Android Fragmentation
Fragmentation is both a virtue and a disadvantage of the Android ecosystem. There are a lot of comparisons of the API level of the Android and iOS operating systems in the network. In this article, we examine the degree of fragmentation of the mobile OS from Google and analyze the impact of fragmentation on developers and users.
Disadvantage:
Android devices are available in all shapes and sizes, with completely different performance standards and screen sizes. In addition, there are many different versions of Android on the market that are simultaneously active at the moment, which increases fragmentation. This leads to the fact that developing applications that can run on all Android devices can be an extremely difficult and time-consuming task.
')
Dignity:
Despite all the shortcomings, fragmentation has many advantages, both for developers and for end users. The presence of cheap smartphones (rarely working on the latest version of Android) contributes to a higher coverage of users than iOS, thus, application developers have a wider audience. Perhaps the application is more difficult to do, but the potential gain is definitely worth it. For consumers, substantial fragmentation contributes to the fact that they choose the exact phone they want - small or large, cheap or expensive, with any combination of different features.
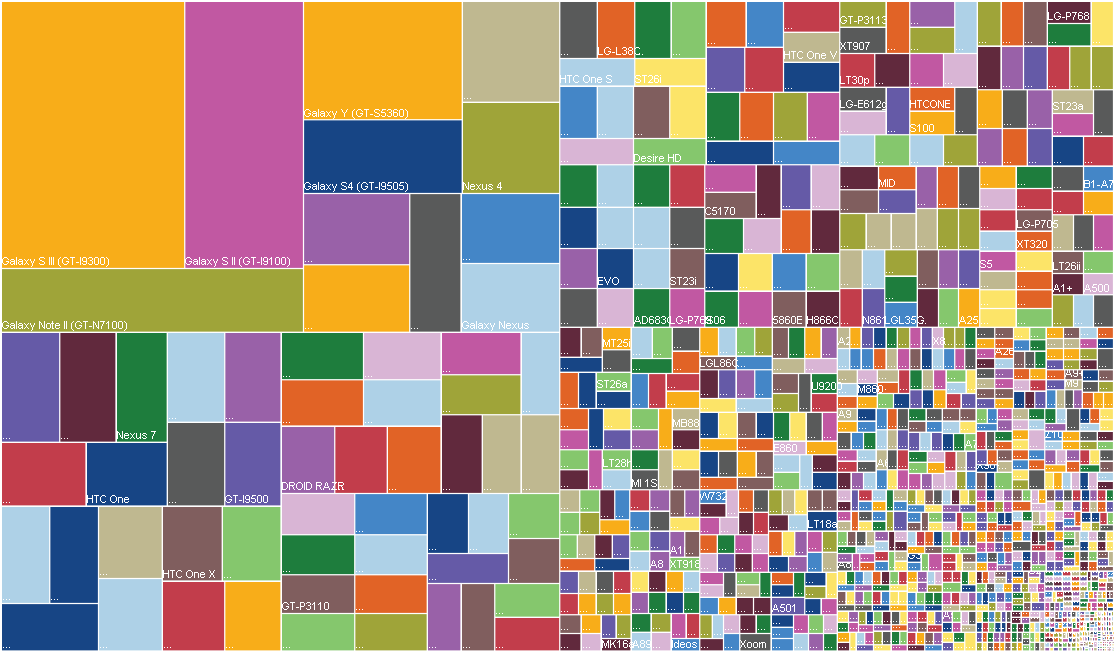
This is the best way to visualize a huge number of different Android devices that the OpenSignal application has downloaded from the past few months. From the developer's point of view, comparing fragmentation year to year, we see that it has tripled, more new devices from around the world are loading the app. If you want to understand the problem of creating an application that will work on all devices, you can start with this diagram.
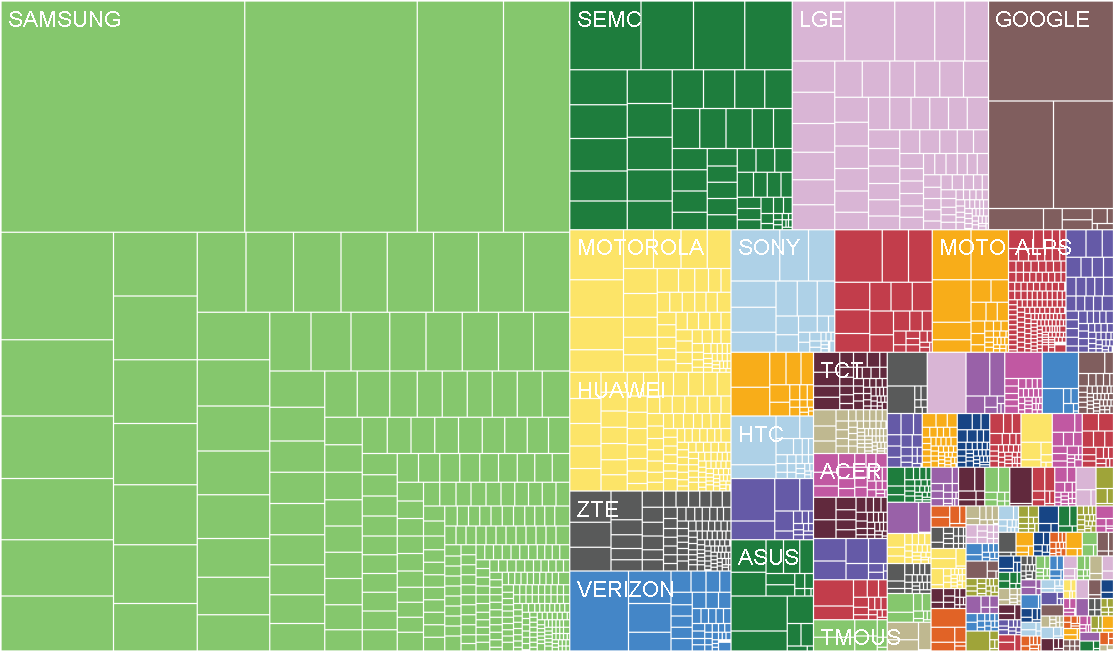
A similar view by brand, we can see how much market share each device manufacturer has, obviously Samsung took the lead. Having calculated the market share for several manufacturers of devices from the top, we see that Samsung dominates with a share of 47.5%, Sony-Ericsson is in second place and has less than one sixth of Samsung's share - 6.5%. Some brands combined into one company have different shares in the diagram, that is, Moto and Motorola are one company and HTC is shown in different shares by region. But even if you combine them, Motorola has only 4.2% of the market, and HTC - less than 3.9%.

