Expert evaluation methods
It is often necessary to choose among a variety of alternatives, with each having different advantages. And how to choose the best, having the opinion of tens or even hundreds of experts?

As the calculation of the rating of a computer game based on the critically acclaimed graphics, gameplay and plot, and the collective choice of the priority task before the appearance of the customer, refers to the methods of expert assessments .
Methods of expert assessments are part of a wide field of decision theory , and expert assessment itself is the procedure for obtaining a problem assessment based on the opinion of specialists (experts) for the purpose of subsequent decision making (choice).
There are two groups of expert assessments:
Roughly speaking, the first group includes the evaluation of articles on the site, voting in polls, etc., when each expert makes a decision independently. Selection of experts is done by means of karma. It is the first group that prevails on the Internet 2 due to the possibility of reaching a larger number of experts.
Methods for measuring objects
The method of simple ranking is that each expert is asked to arrange the signs in order of preference.
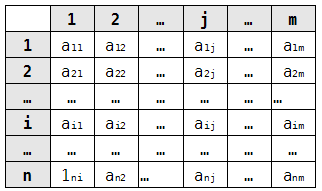
a ij - evaluation of a sign by an expert. n is the number of signs, m is the number of experts.
Then, S i is calculated - the average value of the importance of the trait.
')
Weighting Method (a ij )
The method of successive comparisons is as follows:
In the pairwise comparison it is not necessary, as in the ranking, to order all the objects, it is necessary to identify in each of the pairs a more significant object or to establish their equality. Pair comparison can be carried out with a large number of objects, as well as in cases where the difference between objects is so insignificant that their ranking is almost impossible.
When using the method, a matrix of the size n x n is often compiled, where n is the number of objects to be compared.

When comparing objects, the matrix is filled with elements a ij as follows (another filling scheme can be proposed):
Direct assessment . It is often desirable not only to order (rank the objects of analysis), but also to determine by how much one factor is more significant than the others. In this case, the range of changes in the characteristics of the object is divided into separate intervals, each of which is assigned a specific score (point), for example, from 0 to 10 . That is why the method of direct assessment is sometimes also called the point method .

And now, the most delicious ...
To analyze the results, various methods of mathematical statistics are used . Moreover, they can be combined and vary depending on the type of task and the desired result.
So, let the group of experts estimate any object, then x j is the assessment of the j-th expert, where m is the number of experts.
For the formation of a generalized assessment of the group of experts average values are most often used. For example, the median for which such an assessment is taken, in relation to which the number of large estimates equals the number of smaller ones.
Determination of the relative weights of objects
Sometimes it is necessary to determine how important a particular factor (object) is (significant) from the point of view of any criterion. In this case, they say that it is necessary to determine the weight of each factor. It differs from the formation of a generalized assessment in that it is not the overall assessment of the object that is determined, but an assessment for each of its characteristics.
And
There are many possible methods for processing estimates.
Alternatively, use the Elo rating system for the pair comparison method.
Hierarchy analysis method
Paradox Condorcet
Borda Rule
ELECTRE
Moreover, the result may consist of several algorithms, intertwining with others. For example, the algorithm for calculating the expert’s competence ratio can affect the average assessment of this expert, etc.
In the case of participation of several experts in the survey, differences in their assessments are inevitable, but the magnitude of this difference is important. Group assessment can be considered sufficiently reliable only if there is a good consistency in the responses of individual specialists.
Statistical characteristics — measures of dispersion or statistical variation — are used to analyze the variance and consistency of the estimates.
So, methods for calculating the parsing measure :
Variation range
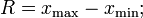
Mean linear deviation

