Cheap dedicated: on what do we save?
I had a lot of controversy to see on the topic of value for money when renting dedicated servers. I had to participate in them. In this post I will try to figure out what can save data centers when such savings are good and when harm. Also, I will try not to point fingers at specific commercial data centers (especially in the “bad” part of the article), since The main purpose of writing this article is an abstracted review of cost reduction mechanisms. The article is not aimed at professionals who have eaten a dog in the maintenance of a data center, but rather at people who are looking after their own DC or just curious.
Power usage. A lot of information about the reduction in operating costs of a data center is reduced precisely to improving energy efficiency. To measure it, even a special PUE coefficient (Power Usage Effectiveness) has been introduced, which is defined as the ratio of the total energy consumption of the data center to the consumption of servers and network equipment only. And besides them, the energy goes to lighting, cooling, is lost due to various transformations (more on this in more detail below).
The second after the servers themselves eater electricity is the cooling system. Proper cooling can save up to 20% on electricity bills. One of the ways to save could be the use of “free cooling”: cold air, cold water, etc. And even such a trifle as stubs in unused stand slots reduces the useless energy consumption, since the air that is supplied for cooling the equipment cools it equipment, not passages between it.
')
Proper placement. Competent and careful selection of a site for the construction of a data center can provide savings on several parameters at once.
1. The presence or proximity of the necessary infrastructure (channels, premises, specialists) will reduce initial and operational costs.
2. The cost of electricity may vary from country to country or even within a country. For example, according to 2012 data in the United States, the cost of 1 kW of electricity varied from 0.062 to 0.25 dollars depending on the state.

3. Some places have an abundance of renewable energy sources or climate features that allow the use of free cooling for most or all of the year. For example, the famous Google innovator in the construction of the Hamina data center in Finland immediately used two advantages of the location. First, the temperature of coastal waters at a depth of about 10 meters all year round is only a few degrees above zero. Secondly, the premises of the old paper mill contained ready-made pipes for collecting / returning this water. It remained to design heat exchangers and a return system that would not disturb the ecosystem. Thanks to this free cooling system, a PUE of 1.1 was achieved. Those. only 10% of the energy over consumption by the server equipment itself was spent on cooling, lighting and other related needs. In the photo below - the heat exchanger in the data center Hamina.
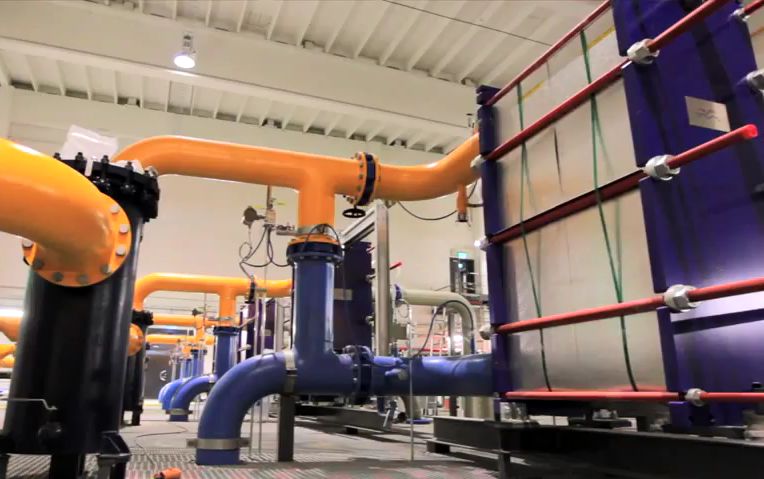

Use of unique technical solutions. Basically, this method can afford the giants of the industry. And so far it is used only for individual solutions, because it is given solely for information. A regular user who is looking for a regular dedicated server is unlikely to be able to find any suggestion that allows to save precisely due to such decisions.
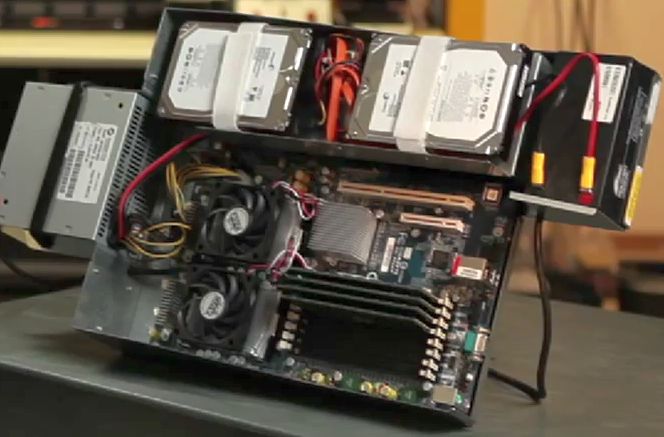
Google has become a pioneer here too. Being a wholesale buyer and having the ability to make individual orders for configuration, he made some adjustments. The calculations showed that it is more economical to supply only 12 volts to the motherboard and convert them to other necessary voltages by internal means. For comparison, the standard version uses a 3.3, 5 and 12 volt supply from the power supply. In addition, the use of only one input voltage made it possible to install a small, battery-free stand-alone battery right into the operating node. Its capacity is enough to power the node for about 3 minutes, which allows you to either shut down the node correctly or wait for the local backup generator to turn on. And at the same time allows you to get rid of the costs and losses associated with the use of a centralized UPS. If someone does not know, or simply did not think about this aspect, a centralized power backup unit generates losses due to the conversion of alternating current to direct current and back. This streamlined server looks like this:

Another example of an individual solution that has saved equipment costs is the Backblaze service, which created its storage service based on conventional user equipment. In general, this is not a method. But because of the specifics of the tasks, he has the right to life. They took the usual motherboard with a Core 2 processor and 4 GB of RAM, instructed additional SATA modules, branchers, and filled the space with so many ordinary hard drives with the maximum available capacity on the market, which could fit, connect and cool. Add here a properly organized RAID, some of your own groundwork, and you’ll have a service that can solve the problem you have — to hold and store a lot of information, sometimes giving access to it if necessary. About this service has repeatedly been written on Habré, because I add only that the rack with such self-assembling servers can store about 750 TB of information.
HP specialists have developed a technical solution that allows significant savings on the construction and management of the data center without sacrificing quality. Their HP POD 240a solution (also known as EcoPOD) allows you to build a Tier 3 class data center and, according to the manufacturer, to create and operate:
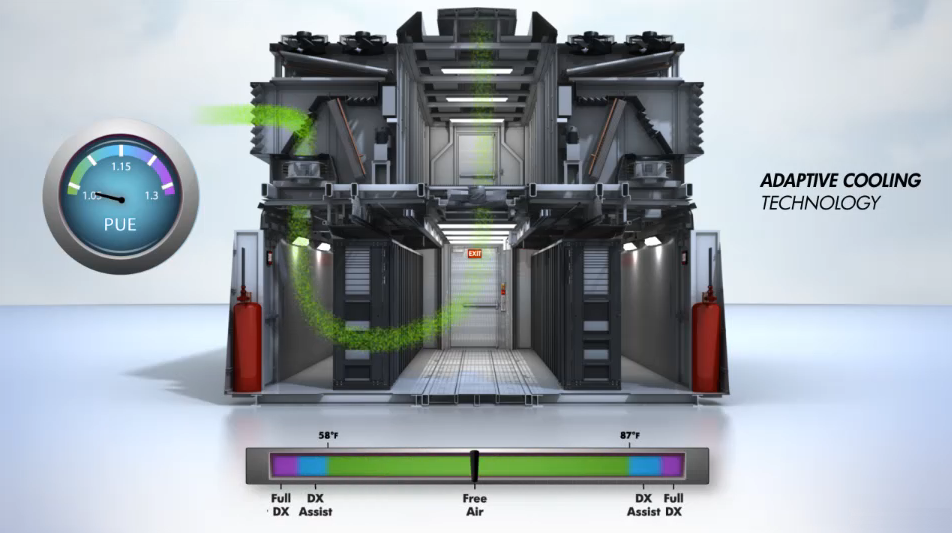
Thanks to adaptive cooling technology, PUE can be achieved in the range from 1.05 to 1.30, depending on the ambient temperature. At temperatures from 14 to 28 C, "free" cooling is used.
Some ways of saving lead to the appearance of services of dubious quality. But there are tasks for which such services have the right to life. Most often, such tasks include educational (play-experiment), test (drive a potential curve and not debugged code) and reservation (server for backups, secondary DNS, etc.). So, thanks to which youmay want to burn and kill, you can still save data centers.
Iron. If the data center has already provided rental services for dedicated servers for a long time, it may well have a number of antique servers based on some burning single-core Pentium 4 or AMD Athlon with a 512 MB RAM and, by luck, not yet sprinkled,near the trash can 80 GB. How long all this will live still - no one knows, because otherwise how to play such decisions you should not choose. Another option is to use cheap home-office hardware for server needs, which will be hard to cope with server-made workloads.
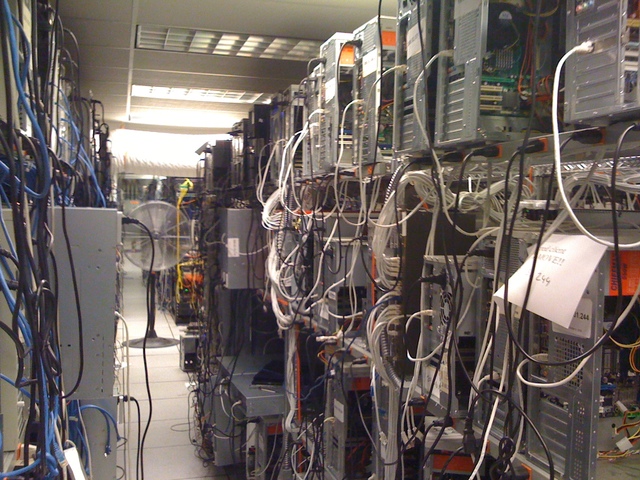