Device fragmentation is not the only problem faced by Android developers; the operating system itself is quite fragmented and over time the degree of fragmentation only increases. The graph above shows this degree in stages, and we can also see a steady decline in the popularity of each version of Android across the white line.

A variety of Android fragmentation is usually compared with iOS. The two pie charts show obvious differences in API fragmentation between the two competing operating systems.
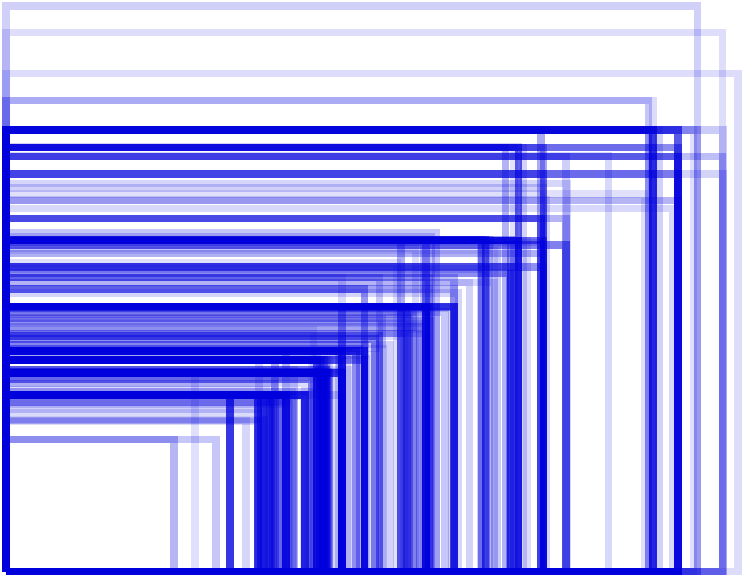
The key to the success of any application is the correct user interface, and Android has two main problems for developers regarding UI. First, brands tend to produce their own system UIs (for example, Touchwhizz for Samsung and HTC Sense), which can change the look of many standard elements. Second, there is no other platform for smartphones that could boast of such a rapid increase in screen sizes. How to help overcome these difficulties is described in article 40 tips for optimizing Android applications . The graph below shows the various physical dimensions of the screens of Android phones, with a darker line - the most popular smartphones.
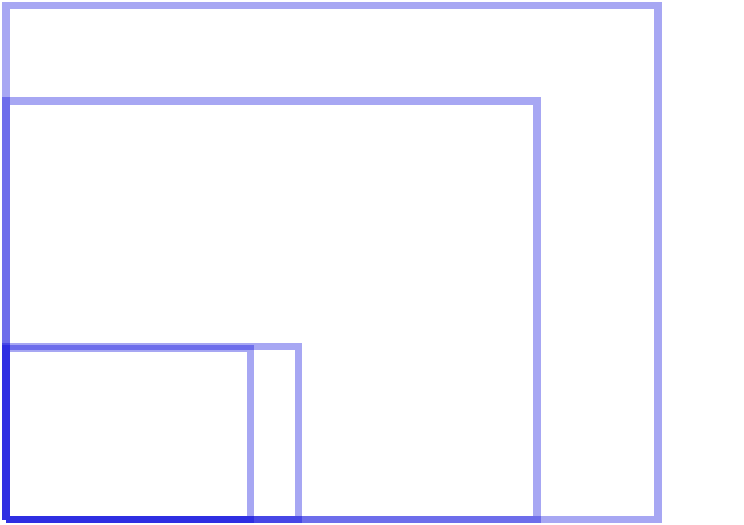
It is very difficult to create a layout of layouts that work well on all these screens. When like iPod-touch, iPhone and iPad have only 4 physical screen sizes - partly due to Apple’s tendency to double the pixel density, increasing the resolution four times (for example, iPad 2 -> iPad 3) while maintaining the physical screen size. The graph below shows the fragmentation of the sizes of iOS screens, compare with Android.
Fragmentation of devices is increasing, and with it the choice of the Android operating system is growing. While fragmentation delivers only a headache to developers who are testing and optimizing their applications for each new device, at the same time, the success of the Android ecosystem cannot be attributed to its fragmentation, Android is available for everyone. Manufacturers of cheaper devices will try to use the latest versions of Android, and fragmentation will help the ecosystem become more global and socio-economic.
Fragmentation geographically expands the Android market - it is not limited to the dispersion of devices and operating systems. It is also important for understanding which devices are currently relevant. Some devices may be relevant for one region, but not popular in another, developers need to take into account differences in network performance in different regions when developing applications. Another factor is battery life; when at the moment the battery life is quite acceptable, it may not be enough in the future. It is important to remember that it is not enough to divide applications only by device.
The report shows that Android fragmentation is growing. Many consider this a disadvantage of Android, and not advantage. So far, of course, fragmentation is associated only with flaws (and as developers we know well about them), but this is not correct. Apple is currently working on a cheap device, the fragmentation of their ecosystem will also increase. Perhaps the Android ecosystem is not entirely correct, but it is imitated.
Disadvantage:
Android devices are available in all shapes and sizes, with completely different performance standards and screen sizes. In addition, there are many different versions of Android on the market that are simultaneously active at the moment, which increases fragmentation. This leads to the fact that developing applications that can run on all Android devices can be an extremely difficult and time-consuming task.
')
Dignity:
Despite all the shortcomings, fragmentation has many advantages, both for developers and for end users. The presence of cheap smartphones (rarely working on the latest version of Android) contributes to a higher coverage of users than iOS, thus, application developers have a wider audience. Perhaps the application is more difficult to do, but the potential gain is definitely worth it. For consumers, substantial fragmentation contributes to the fact that they choose the exact phone they want - small or large, cheap or expensive, with any combination of different features.
FRAGMENTATION OF DEVICES