Standard deviation
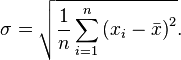
Dispersion
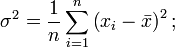
Spearman's rank correlation coefficient
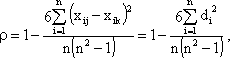
Coefficient (value ) can range from –1 to +1. With complete coincidence of estimates, the coefficient is equal to one. Equality of the coefficient minus one is observed with the greatest difference in expert opinion.
) can range from –1 to +1. With complete coincidence of estimates, the coefficient is equal to one. Equality of the coefficient minus one is observed with the greatest difference in expert opinion.
x ij is the rank ( importance ) assigned to the i-th object by the j-th expert, x ik is the rank assigned to the i-th object by the k-th expert, d i is the difference between the ranks assigned to the i-th object.
Kendell coefficient of concordance
The coefficient can take values ranging from 0 to 1. With full consistency of expert opinions, the coefficient of concordance is equal to one, with complete disagreement - zero. The most realistic is the case of partial consistency of experts.
Speaking about the consistency of expert opinions, it is worth mentioning that ranking does not imply (or does not always imply) distance. That is, one expert A> B> C means that A >> B> C, and the other A> B >> C. And any correlations and calculations of average ratings will not help here. Alternatively, read the consistency index. Something is supposedly the number of contradictory closed chains of expert opinions (the first believes that A is better than B, the second that B is better than C, and the third that C is better than A) to the number of all such chains.
Ratings are usually based on a probabilistic model, so you need to carefully consider the area of their possible application.
The article does not pretend to a complete multi-stage analysis of methods and estimation algorithms, only a superficial description of them. Therefore, if you know the methods and algorithms applicable in this case (not described by me), I will be happy to add them to the article. Or any useful subject literature.
Whereupon I take my leave. All the holiday ramin. And for those who came to look at the girls - here you
www.rae.ru
emm.ostu.ru
teorver-online.narod.ru
www.habarov.spb.ru

As the calculation of the rating of a computer game based on the critically acclaimed graphics, gameplay and plot, and the collective choice of the priority task before the appearance of the customer, refers to the methods of expert assessments .
Short educational program
Methods of expert assessments are part of a wide field of decision theory , and expert assessment itself is the procedure for obtaining a problem assessment based on the opinion of specialists (experts) for the purpose of subsequent decision making (choice).
In cases of extreme complexity of the problem, its novelty, lack of available information, the impossibility of mathematical formalization of the solution process, you have to refer to the recommendations of competent specialists who know the problem perfectly well - to the experts. Their solution of the problem, argumentation, the formation of quantitative estimates, the processing of the latter by formal methods are called the method of expert assessments.
There are two groups of expert assessments:
- Individual assessments are based on using the opinions of individual experts, independent of each other.
- Collective assessments are based on the use of collective expert opinion.
Roughly speaking, the first group includes the evaluation of articles on the site, voting in polls, etc., when each expert makes a decision independently. Selection of experts is done by means of karma. It is the first group that prevails on the Internet 2 due to the possibility of reaching a larger number of experts.
Methods for measuring objects
- Ranking is the arrangement of objects in ascending or descending order of any inherent property. Ranking allows you to choose from the studied set of factors the most significant.
- Pair comparison is the establishment of object preferences when comparing all possible pairs. Here it is not necessary, as in the ranking, to order all the objects, it is necessary in each of the pairs to identify the more significant object or to establish their equality.
- Direct assessment . It is often desirable not only to order (rank the objects of analysis), but also to determine how much one factor is more significant than the others. In this case, the range of changes in the characteristics of the object is divided into separate intervals, each of which is assigned a definite score (point), for example, from 0 to 10. That is why the method of direct estimation is sometimes also called the point method.
The method of simple ranking is that each expert is asked to arrange the signs in order of preference.

a ij - evaluation of a sign by an expert. n is the number of signs, m is the number of experts.
Then, S i is calculated - the average value of the importance of the trait.
')
Weighting Method (a ij )
- all attributes are assigned weights so that the sum of the coefficients is equal to some fixed number (for example, one, ten or one hundred);
- the most important of all signs is given a weighting factor equal to some fixed number, and all the rest are given to coefficients equal to fractions of this number.
The method of successive comparisons is as follows:
- the expert orders all the signs in order of decreasing importance: A1> A2> ...> An;
- assigns a value equal to one to the first attribute: A1 = 1, the other features are assigned weighting factors in fractions of a unit;
- compares the value of the first feature with the sum of all subsequent ones.
In the pairwise comparison it is not necessary, as in the ranking, to order all the objects, it is necessary to identify in each of the pairs a more significant object or to establish their equality. Pair comparison can be carried out with a large number of objects, as well as in cases where the difference between objects is so insignificant that their ranking is almost impossible.
When using the method, a matrix of the size n x n is often compiled, where n is the number of objects to be compared.

When comparing objects, the matrix is filled with elements a ij as follows (another filling scheme can be proposed):
- 2, if object i is preferable to object j (i> j),
- 1, if equality of objects is established (i = j),
- 0 if object j is preferable to object i (i <j).
Direct assessment . It is often desirable not only to order (rank the objects of analysis), but also to determine by how much one factor is more significant than the others. In this case, the range of changes in the characteristics of the object is divided into separate intervals, each of which is assigned a specific score (point), for example, from 0 to 10 . That is why the method of direct assessment is sometimes also called the point method .

