Computer History Museum
Hello to all! 
Last weekend I was fortunate enough to visit a wonderful place - the Computer History Museum , which is located in Mountain View in California, USA.
During my trip I took a lot of photos of the exhibits. In this article, I will show you these pictures (of course, not all), I will tell you about what was happening there. I also want very much to understand everything that I saw in this wonderful place, because the museum contains thousands of exhibits, even to think about each and stand next to it physically will not work during the day.
')
So let's start with the story . In the next few paragraphs, I will provide information from Wikipedia and other sources about the museum itself.
The Computer History Museum is also possible to translate " The History Museum of Computing Technique ", but I prefer option number 1, it begins its history back in 1968 . Gordon Bell in those years engaged in collecting electronics for history and he began with the computer Whirlwind , which I saw and which I will discuss below. The first exhibition “Project Museum” - “Museum Project” was held in 1975 in the lobby of the company DEC, which this same Bell headed. In 1978, the Digital Computer Museum - The Digital Computer Museum moved to another DEC lobby in Marlborough, Massachusetts. 1984 "Computer Museum" - "The Computer Museum" , moved to Boston.
In the late nineties, the museum’s artifacts were divided between two centers — the Computer History Museum here in Silicon Valley and the Boston Science Museum. Since 2003 , the Museum received its place in the former Silicon Graphics building in Mountain View, where it displays its exhibits today.

The main exhibition held in the museum is called “Revolution: The First 2000 Years of Computing” - “Revolution: The First 2000 Years of Computing”, which, in fact, I looked. But there were also a couple of expositions, with which I will begin.
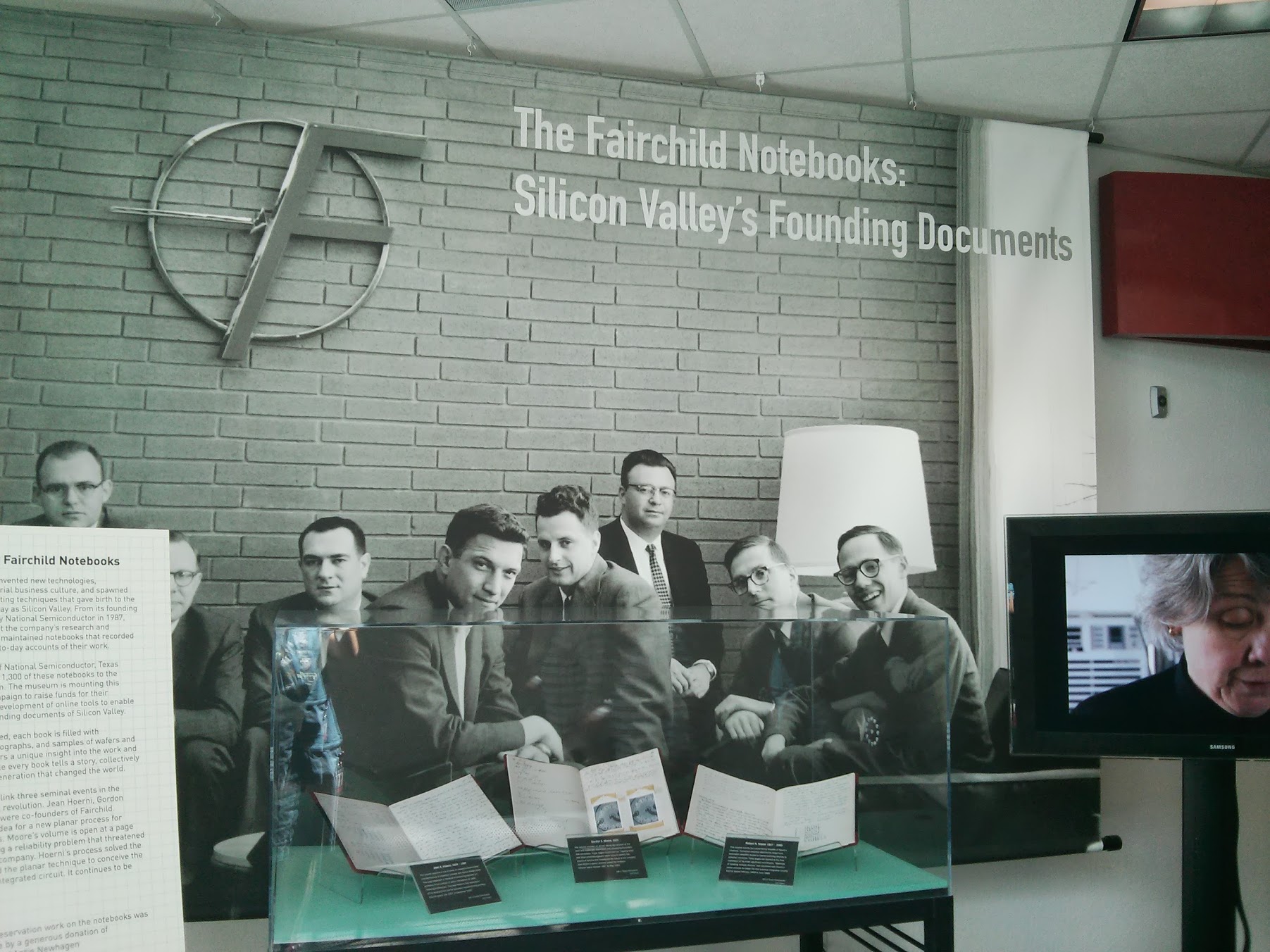

The first exposition I saw in the museum is the recordings of engineers and scientists , dated 1957 and 1959 . The three founders of Frairchild Semiconductor , Jean Hoerni , Gordon Moore and Robert Noyce , described innovative technologies in the construction of electrical circuits and made a revolution in the history of computing technology.
It was during these years around the city of Santa Clara began to form and unite companies for the production of computers and software. Here, really, you can touch the story!
Further along the way we met a fascinating presentation - the work of the Babbage Counting Machine . Two museum staff told and showed how and how this magnificent harmonious mechanism works.
Before our eyes, the polynomial values were calculated with an accuracy of 31 decimal places:
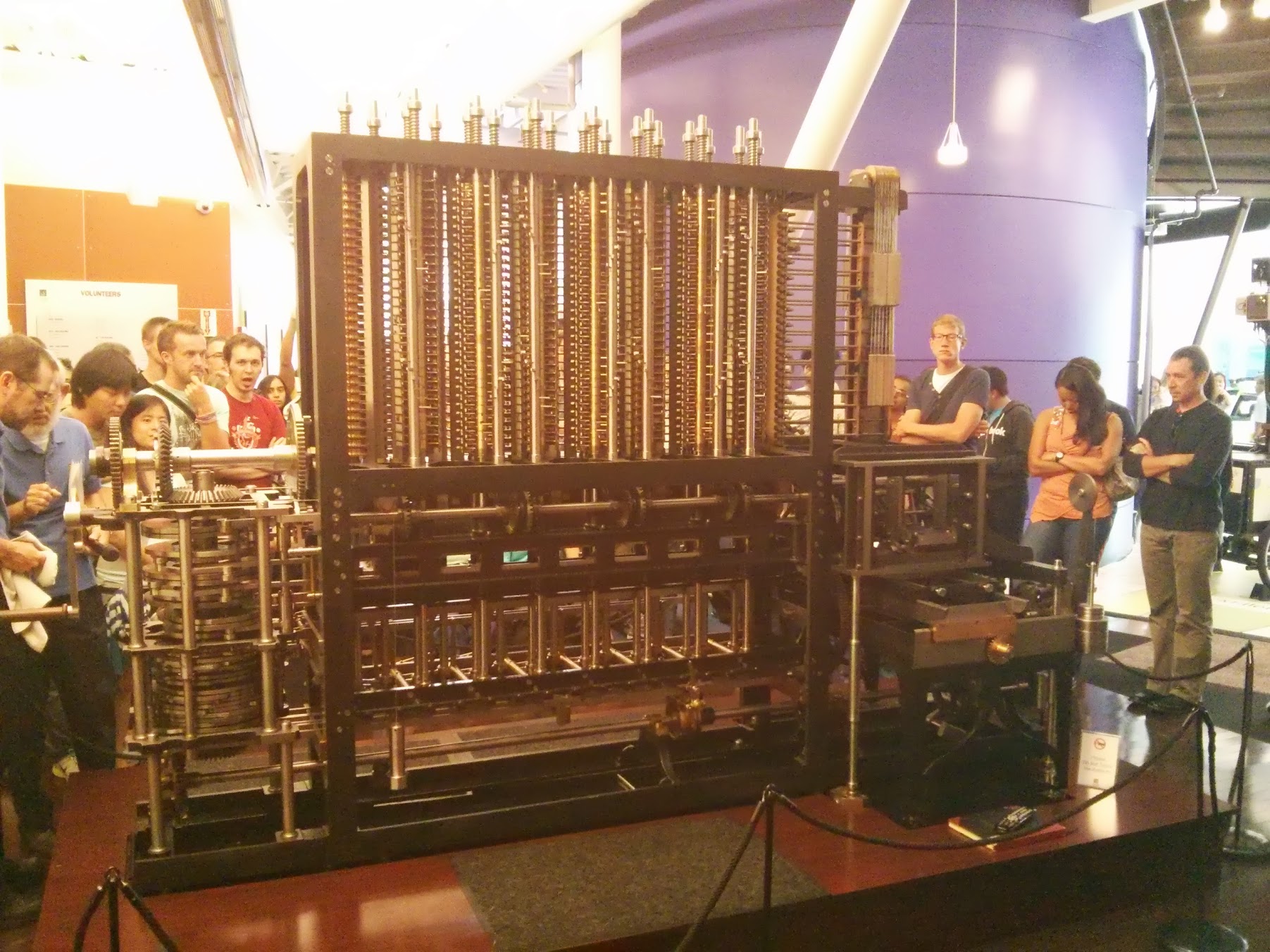
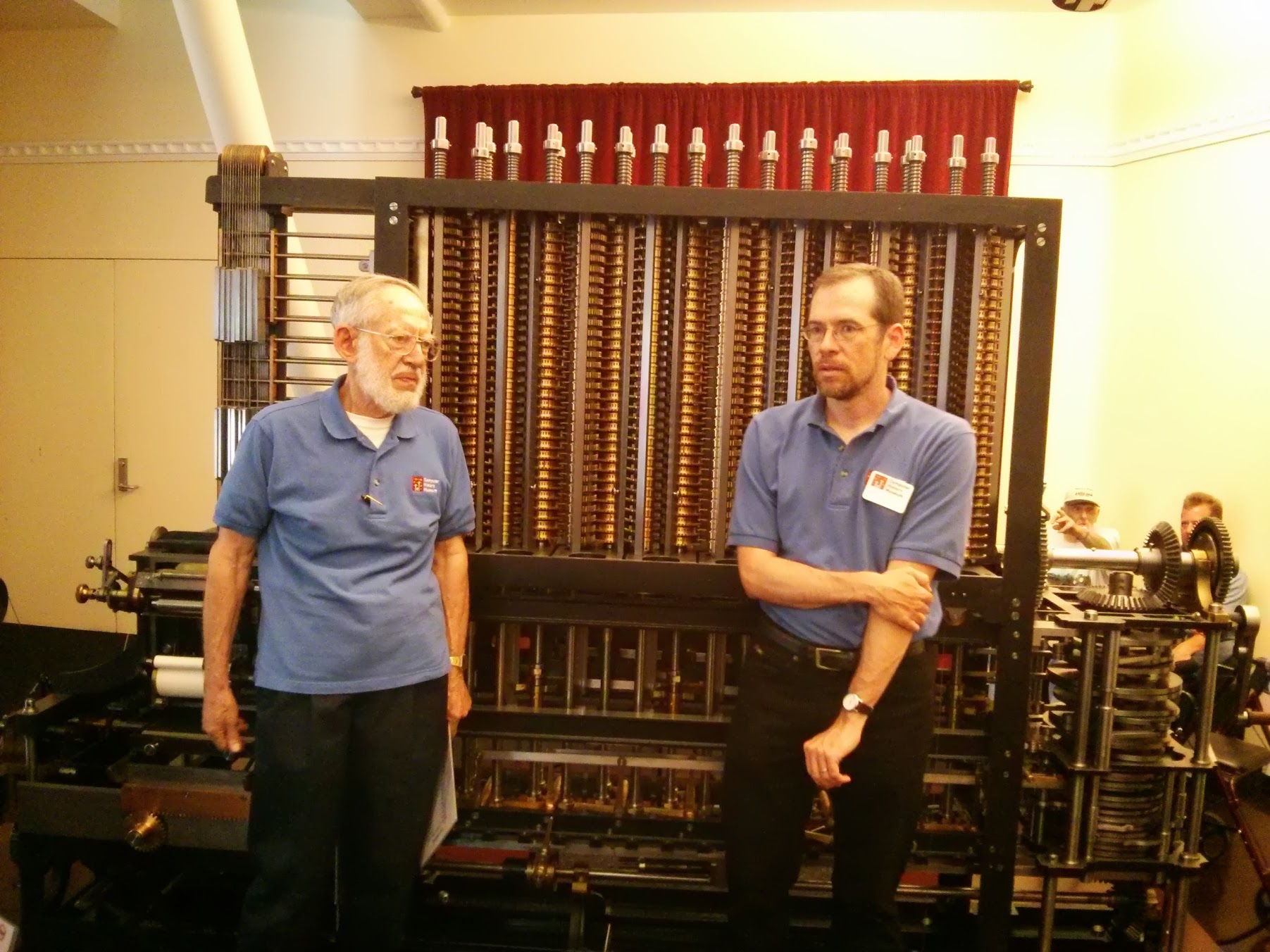
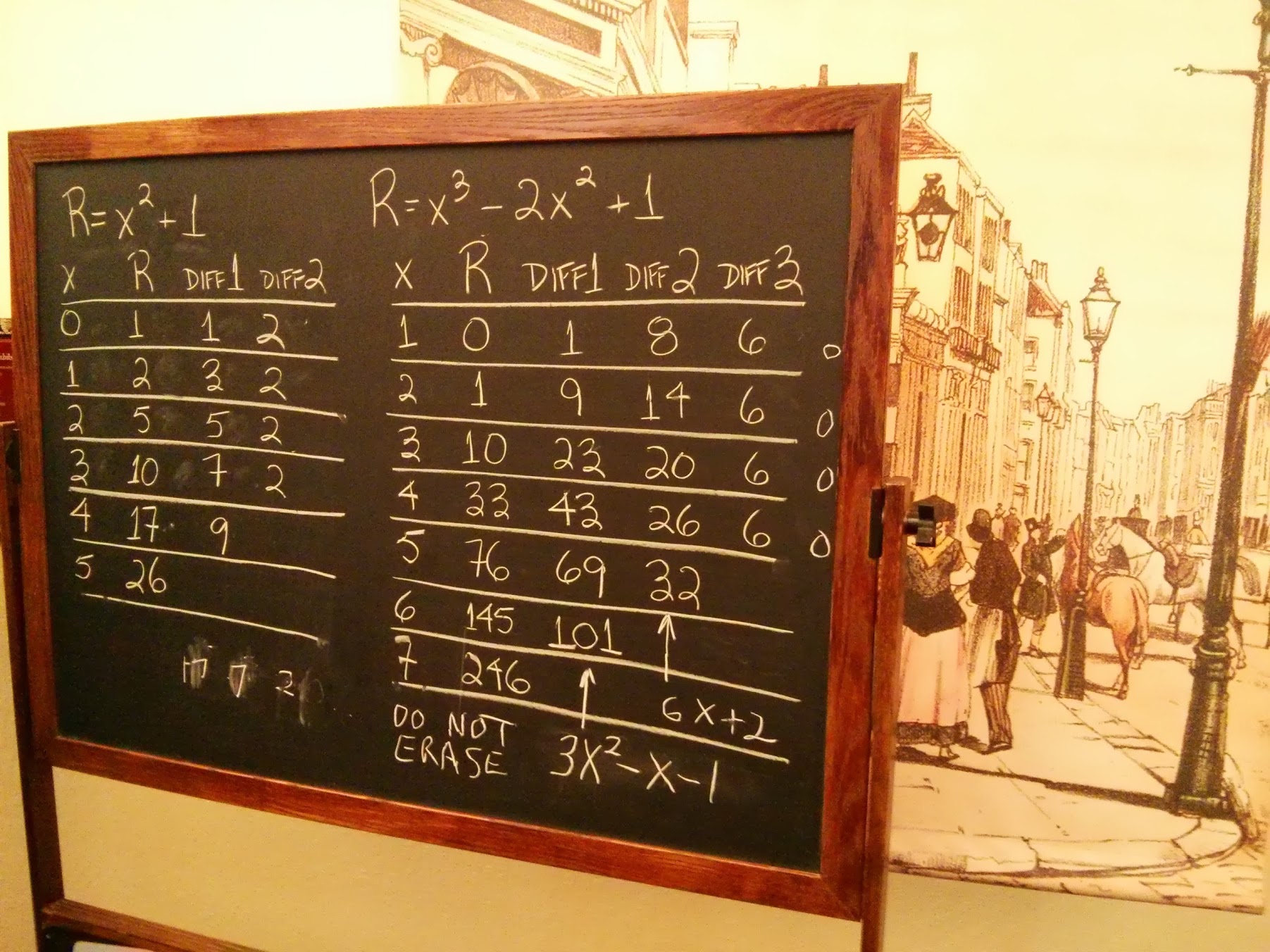
It is noteworthy that this whole mechanism was only in the drawings for a very long time. Only after many years, scientists, having studied the drawings, realized that the machine did work, and created it. In Mountain View there is a copy, the very first machine built is in the London Museum of Science.
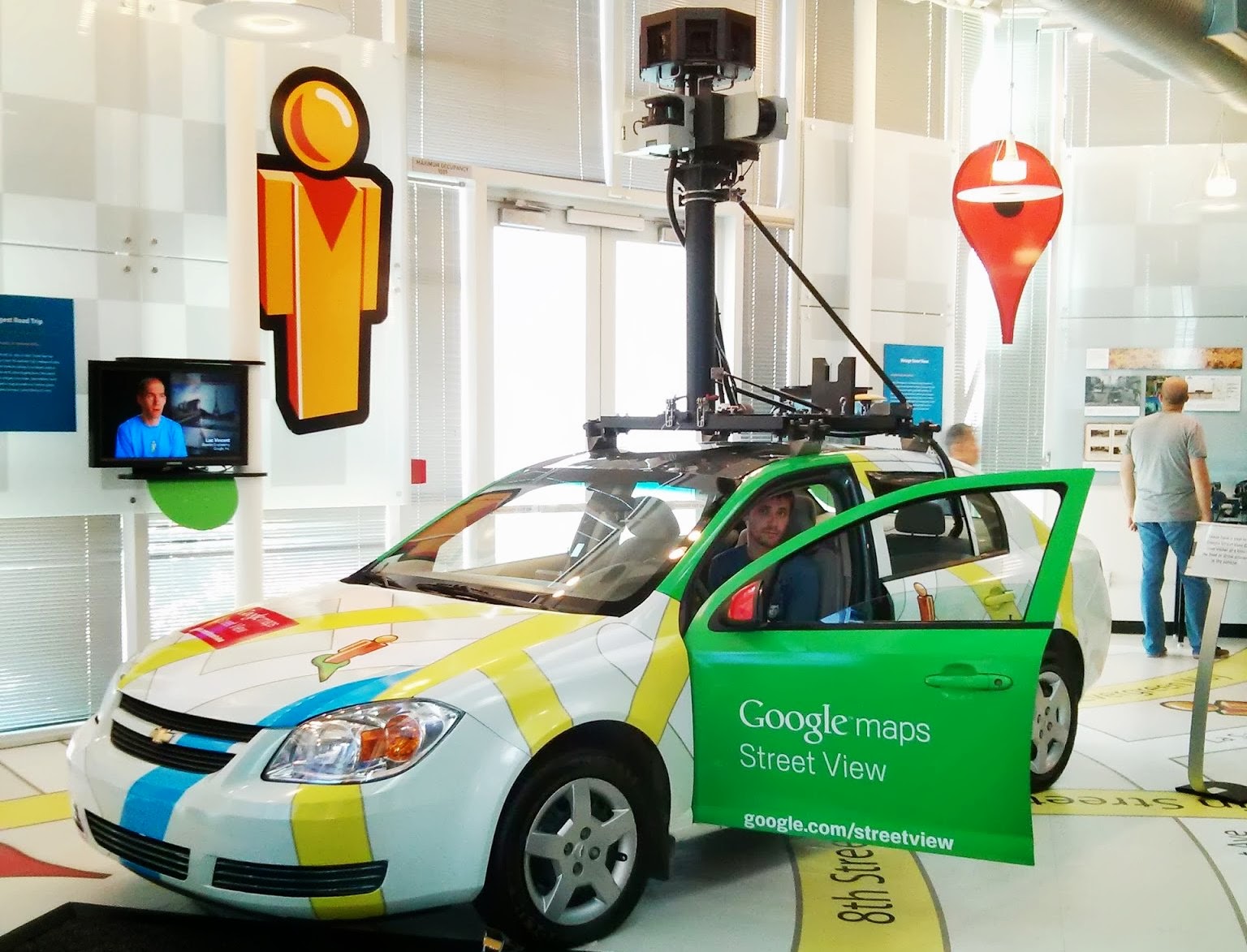
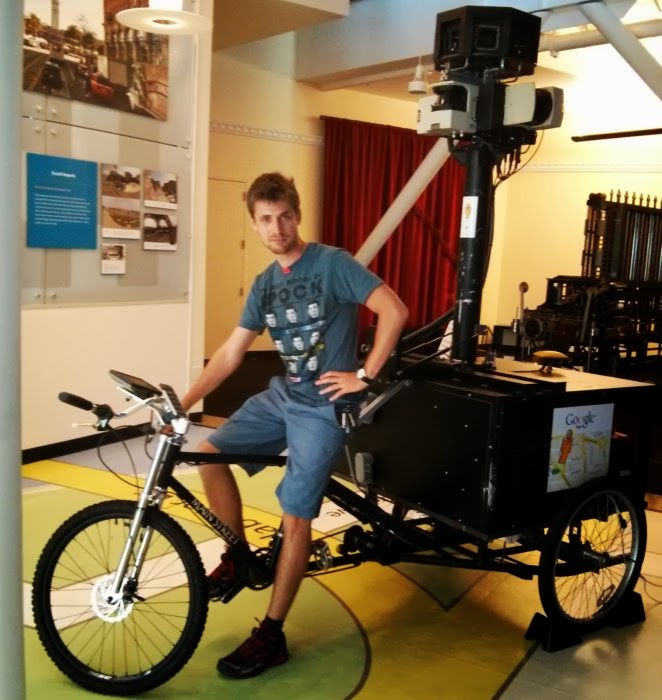
Next on the plan was the exposure of Google Street View. It was shown the main transport, which remove the surrounding species. You could even feel and sit behind the wheel:


