"Pioneers" of the moon race

PS: just a nice photo for the introduction
“ We still don’t know much about the Universe, don’t understand much, but the progress we have achieved should inspire us ,” writes the notorious theoretical physicist Stephen Hawking, who believes that by creating a single theory of the Universe, a complete theory that would describe the Universe from different parties, humanity will become its true masters.
')
Humanity is now faced with the task of mastering our tiny solar system: searching for the simplest forms of life on neighboring planets, improving the mechanism for bringing objects into the space environment (see the “space elevator” option), terraforming, that is, providing the normal conditions necessary for human life Of the earth. The huge mass of the NASA budget is aimed at exploring Mars, and, of course, a man’s flight to this “brown” planet, if it does take place, will be the most ambitious space expedition, in which one-way tickets will be given to those heroes who dare to fly .
In the meantime, the most striking and weighty attempts to explore the place where we all live with you can be considered the feat of Yuri Alekseevich , manned flights to the Moon , as well as the expeditions of the Voyager pair and their predecessors Pioneers took place during the heyday of the American space program. Which, in turn, has repeatedly exceeded any other space project in the history of mankind, as authoritative sources say. “Voyagers,” launched five years after the start of the mission of the tenth and eleventh “Pioneers,” successfully reached the “environs” of Jupiter and Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. At the same time, at the end of the last century, one of these vehicles still overtook “Pioneer”, approached interstellar space and in general became the object most distant from our planet, collected by human hands.

“Voyagers”, by the way, still transmit useful information to earth scientists, allowing, for example, finding out the direction and energy of particles between the so-called boundary shock wave arising from deceleration of the solar wind and heliopause. To study this zone, which people in white coats managed to call the “magnetic highway”, will be another 5-10 years (some sources call the figure of 20 years), then the communication of the vehicles with the Earth will be lost.
The “Pioneers” mentioned in the text, which was launched in 1972, should have been studied by Jupiter and Saturn, as well as the first to inform extraterrestrial civilizations about the existence of the Earth and us. On the hulls of these spacecraft were installed aluminum plates with a special pattern , which, according to the intention of its author, Carl Sagan (Carl Edward Sagan), should tell the aliens where, when and by whom these space pieces of iron were launched with all sorts of scientific good aboard. Moreover, people (a man and a woman) are depicted naked on the plate, for which NASA was criticized, despite the fact that the ministry so concealed the drawing in the um, piquant place.
And who knew that after 26 years, “Voyager-1” with the coordinates of the Solar System will overtake “Pioneers” and become the creation of human hands, capable of being among the first to deliver information encrypted by humans to extraterrestrial life. This will happen, however, very soon: if the light of stars from distant galaxies that went before us for many thousands of millions of years, shows us the state of the Universe in the past (“peering into the Universe, we see it in the past.” - “A Brief History of Time” ), what can we say about objects, like spacecraft. Perhaps, by the time the message will be read by forms of life unknown to us, earthlings will have long been included in the annals of history as an extinct civilization. Whether from their hands, because of the space objects that suddenly fell on you and us, the habitats that could not be tracked among the many flying threats, due to the unsuccessful colonization of the neighboring planets and resource depletion, it does not matter. And, by the way, it will be a shame if our descendants and I do not have time to read the message flown into the solar system from a distant galaxy.
There were only two “Voyagers”, and the mission of these devices was to study the distant planets of our system. Those “Pioneers”, about which I wrote above, have serial numbers “10” and “11”, and it is easy to guess that the family included a whole dozen interplanetary stations, different in design and purpose. In the post-war period, the United States did their best to overtake the Soviet Union in the “lunar race”, therefore, in the summer of 1958, the United States Air Force (NASA was created just 3 weeks before the flight of the first device of the series) began to implement the space program. The task of the first of the “Pioneers” was to enter the lunar orbit and photograph the actual surface of the mysterious satellite of the Earth. The Thor modification DM-18 Able-I, consisting of the Thor rocket itself for the first stage of the flight and the Vanguard rocket for outputting the 39-kilogram apparatus to the Moon, was chosen as the launch vehicle. "Pioneer-0" was supposed to collect scientific data within two weeks after the 60-hour flight.