And now, the most delicious ...
Analysis of the results of expert assessments
To analyze the results, various methods of mathematical statistics are used . Moreover, they can be combined and vary depending on the type of task and the desired result.
Formation of a generalized assessment
So, let the group of experts estimate any object, then x j is the assessment of the j-th expert, where m is the number of experts.
For the formation of a generalized assessment of the group of experts average values are most often used. For example, the median for which such an assessment is taken, in relation to which the number of large estimates equals the number of smaller ones.
Determination of the relative weights of objects
Sometimes it is necessary to determine how important a particular factor (object) is (significant) from the point of view of any criterion. In this case, they say that it is necessary to determine the weight of each factor. It differs from the formation of a generalized assessment in that it is not the overall assessment of the object that is determined, but an assessment for each of its characteristics.
And
There are many possible methods for processing estimates.
Alternatively, use the Elo rating system for the pair comparison method.
Hierarchy analysis method
Paradox Condorcet
Borda Rule
ELECTRE
Moreover, the result may consist of several algorithms, intertwining with others. For example, the algorithm for calculating the expert’s competence ratio can affect the average assessment of this expert, etc.
Establishing the degree of consistency of expert opinions
In the case of participation of several experts in the survey, differences in their assessments are inevitable, but the magnitude of this difference is important. Group assessment can be considered sufficiently reliable only if there is a good consistency in the responses of individual specialists.
Statistical characteristics — measures of dispersion or statistical variation — are used to analyze the variance and consistency of the estimates.
So, methods for calculating the parsing measure :
Variation range
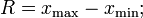
Mean linear deviation

Standard deviation
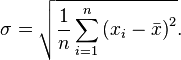
Dispersion
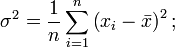
Spearman's rank correlation coefficient
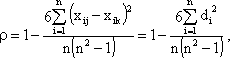
Coefficient (value
 ) can range from –1 to +1. With complete coincidence of estimates, the coefficient is equal to one. Equality of the coefficient minus one is observed with the greatest difference in expert opinion.
) can range from –1 to +1. With complete coincidence of estimates, the coefficient is equal to one. Equality of the coefficient minus one is observed with the greatest difference in expert opinion.x ij is the rank ( importance ) assigned to the i-th object by the j-th expert, x ik is the rank assigned to the i-th object by the k-th expert, d i is the difference between the ranks assigned to the i-th object.
Kendell coefficient of concordance
The coefficient can take values ranging from 0 to 1. With full consistency of expert opinions, the coefficient of concordance is equal to one, with complete disagreement - zero. The most realistic is the case of partial consistency of experts.
Calculation
Is determined by the average rank of the set of features
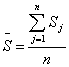
The deviation d j of the average rank of the j-th attribute from the average rank of the aggregate is included:
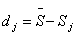
The number of identical ranks assigned by experts to the j-th attribute - t q is determined.
The number of groups of the same rank is determined - Q. The coefficient of concordance is determined by the formula:
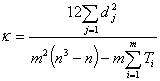
Where

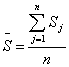
The deviation d j of the average rank of the j-th attribute from the average rank of the aggregate is included:
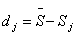
The number of identical ranks assigned by experts to the j-th attribute - t q is determined.
The number of groups of the same rank is determined - Q. The coefficient of concordance is determined by the formula:
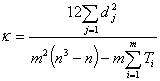
Where

Speaking about the consistency of expert opinions, it is worth mentioning that ranking does not imply (or does not always imply) distance. That is, one expert A> B> C means that A >> B> C, and the other A> B >> C. And any correlations and calculations of average ratings will not help here. Alternatively, read the consistency index. Something is supposedly the number of contradictory closed chains of expert opinions (the first believes that A is better than B, the second that B is better than C, and the third that C is better than A) to the number of all such chains.
Ratings are usually based on a probabilistic model, so you need to carefully consider the area of their possible application.
Conclusion
The article does not pretend to a complete multi-stage analysis of methods and estimation algorithms, only a superficial description of them. Therefore, if you know the methods and algorithms applicable in this case (not described by me), I will be happy to add them to the article. Or any useful subject literature.
Whereupon I take my leave. All the holiday ramin. And for those who came to look at the girls - here you
References:
Wikipedia, the free encyclopediawww.rae.ru
emm.ostu.ru
teorver-online.narod.ru
www.habarov.spb.ru
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/189626/
All Articles