VoIP telephony - how to estimate the real cost of a solution
Introduction
I had an idea to write this material for a long time. Too often, I hear reviews like "the price of a phone in China ..." and then comes the conviction that telephony has become almost a sale of handkerchiefs. On the other hand, complaints about "not working", even the very same Cisco, are also very often. And of course, the question arises - “So how much is this IP telephony really worth,” taking into account the training overhead, proper configuration, etc.?
It helped me to gather the strength of the research of the company “Nemertes Research”, the link to the research is given in the Basement. It should be immediately noted that the main advantage of VoIP over classical telephony, in my opinion, is the possibility of using Unified Communication, i.e. mechanism combining all sorts of communication under one medium. I will not argue the feasibility of such an approach, since it is already chewed enough.
Before starting the research, I also want to make a reservation that the conclusion will be valid for the first year of the solution implementation. This is due to the fact that most of the problems and, as a result, the costs fall on the very first year. These will include, for example, such expenses as personnel training and covering “damage” from the errors of this personnel. I also will not consider subjective moments, such as, “by buying the most famous brand, you can pawn any rollback” or “after training in a brand company it is easier to find the next job”. Evaluation of decisions will be carried out regardless of conjuncture features.
So, the easiest way to compare the cost of the same type of equipment, such as telephone sets. And here the “elbow crush” and price dumping are most visible. As for operating expenses, the picture here is much more confused. It is also difficult to immediately understand exactly which licenses and at what stage will be required. The presentation of the product is always in full functionality, and only then, usually after the first purchase, all the other details are clarified. A significant factor that strongly influences the final costs will also be not technical aspects, but such as the level of trusting relationships with the manufacturer of the solution and compatibility of the solution with the existing infrastructure, availability of operational technical support for the vendor. It is very important to take these indirect factors, the consideration of which is not possible for me in the framework of this article.
The following companies were analyzed in the Nemertes Research study: Alcatel-Lucent, Avaya, Cisco, Microsoft, NEC, Siemens and ShoreTel. I’ll add right away that there are other very worthy representatives in our market, but their assessment requires getting a full range of prices for equipment and services from them.
Initial data
The following three components were selected as the source data:
- Equipment:
- Installation:
- Operating expenses:
Obviously, the numbers will vary greatly depending on the size of the project. The analysis does not take super small and giant solutions and averaging the cost between them. So for the analysis, decisions were taken from 4 to 175 thousand phones.
Main conclusions
The average cost of IP telephony in the first year of use is $ 1.305 per phone. Of these, the average cost of equipment is $ 540, installation $ 61 and operating expenses $ 704 per year. Below is a table of prices for listed vendors separately.

As soon as management sees the figures for which the cost of operating expenses exceeds the cost of equipment, the reaction will not be positive. Of course, I could be mistaken, and management can be with a "Western mentality", welcoming the contribution to the staff, but the costs are unlikely to welcome it. Least of all operating expenses at NEC and most of all at Microsoft. However, these costs management sees, as a rule, for the year. And even then this information is not always available in its pure form. However, the reasoning that these expenses are not obligatory and can be ignored, results in a lack of communication, loss of information and other troubles. Therefore, in my opinion, it would be a mistake not to inform management about upcoming operating expenses. Moreover, I have not seen a manager in my life, who is happy to send my employee to the courses. If this is budgeted and approved by the management, then the probability of certification is much higher.
But from what are such operating expenses. Nemertes Research identifies 4 components:
- Employee time spent per phone unit.
- Material costs for system maintenance
- Subcontractors
- Training and trainings
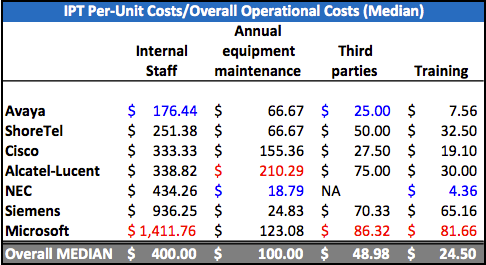
These data were obtained by a survey of companies using IP telephony, since it is obvious that, on the one hand, it is not possible to keep your staff at all and, on the other hand, not to use the services of subcontractors at all. Microsoft is the absolute leader in high costs in operating expenses. Curiously, of the total cost of the costs, the costs of the actual employees of the company are the biggest. According to the same study, conducting courses for employees at least once every two years reduces this figure by 20% due to advanced training. If third-party diagnostics and monitoring tools are used, the cost of the staff itself can be halved. There is an objective reason for the high maintenance costs of Microsoft solutions. Microsoft specialists did not undergo specific training on networks and especially voice solutions, while any Cisco specialist NAT solves problems very quickly. Similarly, for other companies that come from TDM, voice problems, such as non-consistency of codecs, are not new. It should be noted that the maintenance costs of the system also include technical support from the vendor and additional service agreements for repairs, and sometimes 7x24 or 5x8 equipment maintenance support. The cost of the subcontractors most of all at Microsoft, although it should be noted that from the non-compared solutions, the cost of maintaining any freely distributed code, as Asterisk and OpenSER will be many times more.
It is obvious that the total cost of the phone is highly dependent on the size of the project. So the cost of one phone for a project is less than 1000 phones cost an average of $ 1,799 per unit, and more than 1000 can go up to $ 723 per unit. Such a difference is due to lower prices due to the integration of capacity in gateways and servers on the one hand and reduction in maintenance / training costs per communication unit, on the other. Below is a table of comparisons of the cost of a single phone, depending on the size of the project.
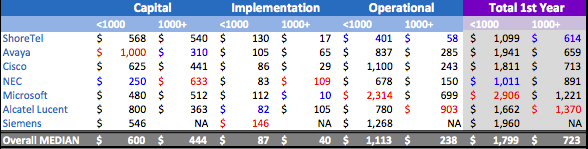
')
Unified Communication Embedded Systems
The idea of combining communications appeared in the early 90s, when a very narrow circle of people knew about IP, and no one thought of using it to transfer media. This, in my opinion, is the reason for such a big difference of opinion, the same is UC. Many understand this concept as text messages and presence information. Many, almost 40% of experts, consider UC applied when several communication solutions, such as voice and video, are implemented within one vendor. Personally, my opinion, UC should be united by a unified system of management and display of all communications tools used in the company. This means that if a company uses a fax, then sending and storing and receiving it should be integrated into various devices / programs used by the company. The same should be with other types of media. Implementing UC in a company is almost impossible without a keen need. I saw a lot of companies that spent a lot of money on a system that nobody uses. The main markets of UC are Contact Centers, where it is simply impossible to work without integration with CRM. Professional associations, such as law firms. Industrial giants with a large territory. Corporate business, for example, network of banks, to reduce the cost of communication between branches. Hospitals for operational personnel search and centralized storage / transmission of information. Recently, requests for Webbinar and video conferencing often began to occur. On average, companies spend $ 520 for a UC user device. Below is a table comparing the prices of the most famous brands.