Connections. In one article by the American authorship, it was mentioned that one 10 Gb / s connection is enough to connect more than 1000 pieces of equipment to the network. If some people's delok listens to this opinion, we have a chance to get a situation in which the network will work, to put it mildly, extremely slowly.
A set of services. There is a wide range of fantasy. This may be, for example, a mixture of a set of useful features with one useless: enough memory and screws, but the processor is the same single-core Pentium. Or a normal processor and memory, but only one hard drive. And the channel is 1 Mbit / s. Of course, you can deliver another screw, raise the RAID, and expand the channel to 100 Mbit / s, but in the end nothing is left of the cheapness. Or a good hardware channel 100 Mbit / s without traffic, but only for the first few GB. And then the width of the channel will be cut to deep sorrow.
Support. This is what distinguishes good service from bad. In cheap versions, you can get gray hair while you wait for a response to the ticket, since The answer can wait a few days. In this case, the probability of getting a response is dry and useless. If your iron fails, you still have to prove it. One can not even hope for advice on problems not related to iron. And if your server was unavailable for 5 hours, in two days you will be proud to say that at the moment there are no problems, and they will even offer to check something.

Infrastructure. Not all data centers are located in specially equipped premises and have dozens of connections with a total width of hundreds of gigabits. Nothing prevents some companies from placing ordinary desktop system managers on racks in a well-ventilatedbarn in a spacious room and have a couple of links there that cannot even withstand light DDoS.

If the DC has a webcam that allows you to look inside the containment, be sure to take advantage of this opportunity. What you see can sometimes save you from serious problems in the future. I think many still remember the fire in one of the DCs with thousands of victims. By the way, that situation taught me to back up to a server in some other country every day.
Everyone chooses a server for himself according to his capabilities and needs. Hypothetically, we could sell configurations starting with AMD Athlon 64 3000+ / 512MB / 1x160GB. But we decided for ourselves that we would be engaged only in servers suitable for use (implying commercial “combat” use). And we advise you, when choosing an inexpensive data center, to clarify how they save money. And we wish not to make a mistake in choosing.
What can and should be saved
Power usage. A lot of information about the reduction in operating costs of a data center is reduced precisely to improving energy efficiency. To measure it, even a special PUE coefficient (Power Usage Effectiveness) has been introduced, which is defined as the ratio of the total energy consumption of the data center to the consumption of servers and network equipment only. And besides them, the energy goes to lighting, cooling, is lost due to various transformations (more on this in more detail below).
The second after the servers themselves eater electricity is the cooling system. Proper cooling can save up to 20% on electricity bills. One of the ways to save could be the use of “free cooling”: cold air, cold water, etc. And even such a trifle as stubs in unused stand slots reduces the useless energy consumption, since the air that is supplied for cooling the equipment cools it equipment, not passages between it.
')
Proper placement. Competent and careful selection of a site for the construction of a data center can provide savings on several parameters at once.
1. The presence or proximity of the necessary infrastructure (channels, premises, specialists) will reduce initial and operational costs.
2. The cost of electricity may vary from country to country or even within a country. For example, according to 2012 data in the United States, the cost of 1 kW of electricity varied from 0.062 to 0.25 dollars depending on the state.

3. Some places have an abundance of renewable energy sources or climate features that allow the use of free cooling for most or all of the year. For example, the famous Google innovator in the construction of the Hamina data center in Finland immediately used two advantages of the location. First, the temperature of coastal waters at a depth of about 10 meters all year round is only a few degrees above zero. Secondly, the premises of the old paper mill contained ready-made pipes for collecting / returning this water. It remained to design heat exchangers and a return system that would not disturb the ecosystem. Thanks to this free cooling system, a PUE of 1.1 was achieved. Those. only 10% of the energy over consumption by the server equipment itself was spent on cooling, lighting and other related needs. In the photo below - the heat exchanger in the data center Hamina.