Further, according to the plan was the main exhibition of the museum:

But just before the exhibition, at the entrance, I don’t know why, there were 3 artifacts, hardly revolutionary:
Calculating Betting Odds, Race Betting, 1930

Panasonic Q Game Console, 2001
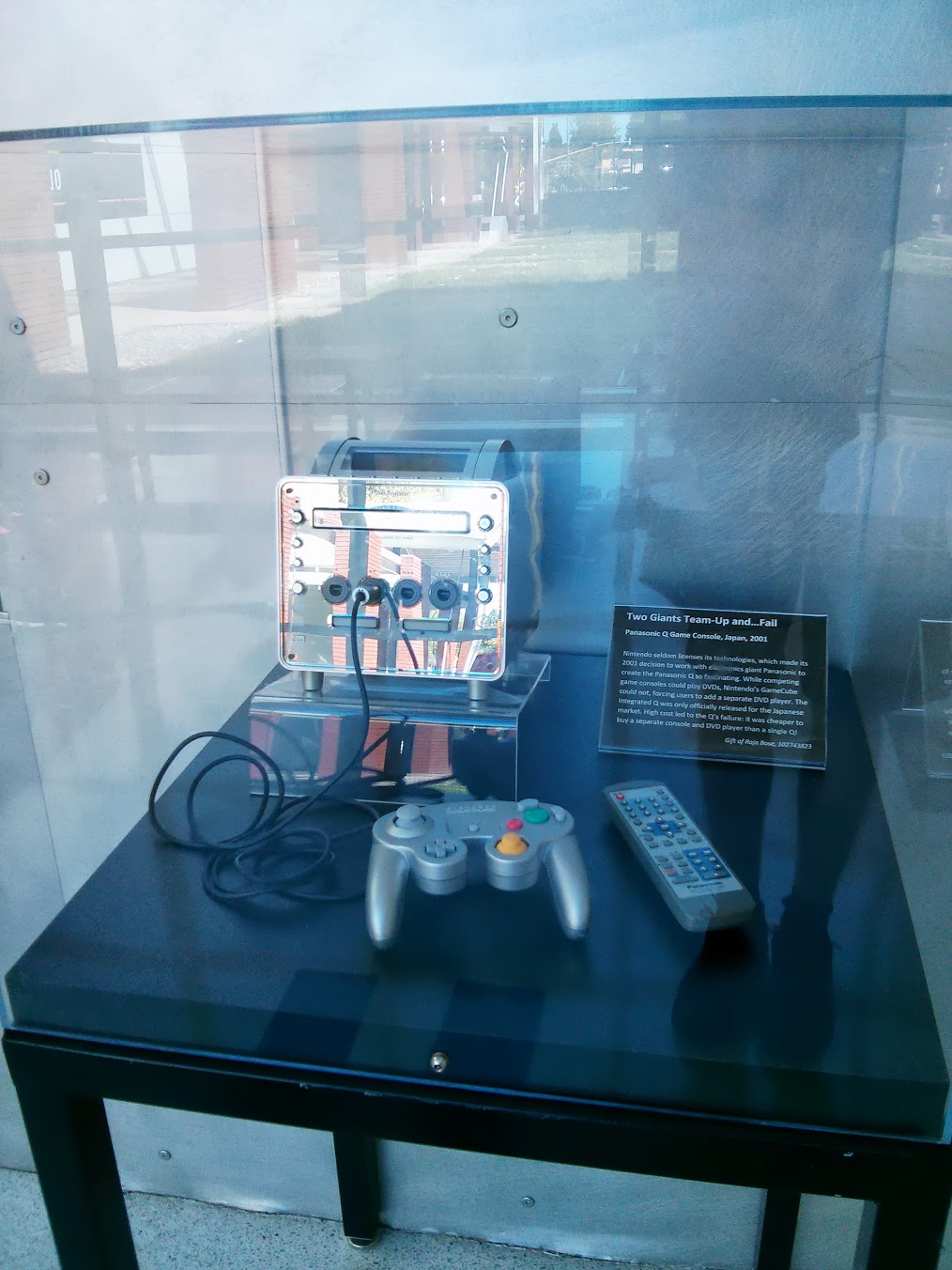

The tablet says that in 2001, Nintendo, having teamed up with Panasonic, released a hybrid - a game console and a DVD player 2 in 1. But it all went down the drain - it was cheaper to buy the same thing separately!
Russian super-computer ELBRUS-2, 1984-1986 (CPU boards)

The main exhibition was in the chronometric order of the history. It all started with the most ancient methods of complex calculations:
Sectors XV - XVIII

Lords Calculator, 1880

I have no idea how something could be counted on it!
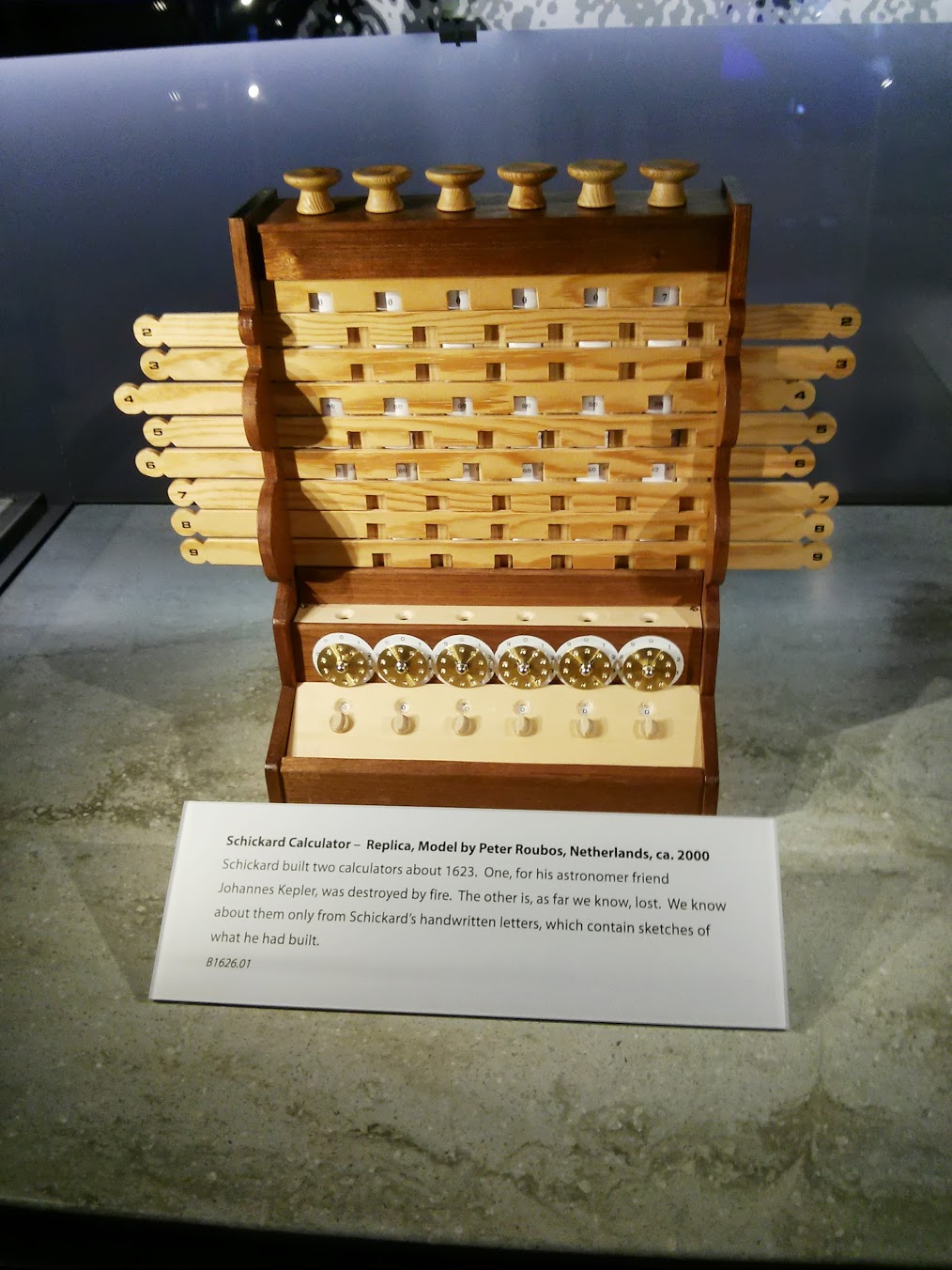
Schickard Calculator , copy of 2000. Originals date back to 1623.

Sumador Chino , Mexico, 1800
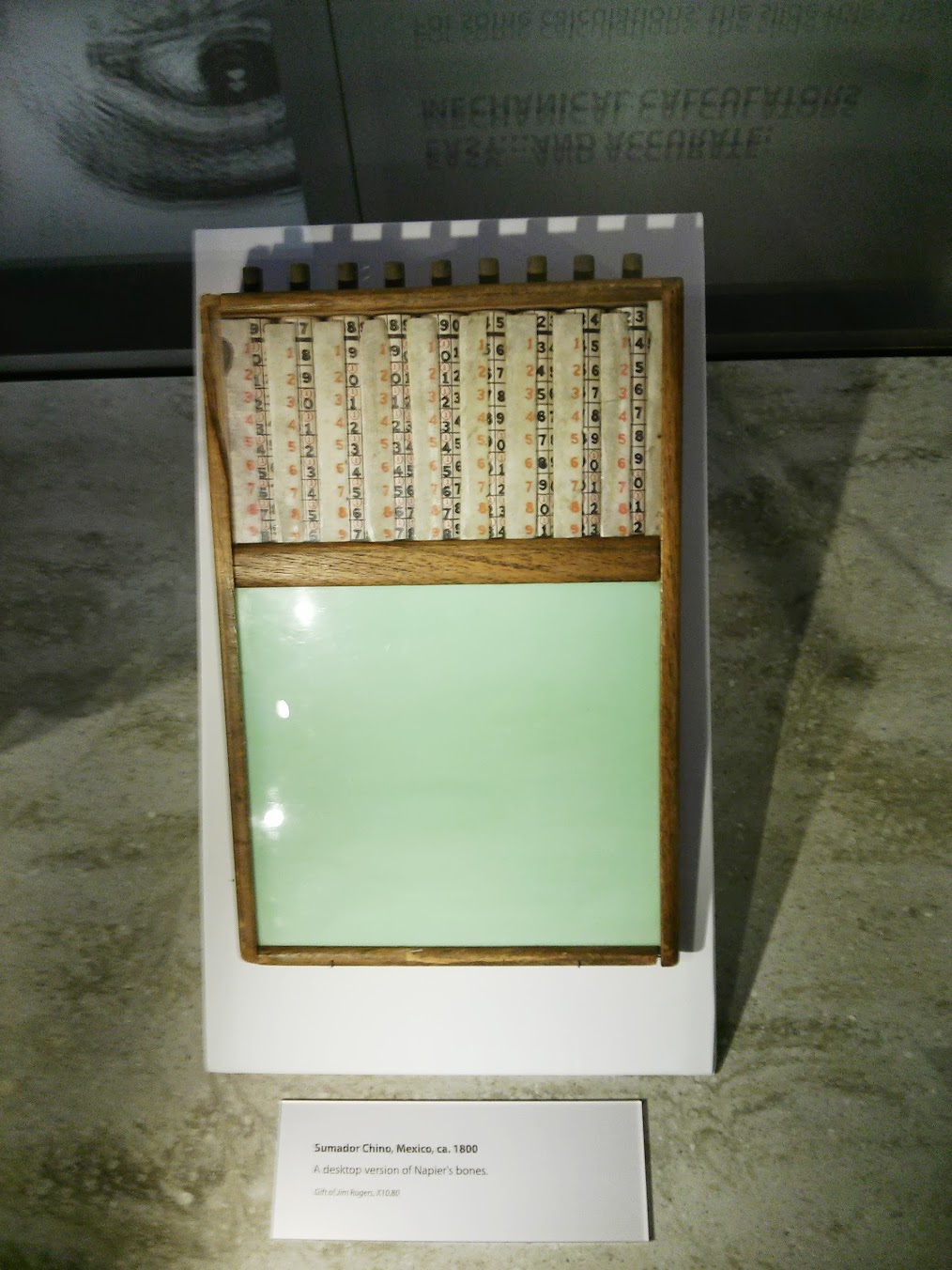
Napier's Bones , England, 1700

Pascal adder (Pascaline) , copy, 1981. Original dates from 1641

Time is Money (TIM) Calculator, 1910

Curta Calculators , Lichtenstein, 1950 - 1960

Mass-produced calculators:
Arithmometer , France, 1850s and FELIX M , USSR, 1932

And some more different calculators:


Type 31 Alphabetical Duplicating punch , IBM, US, 1933

40 column Card Punch , UK, 1954

Model 406 Cards Sorter , UK, 1954

Punch card sorters from IBM, 1949 and 1953
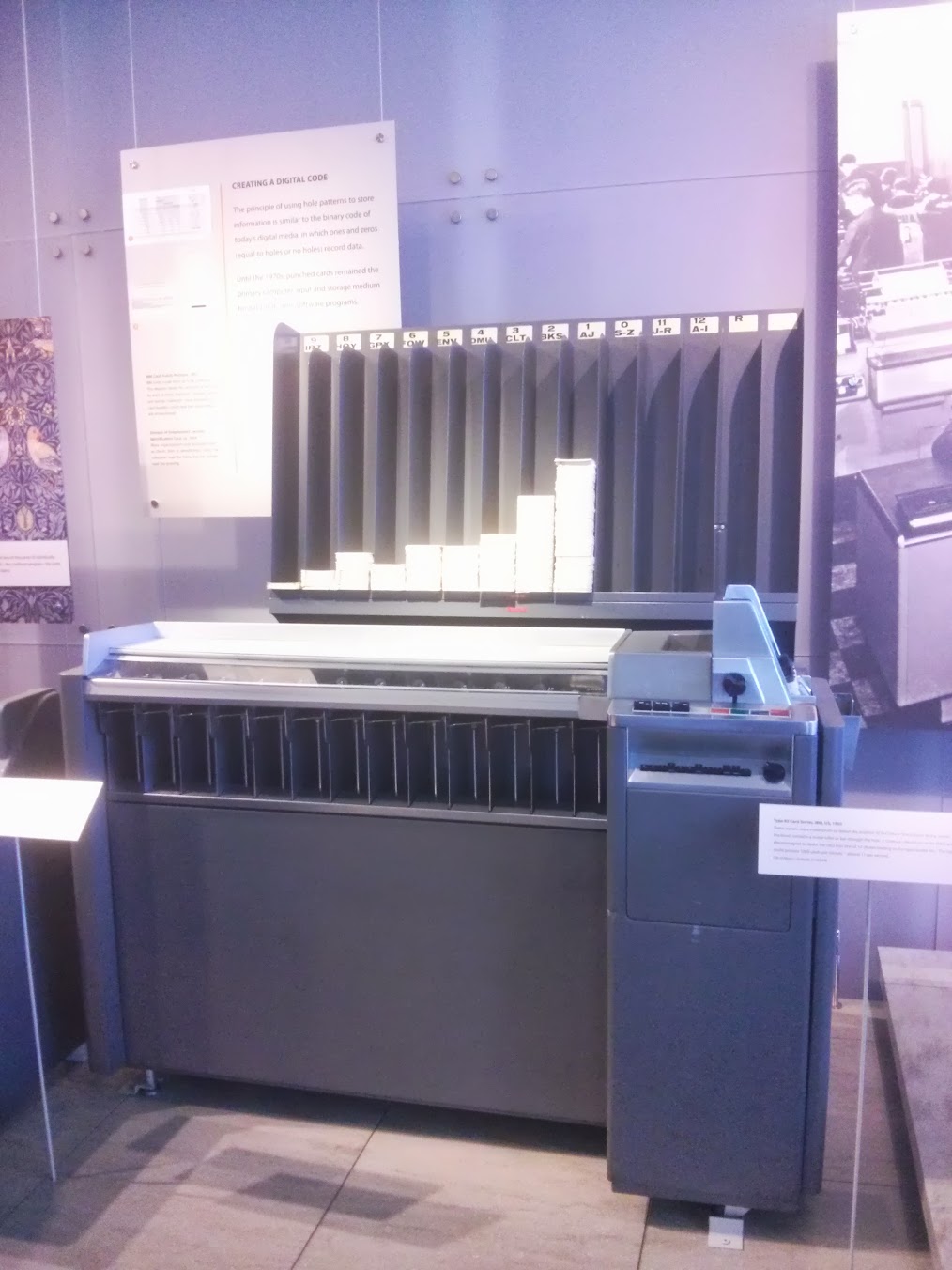