This is the best way to visualize a huge number of different Android devices that the OpenSignal application has downloaded from the past few months. From the developer's point of view, comparing fragmentation year to year, we see that it has tripled, more new devices from around the world are loading the app. If you want to understand the problem of creating an application that will work on all devices, you can start with this diagram.
FRAGMENTATION OF BRANDS

A similar view by brand, we can see how much market share each device manufacturer has, obviously Samsung took the lead. Having calculated the market share for several manufacturers of devices from the top, we see that Samsung dominates with a share of 47.5%, Sony-Ericsson is in second place and has less than one sixth of Samsung's share - 6.5%. Some brands combined into one company have different shares in the diagram, that is, Moto and Motorola are one company and HTC is shown in different shares by region. But even if you combine them, Motorola has only 4.2% of the market, and HTC - less than 3.9%.
Fragmentation of the ANDROID OS VERSIONS

Device fragmentation is not the only problem faced by Android developers; the operating system itself is quite fragmented and over time the degree of fragmentation only increases. The graph above shows this degree in stages, and we can also see a steady decline in the popularity of each version of Android across the white line.
COMPARISON WITH IOS

A variety of Android fragmentation is usually compared with iOS. The two pie charts show obvious differences in API fragmentation between the two competing operating systems.
SCREEN DIMENSIONS
The key to the success of any application is the correct user interface, and Android has two main problems for developers regarding UI. First, brands tend to produce their own system UIs (for example, Touchwhizz for Samsung and HTC Sense), which can change the look of many standard elements. Second, there is no other platform for smartphones that could boast of such a rapid increase in screen sizes. How to help overcome these difficulties is described in article 40 tips for optimizing Android applications . The graph below shows the various physical dimensions of the screens of Android phones, with a darker line - the most popular smartphones.

It is very difficult to create a layout of layouts that work well on all these screens. When like iPod-touch, iPhone and iPad have only 4 physical screen sizes - partly due to Apple’s tendency to double the pixel density, increasing the resolution four times (for example, iPad 2 -> iPad 3) while maintaining the physical screen size. The graph below shows the fragmentation of the sizes of iOS screens, compare with Android.

FINDINGS
Fragmentation of devices is increasing, and with it the choice of the Android operating system is growing. While fragmentation delivers only a headache to developers who are testing and optimizing their applications for each new device, at the same time, the success of the Android ecosystem cannot be attributed to its fragmentation, Android is available for everyone. Manufacturers of cheaper devices will try to use the latest versions of Android, and fragmentation will help the ecosystem become more global and socio-economic.
Fragmentation geographically expands the Android market - it is not limited to the dispersion of devices and operating systems. It is also important for understanding which devices are currently relevant. Some devices may be relevant for one region, but not popular in another, developers need to take into account differences in network performance in different regions when developing applications. Another factor is battery life; when at the moment the battery life is quite acceptable, it may not be enough in the future. It is important to remember that it is not enough to divide applications only by device.
The report shows that Android fragmentation is growing. Many consider this a disadvantage of Android, and not advantage. So far, of course, fragmentation is associated only with flaws (and as developers we know well about them), but this is not correct. Apple is currently working on a cheap device, the fragmentation of their ecosystem will also increase. Perhaps the Android ecosystem is not entirely correct, but it is imitated.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/188738/
All Articles