Use of unique technical solutions. Basically, this method can afford the giants of the industry. And so far it is used only for individual solutions, because it is given solely for information. A regular user who is looking for a regular dedicated server is unlikely to be able to find any suggestion that allows to save precisely due to such decisions.
Google has become a pioneer here too. Being a wholesale buyer and having the ability to make individual orders for configuration, he made some adjustments. The calculations showed that it is more economical to supply only 12 volts to the motherboard and convert them to other necessary voltages by internal means. For comparison, the standard version uses a 3.3, 5 and 12 volt supply from the power supply. In addition, the use of only one input voltage made it possible to install a small, battery-free stand-alone battery right into the operating node. Its capacity is enough to power the node for about 3 minutes, which allows you to either shut down the node correctly or wait for the local backup generator to turn on. And at the same time allows you to get rid of the costs and losses associated with the use of a centralized UPS. If someone does not know, or simply did not think about this aspect, a centralized power backup unit generates losses due to the conversion of alternating current to direct current and back. This streamlined server looks like this:

Another example of an individual solution that has saved equipment costs is the Backblaze service, which created its storage service based on conventional user equipment. In general, this is not a method. But because of the specifics of the tasks, he has the right to life. They took the usual motherboard with a Core 2 processor and 4 GB of RAM, instructed additional SATA modules, branchers, and filled the space with so many ordinary hard drives with the maximum available capacity on the market, which could fit, connect and cool. Add here a properly organized RAID, some of your own groundwork, and you’ll have a service that can solve the problem you have — to hold and store a lot of information, sometimes giving access to it if necessary. About this service has repeatedly been written on Habré, because I add only that the rack with such self-assembling servers can store about 750 TB of information.
HP specialists have developed a technical solution that allows significant savings on the construction and management of the data center without sacrificing quality. Their HP POD 240a solution (also known as EcoPOD) allows you to build a Tier 3 class data center and, according to the manufacturer, to create and operate:
- reduce the cost of creation by about 4 times;
- reduce the time of creation up to 8 times;
- place about 10 times more equipment than a classic DC of the same area;
- reduce cooling costs up to 25 times.

Thanks to adaptive cooling technology, PUE can be achieved in the range from 1.05 to 1.30, depending on the ambient temperature. At temperatures from 14 to 28 C, "free" cooling is used.
On what to save would not be worth ...
Some ways of saving lead to the appearance of services of dubious quality. But there are tasks for which such services have the right to life. Most often, such tasks include educational (play-experiment), test (drive a potential curve and not debugged code) and reservation (server for backups, secondary DNS, etc.). So, thanks to which you
Iron. If the data center has already provided rental services for dedicated servers for a long time, it may well have a number of antique servers based on some burning single-core Pentium 4 or AMD Athlon with a 512 MB RAM and, by luck, not yet sprinkled,

Connections. In one article by the American authorship, it was mentioned that one 10 Gb / s connection is enough to connect more than 1000 pieces of equipment to the network. If some people's delok listens to this opinion, we have a chance to get a situation in which the network will work, to put it mildly, extremely slowly.
A set of services. There is a wide range of fantasy. This may be, for example, a mixture of a set of useful features with one useless: enough memory and screws, but the processor is the same single-core Pentium. Or a normal processor and memory, but only one hard drive. And the channel is 1 Mbit / s. Of course, you can deliver another screw, raise the RAID, and expand the channel to 100 Mbit / s, but in the end nothing is left of the cheapness. Or a good hardware channel 100 Mbit / s without traffic, but only for the first few GB. And then the width of the channel will be cut to deep sorrow.
Support. This is what distinguishes good service from bad. In cheap versions, you can get gray hair while you wait for a response to the ticket, since The answer can wait a few days. In this case, the probability of getting a response is dry and useless. If your iron fails, you still have to prove it. One can not even hope for advice on problems not related to iron. And if your server was unavailable for 5 hours, in two days you will be proud to say that at the moment there are no problems, and they will even offer to check something.

Infrastructure. Not all data centers are located in specially equipped premises and have dozens of connections with a total width of hundreds of gigabits. Nothing prevents some companies from placing ordinary desktop system managers on racks in a well-ventilated

If the DC has a webcam that allows you to look inside the containment, be sure to take advantage of this opportunity. What you see can sometimes save you from serious problems in the future. I think many still remember the fire in one of the DCs with thousands of victims. By the way, that situation taught me to back up to a server in some other country every day.
In conclusion
Everyone chooses a server for himself according to his capabilities and needs. Hypothetically, we could sell configurations starting with AMD Athlon 64 3000+ / 512MB / 1x160GB. But we decided for ourselves that we would be engaged only in servers suitable for use (implying commercial “combat” use). And we advise you, when choosing an inexpensive data center, to clarify how they save money. And we wish not to make a mistake in choosing.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/184244/
All Articles