Type 26 Printing Keypunch , IBM, US, 1949
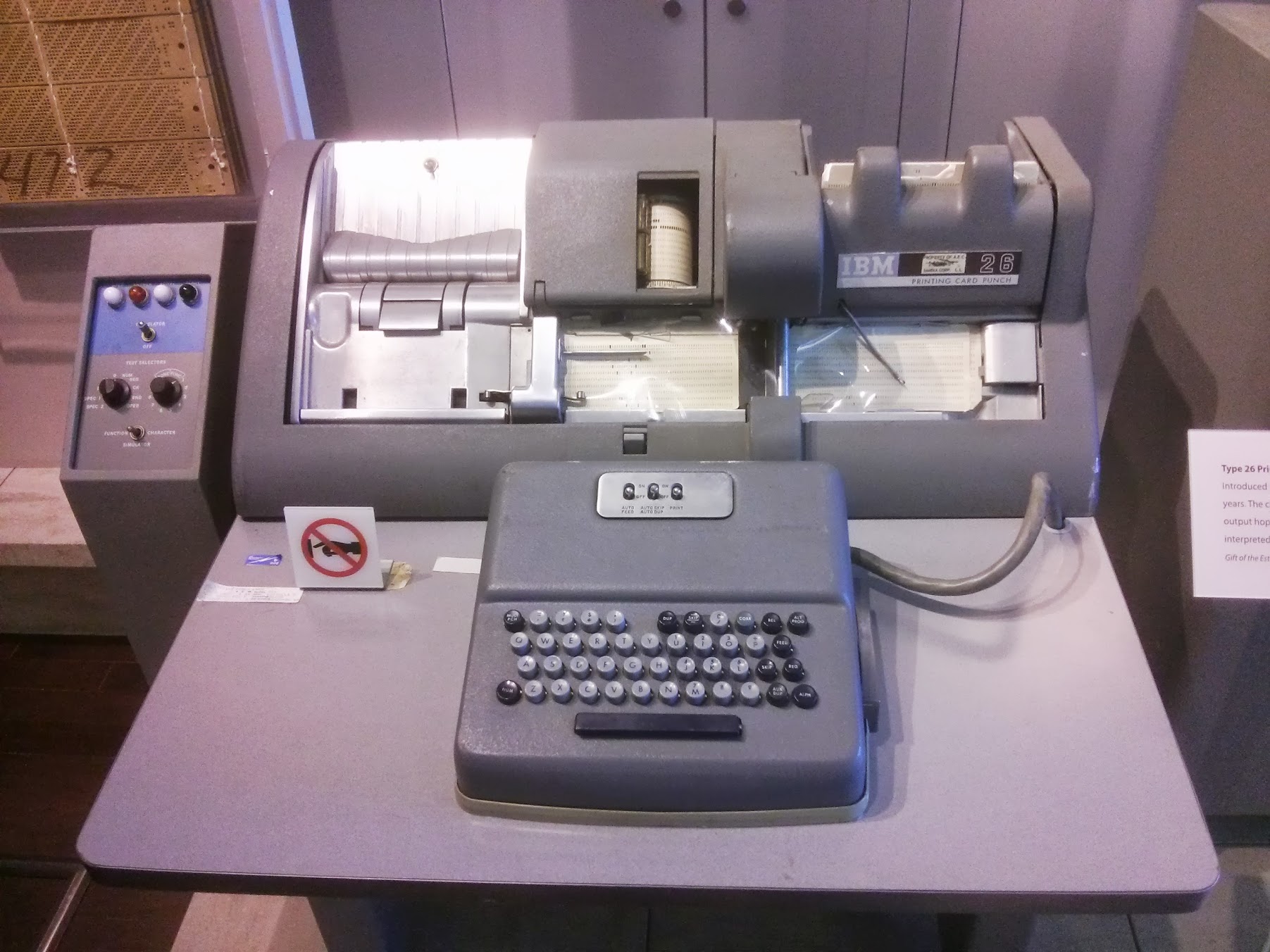

Hollerith's electric tabulating system , copy. The original dates from around 1890.

Stand with bills. Mexican mom and mexican son know how to count something on them

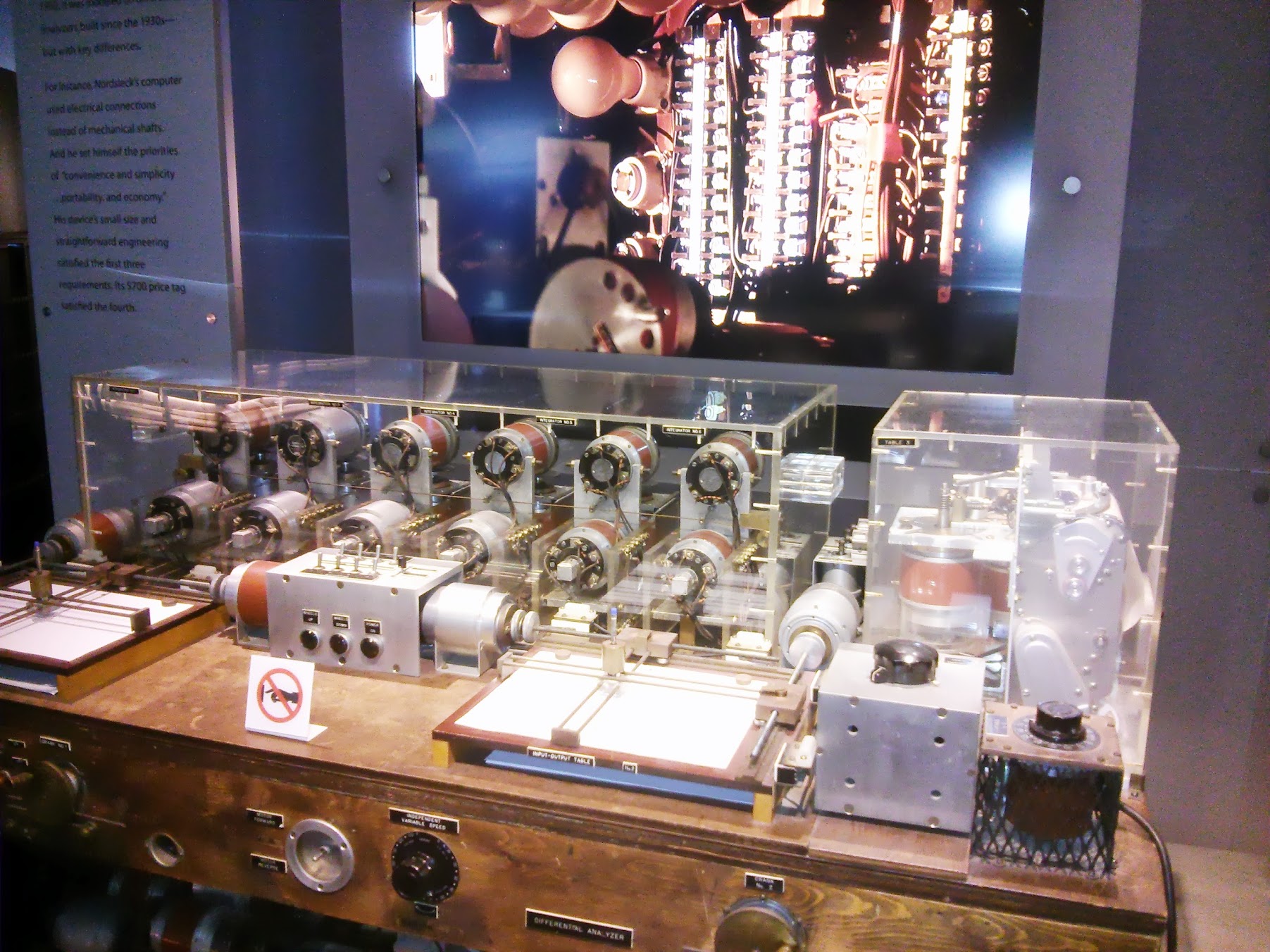
Nordsieck Differential Analyzer , US, 1956
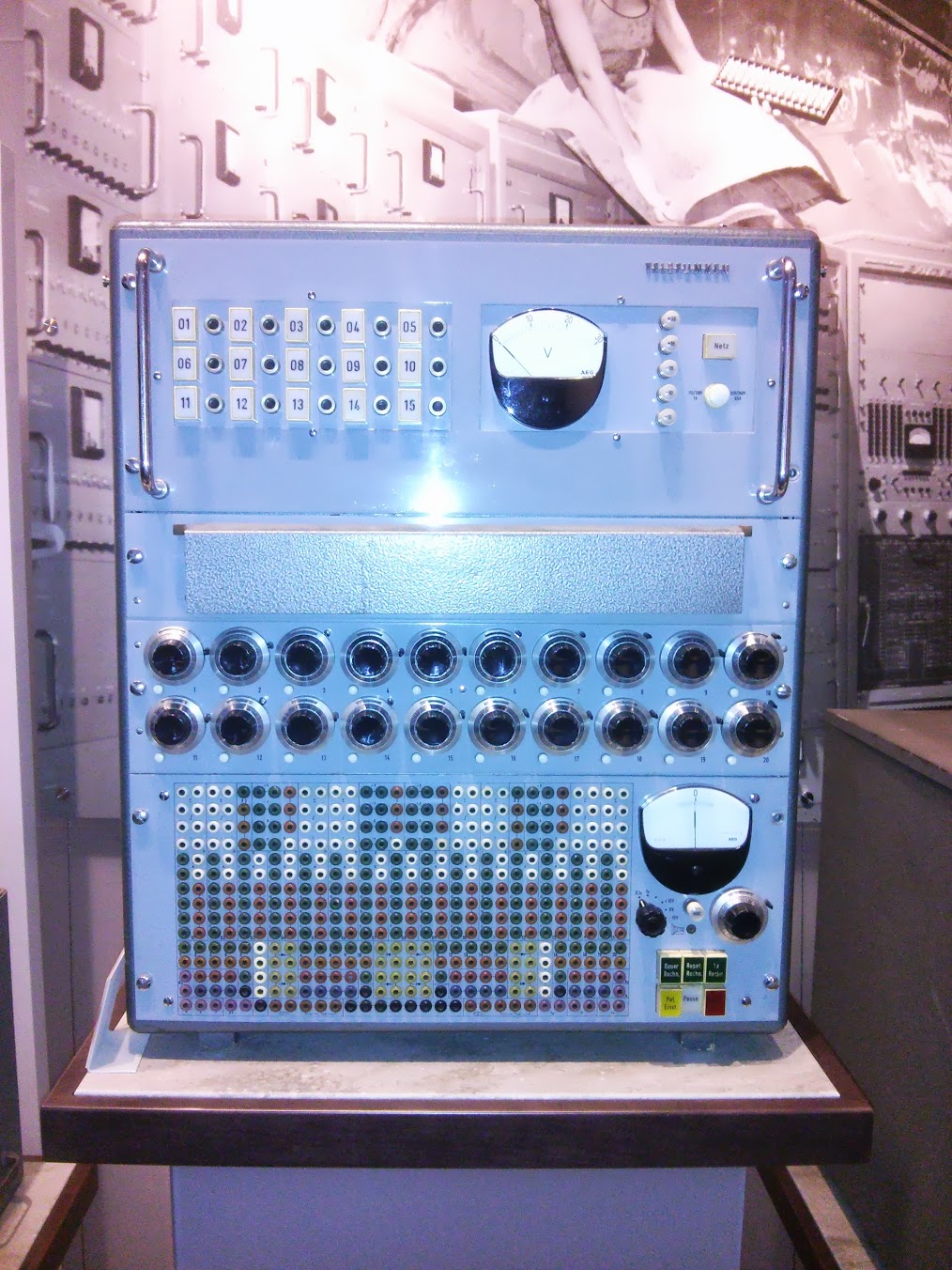
Telefunken RAT 700/2 analog computer , Western Germany, 1959

H-1 Educational Computer , US, 1956

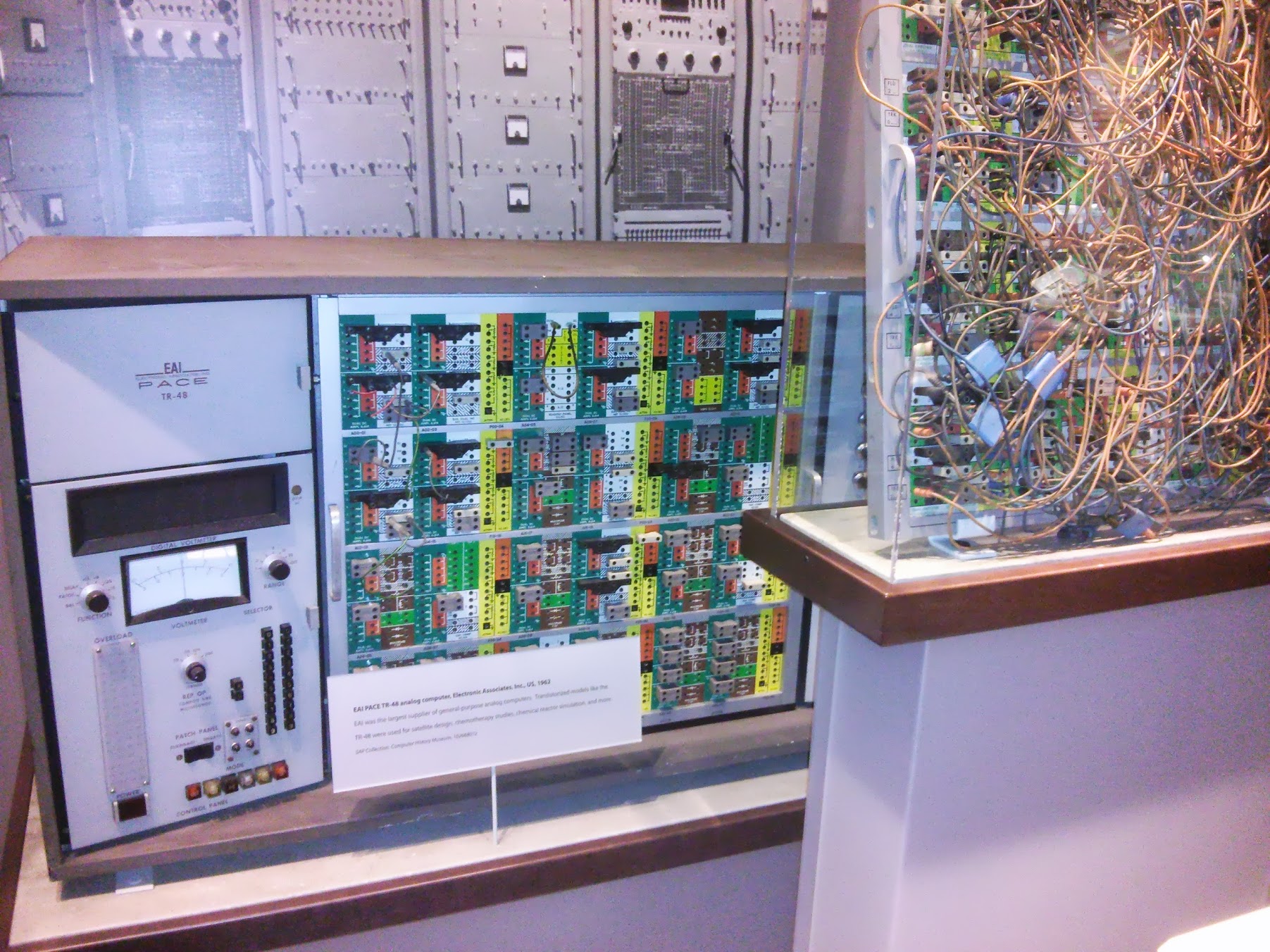
EAI PACE TR-48 analog computer , US, 1962
Trice Computer , US, 1964

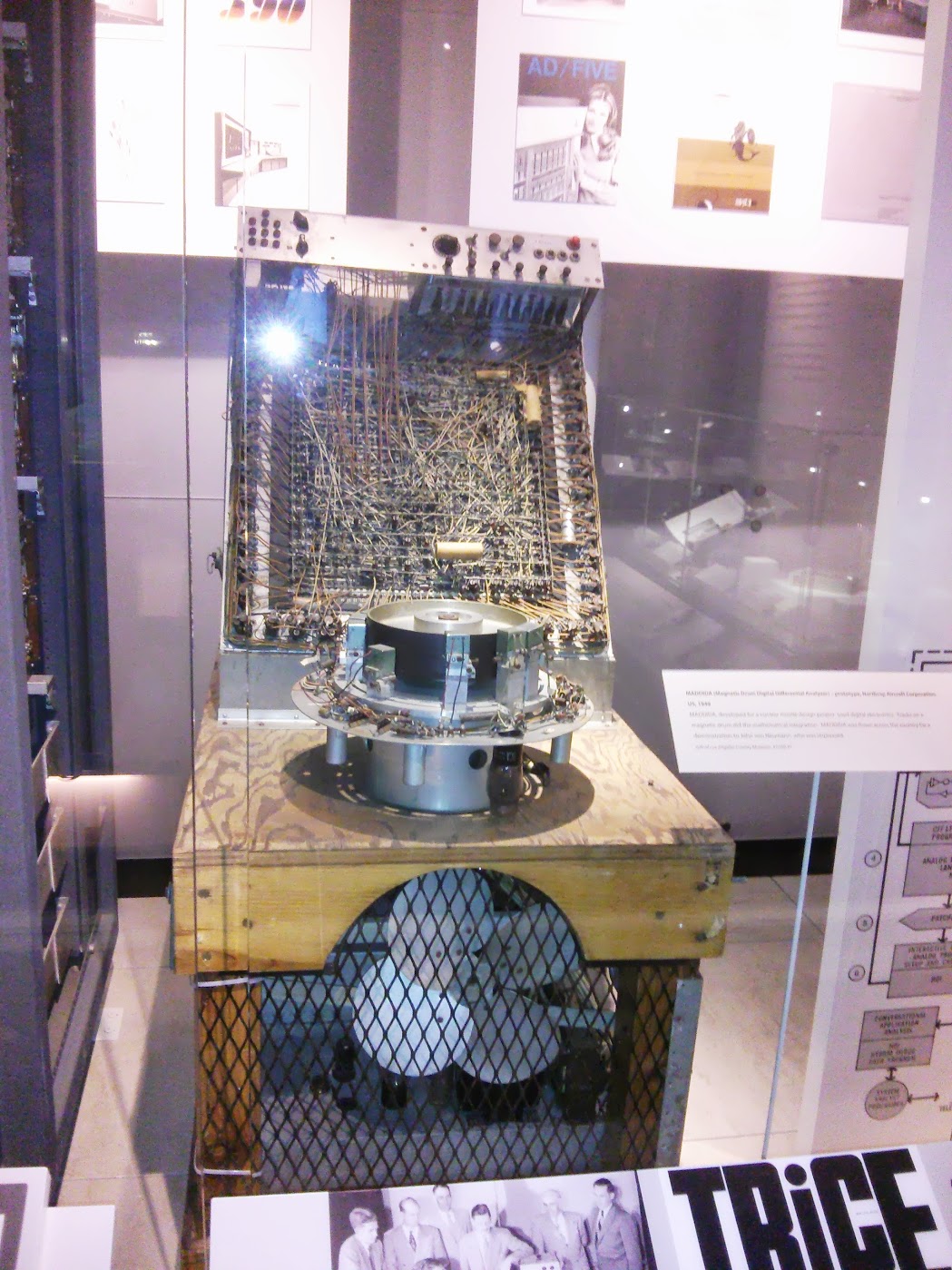
MADDID A , prototype, US, 1949

LEO II paper tape reader control , UK, 1957

In this photo, my wife amiora and a celebrity are the first electronic computer:
ENIAC , US, 1945