The first attempt to bring the lunar probe to the lunar orbit turned out to be a failure: “Zero” never really went into outer space, exploding together with the “Thor” 77 seconds after the start - the “Thor” engines were unable to cope with earth gravity. The launch of subsequent vehicles in the same year of 1958 was assigned to a separate department responsible for the country's space program, NASA. The organization received decent money from the government (the annual budget was $ 100 million), as well as a hard-to-implement (judging by the launch of the first stations to the moon) task.
Booster for “Pioneers”, however, remained the same. Pioneer 1 was the first spacecraft launched by NASA into space. The probe had to be put into lunar orbit to study cosmic rays, magnetic fields, and micrometeorite detection. And this time NASA engineers made a mistake: because of the insufficient thrust of the engines, the rocket with the “First” on board again failed to overcome the Earth’s gravitational field, and the probe finally hung at an altitude of 113854 km. - This is less than a third of the distance to the moon. But, at least, he was able to get some useful information about the radiation belt of the planet for the ministry before plunging helplessly into the Pacific Ocean after 43 hours and 17 seconds of flight.
In November of the same year, a third attempt was made to bring the “Pioneer” series apparatus closer to the Moon. “Pioneer-2” was almost completely identical to its predecessor in its structure, except that the mass of scientific equipment was slightly smaller due to the replacement of the old television system with the new Space Technology Laboratories (STL space technology laboratory), which was to provide the best solution to the scientific tasks of the mission . And for the umpteenth time, the new equipment could not find a use for itself - it did not work out for the third time with the flight: once again the failure of the rocket engine at the same third stage of “acceleration”. “Pioneer-2” was able to climb to a height of only 1,550 kilometers above Africa, having spent 45 minutes in the air.

If we consider the period from 1957 to 1959, the “Thor” missiles of various modifications were launched from cosmodromes 79 times, and 57 of them were test launches. Almost 30 percent of the total number of flights ended in failure, but the main thing was that all three attempts failed to bring the “Pioneers” to the Moon, a person’s attempts to break out of the shackles of near-earth orbit. In the future, NASA used the “services” of other modifications of the Thor rocket family, which sent a large number of unsuited satellites to their orbits and, in general, showed themselves as reliable launch vehicles. The total number of launches of the Tor family is 710 times.
The order for the development of this medium-range missile, by the way, was entrusted to Douglas Aircraft , which in December 1955 won the contract for its production. Shortly before the Americans, it became clear that the old missiles simply did not reach Moscow from stationary launchers deployed in the UK, so that a defeat range of over 2,000 km was required. And the Soviet Union, meanwhile, boasted missiles stationed in the east of Germany and capable of hitting a target within a radius of 1,800 km. As a result, the engineers of the American company completed work on the “Thor” in record time - the “raw” version of the rocket was ready by July 1956. On October 26, Thor was delivered to the US Air Force base in Florida, and on January 25, the 57th, the first launch of the missile itself took place. The debut, like the next three launches, ended in failure: the missiles fell or exploded in the air. Finally, on September 29, 1957, the fifth rocket of the “Thor” family passed the tests, and after two years all the American bases located on the east coast of Great Britain were staffed with “thunder terrorists”.
The rockets, which the military kept in a horizontal position inside the carefully disguised and protected warehouses, could be launched 15 minutes after the click of two human fingers in uniform. Having a weight of just over three tons in the “empty” version and about 50 tons with a full tank of fuel, the new rocket could carry a 1-tonne warhead. In the service of Her Majesty, the Torah lasted until August 1963, after which the missiles and warheads were returned to their historic homeland. The first responsible task fell on the Thor family of engines on August 17, 1958, when the United States launched the “Zero Pioneer” into space.

