of stainless steel, aluminum-magnesium alloys, etc.
- Glass
- Rubber
- Wood (various species) and other exotic materials
Not all materials can be prototyped. For example, some types of plastics that are used in the mass production of electronic devices. In this case, for the manufacture of prototypes are used analogues that most fully convey the properties of the basic materials.
')
When combining different types of materials in one case, it is important to get expert advice, they will help you to correctly implement the docking points, provide the necessary parameters for tightness, strength, flexibility, i.e. compare the desires of the client and the device designer with the actual production capabilities.
2. Overview of modern prototyping technologies: what to choose?
Hull prototypes can be created on equipment for mass production, but other technologies are used. For example, plastic is not molded, but milled or grown, since the creation of a molding mold is a long and expensive process.
The most widespread prototyping technologies today are milling and growing (SLA, FDM, SLS).
The cultivation of prototypes in 3D printers is especially popular, this trendy technology is developing rapidly and even layered on mass production. Today, a variety of products are grown, including metal products and food products, but all this has its limitations. Consider these technologies in more detail, and in the end we will try to choose the best option for creating a prototype case:
SLA (Stereo Lithography Apparatus) is a stereolithography technology that allows you to “grow” a model in a liquid photopolymer that solidifies under the influence of an ultraviolet laser. Advantages: high accuracy and the ability to create large models. The high-quality surface of the SLA prototypes is easy to finish (it can be sanded and painted). An important disadvantage of the technology is the fragility of the model, SLA-prototypes are not suitable for screwing in screws or inspecting the cases on latches.
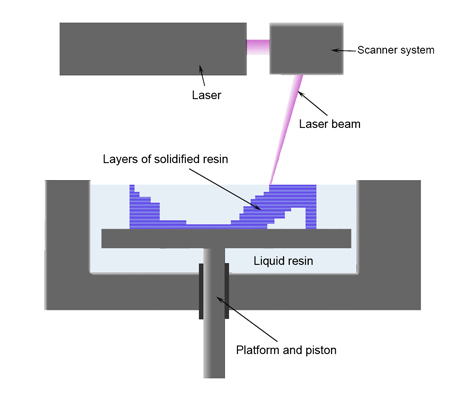
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) - technology of selective laser sintering, allows you to create a prototype due to the layer-by-layer melting of the powder. Advantages: high accuracy and durability, the ability to obtain samples of plastic and metals. SLS prototypes allow for assembly testing of housings using hinges, latches, and complex assemblies. Disadvantage: more complex surface treatment.

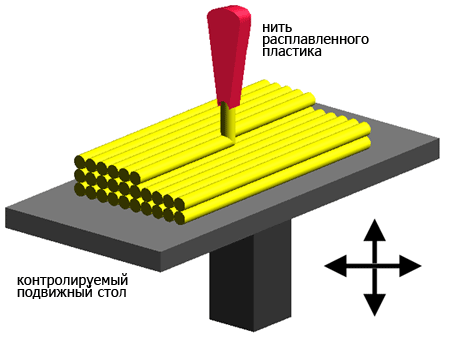
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) - technology of layer-by-layer cultivation of polymer thread. Advantages: maximum approximation of the obtained sample to the factory version of the device (up to 80% strength compared to plastic molding). An FDM prototype can be tested for functionality, assembly and climate. Details of such a body can be glued together and ultrasonic welded, you can use materials ABS + PC (ABS plastic + polycarbonate). Disadvantages: average surface quality, difficulty in final processing.
As you can see, the limitations of various growing technologies do not allow to accurately reproduce and transmit the tactile characteristics of the body. Based on the prototype, it will be impossible to draw conclusions about the real appearance of the device without additional processing. Usually, a limited amount of materials can be used for growing, most often from one to three types of plastic. The main advantage of these methods is the relative cheapness, but here it is important to take into account that the additional processing that is required for a high-quality appearance of the product covers this advantage. Moreover, the quality of the prototype is also influenced by the growing accuracy, which is insufficient to create small-sized buildings. And after processing and polishing the surface becomes even lower.
At the same time milling on machine tools with numerical control (CNC) allows to achieve the accuracy of one order of production with the accuracy of mass production. In this case, you can use the absolute majority of materials that are used in the mass production of shells. The main drawback of milling is the high labor intensity and the need to use expensive equipment, which leads to the high cost of this technology. Although these costs are quite comparable with growing the body, given the long and costly final surface treatment.
3. How to choose a manufacturer of the prototype, what documents to provide the contractor?
When choosing a contractor for the manufacture of prototypes should pay attention to the following features:
- Ready-made prototypes should be fully functional, as close as possible to serial products, so that they can be used for certification, demonstration to the investor, at exhibitions and presentations.
- The manufacturer must work with a wide range of different materials and technologies, provide advice on their choice. So you can choose the best option for your specific project.
- It is desirable that the contractor has a database of proven manufacturers in the CIS and in Southeast Asia, so that you get an estimate of the various options for the timing and cost of manufacturing the various components of your device. So it will be easier to choose the best option.
Recall that in order to manufacture a prototype case you will need to transfer to the contractor an assembly drawing or a 3D model as a file in the STEP format.
We hope that our advice will help you create your own prototype enclosure for electronics ! Questions and comments are welcome.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/192532/
All Articles