Librascope , US, 1956
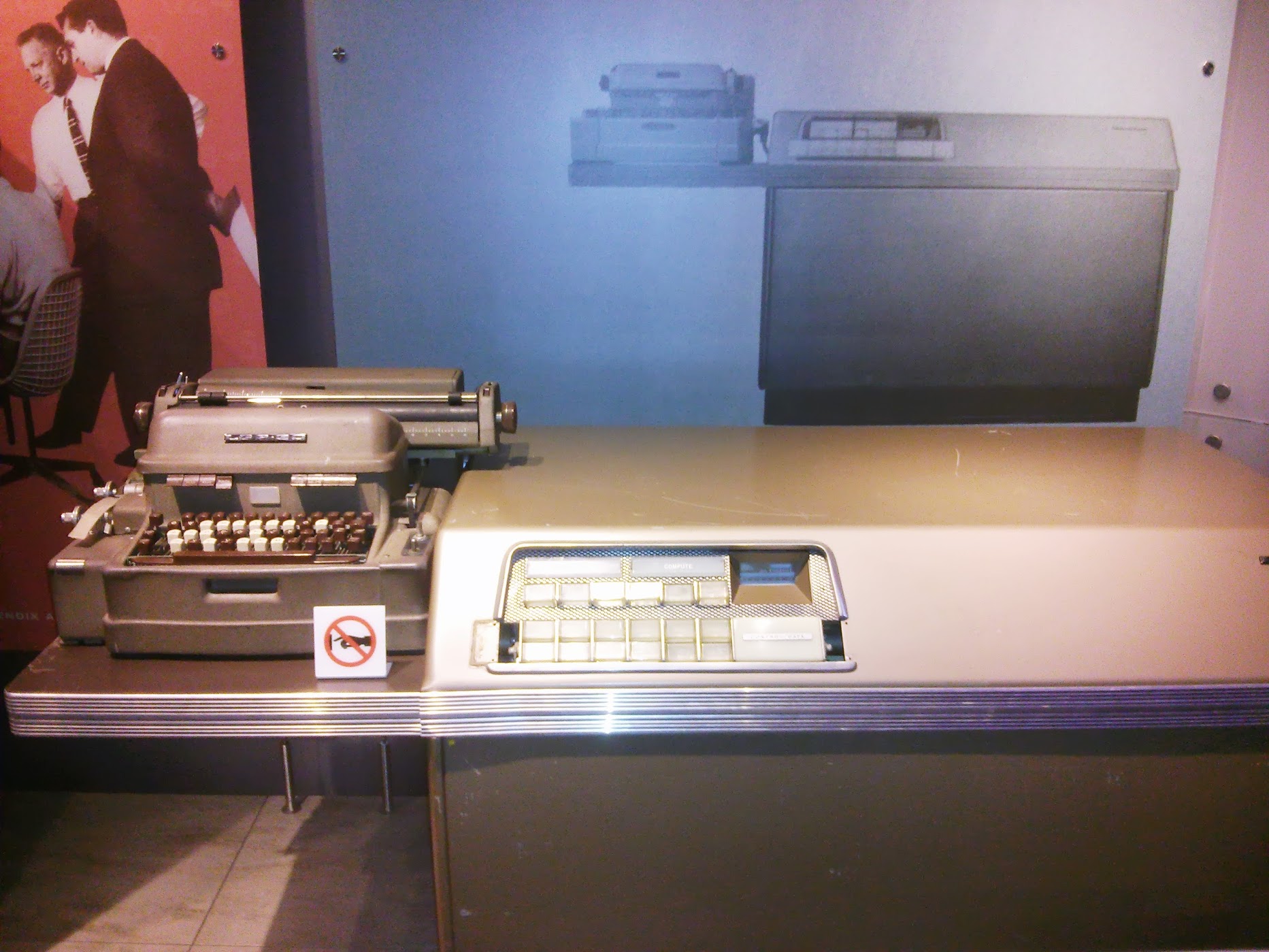

Here it is the language in which these terrible multi-toned pieces of iron worked - FORTRAN

Here is another celebrity in our HIT parade:
UNIVAC I Supervision Control Console , US 1951
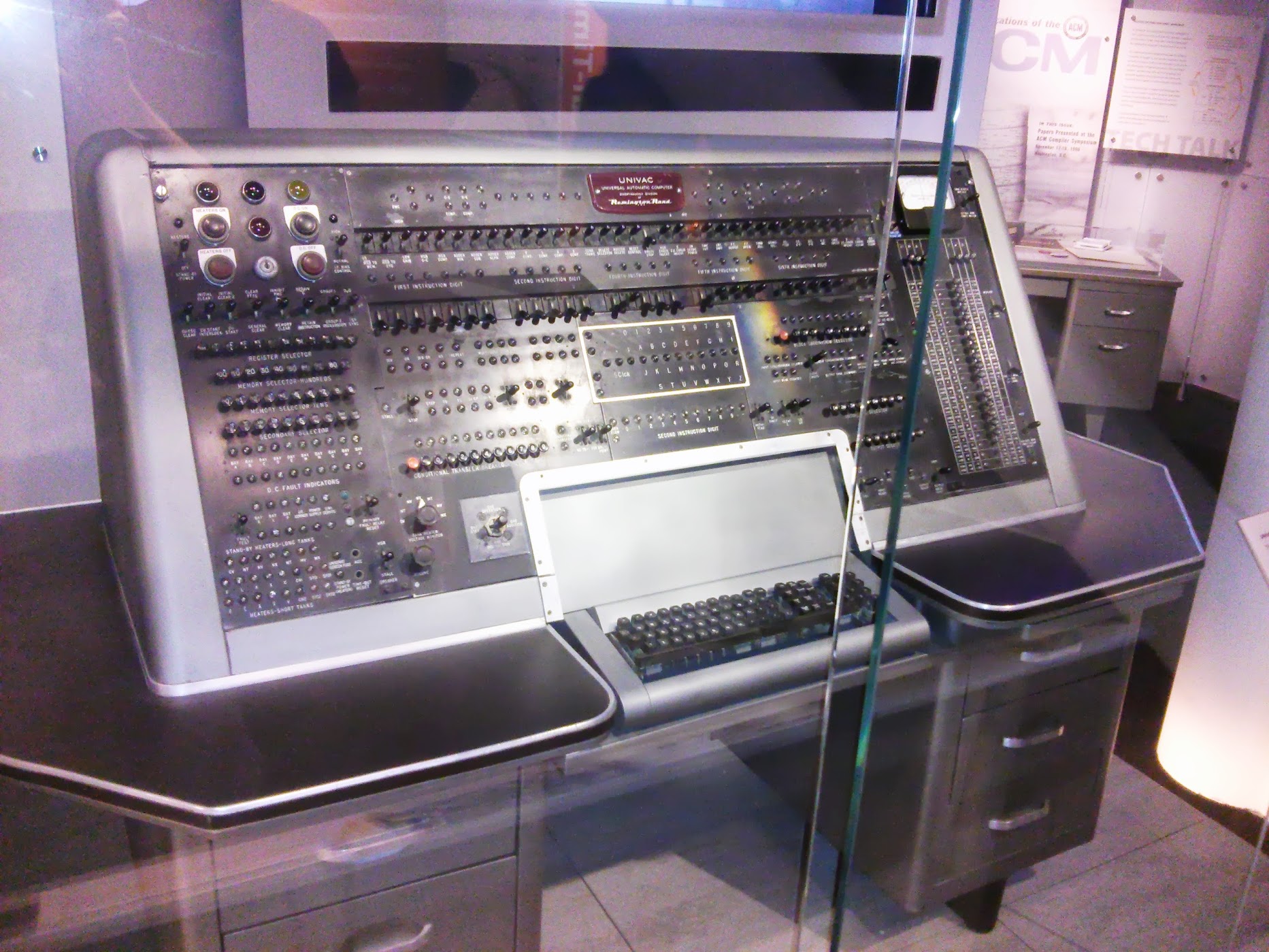

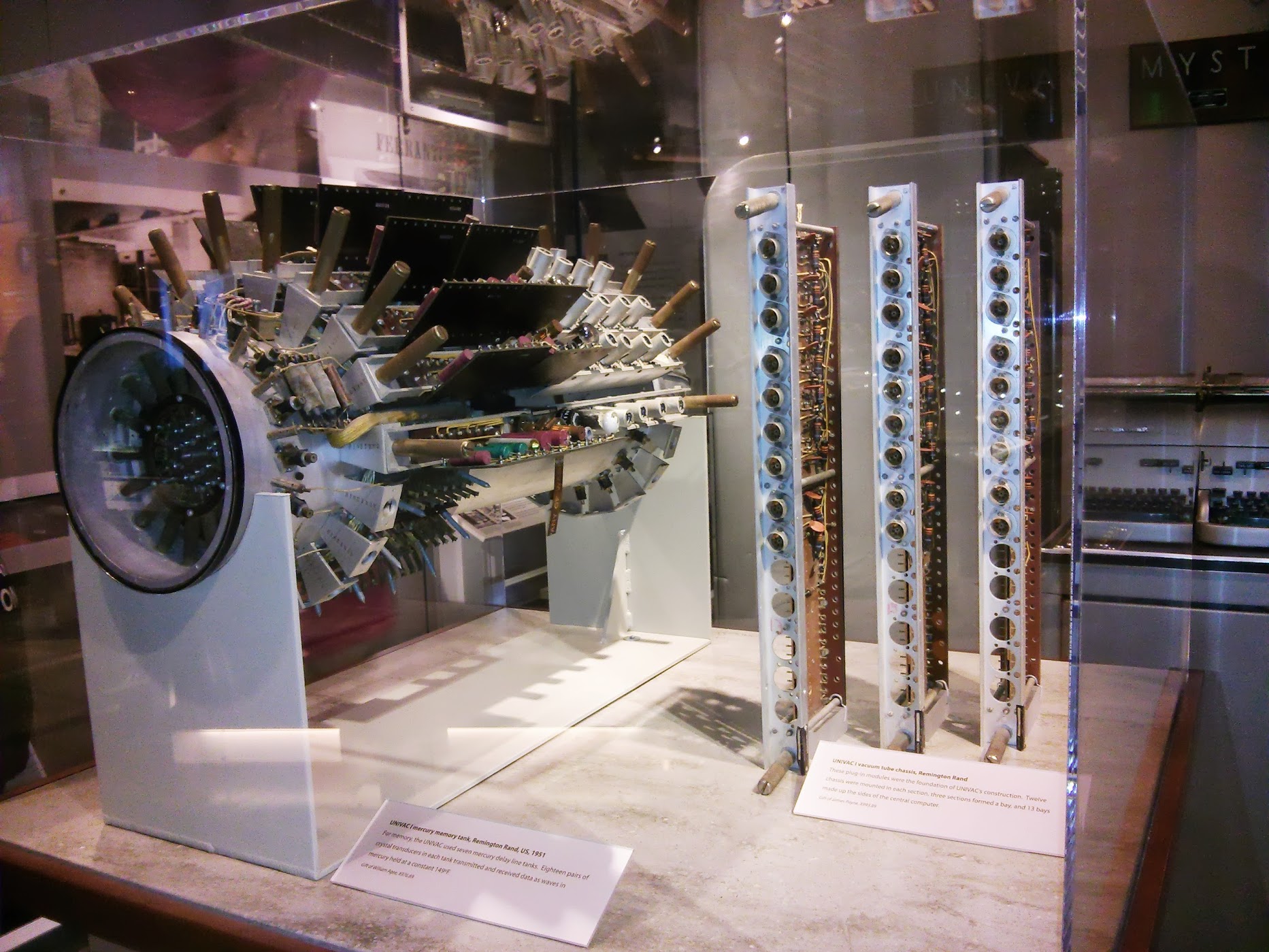
UNIVAC I Mercury Memory Tank and Vacuum tube chasis , US, 1951
Among these giants is a small, but very famous machine.
ENIGMA , Germany, 1935

By the way, next to the photo is a disk with a Kollosus film - a computer, with the help of which it was just deciphered the secret Enigma codes.
JOHNNIAC , US, 1953

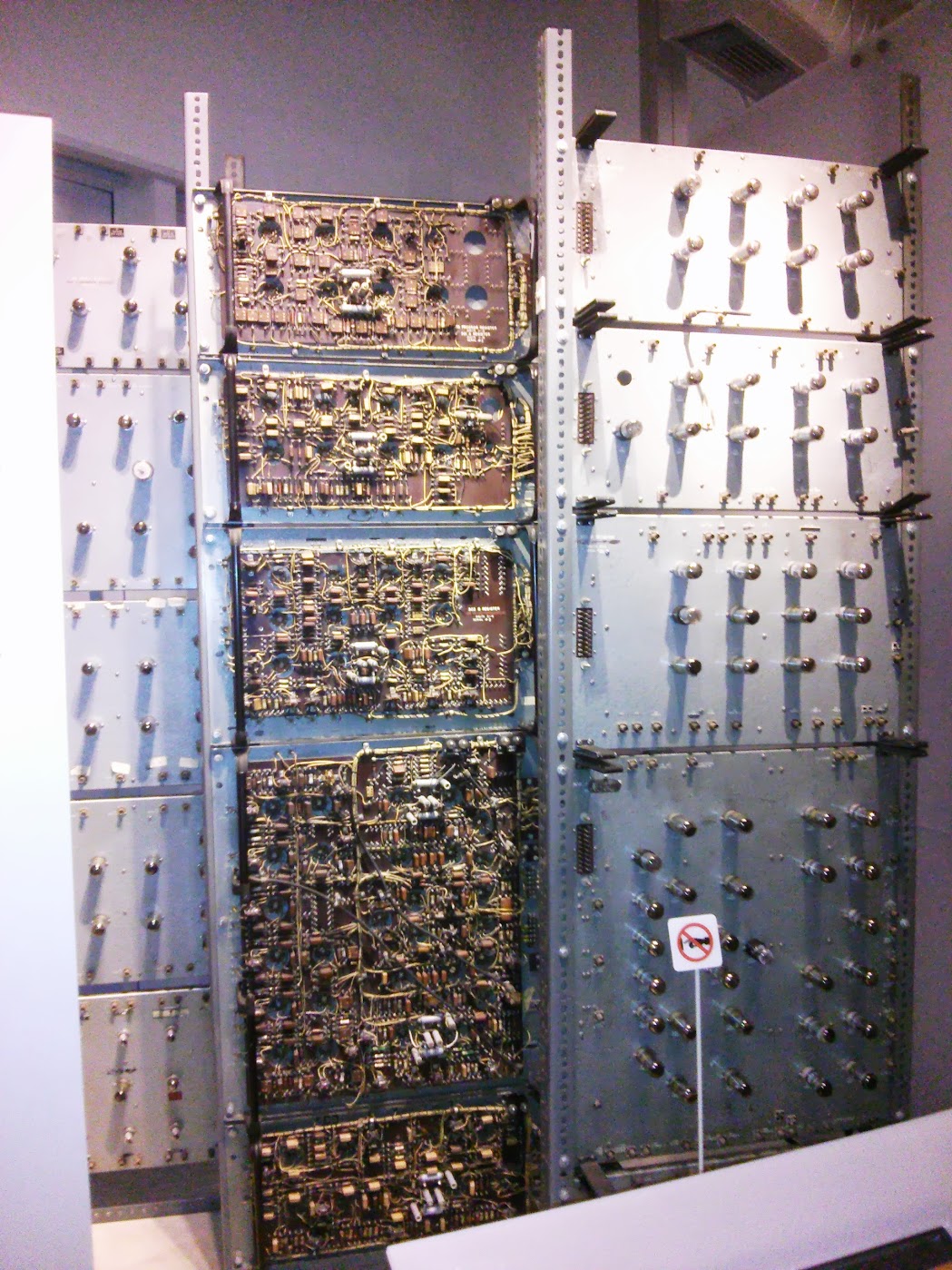
Whirwild Rack , US, 1951
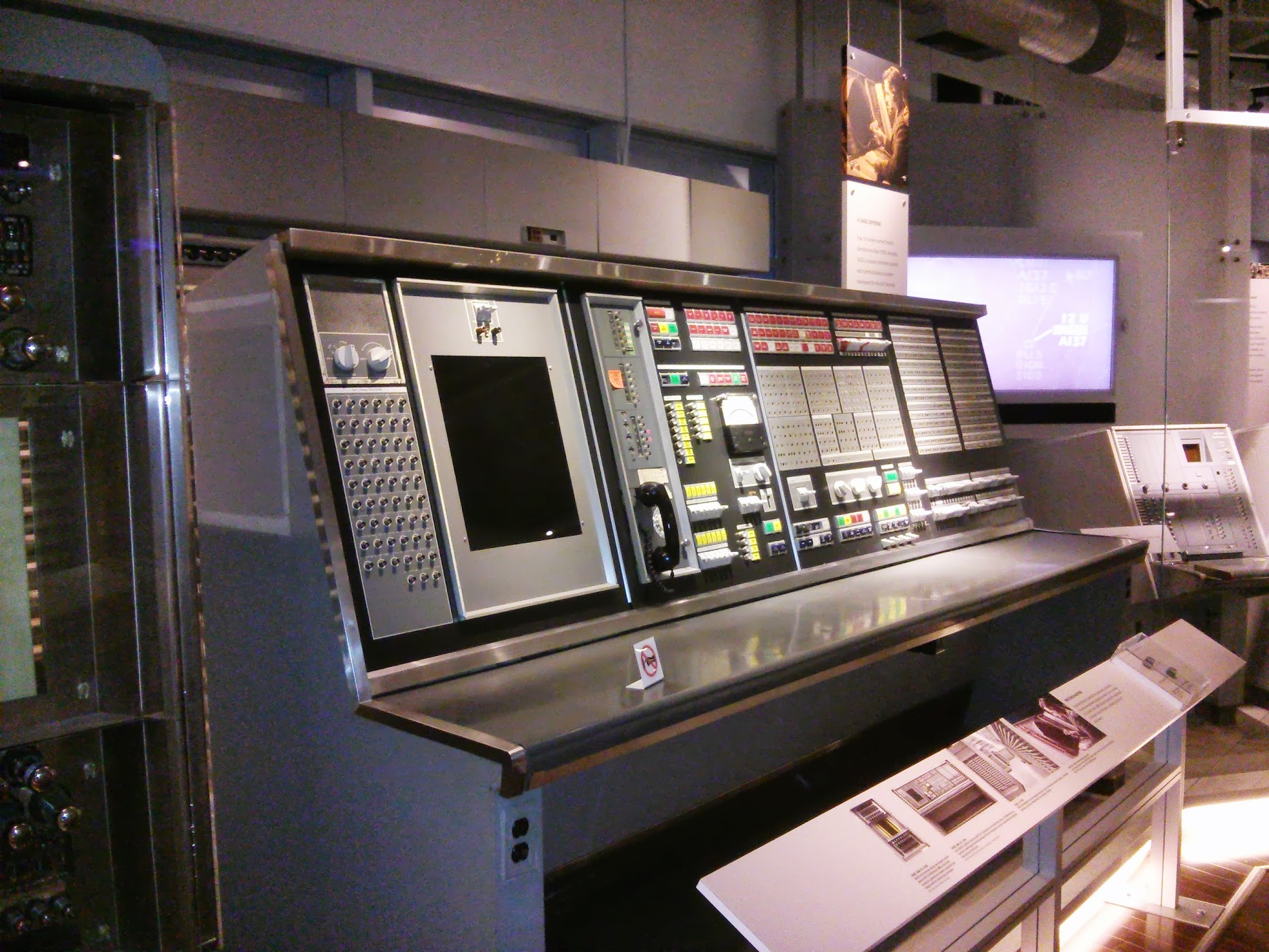
SAGE Weapons Director Console , US, 1958