With the development of smartphones, more and more applications and accordingly UC solutions are moving into the mobile area. On the other hand, manufacturers of programs for mobile devices also go to a meeting with the integration of these devices into a common network. This trend will continue in the near future. Speech recognition tools will soon pass a qualitative barrier to their use as controls. And of course, users want to see the same functionality in a mobile device as in a stationary computer. Based on this, it can be said with confidence that the integration of mobile devices in UC is the goal of making decisions in the coming years. Moreover, most manufacturers provide such solutions very cheap. Below is a table comparing some mobile applications at an average price.

Comparing UC values is an extremely difficult task, since the services provided, their combination and usability are so different that in my opinion it is simply not possible to compare them. An additional complication in this calculation is the total uncertainty in operating expenses. But even this is not the most unpleasant. The hardest thing to understand is whether UC will bring real benefits of use. Most manufacturers offer an all-in-one UC solution with a different set of licenses, but immediately putting the cost of the UC server into the solution. Thus, recommendations for choosing UC and estimating its value can be reduced to the following points:
- Build an accurate behavior model for an employee who needs UC services. If possible, describe in detail his actions for obtaining one or another type of service.
- Ask the manufacturer for a list of successful installations in your area and call them for an opinion. Better yet, visit them and see how it works for them.
- Most companies implementing UC underestimate the budget and installation time. Therefore, if you are an integrator, try to deploy a demo zone first. If you are an end user, get the integrator to accurately calculate and guarantee implementation on time and with budget.
- Pay attention to operating expenses. They may be unpredictable. I have met many times companies that refuse a well-known vendor, when they already exceeded all their expectations during the operation.
- There are companies that already provide such equipment in leasing, which is much more profitable in that if the equipment "does not go", you can refuse it. Such companies should give preference "for all equal"
Below are statistics on the use of UC by industry.

It is also interesting distribution in the use of UC on the size of the enterprise measured in the number of employees. The analysis below is presented for three categories:
- Small: 0-250, only 22.4% use UC
- Medium: 251-2500, the largest percentage of 45.25 UC applications
- Large:> 2500, 32.4% UC application
From this distribution it can be seen that while for small companies, UC does not represent a significant interest, since it does not bring tangible profits, for large enterprises this task becomes technologically too complex and expensive.
In conclusion, I want to note that certainly IP telephony will be universally applied, as happened in international and intercity calls. As for UC, in this area, favorites will change as fast as it did with mobile phone manufacturers. And this is understandable, because the main thing in the end, ease of use. But the difference is that the system is not selected for a year and costs a little more than a handset.
When writing the article were used:
www.webtorials.com/main/resource/papers/avaya/paper39/Telephony_UC_Cost.pdf
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/184228/
All Articles