Veeam Backup & Replication: tips and tricks. Part 2
In the last article I talked about the advantages / disadvantages and ways to improve the work on backup through the technology of direct access to the SAN - Direct SAN Access. Today we continue our story.
Copy Modes in Veeam Backup - Virtual Applause Mode (via VMware Hot Add)
How it works
Briefly and simply it looks like this. After Veeam Backup prepares the virtual machine from the inside, the vSphere command is sent through the vSphere API for Data Protection (VADP) to create a VM disk snapshot, then the vSphere all frozen disks of this snapshot are attached to the VM Veeam Backup Proxy. Accordingly, the proxy perceives them as its disks and pulls out the data from the inside in a block-by-block manner. Accordingly, the vmdk files themselves are accessed via the ESXi host HBA adapters, not via the LAN.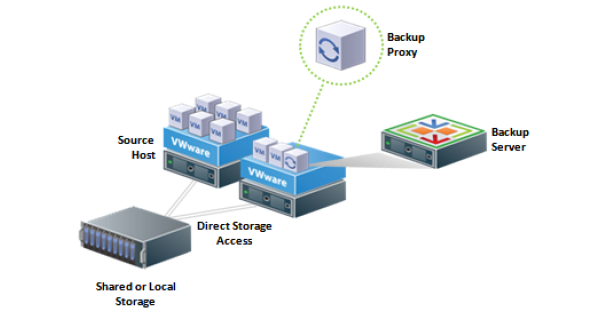
Good
- Easy to set up. Almost every VM with MS Windows OS can become a copying proxy server: during the day it is the application and database servers, and at night they copy each other’s data.
- Fast work on all types of storage, since the ESXi-host I / O stack is used. But I would say that this is the second part of the saying "... quickly runs." For the first part, see below in the “Bad” section.
- Works with all types of storage, including NFS.
- Such a proxy server must be virtual, which means that you can achieve 100% virtualization and not hold physical servers anymore.
poorly
- Sometimes “buggy” . This happens on the side of VMware in the work of its API, so it is difficult to deal with it.
- Affects the degree of consolidation , and hence the cost of the entire solution. While copying Veeam Backup Proxy well eats processors and requires memory. If the load on the VM is constantly high, then there is a possibility that it will be necessary to increase the number of ESXi hosts, and, accordingly, the licenses for them.
- The Hot Add process is a slow process by itself . Connecting a disk to a copied VM can take up to 2 minutes. This is the first part of the saying: “slowly harnesses”.
- HotAdd is a feature of vSphere, and has several limitations:
- The vSphere version must be 4.1 or higher.
- The version of VMware Tools on the VM must match the version of ESXi. Otherwise (this situation may occur in the case of migration or restoration from backup) vSphere can not provide the necessary information for Veeam Backup & Replication to identify VMs as hot-add proxy, which means hot-add mode will not work.
Evil
- Problems snapshots removal. They are not always deleted . The problem is actually on the vSphere API side, but Veeam Backup has a lot of built-in optimizations to solve these problems.
- CBT should be disabled on the backup proxy VM to prevent Hot Add from shutting down when CBT is initialized. Better Backup Proxy does not back up at all. If this is a dedicated server, then there is still no information on it.
- In some cases, a very long shutdown snapshots VM, located on the NFS.
Tips & tricks
- Add an additional SCSI controller VM backup proxy. One SCSI holds 16 disks, and parallel tasks on one backup proxy can lead to a larger number.
- Update vSphere and Veeam . From version to version HotAdd in vSphere gets rid of limitations and problems in the work. A single block size in VMFS5 removed a lot of problems.
- Try increasing the read-ahead buffer . In some cases this may help.
- Do not clone VM backup proxy . Better use the template, and set it as a proxy in the Veeam Backup & Replication console.
LAN Copy Mode (NBD)
How it works
Simple copying over the LAN is done through the ESXi Management Interface.

Good
- Easy to set up. In fact, nothing needs to be set up at all.
- Works with any type of storage. Server location does not matter (unlike Hot Add).
- Very quickly begins work on copying.
- Can be fast - with 10Gb Ethernet.
Evil
- On 1Gb most often very slow. On average, no more than 5-10 MB / s.
- Uses ESXi management interface for data transfer.
On the vSphere, Management side, the interface is strictly limited to the band. From here and not fast speed of transfer follows.
The second problem is that in routed subnets, network access to control interfaces is often closed by firewalls. We'll have to make holes for access.
Tips & tricks
- If possible, trunck host network management interfaces.
- Use on sites with a small amount of changing data. Most likely, it will work faster than other methods of copying in such conditions - Direct SAN Access and Hot Add simply will not have time to accelerate.
- But keep at least one Hot Add server, otherwise a full copy of the VM and recovery will last infinity in NBD mode.
- Remember the clever balancing algorithm: Network backup proxy server has the lowest priority. Consider this when building a backup infrastructure with mixed types of Veeam Backup Proxy.
A common trick for all copy modes
It can shorten up to 5 minutes from processing each VM inside the task.
For Veeam Backup up to version 6.5 (if you are using this), disable VDDK logging (VMware vStorage API).
Create a key with parameter 1:
DisableVDDKNetworkOutput (DWORD)
In version 6.5, logging was removed to a minimum, however, in infrastructures with a large number of disks, shutdown of this minimum can still help.
Create a key with parameter 0:
VDDKLogLevel (DWORD)
Use only on a stable infrastructure, as This will greatly impair the ability to provide support ! Keys for Veeam Backup are created in the HKLM \ SOFTWARE \ VeeaM \ Veeam Backup and Replication branch.
useful links
- Learn more about the new features of Veeam Backup & Replication v7
- Download a free version of Veeam Backup & Replication - Veeam Backup Free Edition
- Read more about the new v7 feature - backup using hardware snapshots .
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/186534/
All Articles