SAGE IBM, US, 1958

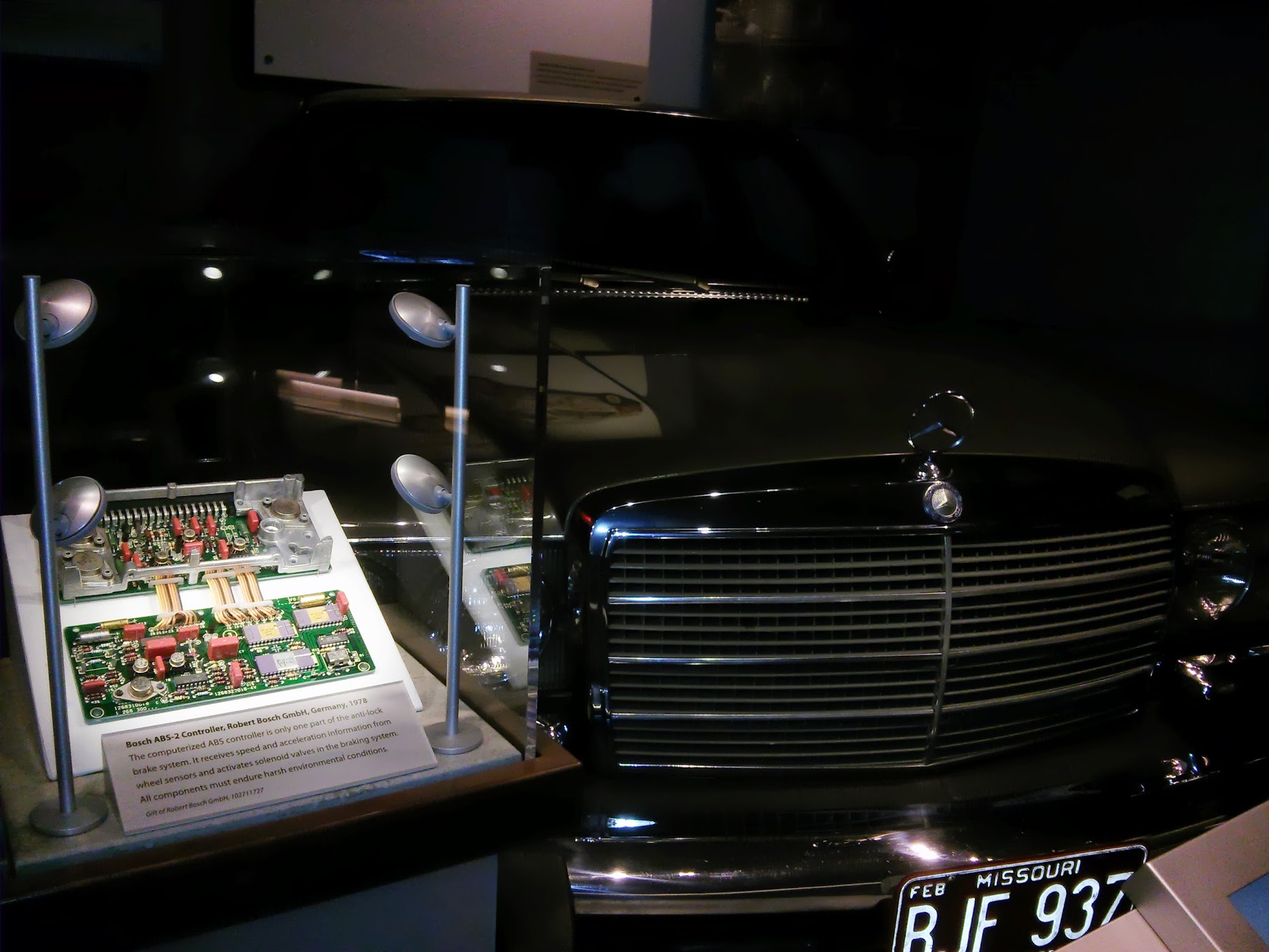
But what we still use in our cars
BOSCH ABS-2 Conctroller , Germany, 1978

Norden bombsight "Sight Head" , US, 1945

IBM System / 360 Model 30 , US, 1964

But the stands with many different generations of data warehouses. Many we still learn, but there are copies completely unknown to me:


Stand with space mission control devices:
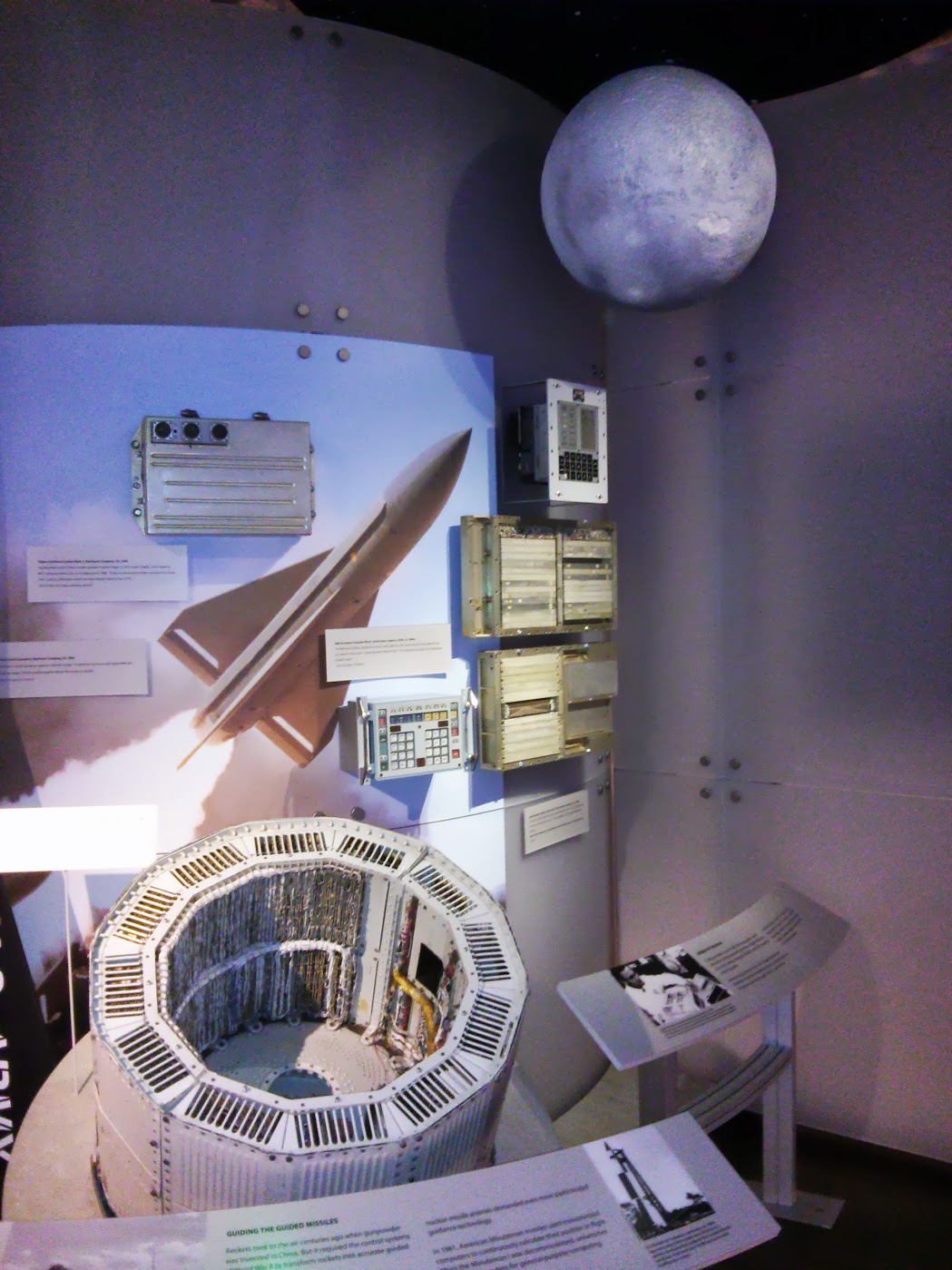