On March 27, 1958, the newly-formed Agency for Advanced Defense Research and Development of the USA announced the planned program “ Mona ”, during which it was planned to deliver five probes to the lunar orbit. The first three vehicles (“Pioneers-0-1-2”) placed on Thor-type missiles, as you know, could not reach the target. The last two were supposed to cope with the gravity of the Earth with the help of the Juno II launch vehicle, the basis of which rested on another medium-range ballistic missile - The PGM-19 Jupiter (the goddess Juno - the wife of Jupiter, hence the name of the rocket). The Americans wanted to be the first to rush past the moon and be the first to photograph the surface of the satellite in its immediate vicinity.
In November 1957, the head of the JPL (Jet Propulsion Laboratory) Research Center, William Pickering, invited the US Army Ballistic Missile Agency to use the Juno II launch vehicle to carry out part of the large-scale Red Socks space project and Mona operation in particular. The so-called “ Red Socks ” project was the American response to the Soviets on their first artificial Earth satellite. The project’s tasks were broadly as follows: as early as June 1958, that is, as soon as possible, to photograph anything related to the Moon, to receive necessarily footage of the satellite side invisible from Earth and thereby hit the whole world with its discoveries! In total, at least nine American probes were to fly to the moon. Looking ahead, I remind you that the USSR was the first to photograph the “dark side” of the natural satellite of the Earth with the help of the Luna-3 space station, thereby securing a priority for itself when choosing the names of craters on the lunar surface.
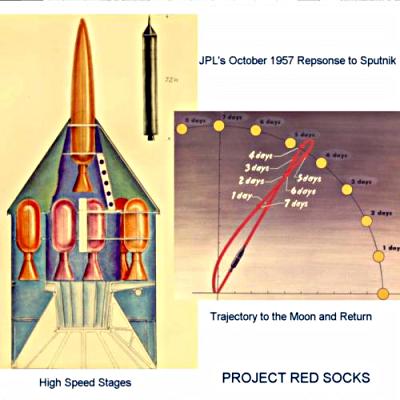
Although Juno II cannot boast of a long service life (only 3 years), it officially has the status of a launch vehicle that was able to emerge victorious from the battle with earth gravity. It happened, however, not immediately. Pioneer 3, which was supposed to fly past the moon after 33.75 hours of speed flight, take a picture of it at a distance of 30,000 km. and “sit down” in the solar orbit, could not rise above 102360 km. above the ground. The reason was the early stopping of one of the rocket engines, which stopped its work by 3.7 seconds earlier than planned, because of which the apparatus did not reach the second cosmic velocity — the minimum velocity that an object must develop in order to overcome the Earth’s gravitational force. Pioneer 3 burned down in the atmosphere over Africa, but managed to transmit temperature data to earth tracking stations, which allowed scientists to discover the second radiation belt of the planet.
On March 3, 1959, the Americans launched the fifth “Pioneer” to the moon. According to the plan, everything had to go as follows: the probe carried on itself special photocells, which were at a distance of 30,000 km. from the moon would be activated thanks to a photoelectric sensor. Having flown past the natural satellite of the Earth and having photographed its surface, the device according to the plan went out into a heliocentric orbit and became a satellite of the Sun. Despite the fact that Pioneer 4 really developed the second cosmic speed and “defeated” the attraction of the Earth, it, like its predecessors, could not fulfill its main task: the probe swept past the moon at a distance of 60,000 km. at a speed of 7230 km / h. Due to the huge difference in the figure, the photosensor simply did not react to the moonlight, so the Earth operators only received information about the radiation situation.
Let me remind you that the Soviet station Luna-1 in January 1959 successfully reached the second space velocity and passed from the moon at a distance of 6 thousand km. In September of the same year, the second “Moon” reached the surface of the satellite. “Luna-3” was the first to photograph the dark side of the moon, and, despite the numerous defects in the picture, the scientists were able to establish the absence of Nazi Germany’s bases on the surface. In 1966, the Soviet automatic station Luna-9 for the first time carried out a soft landing on the lunar "soil."
***
This is the story of the first devices of the Pioneer family, which were never able to complete the tasks assigned to them. In the future, the new probes of the series were engaged in the study of interstellar space, Venus, the Sun, Jupiter, Saturn and Neptune, but this, as they say, is already a topic for another story.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/186794/
All Articles