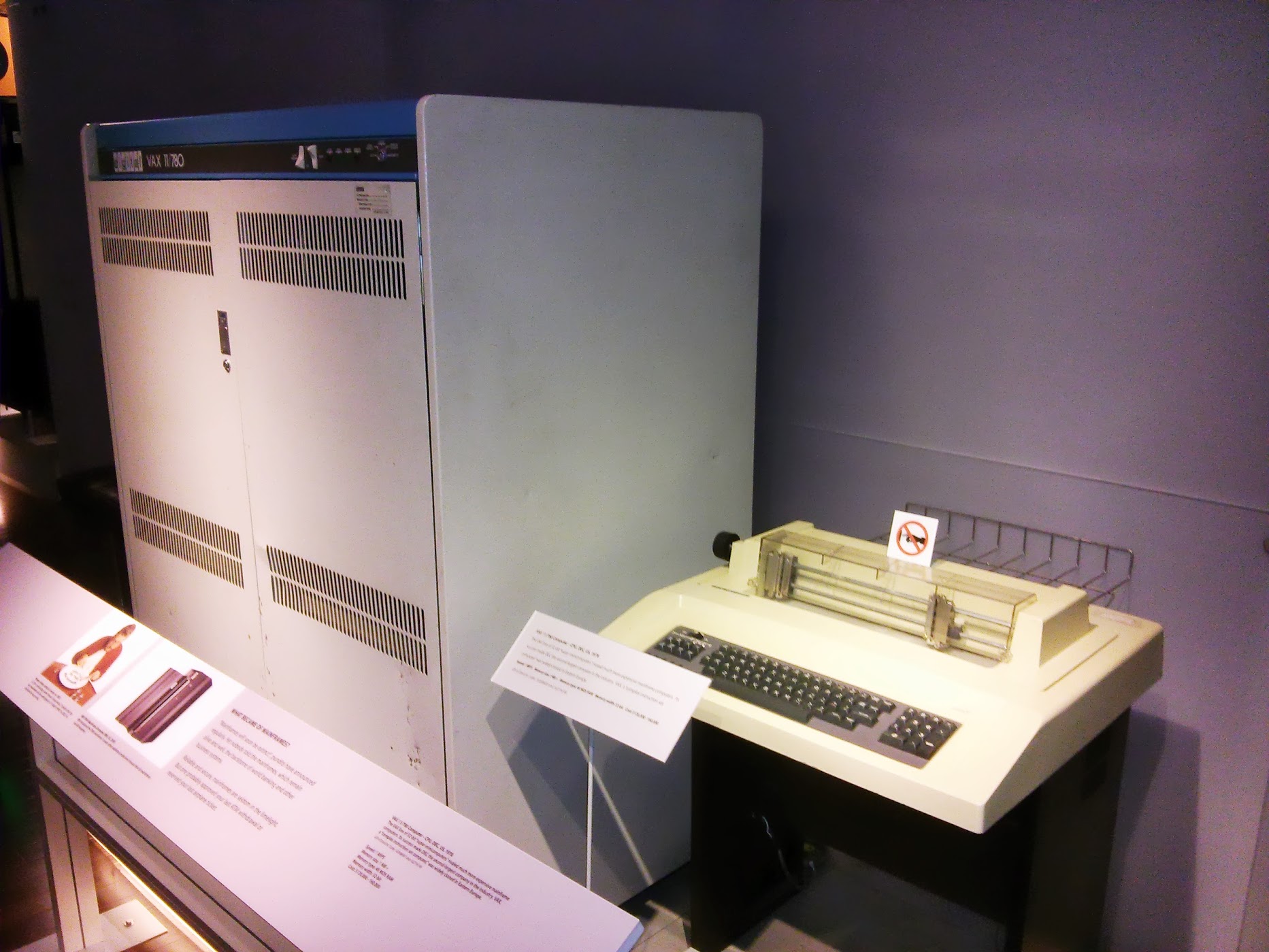
VAX-11/780 Comuter , US 1978

NEAC 2203 , Japan, 1958

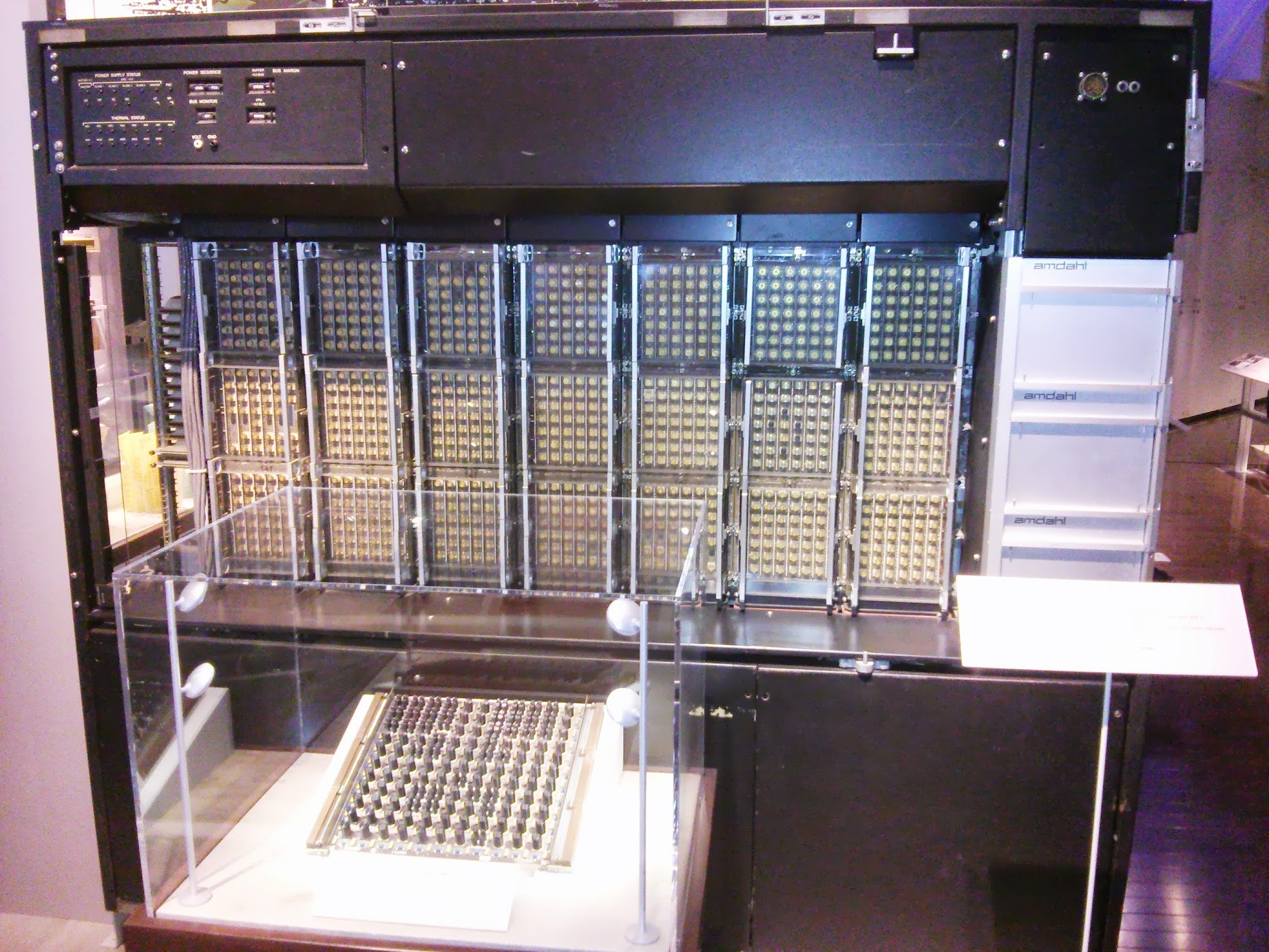
Amdahl 470 / V6 Computer , US, 1957

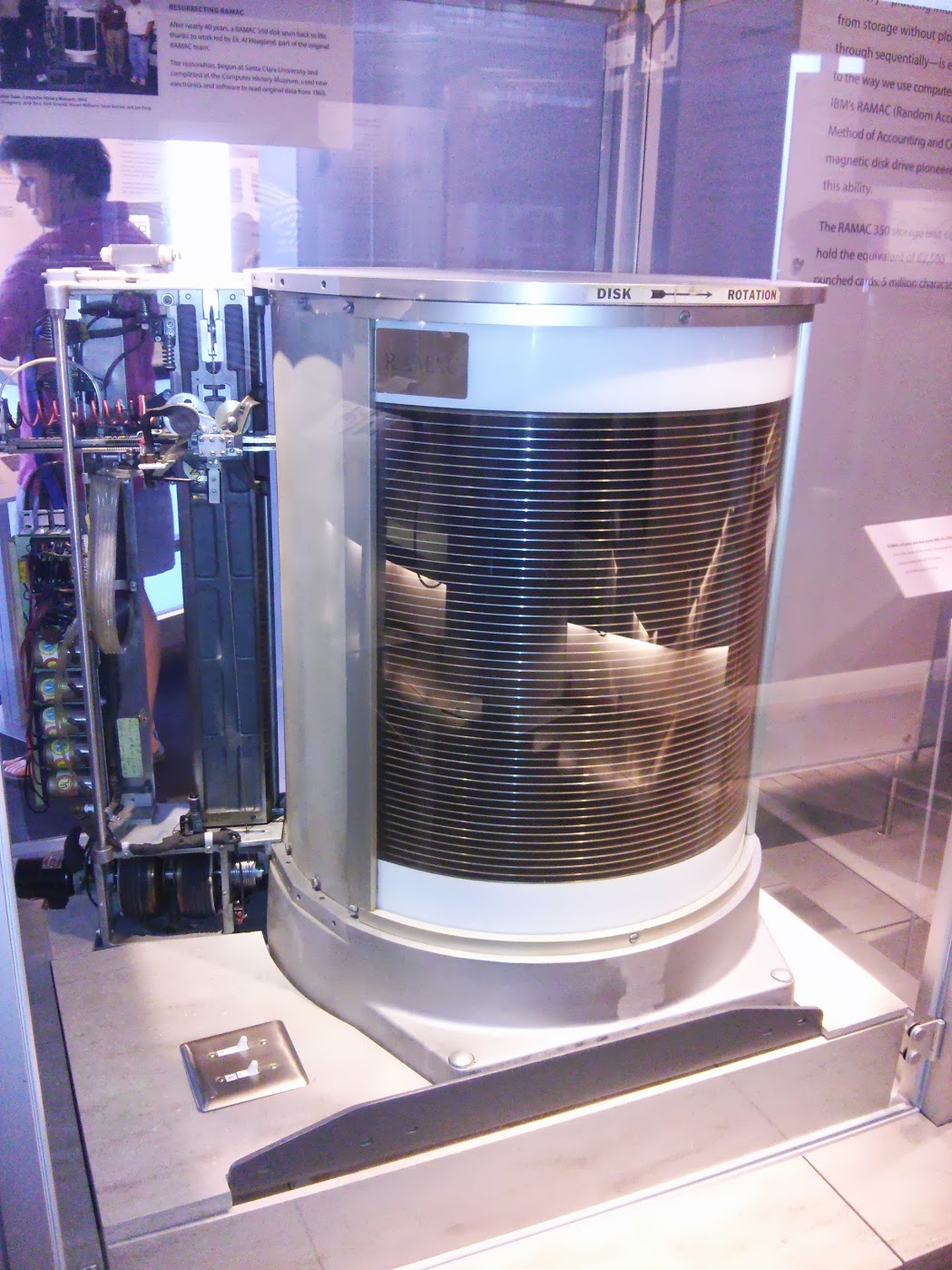
IBM RAMAC Actuator and disk stack , US, 1956
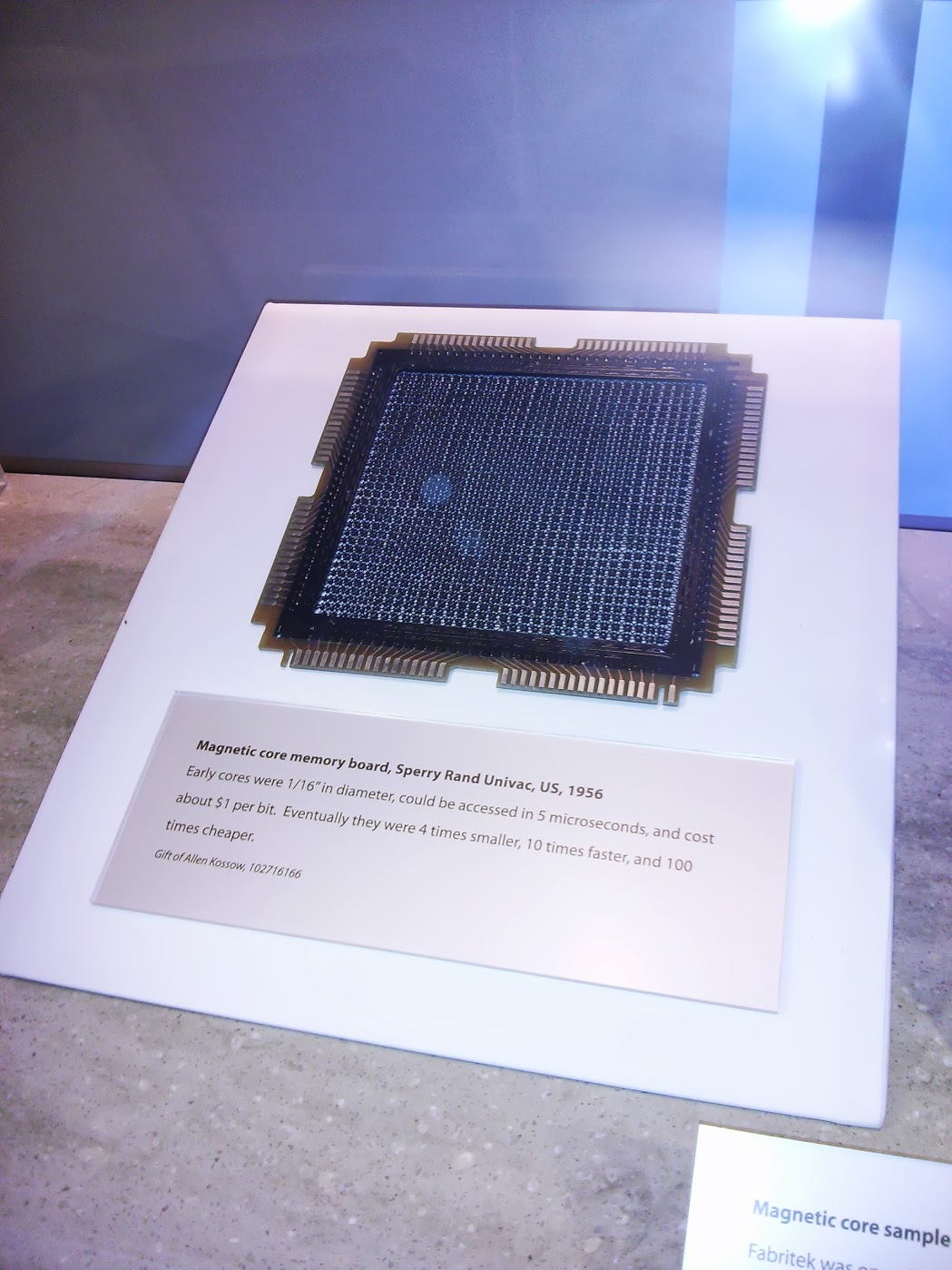
UNIVAC Magnetic core memory boar , US, 1956
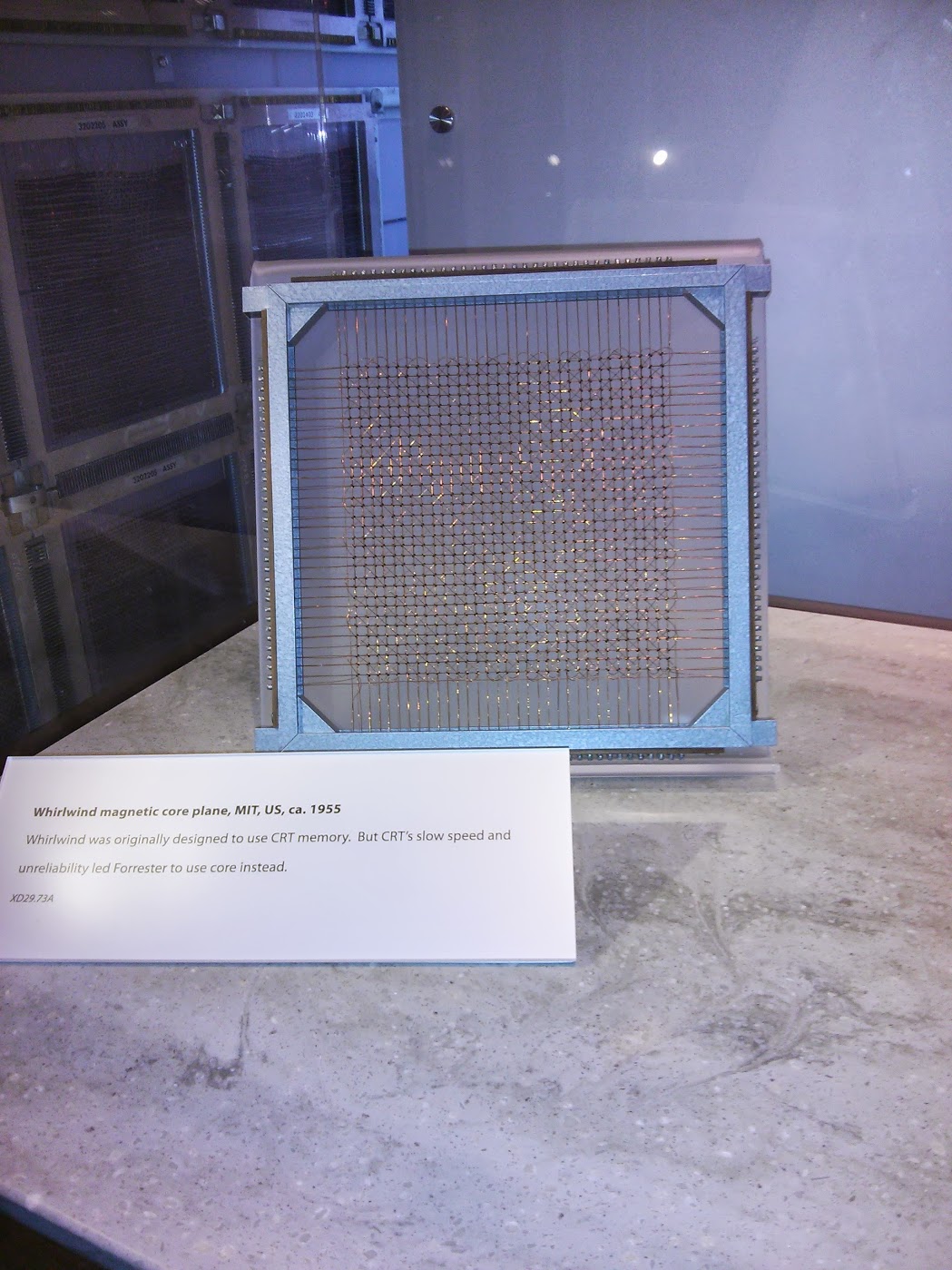
Whirlwind magnetic core memory plane , US, 1955
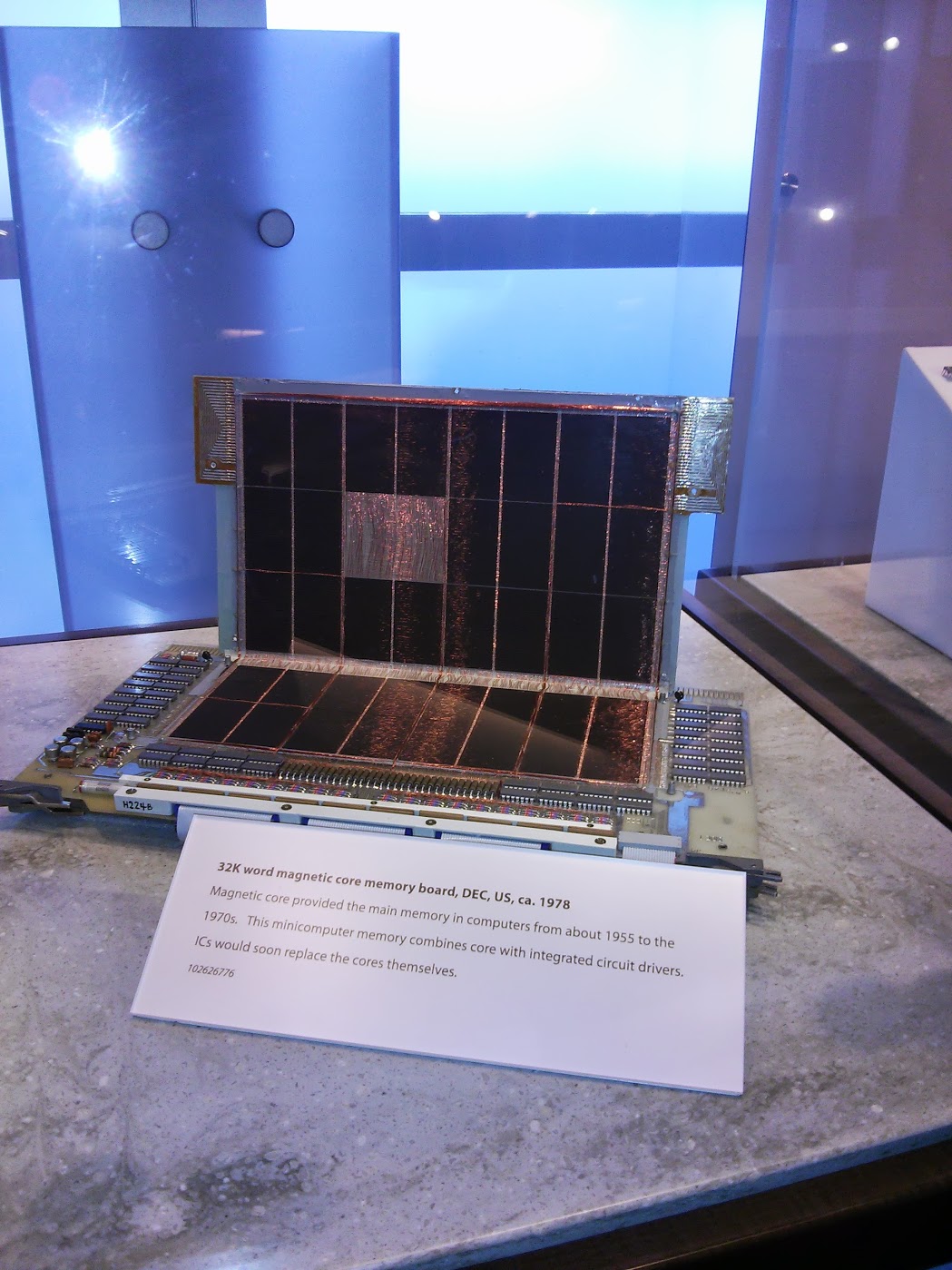
32k word magnetic core memory unit , US, 1978
Examples of developing Flash memory from different years:

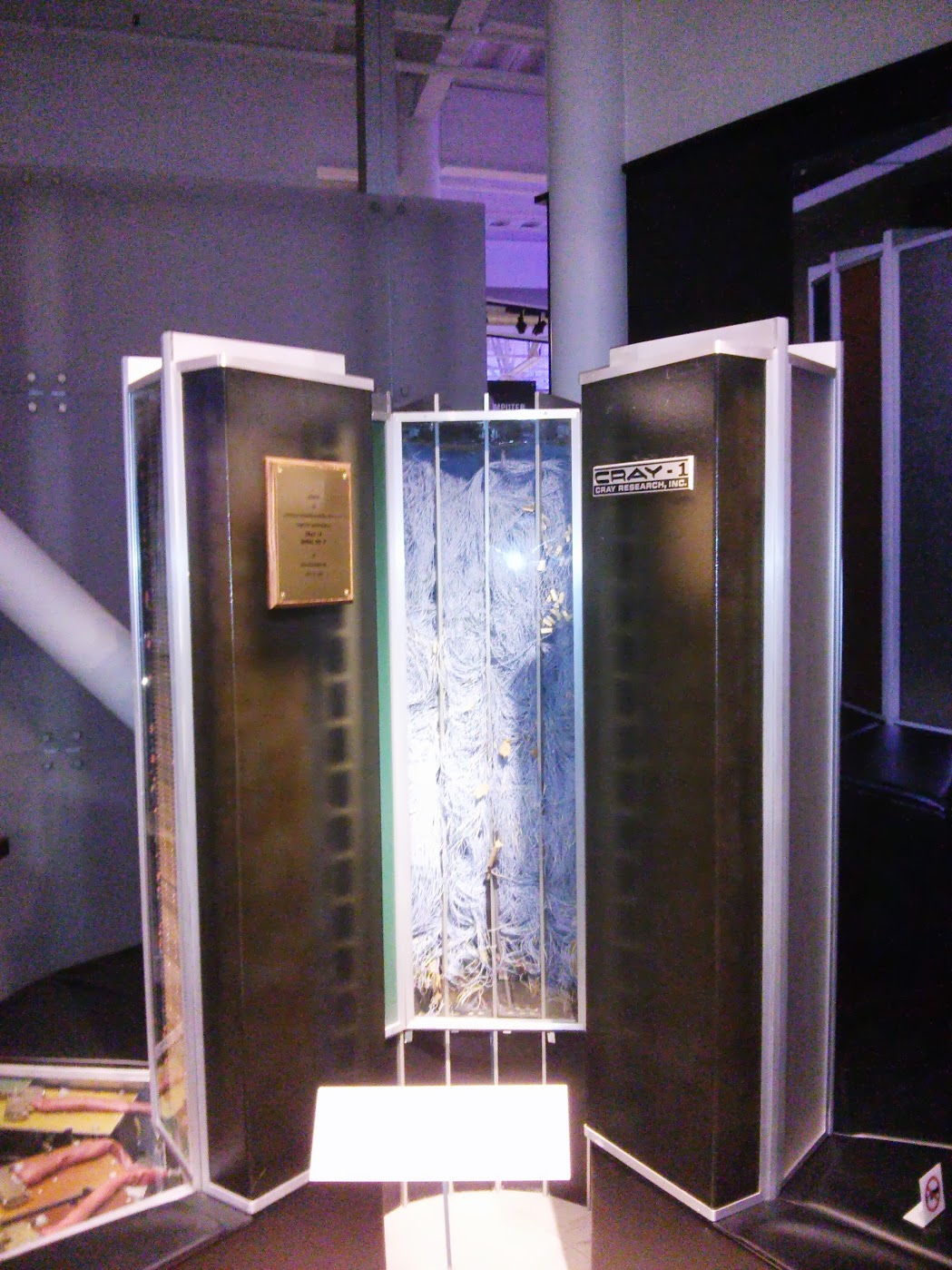
CRAY-1 , US, 1976

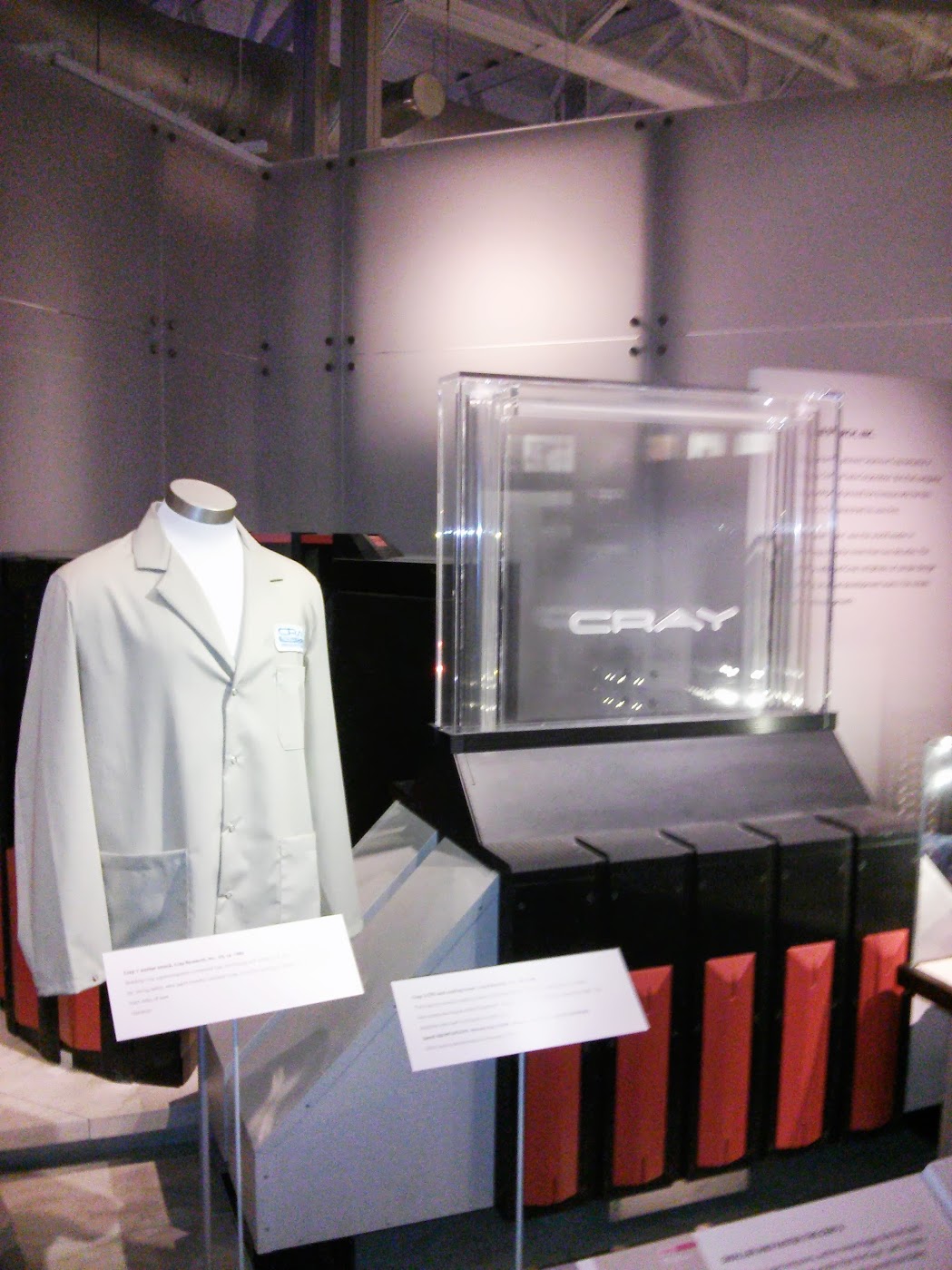
Operator uniform and cooling unit CRAY-1

Kitchen Computer , US, 1969

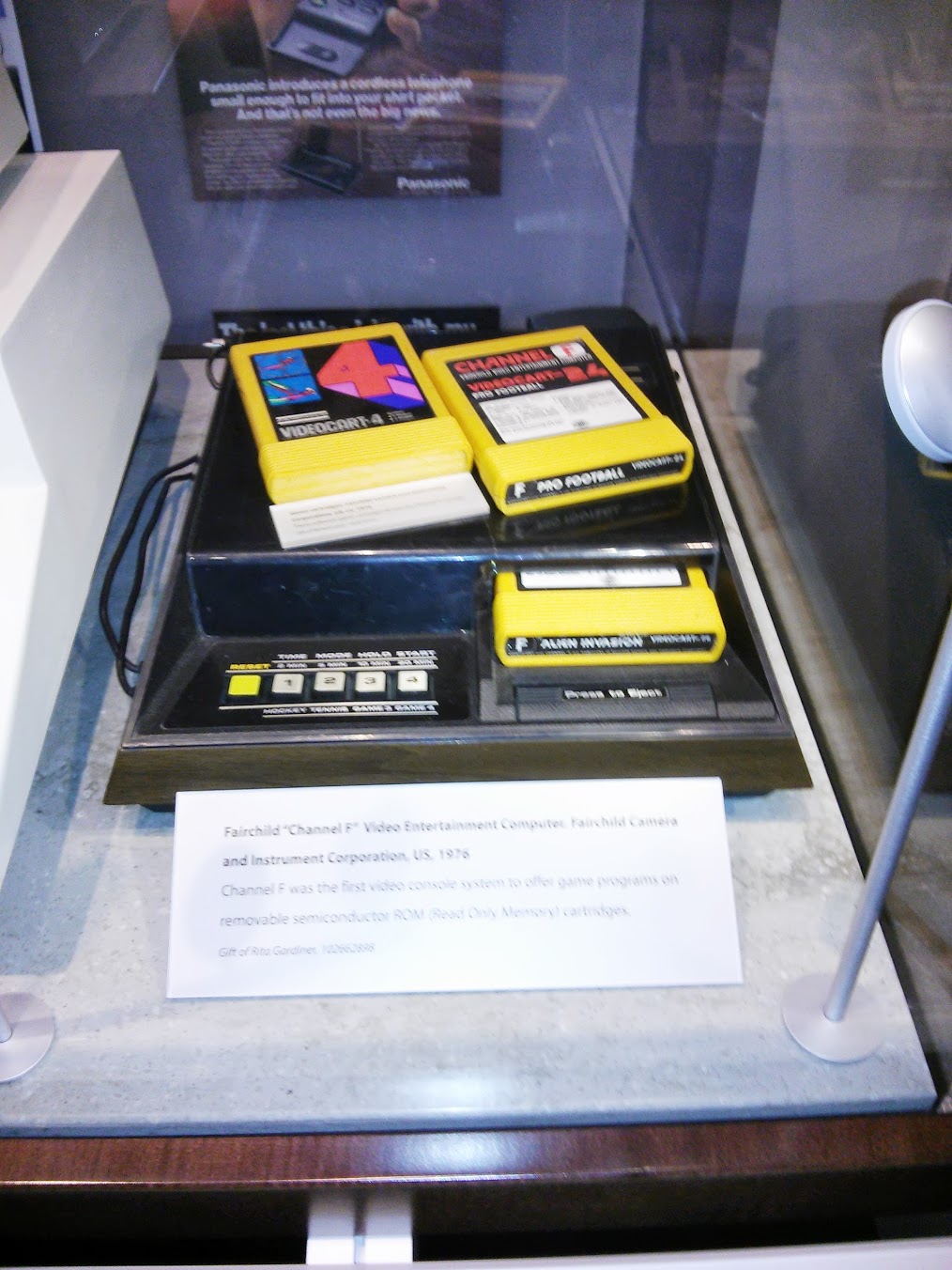
Fairchild "Channel F" Video Intertainment Computer , US, 1976

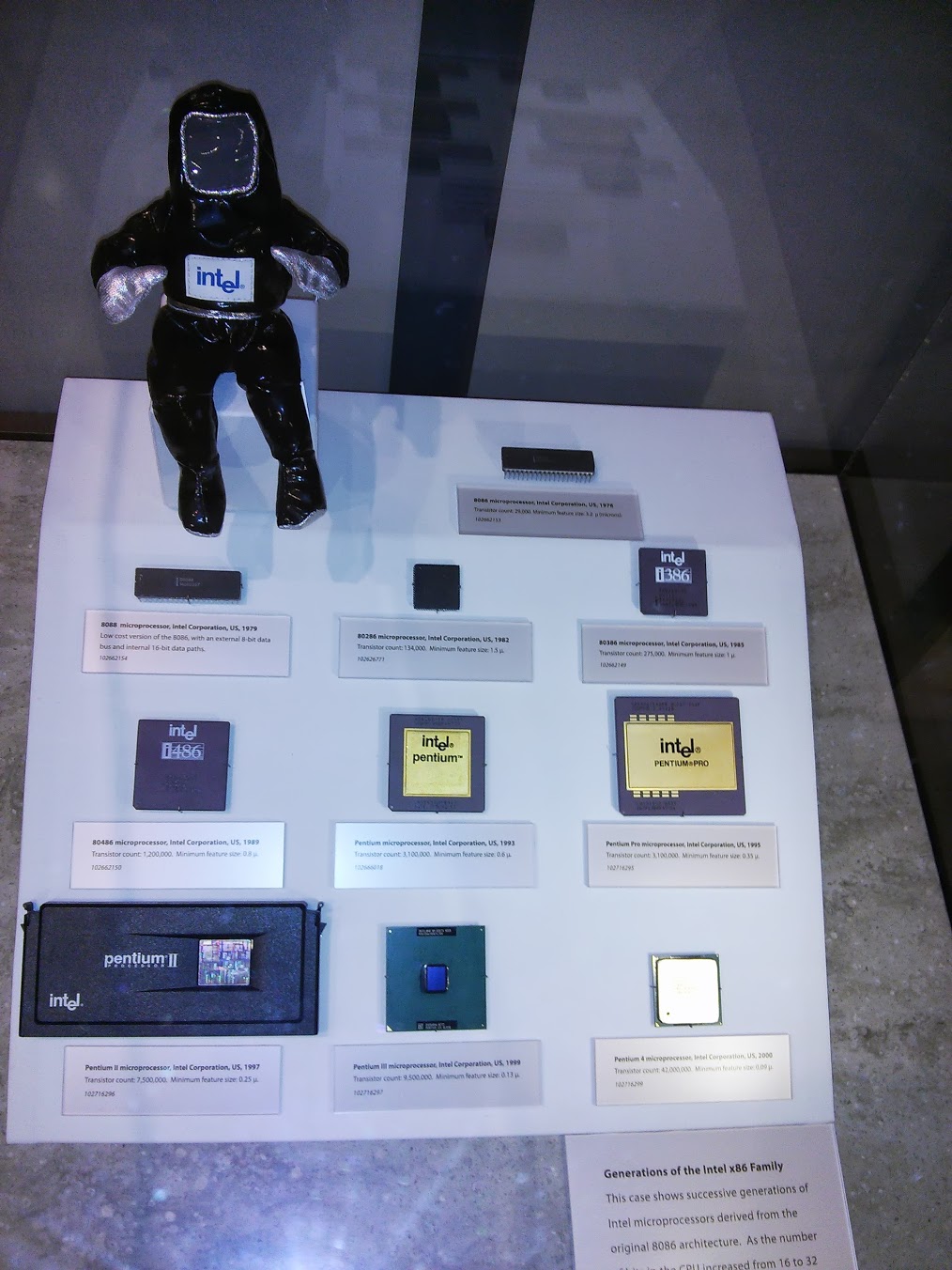
Different generations of Intel x86 processors

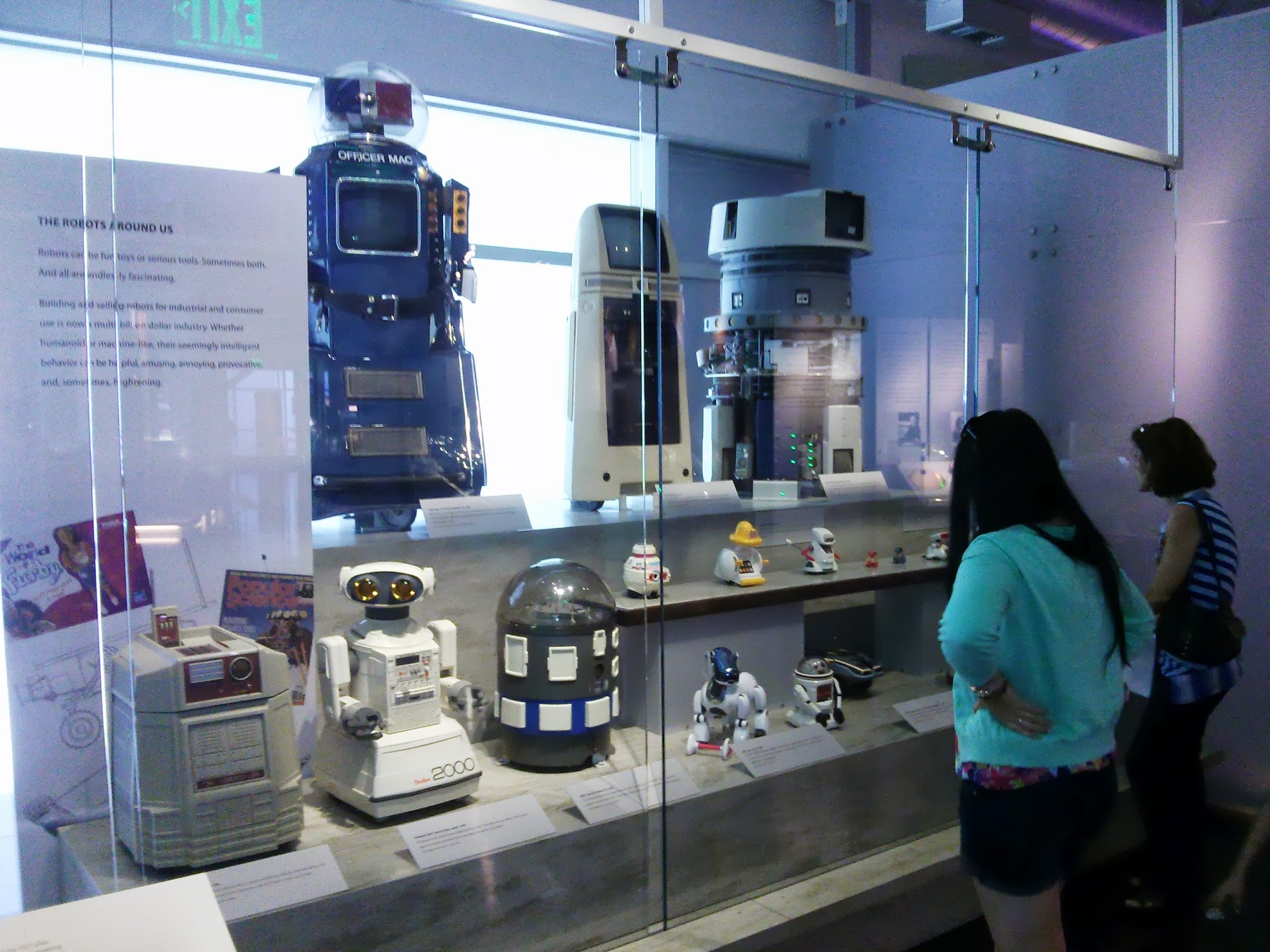
In the section of robotics are shown hundreds of different robots, for example,
Shakey , US, 1969

And other comrades
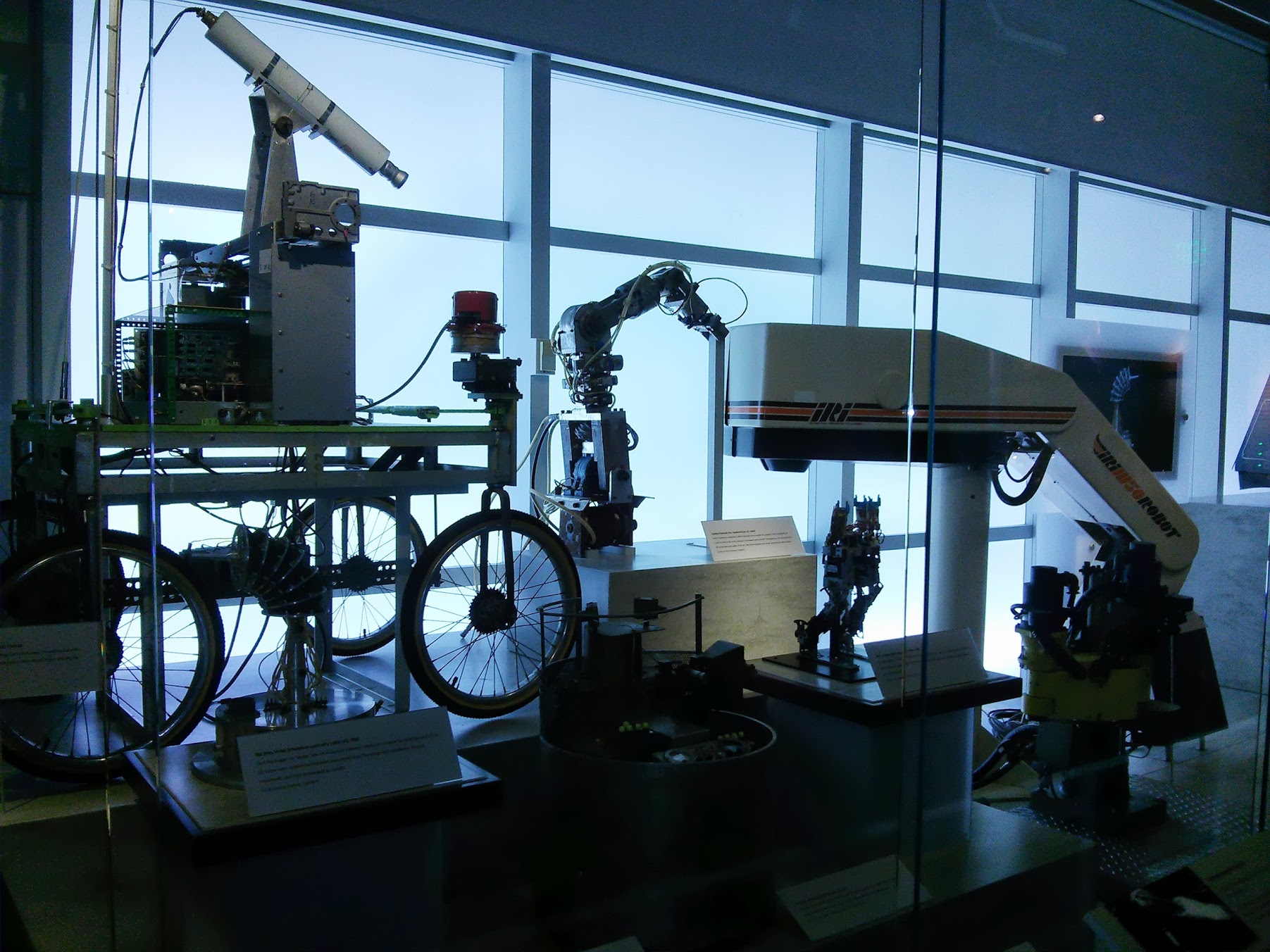


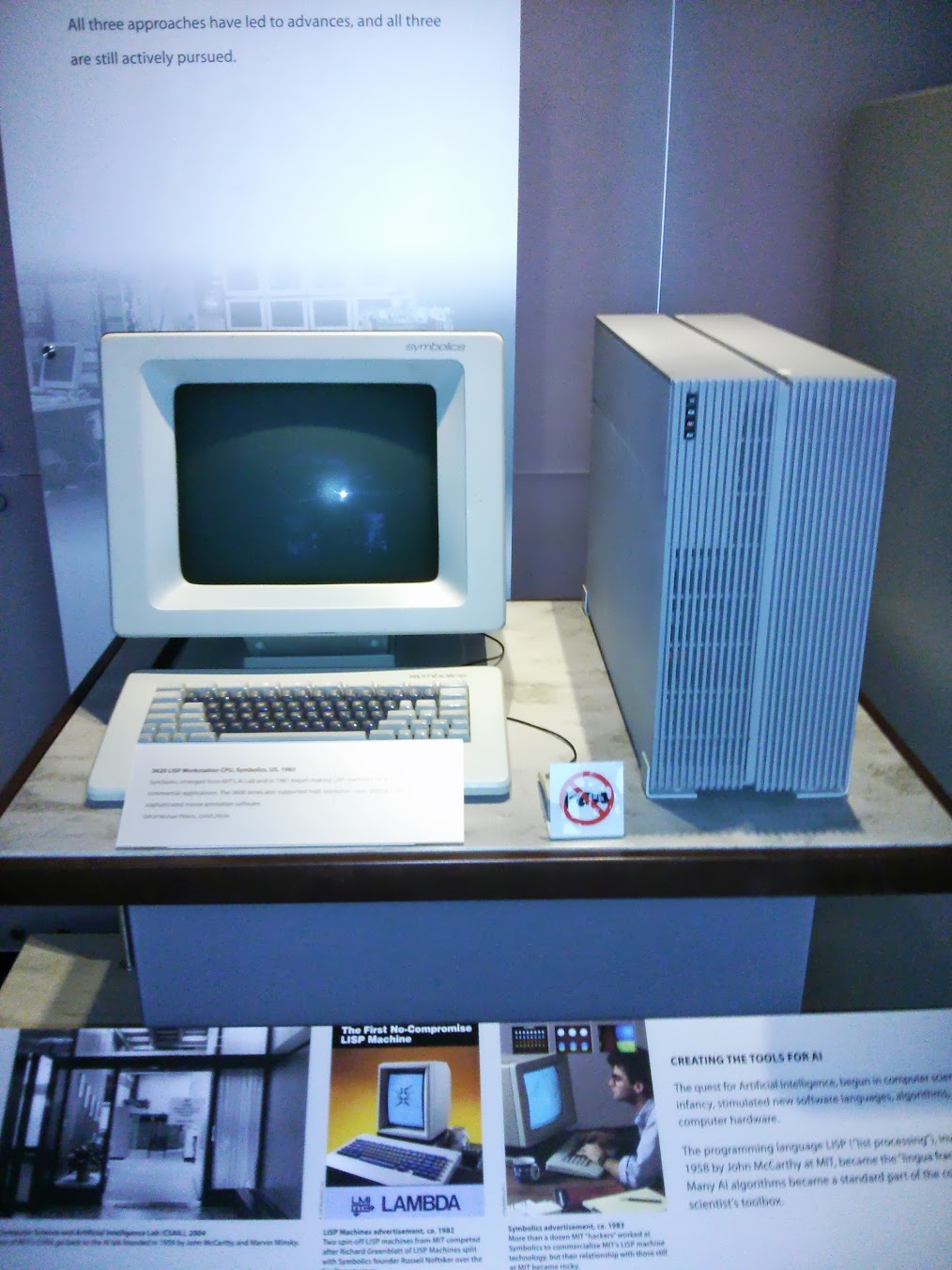
3620 LISP Workstation , US, 1983

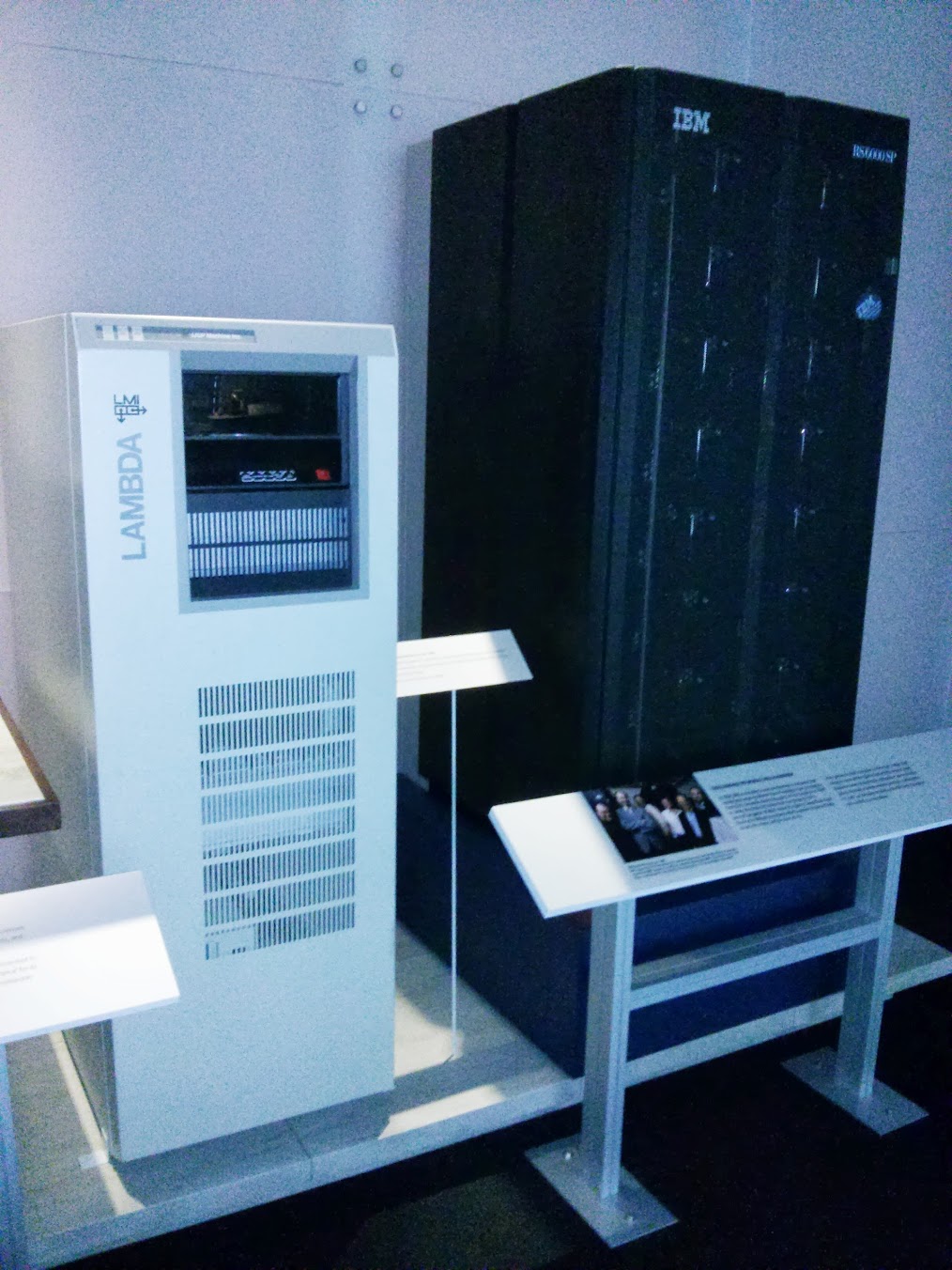
LMI LAMBDA , US, 1986

HP 7586B Graphic Plotter , US, 1984
Professional Iris 4D / 50GT , US, 1988

AutoDESK AutoCAD , US, 1986

The first laser printers:
HP LaserJet (Aka LaserJet Classic) , US, 1984
Apple Laser Writer Plus , US, 1985

Nintendo Game Boy , Japan, 1989

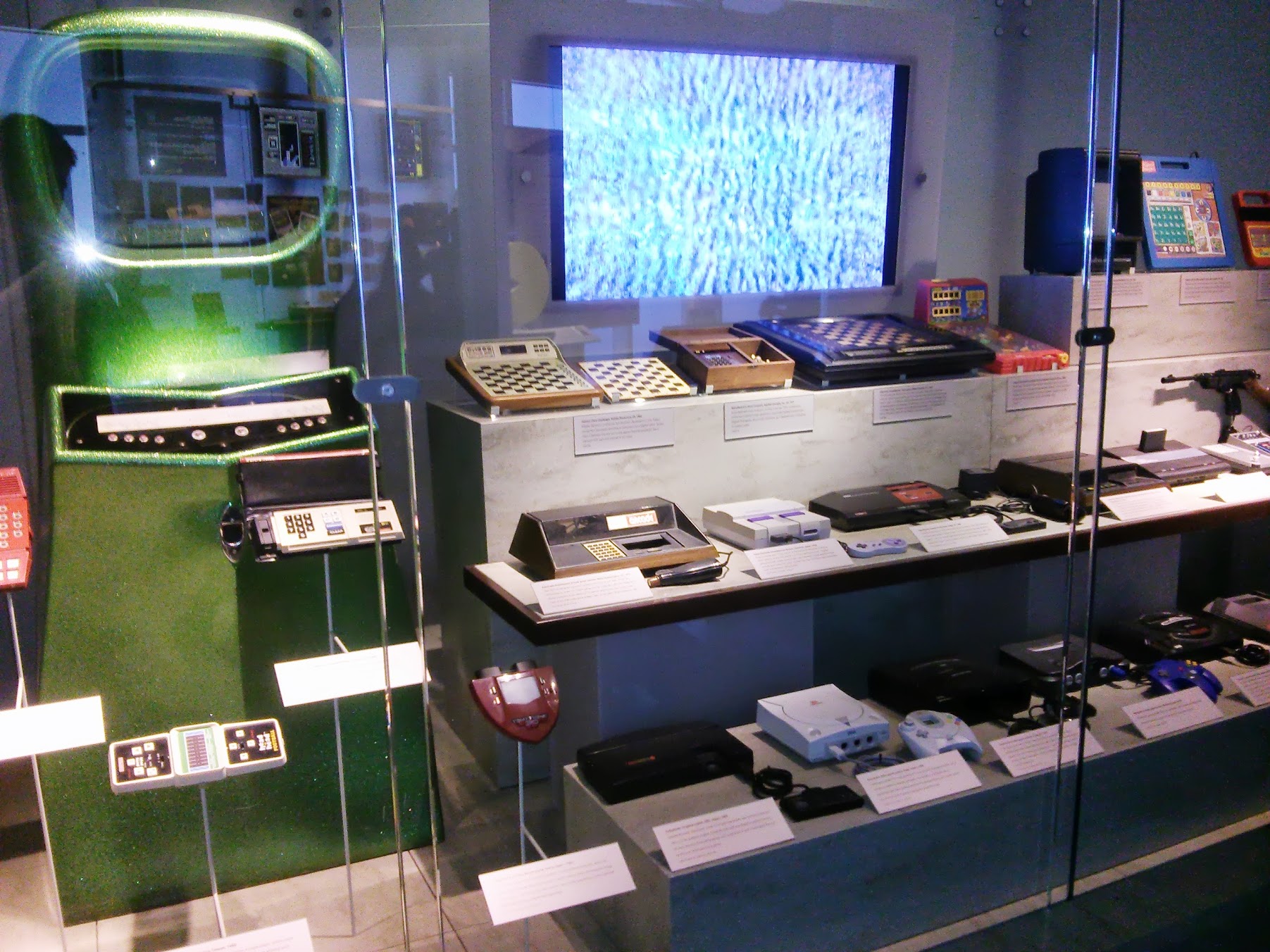
A huge number of game consoles


Our hero!!!
IBM PC , US, 1981

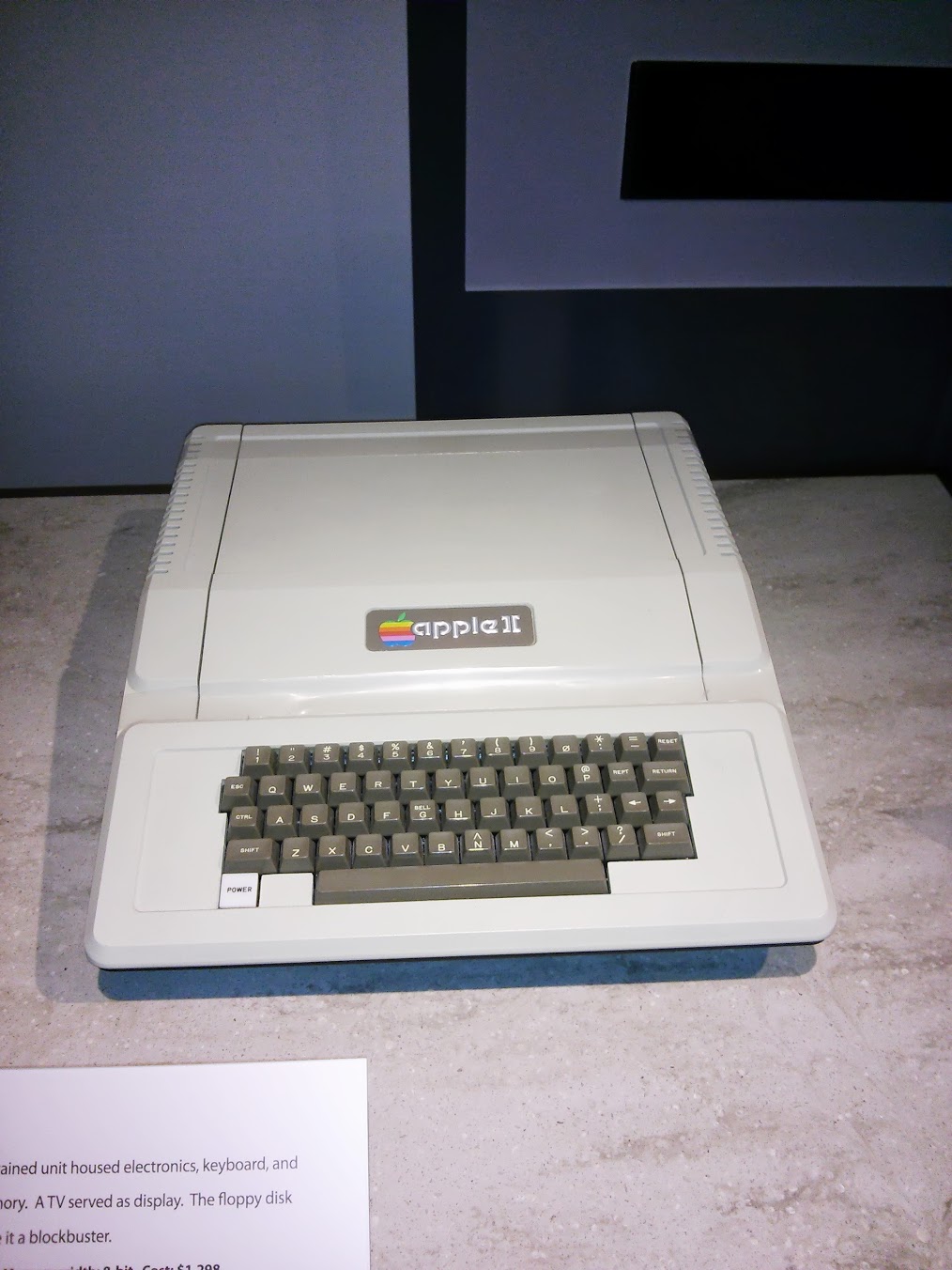
Apple II , US, 1977

Collection of phones 1990 - 1999

Google Server 1999

Unfortunately, I could not fully convey the atmosphere of the museum, but I advise everyone, if possible, be sure to visit this museum. Admission is only $ 15, and the pleasures of the sea.
Thanks for attention!

Last weekend I was fortunate enough to visit a wonderful place - the Computer History Museum , which is located in Mountain View in California, USA.
During my trip I took a lot of photos of the exhibits. In this article, I will show you these pictures (of course, not all), I will tell you about what was happening there. I also want very much to understand everything that I saw in this wonderful place, because the museum contains thousands of exhibits, even to think about each and stand next to it physically will not work during the day.
')
So let's start with the story . In the next few paragraphs, I will provide information from Wikipedia and other sources about the museum itself.
The Computer History Museum is also possible to translate " The History Museum of Computing Technique ", but I prefer option number 1, it begins its history back in 1968 . Gordon Bell in those years engaged in collecting electronics for history and he began with the computer Whirlwind , which I saw and which I will discuss below. The first exhibition “Project Museum” - “Museum Project” was held in 1975 in the lobby of the company DEC, which this same Bell headed. In 1978, the Digital Computer Museum - The Digital Computer Museum moved to another DEC lobby in Marlborough, Massachusetts. 1984 "Computer Museum" - "The Computer Museum" , moved to Boston.
In the late nineties, the museum’s artifacts were divided between two centers — the Computer History Museum here in Silicon Valley and the Boston Science Museum. Since 2003 , the Museum received its place in the former Silicon Graphics building in Mountain View, where it displays its exhibits today.

The main exhibition held in the museum is called “Revolution: The First 2000 Years of Computing” - “Revolution: The First 2000 Years of Computing”, which, in fact, I looked. But there were also a couple of expositions, with which I will begin.
Silicon Valley Founding

The first exposition I saw in the museum is the recordings of engineers and scientists , dated 1957 and 1959 . The three founders of Frairchild Semiconductor , Jean Hoerni , Gordon Moore and Robert Noyce , described innovative technologies in the construction of electrical circuits and made a revolution in the history of computing technology.
It was during these years around the city of Santa Clara began to form and unite companies for the production of computers and software. Here, really, you can touch the story!
Difference Babbage machine (№2). Babbage Difference engine # 2
Further along the way we met a fascinating presentation - the work of the Babbage Counting Machine . Two museum staff told and showed how and how this magnificent harmonious mechanism works.
Before our eyes, the polynomial values were calculated with an accuracy of 31 decimal places:



It is noteworthy that this whole mechanism was only in the drawings for a very long time. Only after many years, scientists, having studied the drawings, realized that the machine did work, and created it. In Mountain View there is a copy, the very first machine built is in the London Museum of Science.
Exposure from Google
Next on the plan was the exposure of Google Street View. It was shown the main transport, which remove the surrounding species. You could even feel and sit behind the wheel:


Revolution: the first 2000 years of computing
Further, according to the plan was the main exhibition of the museum:

But just before the exhibition, at the entrance, I don’t know why, there were 3 artifacts, hardly revolutionary:
Calculating Betting Odds, Race Betting, 1930

Panasonic Q Game Console, 2001

The tablet says that in 2001, Nintendo, having teamed up with Panasonic, released a hybrid - a game console and a DVD player 2 in 1. But it all went down the drain - it was cheaper to buy the same thing separately!
Russian super-computer ELBRUS-2, 1984-1986 (CPU boards)

The main exhibition was in the chronometric order of the history. It all started with the most ancient methods of complex calculations:
Sectors XV - XVIII

Lords Calculator, 1880

I have no idea how something could be counted on it!
Schickard Calculator , copy of 2000. Originals date back to 1623.

Sumador Chino , Mexico, 1800

Napier's Bones , England, 1700

Pascal adder (Pascaline) , copy, 1981. Original dates from 1641

Time is Money (TIM) Calculator, 1910

Curta Calculators , Lichtenstein, 1950 - 1960

Mass-produced calculators:
Arithmometer , France, 1850s and FELIX M , USSR, 1932

And some more different calculators:


Type 31 Alphabetical Duplicating punch , IBM, US, 1933

40 column Card Punch , UK, 1954

Model 406 Cards Sorter , UK, 1954

Punch card sorters from IBM, 1949 and 1953


Type 26 Printing Keypunch , IBM, US, 1949

Hollerith's electric tabulating system , copy. The original dates from around 1890.

Stand with bills. Mexican mom and mexican son know how to count something on them

Nordsieck Differential Analyzer , US, 1956

Telefunken RAT 700/2 analog computer , Western Germany, 1959

H-1 Educational Computer , US, 1956

EAI PACE TR-48 analog computer , US, 1962

Trice Computer , US, 1964

MADDID A , prototype, US, 1949

LEO II paper tape reader control , UK, 1957

In this photo, my wife amiora and a celebrity are the first electronic computer:
ENIAC , US, 1945

Librascope , US, 1956

Here it is the language in which these terrible multi-toned pieces of iron worked - FORTRAN

Here is another celebrity in our HIT parade:
UNIVAC I Supervision Control Console , US 1951

UNIVAC I Mercury Memory Tank and Vacuum tube chasis , US, 1951

Among these giants is a small, but very famous machine.
ENIGMA , Germany, 1935

By the way, next to the photo is a disk with a Kollosus film - a computer, with the help of which it was just deciphered the secret Enigma codes.
JOHNNIAC , US, 1953

Whirwild Rack , US, 1951

SAGE Weapons Director Console , US, 1958

SAGE IBM, US, 1958

But what we still use in our cars
BOSCH ABS-2 Conctroller , Germany, 1978

Norden bombsight "Sight Head" , US, 1945

IBM System / 360 Model 30 , US, 1964

But the stands with many different generations of data warehouses. Many we still learn, but there are copies completely unknown to me:


Stand with space mission control devices:

VAX-11/780 Comuter , US 1978

NEAC 2203 , Japan, 1958

Amdahl 470 / V6 Computer , US, 1957

IBM RAMAC Actuator and disk stack , US, 1956

UNIVAC Magnetic core memory boar , US, 1956

Whirlwind magnetic core memory plane , US, 1955

32k word magnetic core memory unit , US, 1978

Examples of developing Flash memory from different years:

CRAY-1 , US, 1976

Operator uniform and cooling unit CRAY-1

Kitchen Computer , US, 1969

Fairchild "Channel F" Video Intertainment Computer , US, 1976

Different generations of Intel x86 processors

In the section of robotics are shown hundreds of different robots, for example,
Shakey , US, 1969

And other comrades


3620 LISP Workstation , US, 1983

LMI LAMBDA , US, 1986

HP 7586B Graphic Plotter , US, 1984

Professional Iris 4D / 50GT , US, 1988

AutoDESK AutoCAD , US, 1986

The first laser printers:
HP LaserJet (Aka LaserJet Classic) , US, 1984
Apple Laser Writer Plus , US, 1985

Nintendo Game Boy , Japan, 1989

A huge number of game consoles


Our hero!!!
IBM PC , US, 1981

Apple II , US, 1977

Collection of phones 1990 - 1999

Google Server 1999

Unfortunately, I could not fully convey the atmosphere of the museum, but I advise everyone, if possible, be sure to visit this museum. Admission is only $ 15, and the pleasures of the sea.
Thanks for attention!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/192078/
All Articles